Non-medical Prescribing
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is non-medical prescribing (NMP)?
Prescribing by specially trained nurses, optometrists, pharmacists, physiotherapists, podiatrists and radiographers
Working within their clinical competence as either independent or supplementary prescribers
AKA prescribing by anyone who is not a doctor
What are independent prescribers?
Examples
Able to prescribe medicines on their own initiative from the BNF
Doctors
Dentists
Nurse IPs
Pharmacist IPs
Optometrist IPs
Since 2013: chiropodists/podiatrists and other physiotherapists
Since 2016: therapeutic radiographers
What are supplementary prescribers?
Examples
Able to prescribe medicines in accordance with a clinical management plan. This plan is agreed between the supplementary prescriber, a doctor and the patient
Nurses / midwives
Pharmacists
Podiatrists
Physiotherapists
Diagnostic and therapeutic radiographers
Optometrists
Dieticians
In what other situations can medicines be given by NMPs?
Patient Specific Direction (PSD): an instruction given by an IP to another professional to administer a medicine to a specific patient
Patient Group Direction (PGD): a written instruction for the supply / administration of specific medicines by named, authorities health professionals, to a well defined group of patients requiring treatments for a specific condition
How is a Patient Specific Direction (PSD) different to a normal prescription?
Instructions are related to administration of medicines rather than dispensing of medicines e.g. vaccinations
Who can supply/administer under a PGD?

In which act are there exemptions to the general rules on selling, supplying and administering medicines for some groups of HCPs?
Human Medicines Act 2012
Exemptions in the Human Medicines Act 2012 on prescribing for certain HCPs
Podiatrists/chiropodists » can give antibiotics
Midwives/student midwives » can give nyastatin and vitamin K
Occupational health » only registered nurses and drs can supply medicines under occupational health
Optometrists » can give antibiotic eyedrops
Paramedics » can give adrenaline, naloxone
Exemption to the regulation of sale/supply of POMs
Does not apply to the administration of POMs specified in Schedule 19
For the purpose of saving life in an emergency
E.g.
Adrenaline » anaphylaxis
Glucagon / Glucose injections » hypo/hyperglycaemia
Naloxone hydrochloride » drugs overdose
What can doctors prescribe?
Basically everything:
Licensed drugs - POMs, Ps, GSLs
Off label and off license drugs
Unlicensed medicines
Controlled Drugs (CDs)
Appliances or chemical reagents listed in part IX of the drug tariff
Selected List Schemes (SLS)
Borderline substances (ACBs)
What are off label and off license medicines?
A medicine which is used to treat a condition that can be used to treat another condition
What can dentists prescribe?
Can only prescribe products included in the Dental Prescribing Formulary
On an FP10D prescription
What can community practitioner nurse prescribers prescribe?
Can only prescribe products included in the Nurse Prescribers’ Formulary
What can nurse AND pharmacist independent prescribers prescribe?
Any medicine for any medical condition
Any Sch 2, 3, 4 or 5 CD except: diamoprhine, dipipanone, cocaine
What can optometrist independent prescribers prescribe?
Any licensed medicine for ocular conditions
NOT authorised to prescribe CDs
What can physiotherapist AND podiatrist/chiropodist independent prescribers prescribe?
Any licensed medicine that falls within their individual area of competence
Can also prescribe some CDs
What can independent therapeutic radiographer prescribe?
Any licensed medicine for any medical condition within their level of experience of competence and the overarching framework for cancer
Medicines for off-label use
Cannot prescribe CDs
What can supplementary prescribers prescribe?
Any medicines as agreed by the patient and doctor as part of a patient’s clinical management plan
Including any Sch 2, 3, 4 or 5 CDs except: diamorphine, dipipanone or cocaine
What can paramedic independent prescribers prescribe?
Any medicine for any condition, provided it's within their clinical competence and training.
Off-label medicines (not licensed for that specific use)
Selected items from the Community Pharmacy England Selected List Scheme (SLS)
Specific Controlled Drugs, due to recent legislation:
Morphine sulphate (oral/injection)
Diazepam (oral/injection)
Midazolam (oromucosal/injection)
Lorazepam (injection)
Codeine phosphate (oral)
Which prescription forms are available and which prescribers use which for?
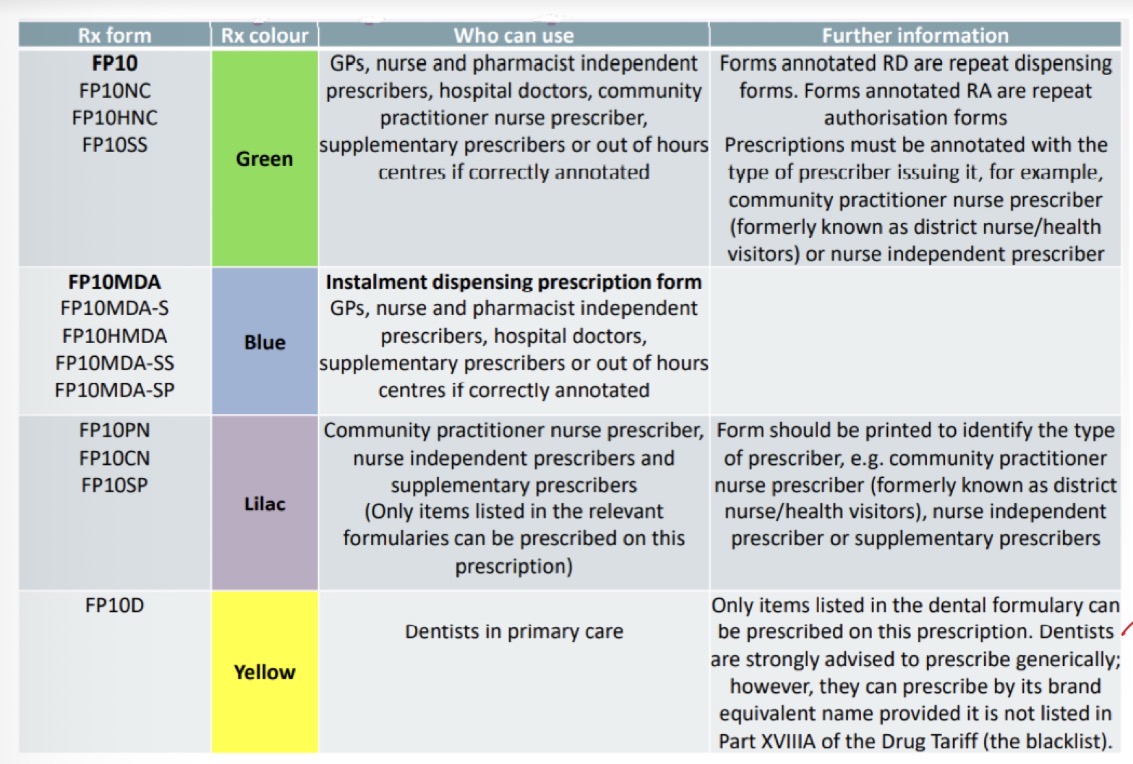
Dentist prescription form rules
If dentist is prescribing on a yellow Rx form, can only prescribe from the dental formulary
If prescribing on a private prescription, can prescribe any medication
Nurse IP prescription form rules
If dentist is prescribing on a lilac Rx form, can only prescribe from the nursing formulary
If prescribing on a private prescription, can prescribe any medication
Privately Prescribed CDs
Private prescribers can only prescribe Sch 2 or 3 CDs privately on a pink private prescription form (FP10PCD)
All private prescribers have been allocated a 6 digit prescriber identification number which must be included on the FP10CD » this is different to their GMC number which is not legally required

Legal requirement for privately prescribed Sch 2 and Sch 3 CDs
6-digit prescriber identification number
Must be included on the FP10PCD
(Different to GMC number which is not legally required)
Where should private prescribers be referred to if they require a private prescriber identification number?
Should be referred to their primary care organisation e.g. NHS England Area Team
PINK PRESCRIPTION =
PRIVATE CD PRESCRIPTION
= patient has to pay

Why is this prescription not legally valid?
Has all the correct details but not on a pink FP10PCD
Which CDs can doctors prescribe?
Sch 2 - 5
Including diamorphine, dipipanone or cocaine for the treatment of addiction
Possession and supply of Sch 1 CDs are prohibited except in accordance with Home Office Authority
Which CDs can dentists prescribe?
NHS Dentists:
Only CDs in the dental prescribing formulary
On an FP10D prescription
Private Dentists:
Any Sch 1 - Sch 5 CD
What are pharmacists advised in relation to CD prescribing by dentists?
To challenge dental prescriptions for Sch 2 or Sch 3 CDs for which there is no recognised dental use
Which CDs can nurse IPs and pharmacists IPs prescribe?
Sch 2 - 5
EXCEPT diamorphine, dipipanone or cocaine for the treatment of addiction
Which CDs can physiotherapist IPs prescribe?
Diazepam, dihydrocodeine, lorazepam, morphine, oxycodone, temazepam by oral administration
Morphine for injectable administration
Fentanyl for transdermal administration
Which CDs can podiatrist/chiropodist IPs prescribe?
Diazepam
Dihydrocodeine
Lorazepam
Temazepam
By oral administration
Which CDs can community practitioner nurse IPs prescribe?
Not authorised to prescribe any CDs
Which CDs can supplementary prescribers prescribe?
Sch 2 - 5
EXCEPT diamoprhine, dipipanone or cocaine for the treatment of addiction
Which CDs can therapeutic radiographer IPs prescribe?
Tramadol
Lorazepam
Diazepam
Morphine
Oxycodone
Codeine
By oral administration
Which CDs can paramedic IPs prescribe?
Morphine sulphate by oral administration or by injection
Diazepam by oral administration or by injection
Midazolam by oramucosal administration or by injection
Lorazepam by injection
Codeine phosphate by oral administration
Benefits of NMP?
Better and quicker access to services
Time-saving
Promotes integrated care
Makes better use of clinical workforce skills by optimising the use of the available skill mix
Gives organisations the flexibility to innovate when designing cost-effective quality services e.g. a lot of clinics led by pharmacists/nurses instead of doctors
Increased choice of services
What were the GPhC requirements to qualify as an IP in the past?
Be registered with the GPhC
Have relevant experience in a UK pharmacy setting
Be able to recognise, understand, and articulate prescriber skills and attributes
Have an identified area of clinical/therapeutic practice with relevant experience
Have a Designated Prescribing Practitioner (DPP) to supervise learning
Complete additional GPhC-accredited training
Meet 32 GPhC-defined learning outcomes
What did the GPhC-accredited IP training involve?
Completion of an accredited independent prescribing programme - typically part-time over ~6 months
Combination of face-to-face teaching and self-directed study
Minimum of 26 days of teaching and learning activities
90 hours (12 days) of supervised practice with a Designated Prescribing Practitioner (DPP)
Qualification must be recorded with the professional regulator once completed
How do pharmacists become IPs currently?
Integrated prescribing training
Prescribing skills are built into the MPharm degree and foundation training year
The GPhC standards now require prescribing competence to be achieved at the point of registration
Supervised practice included earlier
Foundation trainees are supported by Designated Prescribing Practitioners (DPPs) and clinical supervisors during training, rather than years later.
Registration outcome
From 2026, all newly qualified pharmacists will be independent prescribers at the point of registration
No extra course after qualification
The separate IP course is phased out for new entrants.
Prescribing is core to the pharmacist role, not an optional add-on