ECON 2105 UGA Midterm 2
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
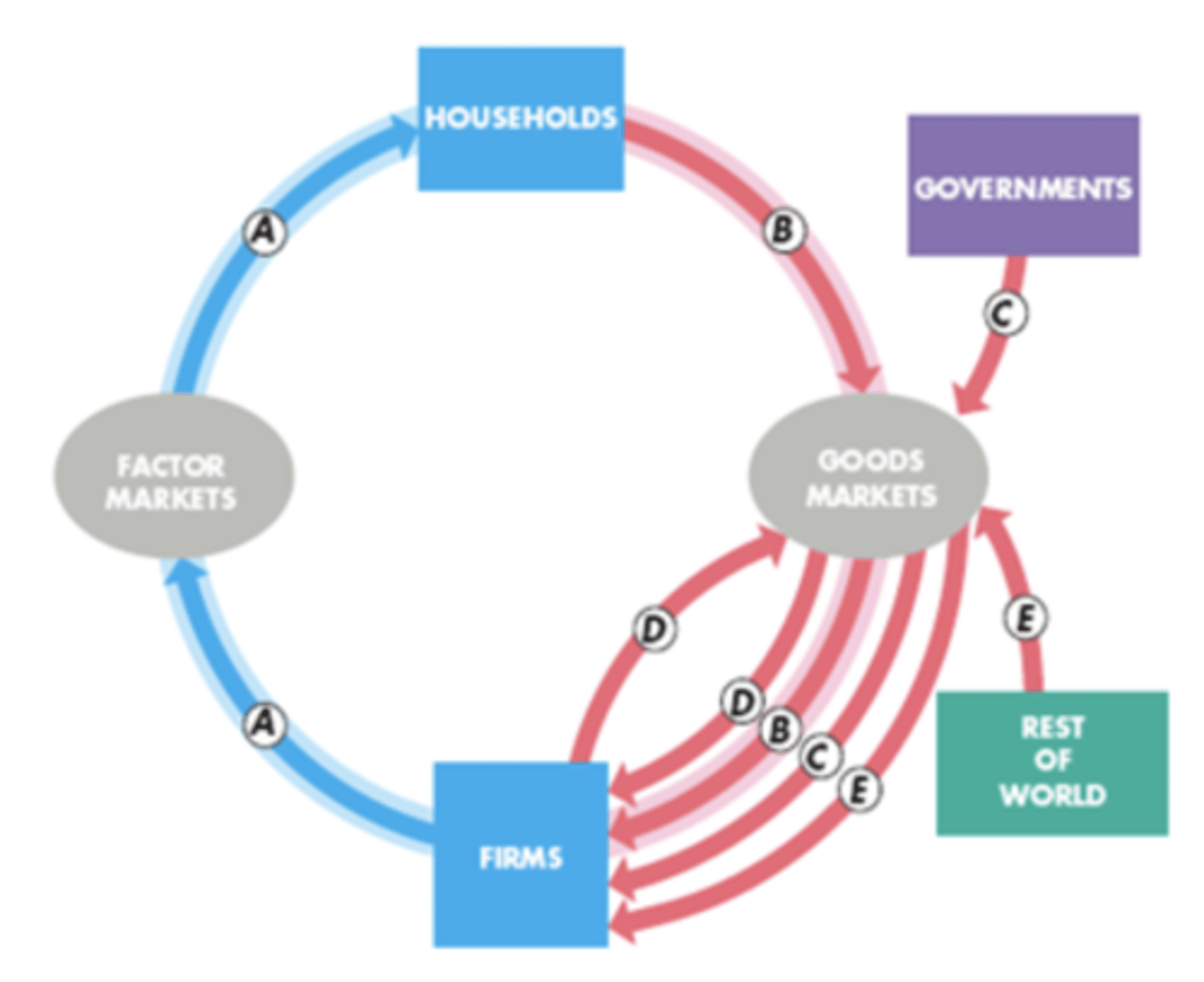
-A (Y) income
-B (C) consumption expenditure
-C (G) Government expenditure
-D (I) Investment
-E (X-M) net exports from rest of the world
Label A-E on the GDP flow chart
Market value of the final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period
GDP definition
productivity and wealth
What two things about a country does GDP measure
the prices at which items are traded in markets
market value definition
(Price X Quantity)
formula to calculate the total dollar value of an item
an item that is bought by its final user during a specified time period
Final Good definition
an item that is produced by one firm, bought by another firm and used as a component of a final good or service
intermediate good definition
only final goods
Does GDP include final goods, intermediate goods, or both?
(B) payments from households to firms (largest component of GDP)
consumption expenditure definition
(D) payments from firms to firms (EX: if UPS buys a new delivery van)
investment
gross investment: the total amount spent on both new capital and replacement capital
net investment: the increase in the value of capital
2 different types of investment and their definitions
(C) payments from governments to firms
(doesn't include taxes)
government expenditure definition
(E) payments from the rest of the world to US firms
the net value of exports and imports
next exports definition
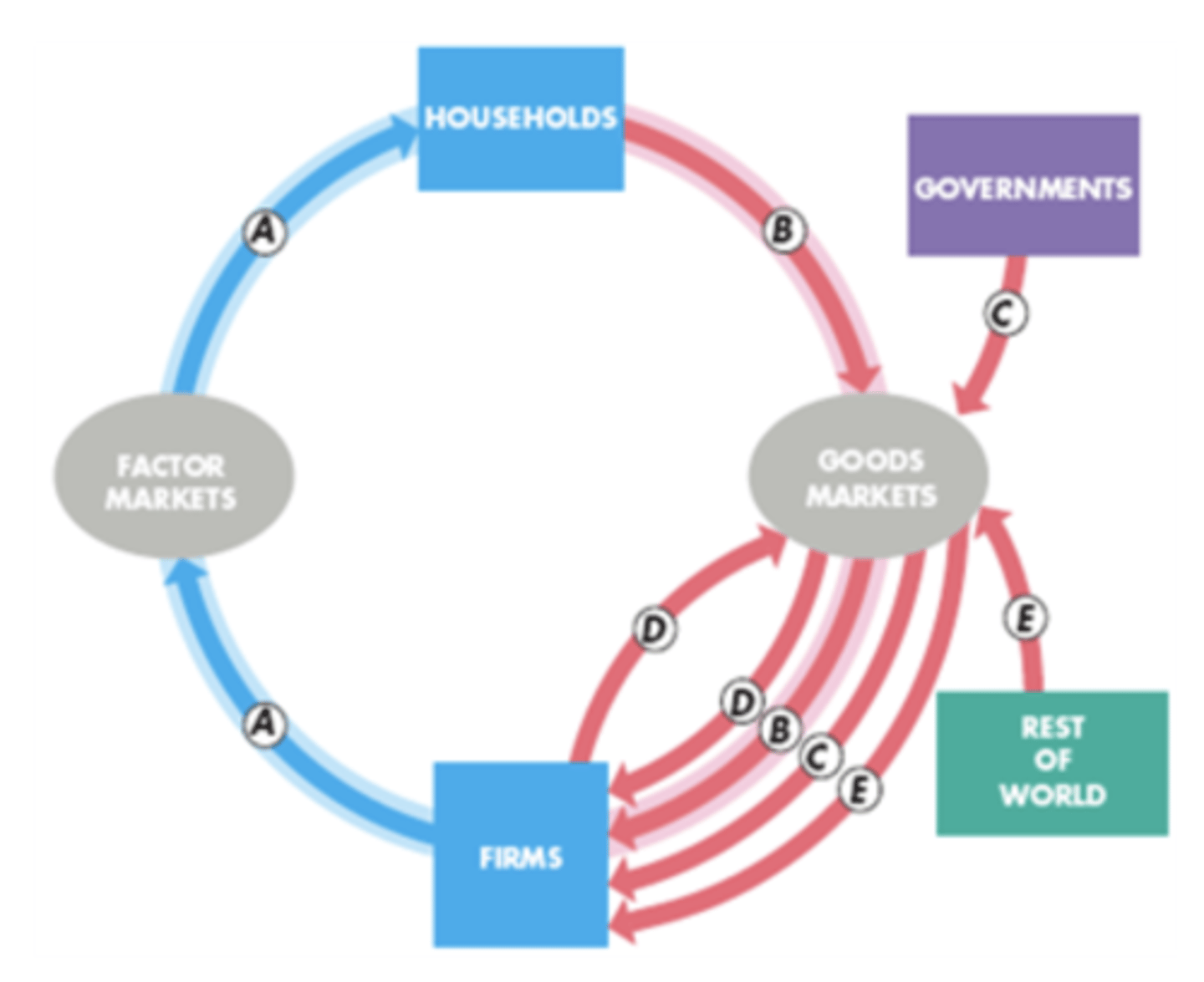
(A) payment flows from firms through factor markets to households (most income is wages, also includes interest, profits and rent)
income definition
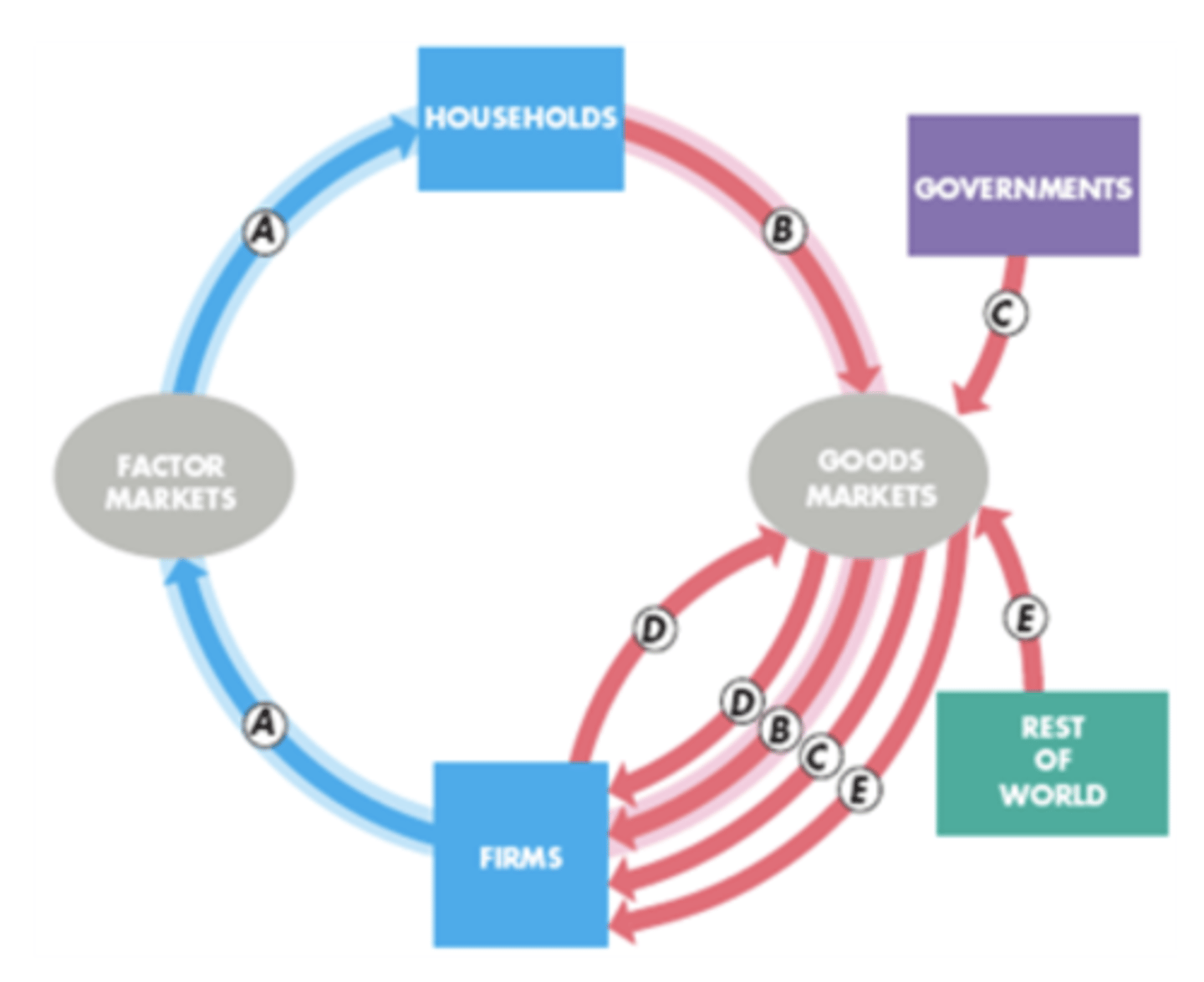
B+D+C+E (in real text E might be X-M)
aggregate expenditure formula in terms of A-E on graph
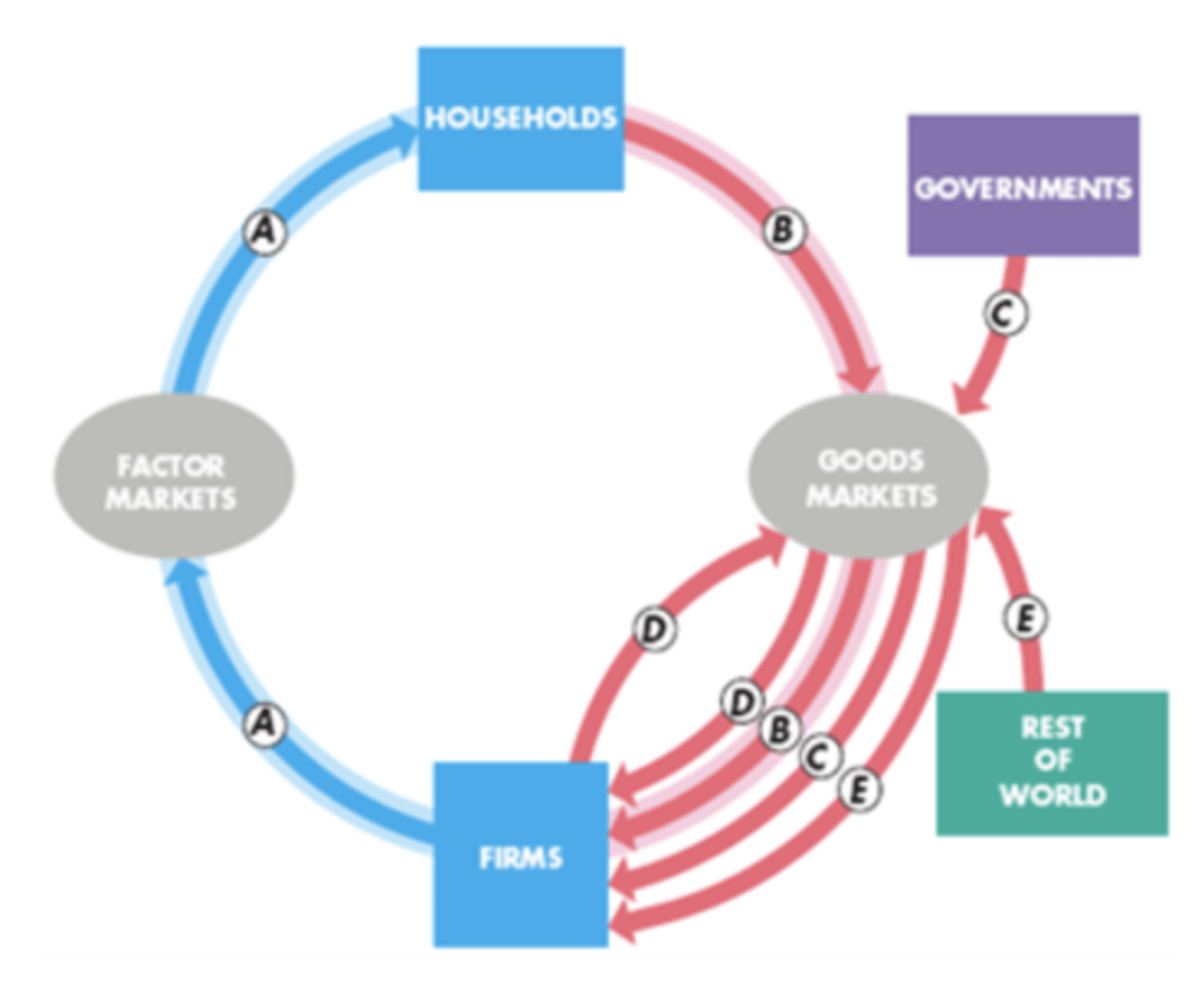
A
aggregate income formula in terms of A-E on graph
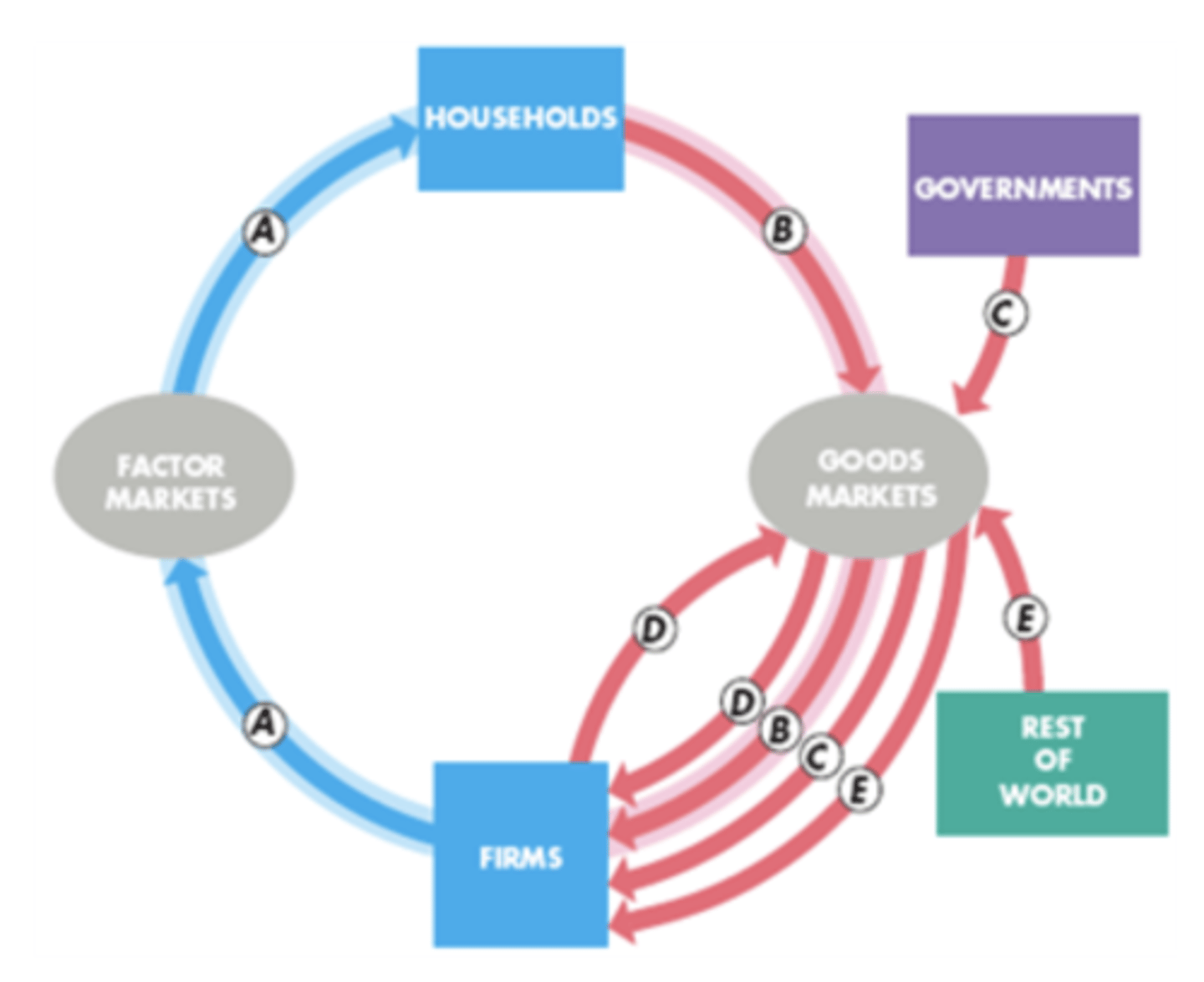
A=B+D+C+E (in real text E might be X-M)=GDP
GDP formula in terms of A-E on graph
the value of final goods and services produced in a given year when valued at the prices of that year
nominal GDP definition
the value of final goods and services produces in a given year when valued at the prices of a reference base year
Real GDP definition
Real GDP per person= Real GDP/ population
what is the formula to track standard of living (based off of GDP) of the average resident over time?
fluctuations
What is it called when real GDP bounces around from year to year
the highest level of GDP that is sustainable in the long run, given the factors of production that are available
potential GDP definition
the business cycle
What is the pattern called that the fluctuations follow?
1. expansion: real GDP increases
2. Peak: Real GDP hits a temporary high point
3. Recession: Real GDP decreases
4. Trough: Real GDP reaches a temporary low point
What are the four stages of the business cycle
1. while it repeats, the timing is irregular
2. we don't know we
What two things do we know about the business cycle?
(purchasing power parity (PPP))
•PPP approach uses the same prices to calculate the value of each country's products
What does PPP mean and what is its application
-household production: things made at home for home use
-Underground economic activity: Goods and services that are paid for but that aren't observed by the government
-Leisure: Activities that people do for fun, rather than to produce something
-Environmental quality (clean air, clean water, etc.) is valuable
-new inventions: prices are impossible to compare to when they didn't exist
What does Real GDP not measure
-Human development index
-green net national product
-happiness index
3 other measures of economic well-being are
-bad for me to be unemployed
-bad for economy when too many people are unemployed
-less consumption today and less growth tomorrow
What are the 3 reasons why unemployment is bad
-experience
-increased human capital
What 2 things does work earn besides income?
every 10 years
When is the US Census recorded?
monthly survey of a small sample (60,000) of US households
When is the Current population survey (CPS) recorded?
total population and working-age population
What does the CPS differentiate between?
over 16 and not institutionalized
working age population requirements
people who can work and are either working or trying to find work
who is in the labor force?
people who are not working and are not trying to find work
who is not in the labor force?
unemployed and employed
the labor force is made up of both people who are _________ and __________.
-tried to find a job within the last 4 weeks
-got laid off from job and waiting to get called back to work the same job
-new job is lined up and will start work within 30 days
unemployment requirements (very specific)
not in labor force
What is it called when you want a job, but haven't tried to find one in over 4 weeks?
-unemployment rate
-employment-to-population ratio
-labor force participation rate
What are the 3 labor market indicators?
(number of people unemployed)/
(number of people in the labor force)
x100
unemployment rate formula
6.4%
what is the average unemployment rate over the past few decades?
decreases
unemployment usually _________ during expansion
increases
unemployment usually ________ during recession
unemployment rate fluctuates a lot
does employment rate fluctuate or stay steady?
(number of people employed)/
(working age population)
x100
employment to population ratio formula
tends to be about 60%
Rises during expansions (good times)
Falls during recessions (bad times)
out of all the people in the working age population what percent have a job?
when does it rise and fall?
(labor force) /
(working age population)
x100
labor force participation rate formula
Tends to be around 64%
Recession à Many people lose jobs à Some of those people quit looking for new jobs (leave labor force) à LFP rate falls
Out of all the people in the working age population, what percent are in the labor force?
When does it rise and fall?
she is actually not in the labor forced at all and can be categorized as a marginally attached worker
EX: Carla has no job she is ready to work and wants to work but she hasn't searched for any jobs in the last 4 weeks.
Is Carla "employed" or "unemployed"?
A marginally attached worker who has stopped looking for a job because of repeated failure to find
discouraged worker definition
no he has a job and is employed but can be labeled as economic-part time workers
EX: Dennis wants a full-time job, but right now he only has a part-time job.
Is Dennis unemployed?
-Finding a first job
-Switching jobs
-Someone retires and someone else takes their place
3 Good reasons for unemployment aka frictional unemployment
the portion of unemployment that's due to changes in the skills needed to perform jobs or changes in the locations of jobs.
structural unemployment definition
The changes in unemployment due to fluctuations in the business cycle
cyclical unemployment definition
•During an expansion, cyclical unemployment shrinks.
•During a recession, cyclical unemployment grows.
what happens cyclical unemployment during recession and expansion
the level unemployment would be if there were zero cyclical unemployment today.
natural unemployment definition
On days when there is actually zero cyclical unemployment
full employment definition
might be > or < or = the natural unemployment rate
Options for Actual unemployment rate today
-Population gets younger
-Rate of technological change goes up
-Unemployment benefits become more generous
3 reasons why natural unemployment rate might go up
output gap
what is the term for the difference between real GDP and potential GDP
-unemployment rate > natural unemployment rate,
-so real GDP < potential GDP
-so output gap is negative.
What happens to the output gap during under productive days
-unemployment rate < natural rate,
-so real GDP > potential GDP
so output gap is positive
What happens to the output gap during over productive days
the average level of prices for all goods
price level definition
A persistently rising price leve
inflation definition
A persistently falling price level
deflation definition
Inflation or deflation that comes as a burst or a surprise is a problem
when is inflation/deflation a problem?
-redistribute income
-redistribute wealth
-lower real GDP and employment
-divert resources away from production
What are 4 potential results of unexpected inflation or deflation
-Unexpected inflation that year à The worker can't buy as much as they expected! Worker is poorer.
-Employer is paying less than expected. Employer gets higher profits.
Why is redistributing income a problem
-Inflation/deflation during that year:
-Does affect the value of the repayment
-But doesn't affect the value of the initial loan.
•Unexpected inflation, Borrower "wins."
•Unexpected deflation, Lender "wins."
Why is redistributing wealth a problem
•Unexpected inflation can temporarily boost real GDP above potential GDP.
•But it eventually leads to an even bigger drop in real GDP.
•Unexpected deflation: Also bad.
-Borrowers are made poorer, have less to spend.
-Can drive real GDP down
why is lowering real GDP and unemployment a problem?
-It becomes hard work to figure out how to manage your money.
-Lots of productive work has to be foregone in order to manage money instead.
-Things get really bad when there is hyperinflation
why is diverting resources away from production a problem
compare current prices to average prices from a specified date in the past
What is the CPI designed to do
CPI = (Cost of CPI basket at current prices) /(Cost of CPI basket at base period prices) × 100
CPI formula
The stuff that the average household bought in the base year
What goes in the CPI basket
(CPI this year - CPI last year)/(CPI last year) × 100
CPI inflation rate formula
inflation
when price level up there is (inflation or deflation)
deflation
when price level goes down there is (inflation or deflation)
inflation is high
when inflation goes up quickly_______________
inflation is low
when inflation goes up slowly_______________
1.New goods bias
2.Quality change bias
3.Commodity substitution bias
4.Outlet substitution bias
4 ways that CPI is biased
overestimates
with biases the CPI inflation rate (over or under) estimates actual inflation
-Another measure of price level
-Like CPI, just uses different basket
what is the PCE index
no
-a poor country can have high economic growth
-a rich country can have low economic growth
is economic growth dependent on a country's wealth
Real GDP tells us how productive the entire country is while Real GDP per person tells us how high the average standard of living
what is the difference in Real GDP and GDP per person?
growth rate of real GDP- Growth rate of population
real GDP per person formula
- the country wasn't at full employment last year, but now it is (last year's production was inefficient, but this year's is efficient also not economic growth)
-production possibilities expanded (economic growth)
What are two reasons GDP is higher this year than last year
percentage increase in a variable in one year
annual growth rate definition
if a variable grows at x% each year, it will take about (70/x) years for the variable to double
What is the rule of 70
land: can't change
Capital and entrepreneurship: can change how much we will have tomorrow but not today
labor: can change how much we have today
How does GDP depend on the 4 factors of production
potential GDP
___________ is achieved when the quantity of labor employed is the full employment quantity
-aggregate production function
-aggregate labor market
Potential GDP model 2 components