lab 15-- Antimicrobial Drugs and Difference between Fungi and Bacteria (copy)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
be able to define zone of inhibition
clear zone area surrounding the disk where no bacteria grew
susceptible
An organism inhibited by the recommended dose at the infection site of an antimicrobial agent.
intermediates susceptible
An organism that may require a higher dose of antibiotic for a longer period of time to be inhibited.
resistant
An organism is not inhibited by the recommended dose, at the infection site of an antimicrobial agent.
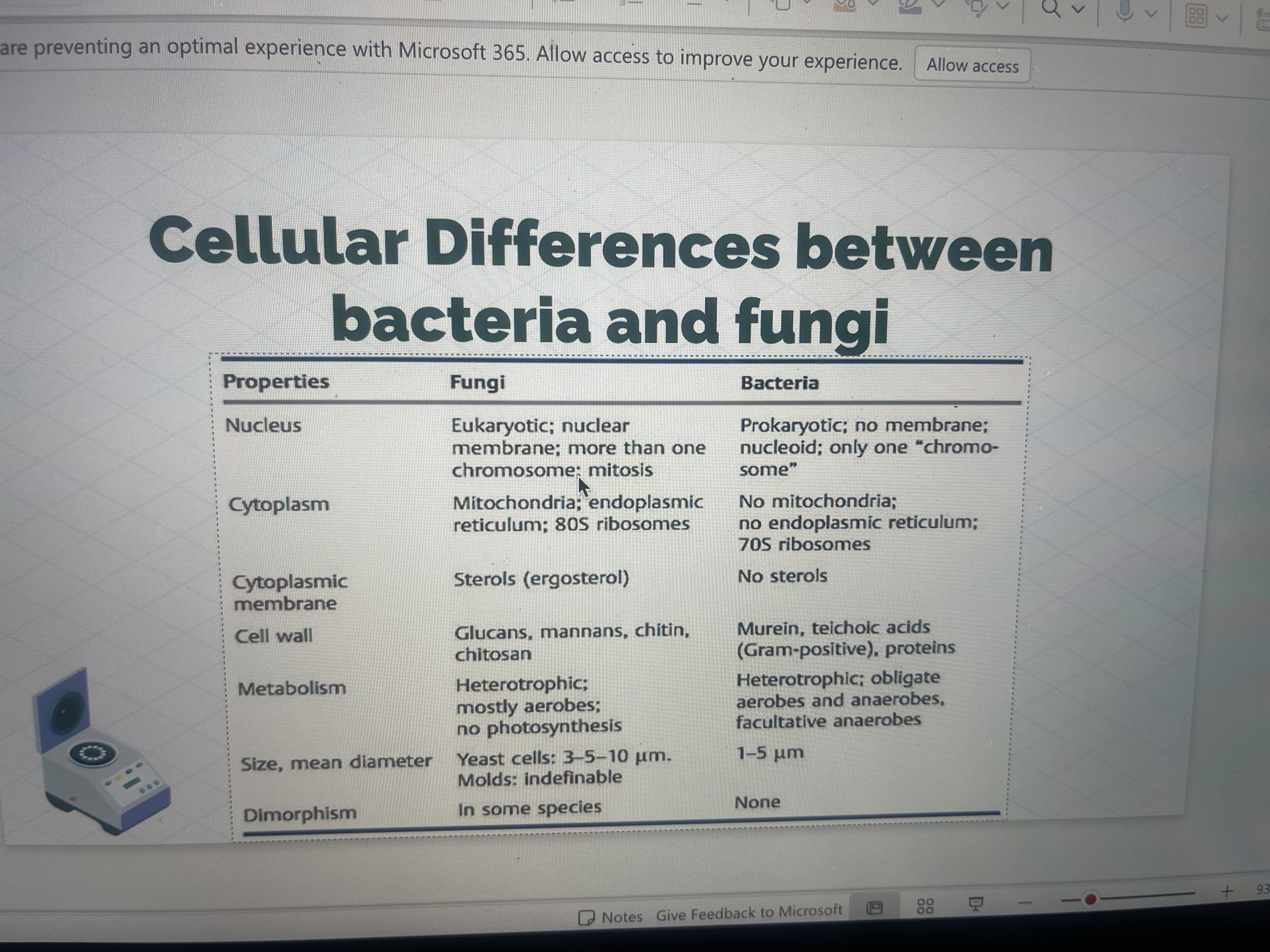
Are yeast and bacteria affected by anti microbial drugs the same way?
no→Bacteria are prokaryotic, meaning they have peptidoglycan cell walls, ribosomes (70S), and different metabolic pathways. Antibiotics targeting cell wall synthesis (e.g., penicillin) or ribosomes (e.g., streptomycin) work against bacteria but not yeast.→Yeast are eukaryotic fungi, meaning they have chitin in their cell walls and 80S ribosomes. Antifungal drugs like fluconazole (targets ergosterol synthesis in the cell membrane) work against yeast but not bacteria
Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis (cell wall synthesis inhibitors): Ampicillin and Streptomycin →
Prevent bacteria from forming a strong cell wall, leading to lysis (works only on bacteria, not yeast)
Inhibition of protein synthesis (ribosome-targeting antibiotics):Streptomycin →
→ Binds to bacterial 70S ribosomes, stopping protein synthesis (only affects bacteria)
Disruption of fungal cell membrane (ergosterol synthesis inhibitors):Fluconazole →
Inhibits ergosterol production in yeast membranes (only affects yeast, not bacteria).
Nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors:Nourseothricin (Nat) →
Targets RNA synthesis in yeast and some bacteria.