Bio 112 Exam 2
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
4 Types of Tissues
Connective Tissue: plays a role in support
Nervous Tissue: controls and coordinates body function
Muscle Tissue: functions in movement
Epithelial Tissue: covers the outside of the body, lines organ surfaces, form glands
Types of connective tissue and where they’re found
Loose CT: adipose/fat, reticular connective tissue
Dense CT: tendons, ligaments
Supportive CT: bone, cartilage
Fluid CT: blood, lymph
Where is nerve tissue found?
Brain, spinal cord, nerves throughout the body
Types of muscle tissue and where they’re found
Skeletal muscle: bladder, rectum
Cardiac muscle: Heart
Smooth muscle: Blood vessels, walls of digestive tract
Where is Epithelial tissue found?
Skin, lines organ surfaces, form glands
Why is epithelial tissue important for homeostasis?
Control exchange of materials across its surface
Membrane proteins regulate the transport of molecules and ions
Homeostasis depends on this regulation of transport
What is the polarity of Epithelial tissue and its importance?
Apical side (faces outer environment)
Lines organs and secretes mucus
Basolateral side (faces the inside)
attaches epithelial tissue to basal lamina
What are the differences between cells, tissues, organs, organ systems?
Cells have similar functions and are organized into tissues, Tissues are organized into specialized structures called organs, organs are part of a larger unit called organ system.
Are organs made up of one type of tissue?
No, organs are made up of many types of tissue.
How does body size affect an animal’s physiology?
As an organisms size increases, its mass-specific metabolic rate must decrease.
What is the cell surface volume ratio?
Controls the rate at which nutrients enter/exit the cell and rate at which they are used. Most optimal is HIGH surface area and LOW volume.
What is the consequence of rapid volume increase more than surface area?
The Basal Metabolic Rate decreases because it is inversely proportional to the mass of an animal.
What does surface area control?
Diffusion rate
What does volume control?
Metabolic rate
What are 3 ways for a structure to have a high surface area volume ratio?
Flattening (I.e. fish gills)
Folding (I.e. small intestine)
Branching (I.e. blood vessels)
What is homeostasis?
Maintaining the internal environmental parameters; keeping things constant
What tissue type is important for homeostasis?
Epithelial Tissue
How do homeostatic systems function?
Homeostasis is reliant on Negative feedback.
Sensor
Structure that detects some aspect of the external or internal environment and sends that information to the integrator
Integrator
Component of the nervous system that evaluates incoming sensory information and determines potential responses
Effector
Any structure that helps return to the desired normal condition, set point, via signals from the integrator
What are the 4 mechanisms of heat exchange?
Conduction
Direct transfer of heat between two physical bodies in contact
I.e. Turtle basking on a rock, heat transfers from rock to turtle
Convection
Heat exchanged between a solid and liquid or gas, rather than two solids
I.e. heat transfer occurs from water to the turtle
Radiation
Exchange but no physical contact
I.e. Sun radiates heat unto the turtle
Evaporation
occurs when liquid turns into gas
I.e. water evaporates off of the turtle shell
Homeotherm vs Heterotherm
Homeotherms - Keep body temperature constant
Heterotherms - Tolerate changes in body temp
Endotherm vs Ectotherm
Endotherm - produces own heat
Ectotherm - relies on heat from the environment
What is the difference between the CNS and the PNS?
Central nervous system - Brain and Spinal Cord
Peripheral nervous system - All of the components of the nervous system outside the CNS are part of the PNS
Sensory cells in PNS sense stimulus, send to neurons in PNS, when activated send signal to CNS to interneurons, interneurons tell motor neurons to activate effectors/ glands/ muscles
What are the 3 types of neurons?
Sensory neurons (In PNS)
transmit information to the brain and spinal cord
Interneurons (In CNS)
makes connections between the sensory neurons and motor neurons
Motor Neurons (In CNS)
nerve cells that send signals to effector (response) cells in glands or muscles
What are the 3 parts of a neuron?
Dendrite
Receives the chemical signals
Soma/Cell Body
Integrates the electrical signal
Axon
Propagates the electrical signal (passes it on)
How do neurons communicate?
Electrical signaling
What is a synapse?
The place where 2 neurons communicate and connect with each other without touching.
How is a membrane potential created?
By the difference in charge between the ions located on the outside and inside of the cell membrane. The membrane potential inside of a cell will be negative.
What is the unit of the membrane potential?
mV
What is the resting membrane potential neurons?
-65 mV to -80 mV
Where are the potassium and sodium concentrations highest?
Potassium concentration is higher INSIDE the cell and sodium concentration is higher OUTSIDE the cell.
What are the 2 mechanisms to maintain membrane potential?
K+ Leak Channels
Na+/K+ ATPase Pump
3 sodium goes out and 2 potassium goes in
How does the change in ion flow affect the membrane potential?
Ion flow in and out of the membrane changes the membrane potential.
Depolarization vs Hyperpolarization
Depolarization - less negative, more positive than resting membrane potential
Hyperpolarization - more negative than resting membrane potential
What are the 3 phase to the action potential?
Depolarization
Membrane potential becomes less negative and moves toward a positive charge/value
Na+ enters the cell
Repolarization
Changes the membrane back to a negative charge
K+ leaves the cell
Hyperpolarization
Membrane potential becomes more negative than resting potential
Momentary, then returns back to resting potential
What does it mean that action potential is an “All or Nothing” event?
MUST PASS THRESHOLD in order to fire an action potential
How do voltage-gated channels function?
Voltage-gated channels are channels in the plasma membrane that open and close in response to changes in voltage
What is a role of myelin in action potential propagation?
Myelin acts as electrical insulation preventing the ions from leaking out as it spreads down the axon.
What cells produce myelin in the CNS?
Oligodendrocytes
What cells produce myelin in the PNS?
Schwann cells
What is the node of Ranvier?
The sections of exposed axon between segments of myelin sheath that contains dense areas of voltage-gated Na+ channels. (concentrator)
How does action potential induce the release of a neurotransmitter?
Action Potential arrives near the synaptic cleft.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open. Ca2+ enters presynaptic
cells.Synaptic vesicles fuse with presynaptic membrane, then
release neurotransmitter.Ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane open when neurotransmitter binds; flow of ions causes change in postsynaptic cell potential.
Ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane then close as neurotransmitter is broken down or taken back up by presynaptic cell.
What type of vesicles store neurotransmitters?
synaptic vesicles
Presynaptic cell vs Postsynaptic cell
Presynaptic - sending cell
Postsynaptic - receiving cell
What ions and channels induce synaptic vesicle fusion?
Ca2+
How do neurotransmitters affect the postsynaptic cell?
Neurotransmitters act as ligands that bind to ligand-gated channels on the postsynaptic membrane causing the flow of ions along the electrochemical gradient. This causes a change in the post-synaptic membrane potential.
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) vs Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) - causes the membrane to depolarize, increasing the likelihood of an action potential
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) - causes the membrane to be hyperpolarized, decreasing the likelihood for an action potential
What are the 2 major divisions of the PNS?
Somatic system - controls conscious movement (voluntary movement)
Autonomic system - controls internal processes; unconscious movement (involuntary movement)
What are the 2 divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System?
Parasympathetic - promotes relaxation or digestion
Sympathetic - prepares organs for stressful situations; “fight or flight”
What are the 4 structures of the brain?
Cerebrum - responsible for conscious thought and memory
Cerebellum - responsible for coordination of complex motor patterns
Diencephalon - responsible for information relay and control of homeostasis
The Brain Stem - responsible for information relay; autonomic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive system
What are the 3 processes in the sensory system?
Transduction - convert stimulus to action potential
Amplification - amplify signal
Transmission - transmit signal to brain
What are the 7 types of sensory receptor cells?
Nociceptors
Stimulated when there is a harmful stimulus. (I.e. tissue injury)
Thermoreceptors
Detect change temperature
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to distortion caused by pressure changes
Chemoreceptors
Perceive presence of specific molecules
Photoreceptors
Respond to wavelengths of light
Electrorecptors (uncommon)
Detects electrical fields
Megnetoreceptors (uncommon)
Detects magnetic fields
What the common sensory stimuli?
Smell
Sound
Sight
Pressure
Temperature changes
How do sensory stimuli affect action potential?
Sensory stimuli change the membrane potential of sensory receptor, resulting in a change of the firing rate of action potential sent to the brain.
Are receptor cells specific?
Yes, receptor cells are highly specific in that each sensory neurons sends its signal to specific area of the brain.
What is the Mechanoreception sensory system?
Pressure sensing systems used for hearing, physical pressure on the skin, the movement of muscles, and stretching of blood vessels.
How do hair cells transduce pressure changes into sensory neuron firing?
When there is a stimulus, pressure wave, the stereocilia bend
The potassium channels open
The Membrane depolarizes because there was more potassium outside of the cell
Then calcium flows inside the neurotransmitter
This induces the fusion of vesicles
Then the neurotransmitter is released
What is the Importance of stereocilia and the kind of channels on them?
Stereocilia are projections that are connected to each other via Potassium Channels. Ions flow into the cell through the potassium channels.
What happens if hair cell bending hyperpolarizes the membrane?
If hyperpolarization occurs, less neurotransmitters are released and leads to inhibition of postsynpatic sensory neurons.
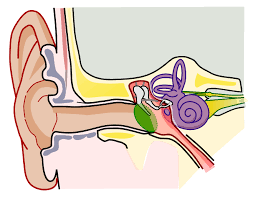
What’re the 3 main parts of the mammalian ear structure?
Outer Ear
Middle Ear
Inner Ear
How do changes in air pressure lead to bending of hair cells in the cochlea?
The fluid in the cochlea is disrupted by the mechanical vibrations which cause the hair cells to bend.
What is the path of sound in the ear and functions of structures?
The outer ear collects pressure waves and funnels them into the ear canal where they strike the tympanic membrane
The tympanic membrane vibrates and passes the vibrations into the ear ossicles
The stapes, last ossicle, vibrates against the oval window
The oval window generates waves in the fluid inside the cochlea
The hair cells sense the pressure waves in the fluid
What structures of the ear amplify sound?
The 3 ossicles amplify the vibrations of the tympanic membrane
What structure allows hair cells to be sensitive to different frequencies?
The Basilar Membrane
Where are hair cells located in the cochlea?
The middle chamber, sandwiched between the tectorial and basilar membrane.
What is the Lateral Line System?
A series of canals in fish and larval amphibians that contains hair cells which detect pressure changes underwater.
What is the Photoreceptor Sensory System?
The organs involved in sensing light changes that range from simple-light sensitive eyespots to sophisticated, image-forming eyes. The sensory ability correlates with the environment it lives and its mode of life.
What is the structure of the insect’s compound eye?
Composed of hundreds or thousands of light - sensing columns called ommatidia. Each ommatidia has a lens that focuses light onto a small number of receptor cells.
What are the 6 major structures of the vertebrate eye and function?
Sclera - the tough outermost layer; “white of the eye”
Cornea - a transparent sheet of connective tissue formed by the front of the sclera
Iris - round muscle that can contract or expand to control the amount of light entering the eye
Pupil - hole in the center of the iris
Lens - a curved clear structure that focuses light with the cornea
Retina - the area in the back of the eye that receives light focused by the lens and cornea
What are the 3 different layers in the retina?
Photoreceptors - form a layer at the back of the retina
Bipolar cells - intermediate layer of connecting neurons
Ganglion cells- form the front or innermost layer of the retina and whose axons project to the brain via the optic nerve
What is the name of the photoreceptor cells in the retina?
Rods and Cones
What is the difference between rods and cones in term of light detection?
Rods - sensitive to dim lights and not color
Cones - stimulated by different wavelengths of light (colors)
What is the Rhodospin complex? The effect of light on retinal and ospin?
The Rhodospin is a transmembrane protein complex of pigment (Retinal) and Opsin (protein). The complex is activated when light changes the shape of retinal and activates the Opsin.
Explain the signaling pathway(PDE and cGMP) in rods stimulated by light
Rhodspin is activated when light causes retinal to change shape
Activates membrane protein transducin, which activates Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
PDE breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) to guanosine monophosphate (GMP)
cGMP sodium gated channels close
Na+ decreases, then neurotransmitter release decreases
How is color vision possible?
There are 3 types of cones, each with a different type of opsin that responds to distinct wavelengths of light. The brain senses the color by integrating the signals from all three opsins.
Short - blue light
Medium - green light
Long - Red light
What is Chemoreception?
The result of a molecule binding to the chemoreceptor and transducing electrical signals in the body.
What are taste cells? Where are they found?
Taste cells are taste-sensing chemoreceptors that synapse to sensory neurons and are found in taste buds in groups of 100. The taste buds are scattered around the mouth and throat, but mostly on the tongue.
What are Olfactory Receptors connected to?
Each Olfactory neurons has one type of receptor, and neurons with the same receptors all project to the same Glomerulus in the Olfactory bulb.
What are some other sensory systems found in animals?
Thermoreception - detects change in temperature
Electroreception - detection in electrical fields
Magnetoreception - detection in magnetic fields