chemistry topic 1
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Development of atomic model
Dalton-tiny hard spheres-All substances are made of atoms. Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed.
Thomson-plum pudding model-negative electrons are scattered throughout soft blobs of positively charged material.
Rutherford-alpha particles shot at gold foil,discovered dense region in the middle (nuclues),electrons travel around nucleus
Calculate the relative atomic mass
= (mass of isotope-A x % of isotope-A) + (mass of isotope-B x % of isotope-B) / 100
Mendeelevs arrangments
in order of atomic mass,but left gaps for non discovered elements. realised elements with similar properties belonged in the same groups
metals vs non metals
metals-react to form + ions,loose elements in order to form these ions,forming stable structure like noble gas
non-metals- form - ions,gain electrons to be stable like noble gas
ionic bonds
transfer of electrons to produce a full outer shell between METAL and NON METAL
form cations and anions
FORCE OF ATTRACTION BETWEEN OPP CHARGED IONS =ELECTROSTATIC FORCE
ionic compounds
High melting and boiling points
Conduct electricity-but only as water/liquid=ions are free to move (delocalised)
-ide/-ate
-ide= non metal forms a negative ion
-ate=when a compound contains oxygen asw another element,NON METAL FORMS THIS ONLY
lattice structure
a giant structure of ions
held by strong electrostatic forces,which act in all directions
regular arrangement of ions
covalent bonds
sharing of electrons,with NON METALS
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
leads to formation of molecules=SIMPLE/GIANT COVALENTS
Simple molecular substances COVALENT RMBR!
low boiling and melting points=weak intermolecular forces
dont conduct electricity=no overall charge -but when broken down in water they do
Many are insoluble in water, but some are soluble=can form intermolecular forces with water stronger than water molecules
Giant covalent structures
strong intermolecular forces
high melting and boiling points
some conduct electricity
insoluable in water
metallic bonding
giant structure of atoms arranged in regular patterns
delocalised electrons = contains heat and electricity=gives strong metallic bonds
high melting and boiling points
STRENGTH
malleable=atom layers can slide over eachother
Electrostatic forces
coductivity=ability for electrons to moce
INsoluable
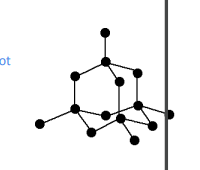
Diamond
carbon joined to 4 other carbon atoms
no free electrons=cannot conduct
rigid strucute w strong covalent bonds =cutting tools/diamond tipped drils
high melting points
graphite
bonded to 3 other carbons=forms layers w hexagonal rings
layers can slide=weak intermolecular forces=soft & slippery
one delocalised electron = conducts electricity
pencils/lubricants/electrodes
Graphene
-single layer of graphite
high melting points
strong =regular arrangement
useful in electronics and composites
Fullerenes
molecular form of carbon with hollow shapes eg nano tubes and buckyballs
based on hexagonal rings of carbon atoms, but they may also contain rings with five or seven carbon atoms
first fullerene to be discovered was Buckminsterfullerene (C60), which has a spherical shape
Carbon nanotubes
cylindrical fullerenes,high length to diameter ratios
used in nanotech,electronics and tennis racket frames
high tensile strength(tension)
conduct electricity
Buckyballs
spheres of carbon atoms
weak intermolecular forces
little energy=low boiling points and slippery
polymers
large molecules with repeat units
strong covalent bonds
solids at room temp
allotropes
two subsatnces made from same elemetns,same physical state but different structures rg diamond and grpahite
law of conservation mass
total mass before a reactions=totals mass after
concetraition of a solution
mass/volume
cm³ to dm³?
/1000
What is the definition of one mole of particles of a substance?
The Avogadro constant number of particles of that substance
or
a mass of ‘relative particle mass’
How do you calculate the number of moles of a substance? (2 equations)
Number of moles = mass (g) / relative formula mass
Number of moles = number of particles / Avogadro’s constant