Learning Targets Chapter 9 (Muscles)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:54 PM on 5/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
1
New cards
**4 Functions of skeletal muscles**
* Movement
* Posture
* Stabilize
* Body heat
* Posture
* Stabilize
* Body heat
2
New cards
Epimysium
surrounds entire muscle (keeps shape)
3
New cards
Tendon
connects muscle to bone
4
New cards
Perimysium
wraps muscle fibers into fascicles
5
New cards
Endomysium
surrounds each muscle fiber
6
New cards
Fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
7
New cards
Fiber
muscle cell
8
New cards
Myofibril
contractile organelles, makes up 80% of fiber, contains sarcomeres
9
New cards
Sarcomere
multiple units of myofilaments, contractile unit of actin and myosin
10
New cards
Actin
thin protein filament
11
New cards
Myosin
thick protein filament
12
New cards
Myofilament
one unit of actin/myosin filaments
13
New cards
Z-line
connects each myofilament
14
New cards
Order of muscle fiber parts from largest to smallest
1\. muscle fibers
2\. myofibrils
3\. sarcomeres
4\. myofilaments
2\. myofibrils
3\. sarcomeres
4\. myofilaments
15
New cards
Myoglobin
is the protein used to store oxygen in the muscle
16
New cards
Glycosomes
storage unit of glycogen (glucose)
17
New cards
T-tubules
an extension of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, continue to carry the electrical signal, allow communication so all sarcomeres contract at the same time
18
New cards
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
help to carry the electrical impulse into the muscle, stores calcium
19
New cards
Neuromuscular Junction
where one nerve ending and one muscle fiber meet
20
New cards
Sodium
the sodium enters the muscle fiber and results in depolarization (loss of resting membrane potential)
21
New cards
Calcium
binds to troponin to allow myosin to connect to actin
22
New cards
1st step of muscle contraction
The neurotransmitter releases ach into the synaptic cleft
23
New cards
2nd step of muscle contraction
Ach binds to receptors on sarcolemma an creates action potential
24
New cards
3rd step of muscle contraction
Action potential travel to the t-tubules
25
New cards
4th step of muscle contraction
Electrical signal causes sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium
26
New cards
5th step of muscle contraction
Calcium binds to troponin on actin
27
New cards
6th step of muscle contraction
Myosin is able to bind to actin and create power stroke
28
New cards
7th step of muscle contraction
Sarcomeres shorten causing muscle contraction
29
New cards
8th step of muscle contraction
Signal ends and calcium is reabsorbed into sarcoplasmic reticulum
30
New cards
9th step of muscle contraction
Myosin disconnect from actin
31
New cards
10th step of muscle contraction
Actin returns to original position (lengthening)
32
New cards
11th step of muscle contraction
Muscle relaxes
33
New cards
Latent phase
when nothing is occurring (at beginning)
34
New cards
Contraction phase
when muscle is depolarized (the peak of the graph)
35
New cards
Relaxation phase
when the muscle relaxes (the down slope of the graph, after the peak)
36
New cards
Muscle twitch
is a brief contraction, most common in body, homeostasis
37
New cards
Sustained (tetanus)
the muscle does not relax, not sustainable in the body
38
New cards
Large motor unit
Large muscle, for board movements
39
New cards
Small motor unit
Small muscles, the finer movements (fingers)
40
New cards
Muscle tone
The healthy state of muscle, always semi-contracted, firm and ready to respond
41
New cards
Wave summation
muscle does not fully relax between each contraction, so beach contraction is stronger
42
New cards
Multiple motor unit summation (recruitment)
multiple motor units acting at the same time within a muscle
43
New cards
Muscle fatigue
The muscle can not contract, it has a lack of ATP, cramp
44
New cards
Aerobic exercise
an exercise that uses oxygen to make ATP(running)
45
New cards
Anaerobic exercise
does not use oxygen to make ATP, instead uses glucose/glycogen (swimming)
46
New cards
Isometric
muscle contraction occurs but stays the same length (wall sits, plank)
47
New cards
Isotonic
muscle contracts and shortens (running, walking, bench press)
48
New cards
Muscles have 3 types of fibers
* Slow oxidative
* Fast oxidative
* Fast glycolytic
* Fast oxidative
* Fast glycolytic
49
New cards
Muscle fibers
* some areas have more of a certain type
* activated at different times, when needed
* activated at different times, when needed
50
New cards
Slow oxidative
* used all the time
* found in the back, neck, spine, posture
* thin
* found in the back, neck, spine, posture
* thin
51
New cards
Slow oxidative
* slow contraction speed
* lots of mitochondria
* lots of mitochondria
52
New cards
Slow oxidative
* high blood flow
* high myoglobin
* high myoglobin
53
New cards
Slow oxidative
* small motor units
* high aerobic endurance (low fatigue)
* high aerobic endurance (low fatigue)
54
New cards
Fast oxidative
* twitch movements, fast
* lots of mitochondria
* lots of mitochondria
55
New cards
Fast oxidative
* uses some glycogen
* high blood flow
* high blood flow
56
New cards
Fast oxidative
* high myoglobin
* medium motor units
* medium motor units
57
New cards
Fast oxidative
* not much endurance (medium rate of fatigue)
* legs, arms
* legs, arms
58
New cards
Fast glycolytic
* very fast, fight or flight reaction
* legs and arms
* thick
* legs and arms
* thick
59
New cards
Fast glycolytic
* not many mitochondria
* low blood flow
* low blood flow
60
New cards
Fast glycolytic
* low myoglobin
* large motor unit
* high fatigue (no endurance)
* large motor unit
* high fatigue (no endurance)
61
New cards
Benefits of exercise
\-More oxygen flows to the muscle which means better endurance in those muscles and muscle tone
**Endurance training**
* Grow more blood vessels to supply more oxygen
* Make more myoglobin
**Strength Training**
* More myofibrils (muscle stronger)
* Contractions stronger
* Muscle fibers swell
**Endurance training**
* Grow more blood vessels to supply more oxygen
* Make more myoglobin
**Strength Training**
* More myofibrils (muscle stronger)
* Contractions stronger
* Muscle fibers swell
62
New cards
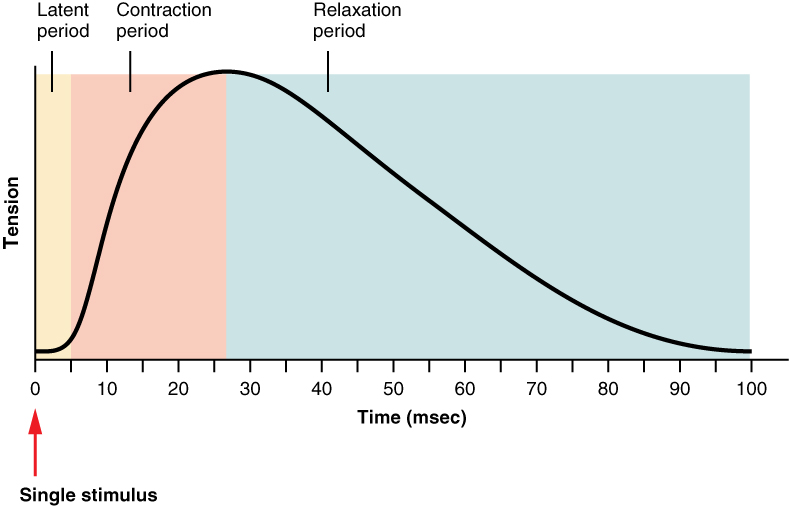
Muscle Twitch
63
New cards
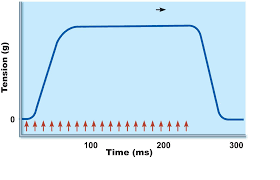
Tetanus
64
New cards
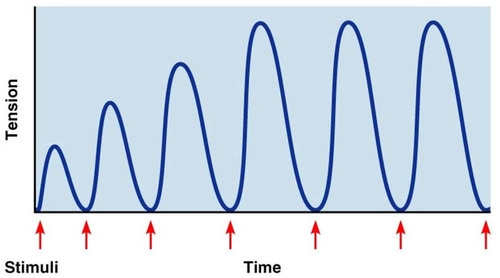
Treppe
65
New cards
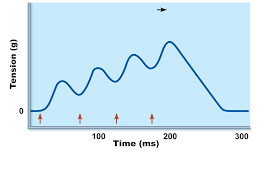
Wave Summation
66
New cards
Excitability
ability to respond to stimuli, ex. shivering
67
New cards
Contractility
ability to shorten forcibly (flexing)
68
New cards
Extensibility
ability to extend or stretch
69
New cards
Elasticity
ability to recoil and resume its resting length after stretching
70
New cards
Functions of connective tissue coverings
1. transmit the contraction from muscle fibers to the bone
2. contribute to muscle elasticity and reinforce/hold muscle together
3. provide route for blood vessels and nervous to and from the muscle (typically one artery and one nerve per muscle which branch once inside)
71
New cards
Functions of connective tissue coverings
2. contribute to muscle elasticity and reinforce/hold muscle together
72
New cards
Functions of connective tissue coverings
3. provide route for blood vessels and nervous to and from the muscle (typically one artery and one nerve per muscle which branch once inside)
73
New cards
Origin
less movable part of muscle attachment point, stationary
74
New cards
Insertion
movable part of a muscle attachment point
75
New cards
1st source of energy used
ATP
76
New cards
2nd source of energy used
Creatine
77
New cards
3rd source of energy used
Glucose
78
New cards
Oxygen Debt
difference of oxygen needed and oxygen given to muscles, owe muscle oxygen (causes deep breathing)
79
New cards
Oxygen Debt example
need 6.1 oxygen, only take in 1.2L, have a debt of 4.8L
80
New cards
Muscular dystrophy
group of muscle destroying disease
81
New cards
Steroids
enhance mass (raise oxygen carrying capability of muscles)