Lens
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
lens
avascular, transparent elliptic structure that aids in focusing light rays on the retina; located w/in posterior chamber anterior to the vitreous and posterior to the iris; suspended from ciliary body and zonular fibers; malleable
embryologic development
the structure of the adult lens is determined during _________
lens vesicle
first lens like structure observable in developing embryo; composed of a layer of epithelial cells that form a hollow sphere
posterior
which cells of the lens differentiate and elongate to form the primary lens fibers?
no
is there posterior epithelium in the adult lens?
germinative zone of epithelium anterior to lens equator
where does cell division occur during the post developmental life of the lens?
biconvex
what is the shape of the lens?
posterior
the ______ surface of the lens has the steeper curve
lens thickness
distance from anterior to posterior pole
lens diameter
nasal to temporal measurement of the lens
surface curvatures, refractive index, change in index, length of optical path
what factors affect lens refraction?
20D
what is the refractive power of the unaccommodated lens?
gradient
the lens has a _____ refractive index
optical density
the lens has a gradient refractive index because of the changes in _____ throughout the lens
center
where is optical density the highest in the lens?
protein concentration
the refractive index is a factor of __________ within lens fibers
14D, 8-12yo
what is the maximum power of the lens in accommodation and what age is it reached at?
presbyopia
decreasing accommodative power with age
0
what is the accommodative power of the lens at age 50?
anterior pole
thickness of lens capsule at ______ increases with age
lens capsule
consists primarily of collagen; elastic; encloses all lens components and helps mold shape of the lens; provides immune privilege to the lens
B

lamellar arrangement of fibers
why is the lens capsule elastic?
no
does the lens capsule contain elastic fibers?
anterior epithelium
what part of the lens secretes the lens capsule?
yes
does the lens expand through life?
water & small solutes
what is the lens capsule permeable to?
zonular fibers
what counteracts the spherical shape the lens prefers to take?
capsule
where do zonular fibers insert?
zonular lamella
outer superficial zone of lens capsule that consists of zonules interconnected with matrix
anterior lens epithelium
adjacent to anterior lens capsule; cuboidal epithelium; secrete anterior capsule and are site of metabolic transport mechanisms
A
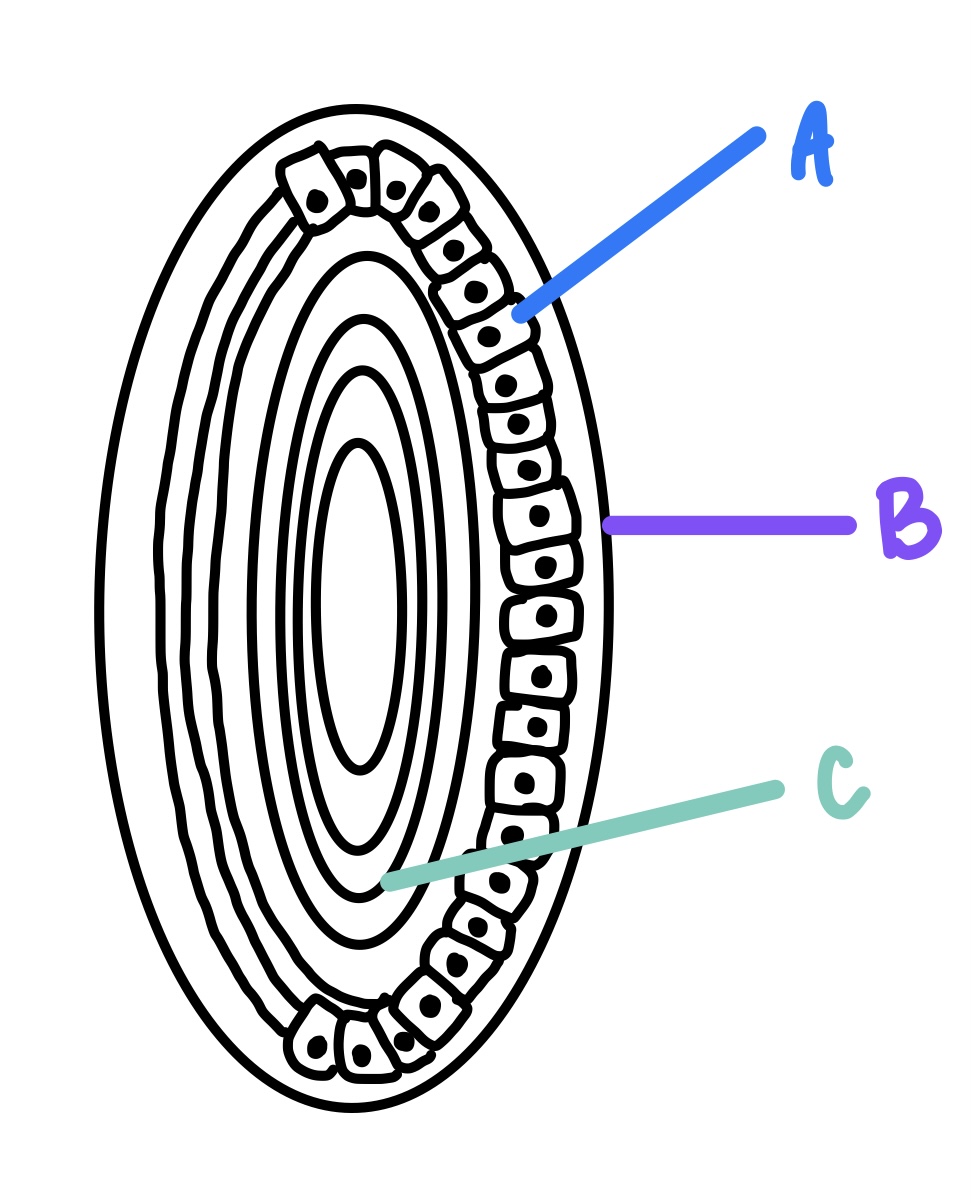
capsule
the basal aspect of anterior epithelium is oriented towards what?
center of lens
the apical portion of anterior epithelium is oriented towards what?
desmosomes & gap junctions
what joins the lateral membranes of the epithelial cells?
no
are tight junctions present in the lateral membranes of the anterior epithelium?
germinal zone
band of cells in preequatorial region that lies just anterior to equator; location of cell mitosis in lens
posterior pole
basal aspect of forming lens fibers stretch towards what?
anterior pole
apical aspect of forming lens fibers stretch towards what?
apical side
where do the cellular nuclei move as each layer of forming lens fibers elongates?
lens bow
arcuate shaped line that connects the dots of cellular nuclei in the lens, towards the anterior aspect
loses cellular organelles
what occurs when an elongated cell becomes a lens fiber?
outer
new lens fibers are laid down ______ to the older fibers
longer
superficial lens fibers are _____ than deeper fibers
youngest
_______ cells lie directly below epithelium and capsule
secondary lens fibesr
all fibers formed from mitosis in germinative zone
nucleus
once the _____ is lost, the mature lens fiber has lost its attachment to basement membrane
growth factors
accumulate in lens capsule, concentration & distribution direct cellular processes
anterior
growth factors that influence proliferation and migration are concentrated along the _______ surface
equator
growth factors that influence differentiation are concentrated at the _______
fiber mass
biomolecules that regulate interactions among actin filaments, adhering junction integrins, and ECM increase what?
significant protein synthesis
___________________ must occur to form crystallins, aquaporin channel proteins, and gap junction components as fibers elongate
increases
as fiber elongates, cell membrane permeability _______
suture
joining of elongating fibers from opposite sides of the lens forms this
suture formation
what triggers cell organelle death in lens fibers?
interdigitate
membranes of adjacent fibers are said to __________, forming interlocking junctions along their lateral sides that help stabilize fibers
throughout life
lens fiber production continues _____________
concentric layers
how is growth of lens fibers organized?
crystallins
proteins lens fiber cytoplasm that make up 40% of the net weight of the fiber; distribution contributes to the gradient refractive index; soluble
epithelium fiber interface
border b/t apical membrane of anterior epithelium and apical membrane of elongating fiber; site of nutrient and ion exchange
A

gap junctions
extensive network of these throughout lens along lateral fiber membranes account for facility with which nutrients and ions move within the lens
no
are gap junctions evenly distributed throughout the lens?
towards equator and in outer layers
where are gap junctions more concentrated?
primary lens fibers
form very core center of lens, embryonic nucleus
secondary lens fibers
lens fibers outer to the embryonic nucleus core
higher
lens cortex has a ______ water content than nucleus
1.38
refractive index of lens cortex
1.41
refractive index of lens nucleus
actin
insoluble protein in the lens that is a key component of cytoskeleton of the lens fiber
microtubules
part of cytoskeleton and help stabilize fiber membrane; role in transporting vesicles to ends of elongating fibers
fetal nucleus
includes embryonic nucleus and the fibers surrounding it that are formed prior to birth
adult nucleus
includes embryonic and fetal nucleus and fibers formed from birth to sexual maturation
lens cortex
contains fibers formed after sexual maturation
upright Y
describe the structure of the anterior suture
inverted Y
describe the structure of the posterior suture
zonules of zinn
threadlike fibers that attach lens to ciliary body; microfibrils
basement membrane of nonpigmented ciliary epithelium
where do zonules of zinn arise from?
lens capsule
most zonule of zinn fibers attach to what?
primary zonules
zonules that attach to the lens
secondary zonules
join primary zonules with each other or connect processes to one another or to the pars plana
tension fibers
anchor primary zonules to ciliary valleys to form a fulcrum
relaxed, stretched
when emmetropic eye is viewing a distance object, the ciliary muscle is ______ and the zonules are ______
accommodation
increase in power that occurs to view a near object
increases
lens thickness _____ anterior to posterior in accommodation
thins
lens _____ along equator in accommodation
forward
anterior lens surface moves _____ in accommodation
no
does the posterior pole change positions in accommodation?
retinal blur
what is the stimulus that initiates the accommodative mechanism?
cone stimulation
accommodative mechanism is dependent upon what photoreceptors?
passive
vitreous has a _____ role in accommodation
widening, increasing, decreasing
accommodation can cause a _______ of intertrabecular spaces, ______ aqueous outflow and ______ IOP
0
what is the objective measurement of accommodation near age 50?
absence of blood vessels, few cellular organelles, orderly fiber arrangement, short distance b/t components of differing indices
what things contribute to transparency of the lens?
sodium potassium pumps
these things help maintain electrolyte balance, located in lens epithelium
anaerobic glycolysis
main source of energy/ATP required for cellular metabolism and replication within the lens
aqueous humor
where does the lens get glucose from?
epithelium/superficial fibers
where is aerobic glycolysis limited to in the lens?
100microns
thickness of lens cortex where organelles are still present
epithelial cells and new fibers
where is ATP activity higher in lens?
no
is the lens nucleus capable of protein synthesis?
facilitated diffusion
glucose uptake occurs by what process?
intercellular flow
removes metabolic waste from lens