cell divison
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
interphase
when cell is not dividing but making new organelles, enzymes and cytoplasm in preparation for cell division
mitosis
the division of one nucleus into two identical nuclei each with the same number of chromosomes and identical genes
function of spindle
contract, pull chromosomes apart and move them to poles of cell
name a group of disorders which cells lose control of rate of mitosis and cell division + two possible causes
cancer + UV rays / X rays
two events that occur during prophase
The nuclear membrane starts to break down
Spindle fibres appear in the cytoplasm.
two events that occur during metaphase
the nuclear membrane is fully broken down
The chromosomes line up across the equator (centre) of the cell.
how does cell division occur in animals
A cleavage furrow forms, deepens and splits the large cell with two nuclei into two identical animal cells.
how does cell division occur in plants
Cell plates form in plant cells. These form two new cell walls; forming two identical plant cells.
haploid(n) v diploid (2n)
haploid- one set of chromosomes eg. gametes
diploid-two sets of chromosomes eg.somatic cells
cell continuity
cells develop from pre-existing cells
meiosis
one cell divides to produce four new cells
meiosis
production of gametes
which phase; growth in multicellular organisms
mitosis
two events that occur during interphase
photosynthesis
respiration
whats the function of mitosis in multicellular organisms
growth and repair
4 stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telephase
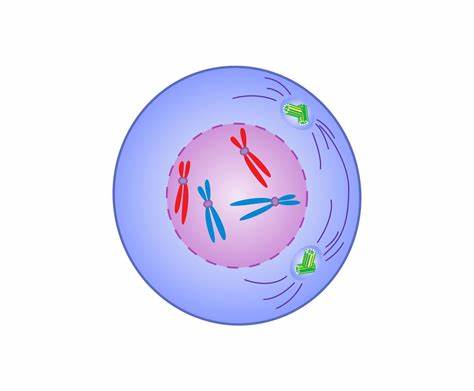
what stage is this
prophase
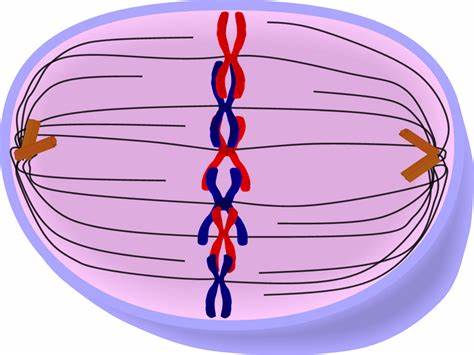
what stage is this
metaphase
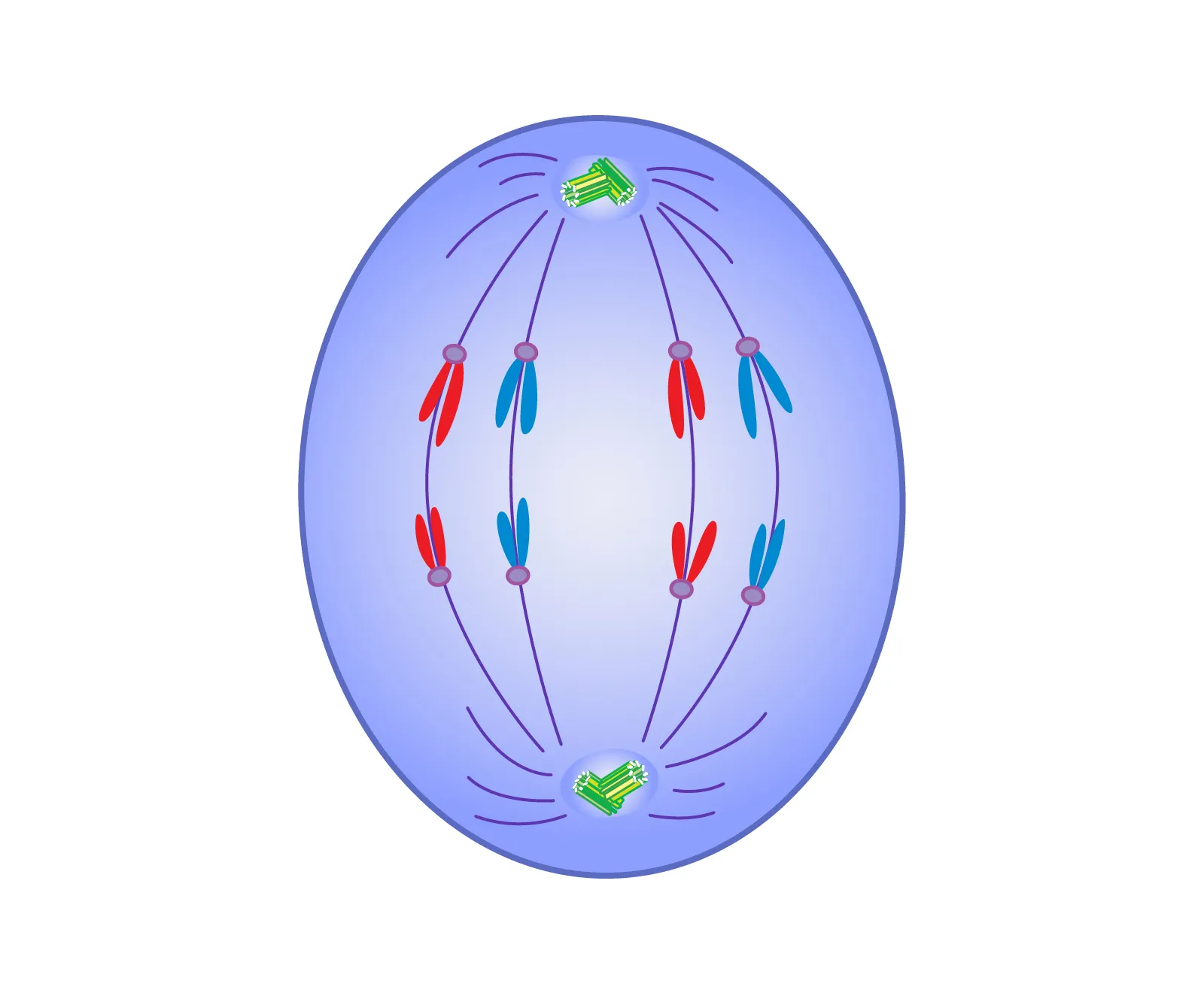
what stage is this
anaphase
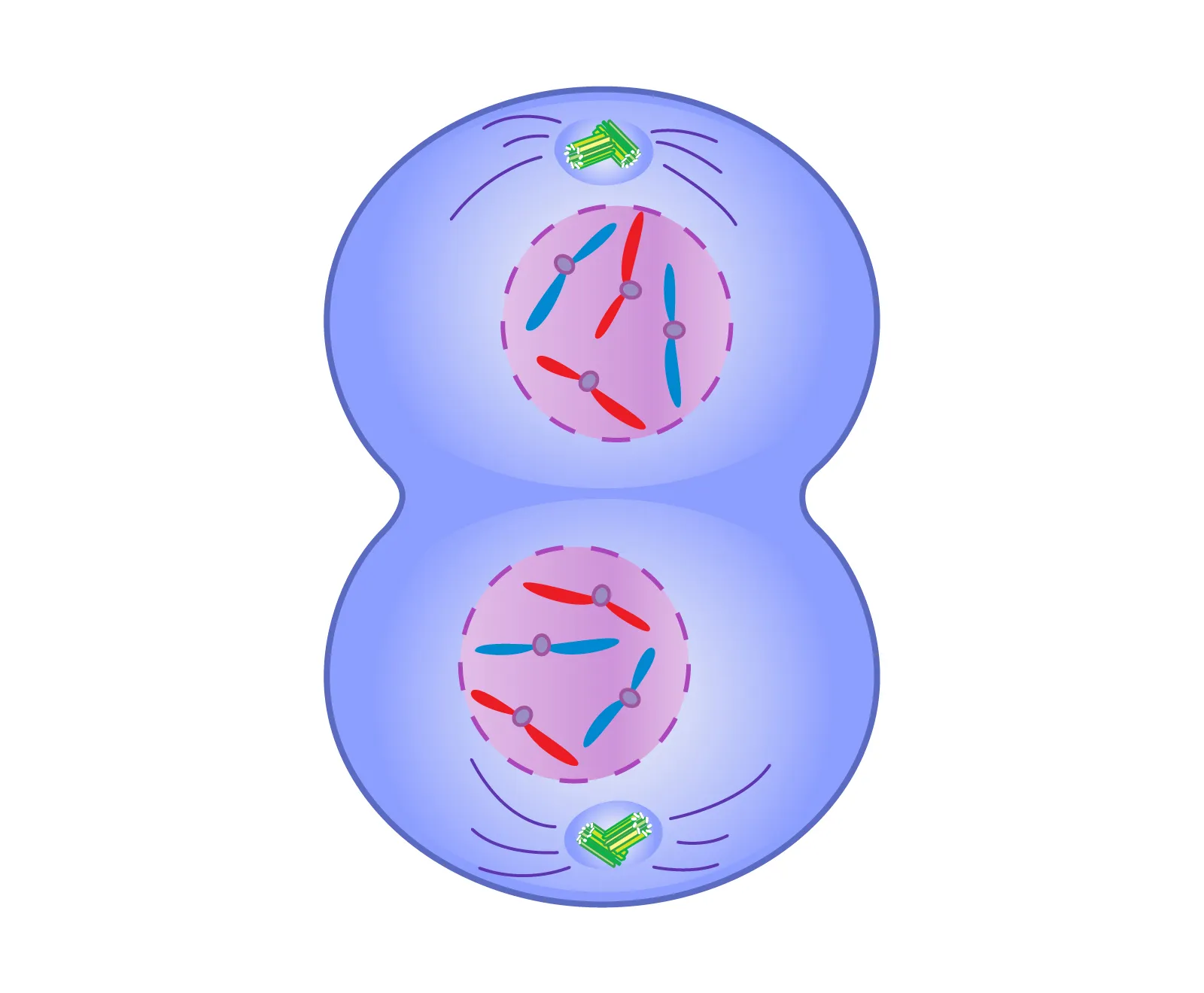
what stage is this
telophase
what is cancer
disorder where rate and number of mitotic divisions are uncontrolled
what type of microscope used
compound light microscope
define mitosis
a form of nuclear division, where one nucleus divides to form two identical daughter nuclei
meiosis V mitosis
meiosis; halves chromosomal number.4 daughter nuclei formed.introduces genetic variation.
mitosis;maintains chromosomal number.2 daughter nuclei formed.genetically identical
why mature human red blood cells do not undergo mitosis
no nucleus