Biomechanics
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Linear Motion
Where movement is along a straight or curved line, there is no rotation & all body parts move in the same direction at the same speed. e.g. a cyclist who stops pedalling
Rectilinear Motion
Movement is linear & occurs through a straight line e.g. a basketball chest pass
Curvilinear Motion
Movement is linear by objects move through a curved trajectory. e.g. the trajectory of the ball as it is shot into the goal in netball
Angular Motion
Where all the parts of a body move through a rotational pathway, through the same angle, in the same direction & at the same time. It is the rotary movement without an axis. e.g. when a gymnast performs a giant on the bar
General Motion
A combination of linear & angular motion. e.g. a cyclist moving in a straight line as a result of the rotation of the legs about the hip joint
Distance
How far you have travelled from your start to finish point, regardless of direction. Measured in total distance covered
Displacement
Measures the overall change in position of a person and is measured in magnitude & direction
Speed
A measure of the distance an object travels per unit of time.
Distance travelled / by time taken
Velocity
Speed in a given direction
Displacement / time
Acceleration
The rate at which the velocity of a body changes with respect to time
Change in velocity / time
Acceleration due to Gravity
The naturally occurring force resulting in downward acceleration on a body at a constant rate of -9.8m/s
Uniform acceleration
When a body accelerates at a constant rate in both magnitude & direction
Angular displacement
The difference in the angle between the start & end position of the body
Angular distance
The sum of all the angles as a body moves from its start position to its end position
Force
An interaction that, when unopposed, will change the. motion of an object
Mass x Acceleration
External Forces
The result of the interaction between the body & the environment e.g. gravity
Internal Forces
Result from structures of the body that interacts to produce movement e.g. the action of muscles & tendons that act together to produce forces causing movement
Contact Forces
A type of external force that acts on an object that comes into direct contact with another e.g. frictional or air resistance forces
Non-contact Forces
A type of external force that acts on objects without coming into direct contact with one another e.g. gravity
Newton’s 1st law
A body continues in its state of rest or state of motion unless acted upon by force
Inertia
The amount of resistance to a change in a object’s state of motion
Newton’s 2nd law
The acceleration of a body is proportional to the force applied to it & inversely proportional to the object’s mass
Momentum
A measure of the amount of motion possessed by a moving body.
Mass x Velocity
Impulse
The application of force over a period of time to change the momentum of an object
Force x Time
Newton’s 3rd law
For every action, there is an equal & opposite reaction
Ground reaction forces
The force exerted by the ground on a body in contact with it
Conservation of momentum
The total momentum of two objects before & after impact are equal
Resistance
The weight or load to be moved
Axis
The pivot point or fulcrum around which the lever rotates
Effort
The application of force or effort
Effort/force arm
The distance between the fulcrum & the point at which the force is applied
Resistance arm
The distance between the fulcrum & the centre of the resistance
Effort force
Force exerted on the lever
Resistance force
Force exerted by the lever
Force multiplier
Increasing the application of force by making the force arm longer than the resistance arm
Speed multiplier
Increasing movement speed by making the resistance arm longer than the force arm
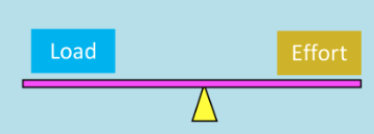
1st class lever
The axis is located in the middle, with the force & resistance on either side e.g. heading a soccer ball
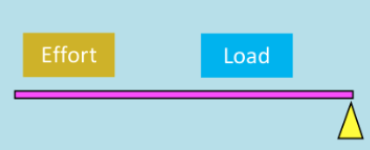
2nd class lever
The axis is located at the end, with the resistance in the middle & force applied at the end. e.g. performing a calf raise
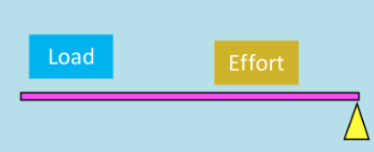
3rd class lever
The axis is located on one end, with the application of force in the middle & resistance applied at the opposite end. e.g. a bicep curl
Projectile
An object propelled into the air or water & affected only by the forces of gravity & air resistance
Static balance
The ability to hold a stationary position. e.g. holding a handstand
Dynamic balance
The ability to hold a moving position to execute an outcome. e.g. riding a skateboard
Centre of Gravity
The theoretical point in an object, located either inside or outside of the body, where all of the body’s mass is equally distributed
Line of gravity
An imaginary vertical line passing downwards through the centre of gravity to the ground or surface the person is on
Base of Support
The area bound by the outermost regions of contact between a body & support surface