1 Arterial Leg Wounds
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are Risk Factors for PAD?
Age 65+
Age 50-64 with risk factors for atherosclerosis (DM, smoking hx, dyslipidemia, HTN), CKD, family history PAD
Age< 50with DM+ 1 more atherosclerosis risk factor
Persons with known atherosclerotic disease in another vascular bed
what are Foot Wound Risk Factors in People with PAD?
Previous foot wound or amputation
Charcot foot
DM with poor glycemic control
CKD (chronic kidney disease)
Peripheral neuropathy
Corns or callouses
Ongoing smoking
What does arterial leg wounds look like?
Thin, Shiny, dry skin
Hair loss on ankle and foot
Dystrophic (thick) or yellow toenails
Elevation pallor
Dependent rubor
Decreased temperature
Absent or diminished pulses
Cyanosis
Ischemic pain

what anatomical locations are common with arterial leg ulcers?
Typically at foot and malleoli
Between toes
Tips of toes
Pressure points (heel or lateral foot)
Sites of trauma or footwear rubbing
What the typical presentation of arterial leg wounds?
Location: distal to ankle, usually at foot and malleoli, sites of pressure from footwear, trauma, pressure
Wound base: pale or necrotic
Wound edges: well-defined, “punched out”
Periwound: thin, shiny, may be blanched or purpuric; hair loss and nail changes common
Pain: often severe, commonly worse with limb elevation
What are subsets of LE PAD?
Asymptomatic PAD
Symptomatic PAD
Critical limb-threatening ischemia
Acute limb ischemia
What past medical history could affect a PAD foot exam?
Previous ulcer/ischemia, amputation, deformity callous
Current PAD/ischemia/wound symptoms
Tobacco use
Diabetes
Retinopathy
CKD
Neuropathy
What should be examined in a PAD foot exam?
Skin integrity
Foot deformity
Sensory: 5.07 with 1 additional (sharp, temp, or vibration)
Pulses legs and feet
What should be screened in a PAD foot exam?
Footwear
Foot hygiene
Physical limitations to foot self-care
Does patient know components and perform foot self-care?
how do we test for arterial insufficiency?
Vascular testing
ABI
Arterial ultrasound if ABI < 0.6
speak with primary care provider about results
ask for vascular surgery consult
Toe brachial index if ABI >1.4
Buerger's test:
elevate limb 45 degrees for 1-2 minutes, observe, place in dependent position
when performing an ABI for arterial ulcer management, if the ABI is <.6, we should use an _______, and if the ABI is >1.4, we should use the ______
arterial ultrasound
toe brachial index
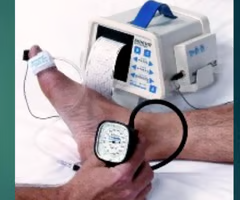
How do you prevent PAD wounds?
Foot self-care education
Foot inspection every health care visit
Therapeutic foot wear for high risk patients
Comprehensive foot evaluation yearly
Referral to a foot specialist when available
How do you care for a PAD wound?
Protect and offload area.
Sharp debridement of nonviable tissue as indicated. Leave any stable, dry eschar in place.
Appropriate dressings. For stable, dry eschar, apply povidone iodine and gauze.
Monitor for infection.
Control edema as able
How should PAD wound management by Medical Team look like?
Vascular surgery referral
Management of infection and/or inflammation
Pain control
Smoking cessation
Glycemic control
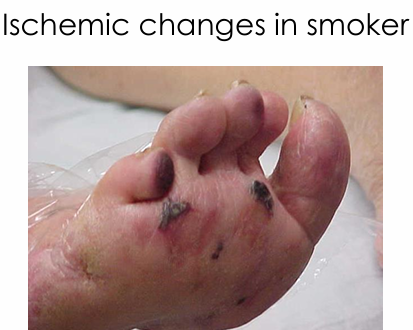
What should be considered for CLTI(Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia) where surgery is not an option?
Arterial intermittent pneumatic compression
When you find Gangrene in outpatient or non-acute setting, what is the next step?
Obtain urgent referral to vascular surgeon, be in communication with primary physician and document this. Consider ER if gangrene moist or worsening (i.e. toe turning purple)
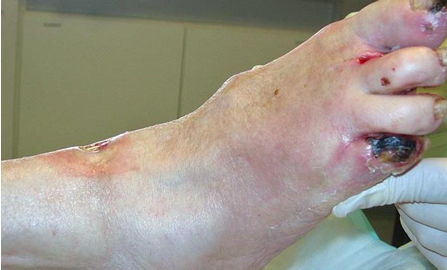
When you find Gangrene in acute setting, what is the next step?
notify physician, ask to order arterial ultrasound & vascular surgery consult
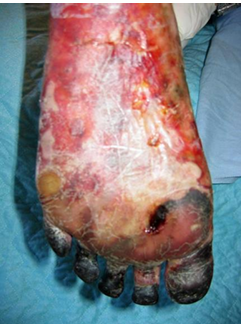
What is the goal for managing Arterial ulcers?
minimizing tissue loss; if possible, intact skin surface on a functional foot
what lifestyle and exercise programming should be done for arterial ulcer management?
Exercise in a home or community setting, prescribed by appropriate health care provider, with careful consideration to wound location
Patients who smoke should be counseled at every visit to quit and referred to smoking cessation program
what may the patient deal with if they have mixed venous and arterial insufficiency?
neuropathic, trauma and pressure
what is the treatment for mixed vascular disease?
Treat the cause if possible
Ask for referral to vascular surgeon.
No compression bandaging if ABI ≤0.5
Local Wound Care