AP Psychology Unit 1: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Try to get uncooked for this horrid test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Nature Vs. Nurture
What plays a bigger factor in one’s behavior: genetics or their enviorment
Behavior Genetics
Explores the genetic and Enviormental roots of human differences
How do behavior genetisitcs explain our indivudal differences?
They compare our enviorment vs. our genetics to explain our behavior
Heredity
The genetic transfer of charecterisutsc from parent to offspring
Genome
the complete set of genes or genetic material present in a cell or organism.
Dif between monozygotic and dizygotic twins
Mono=one egg splits (identical), Dizygotic=two eggs drop at the same time (fraternal)
Epigentics
how enviorments influence our genetics
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
Central and Periphreal
What makes up the central nervous system
The brain and Spinal Chord
What is the Periphreal nervous system
broken down into 4 other, on the outside, every neuron that is not your brain or spinal chord (connects the CNS to the body)
Autonomic nervous system
self-regulated bodily functions (you do not have to think about them)
Somatic nervous system
voluntary movements and responses
Sympathetic nervous system
arousing (stress-response, fight or flight, or freeze, or fawn, hightened state)
Parasympathetic nervous system
calming, helps maintain homeostasis
Afferent neurons
sensory neurons
Efferent neurons
Motor neurons
What are the primary information processors in the nervous system?
Neurons
What is the main function of glial cells?
support neurons
What happens when a neuron reaches the threshold potential?
it deploarizes
What does a Dendrite do
Receives signals from other neurons and brings in information (branches)
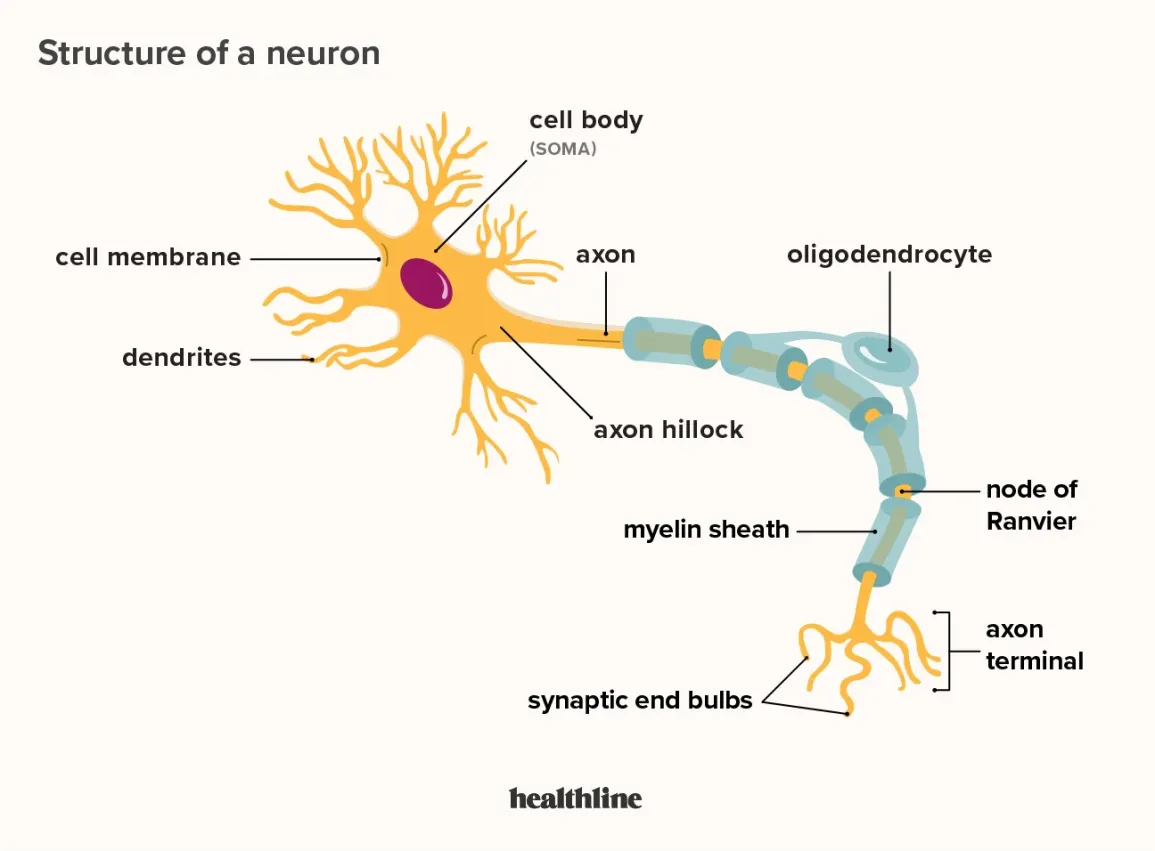
Soma
Cell’s body; contains nucleus and DNA
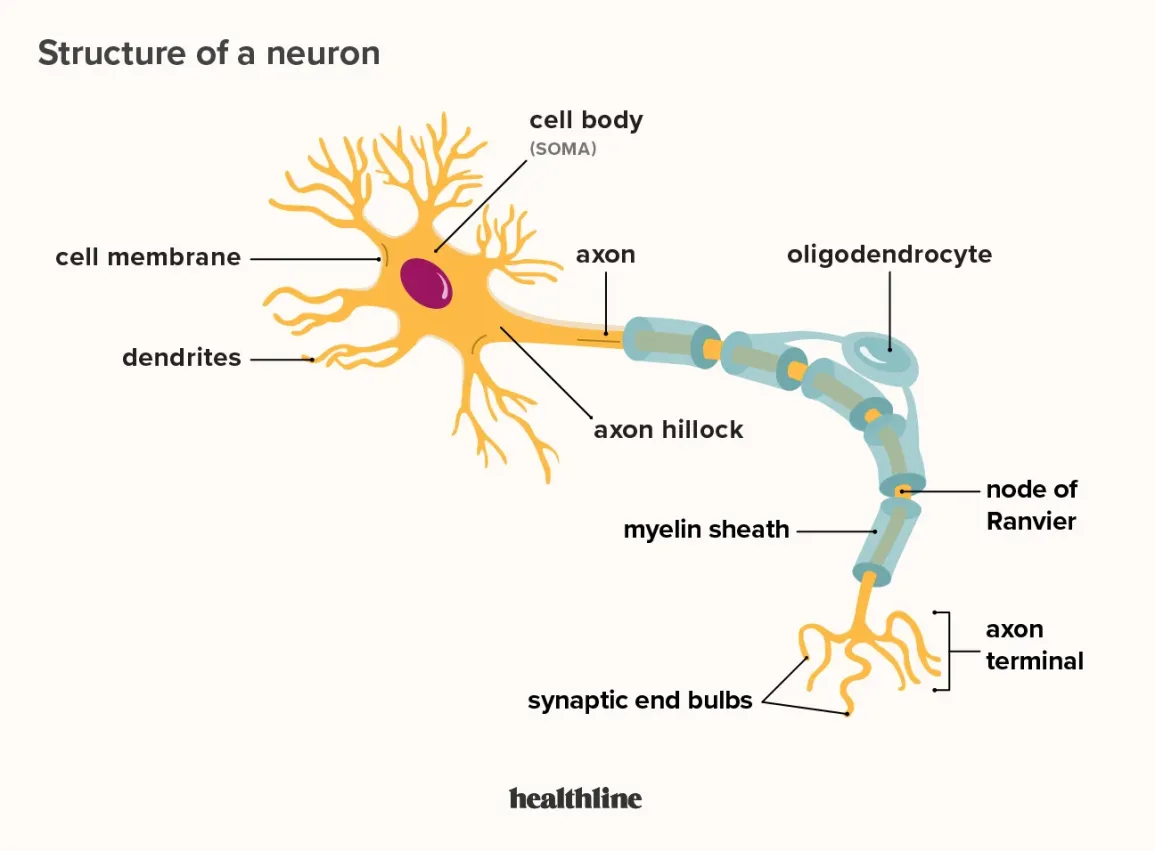
Axon
Carriers signals from one end to the other (trunk)
Axon terminals or Terminal buttons
sends singlas to next neuron (roots)
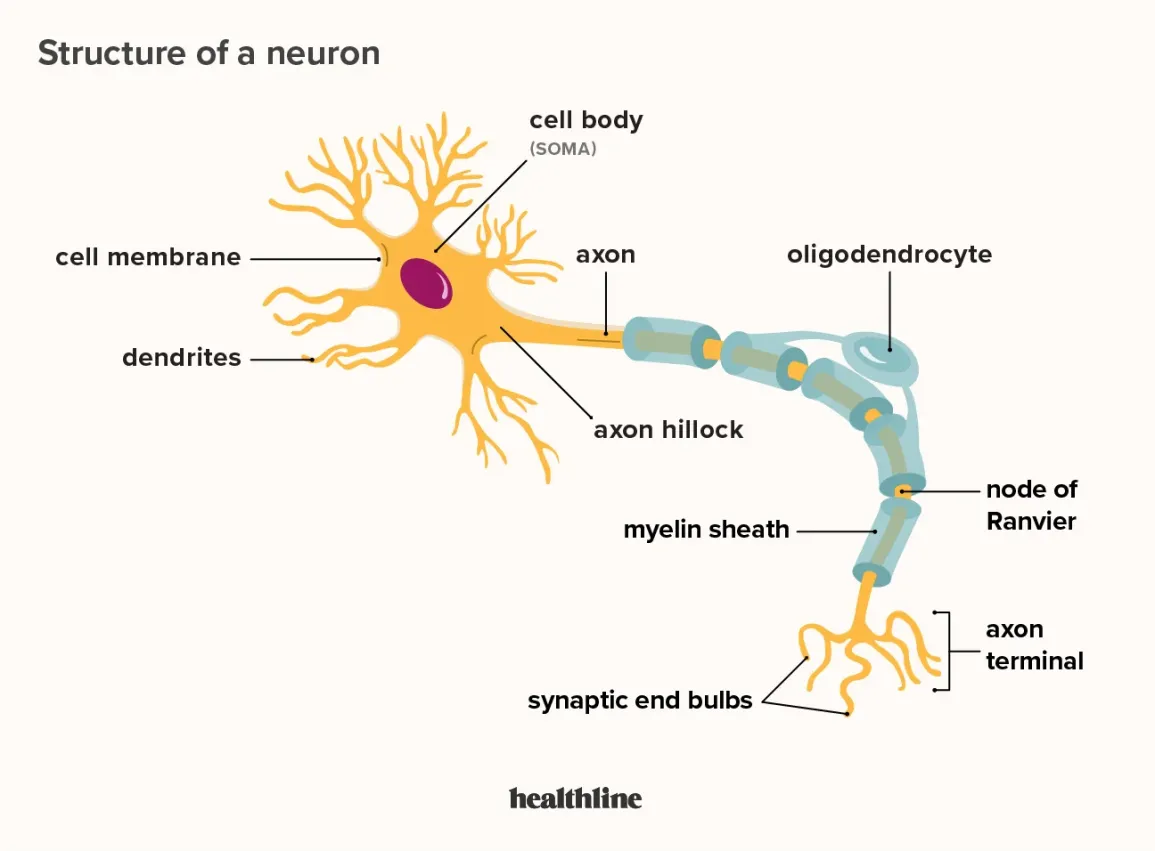
Myelin Sheath
Covers the axon; insulates and protects the axon (bark)
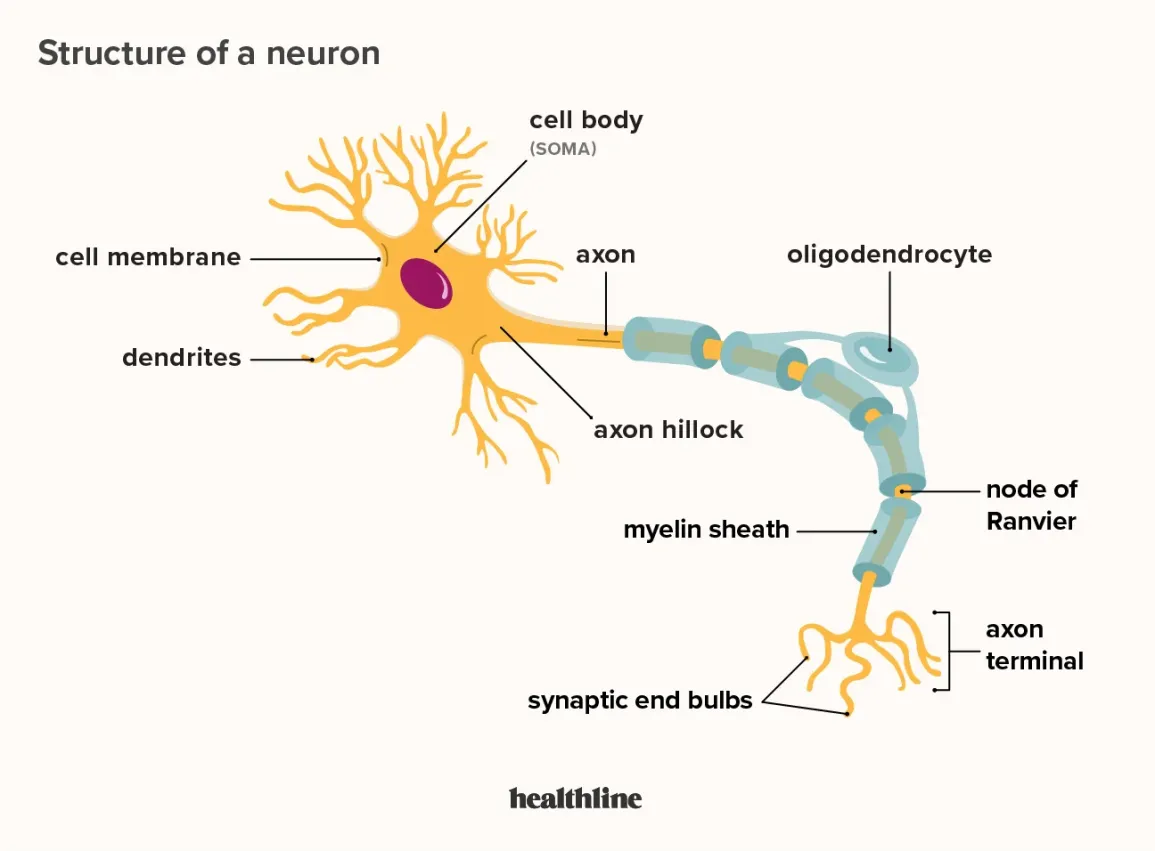
Nodes of Ranvier
a gap between the myelin sheaths
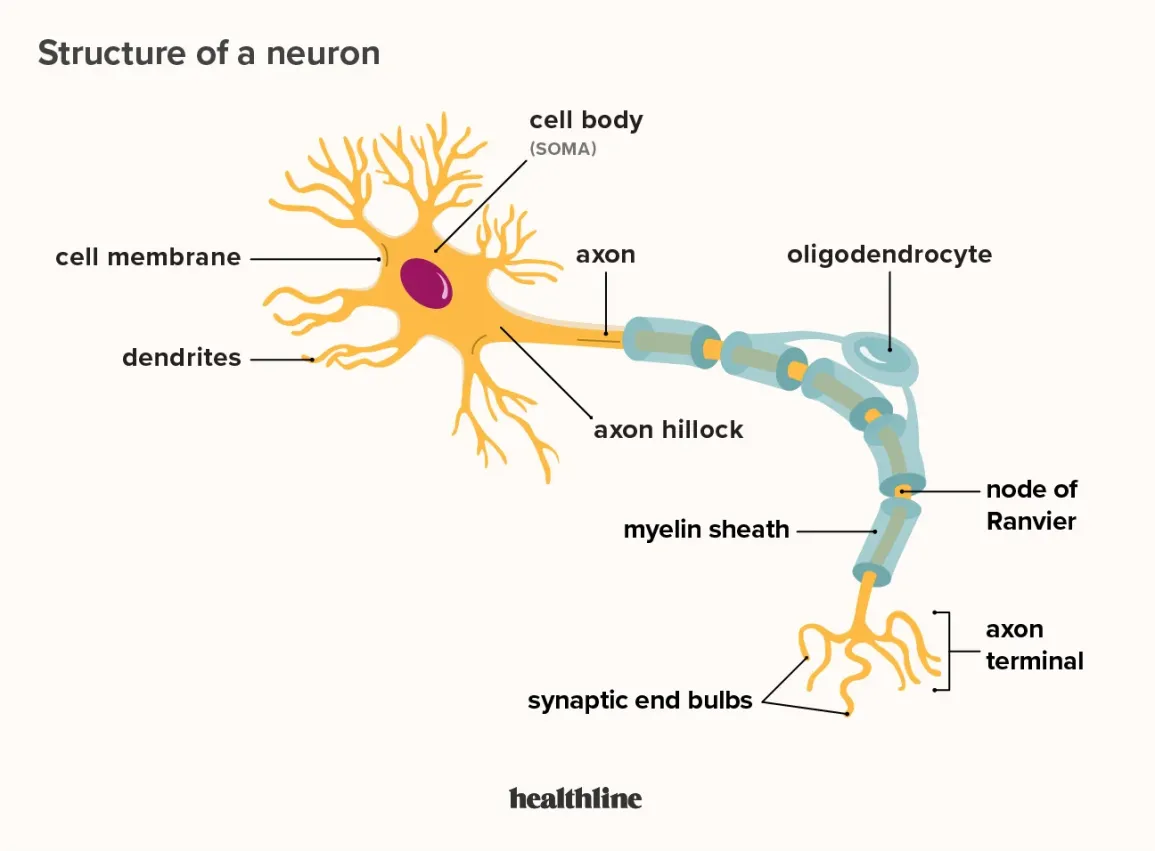
What is the purpose of Schwann cells
they produce myelin for the myelin sheath and the nodes of ranvier
What is the purpose of Glial Cells
surrounds the neuron, provides extra protection and nourishment to neurons. (worker bees) (Support neurons)
How does information pass through a neuron
the neurone sends a message by firring an impulse called the action potential
Aspects of Nerual Transmission:
Threshold
the level of stimulation to trigger a neutral impulse
Action potential
a brief electrical charge that travels down a neurons axon
Resting Potential
The neuron is positive outside and negative inside (selectively permeable)
Refractory Period
a brief resting pause that occurs after a neurons has fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon reutnrs to its resting state
All or none response
a neuron either fires with full strength or does not fire at all (like a gun)
Neurotransmitters
chemcial messagers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Synaspe or synaptic cleft
the meeting point between neurons
Reuptake
the left over chemicals that were it used get absorbed by the axon terminal
Acetylcholine (ACh)
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
dopamine
influences voluntary movement, learning, attention, and memory
serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
norephinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal
GABA
(most common inhibitor) natural tranquilizer, involved in calming you down
glutamte
excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in memory
endorphins
influence the perception of pain and pleasure
substance P
invovled in pain perception and immune response
Agonists
increasing/mimicking a neurotransmitter action (caffeine and opiods) “acting like”
Antagonists
blocking neurotransimmters from releasin; block receptor sites (Botox and narcane)
hormones
slow chemical messangers of endocrine system
Pituary Gland
master gland (controls all the glands)
Endoctrine System:
Adrenaline
prepares the body for emergencies
Oxtocin
Facilitates location and improves relationships (bonding hormone)
Melatonin
Plays a role in managing your sleep (wake cycle and circadium rhythym)
Leptin
helps control hunger
Ghrelin
Tells your body you’re hungry
What are psychoactive drugs
chemicals you take that are altering your mood or perception
Hallucinogens
drugs that distort perception, cause false sensory hallucinations, impair memory, and givesensations of relaxation and/or euphoria
Depressants
drugs that slow things down (increase relaxation and decrease arousal)
Stimulants
Drugs that excite neural activity (increase energy, decrease apatite, briefe feelings of euphoria)
what do Biological psychologist focus their research on
they focus on how the body and brain enable emotions, memories, and sensory experiences, as well as genes vs. enviorment
The Biopsyschosocial Apporach
Biological, physical, psychological
Neurogensis
Creating new neurons/brain cells
Neuroplasticity
The brain’s ability to rewire itself if it is damaged
Lesion
A cut in the brain (sometimes purposeful to stop things like seizures from spreading)
EEG
electordes places on the scalp that measures electron activity in neurons (swim cap with wires example)
MEG
looks at magnetic waves in your brain
PET
shows brain activity (radioactive glucose)
MRI
ONLY STRUCTURE (gives detailed pictures of your soft tissue) (uses magnetic field)
fMRI (functional MRI)
shows activity and structure
CT
Strucutral scan (uses x-ray)
Hindbrain evolutonal purpose:
survival
Midbrain evolutional purpose:
Movement, sensation
Forebrain evoluinalary purpose:
allows for more sophisticated responses to the environment, processes sensory information
Brainstem
autonomic survival (ex. breathing) above spinal chord
Thalamus
sensory "switchboard”, directs everything EXCPET SMELL
Reticular formation
helps tell the thalamus what’s more important (fire alarm example), helps control arousal
Medulla
controls breathing and heartbeat, base of brainstem
Pons
controls movement and sleep (bigger swollen parts of the brain stem)
Cerebellum
movement, balance, posture, processes sensory input, judgement of time, enables nonverbal memory and learning (one of the first parts affects by alchohol)
Hypothalamus
deals with addiction, helps regulate homeostasis (things like fullness, body temp, endoctrine system via the pituitary gland) dopamine is stored here (if damaged the body can not regualte itself)
Amygdala
focuses on aggression and fear (survival emotions)
Hippocampus
responisble for processing and storing explicit memories of facts and events (linked with smell)
Corpus Callosum
Joins the two hempispheres, allows for the communication between both sides of the brain
Pituitiary Gland
master gland, connected to hypothalamus, releases hormones throughout the body
Pineal Gland
Produces melatonin, regulates body’s sleep cycle
Frontal Lobe
ability to recognize future consequences, making judgement, planning and decision making, abstract thought, personality
Motor Cortex (FL)
Sends signals to our body to control muscle movement (like writing, “fine motor skills”), more area=more control
Broca’s area (FL)
responsible for controlling muscles that produce speech (only in the left hemisphere)
Parietal Lobes
math and spatial abilities (top of the head)
(in parietal lobe) Somatosensory Cortex
takes in sensory input from corresponding body parts
Temproal Lobes
Above the ears, has auditory areas, receives input from opposite ear, assists with memory
Auditory Cortex (TL)
orginzation and processing of auditory information
Wernickes Area (TL)
responsible for language comprehension
Occipital Lobe
above cerebellum, receives info from visual fields of opposite eyes for visual processing
Visual Cortex (OL)
orgnization and processing of visual information
What are association areas
any part of the brain that is not dealing with primary motor or sensory functions
Differences between the left and right hempispheres
left: logic, thought, language abilities, analytical
Right: creativeness, impulsive, emotional thought
What does cognitive neuroscience explore
how our physical brain links with our non-physical consciousness
Dual Processing
the idea that the mind operates on two independent tracks simultaneously: a fast, automatic, and intuitive track (System 1/unconscious mind) and a slower, deliberate, and analytical track (System 2/conscious mind)
Parallel Processing
the brain's ability to handle multiple streams of information simultaneously, rather than one at a time (unconscious mind)
Sequntial Processing
the brain's ability to handle multiple streams of information simultaneously, rather than one at a time (conscious mind)
Blindsight
the ability to respond to visual stimuli without conscious awareness of seeing them. Individuals with blindsight can perform actions like locating an object or navigating around obstacles, even though they are physically blind and have no conscious visual experience.