Complete pelvic girdle, SI, L-Spine, Sacrum, Coccyx A&P 1/31/26
1/301
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
302 Terms
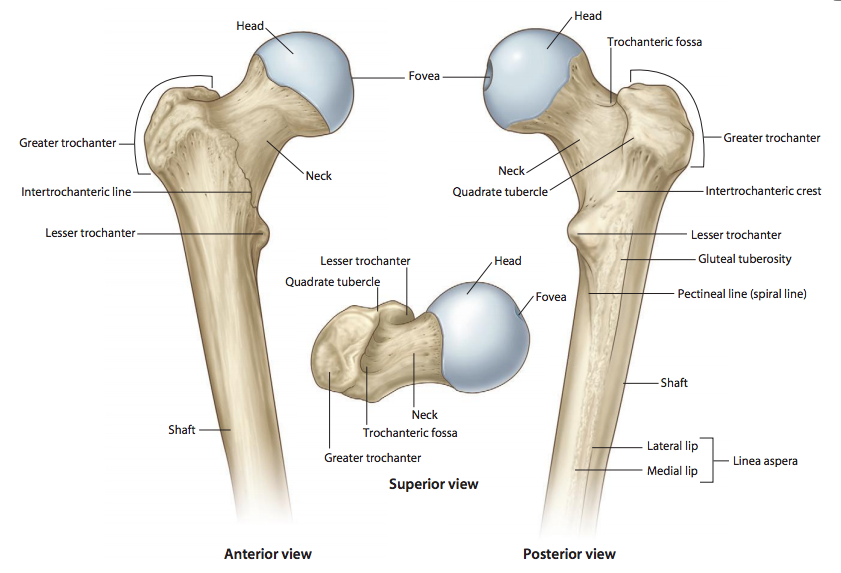
What is the round, proximal end of the femur that articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis
Femoral head
What is the narrow region just below the head of the femur
Femoral neck
What is the large lateral projection on the proximal femur where muscles attach
Greater trochanter
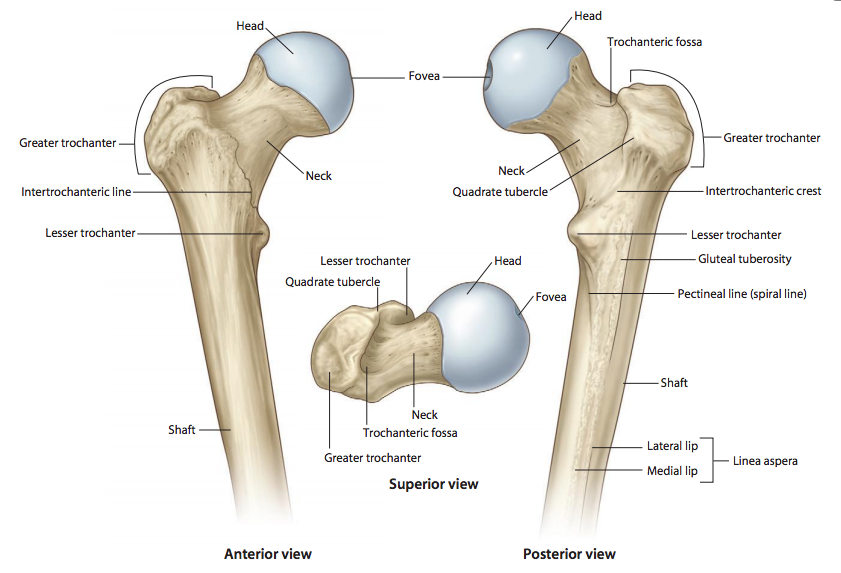
What is the smaller medial projection on the proximal femur where muscles attach
Lesser trochanter
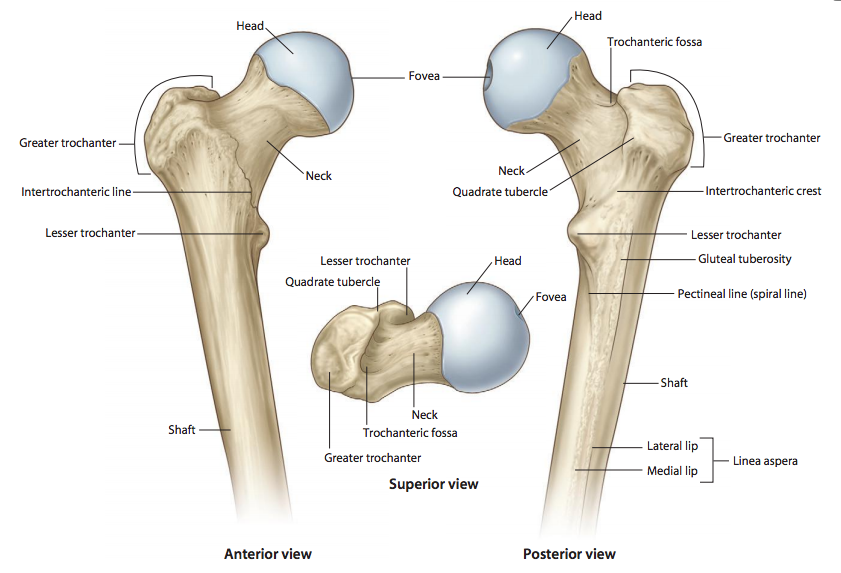
What is the posterior ridge connecting the greater and lesser trochanters
Intertrochanteric crest
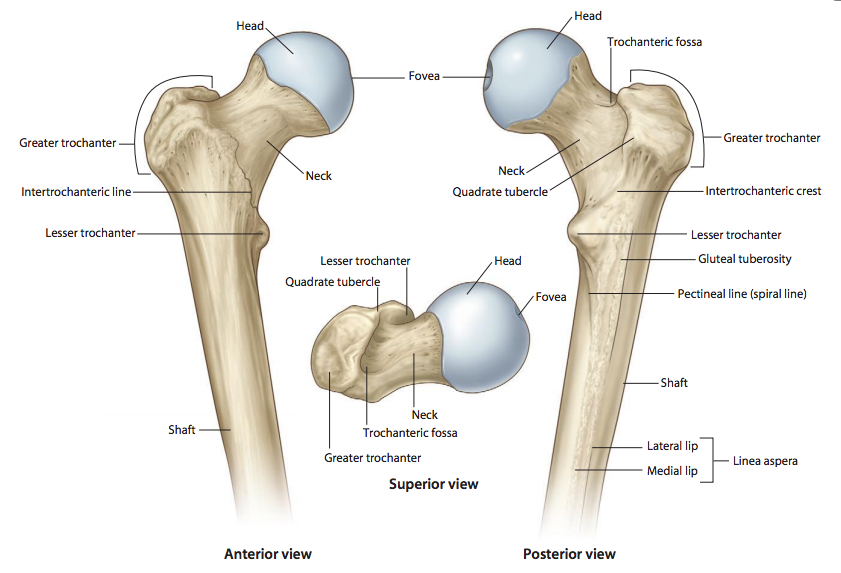
What is the anterior line connecting the greater and lesser trochanters
Intertrochanteric line
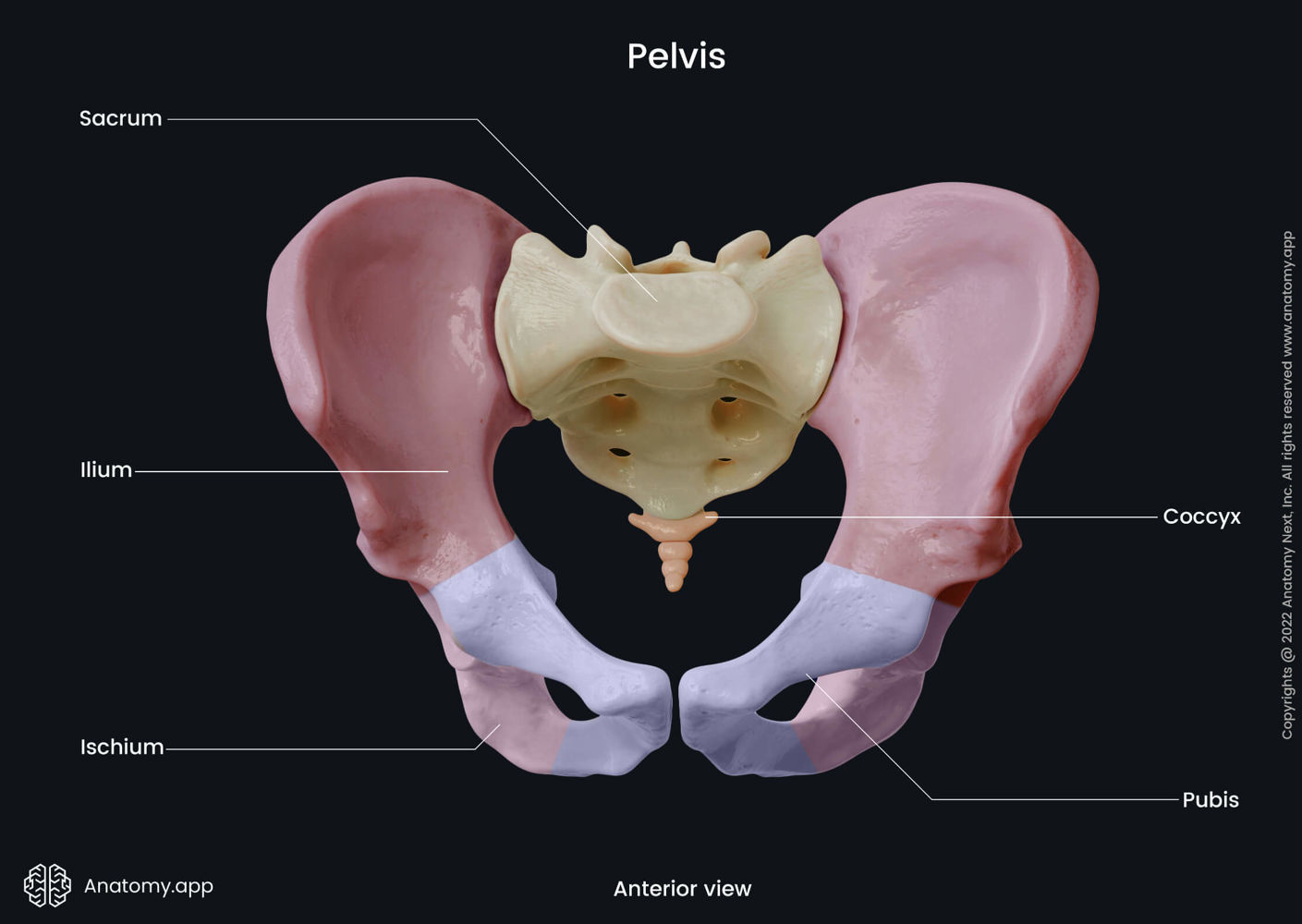
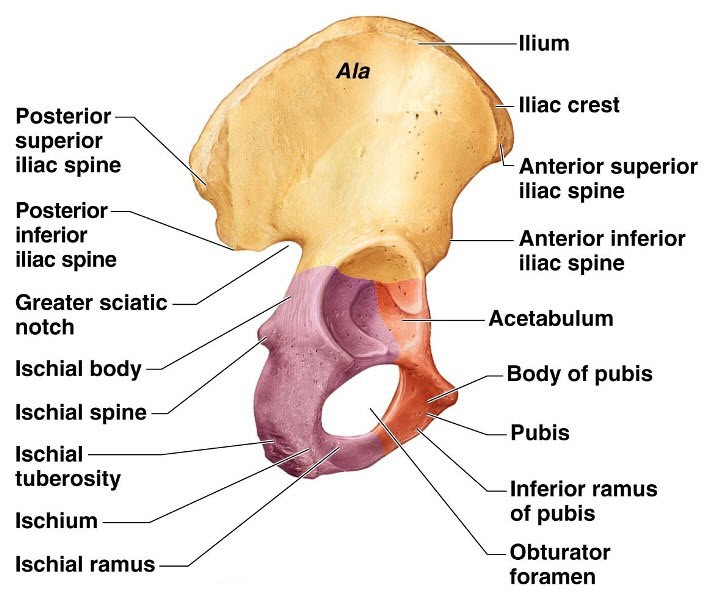
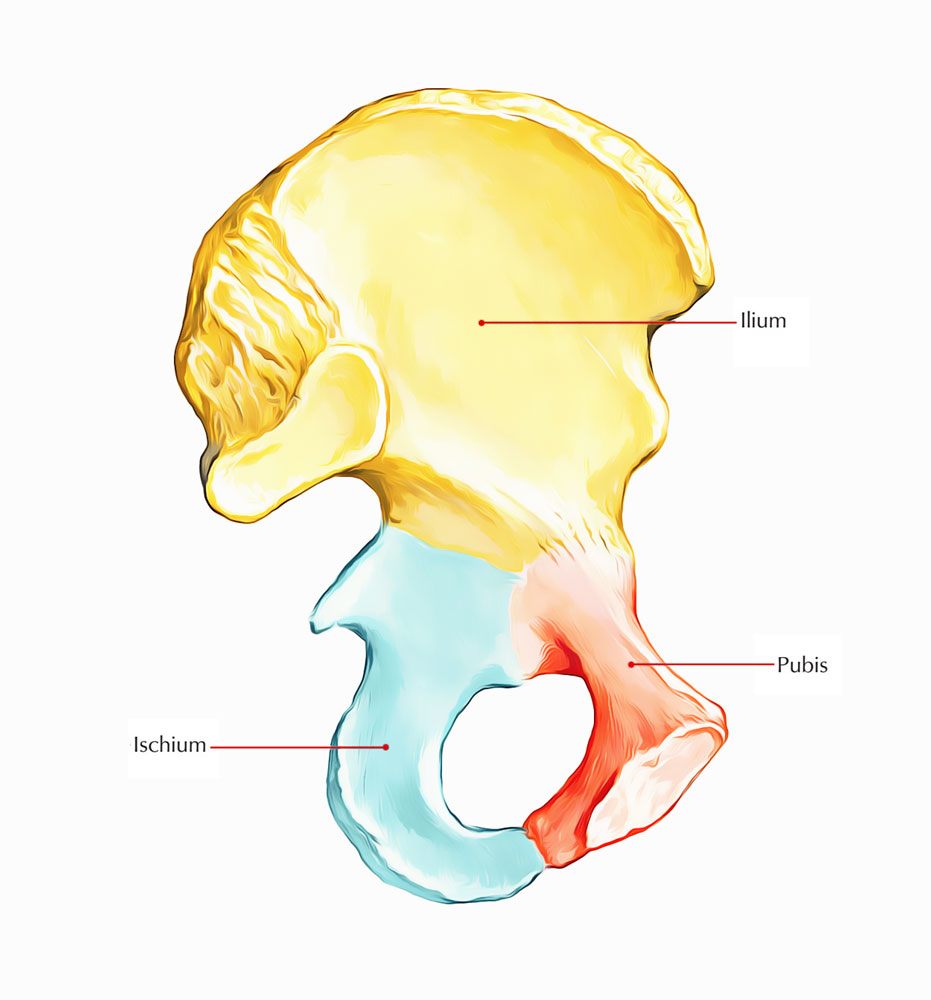
What is the upper, wing-like portion of the hip bone
Ilium
What is the main central portion of the ilium
Body of ilium
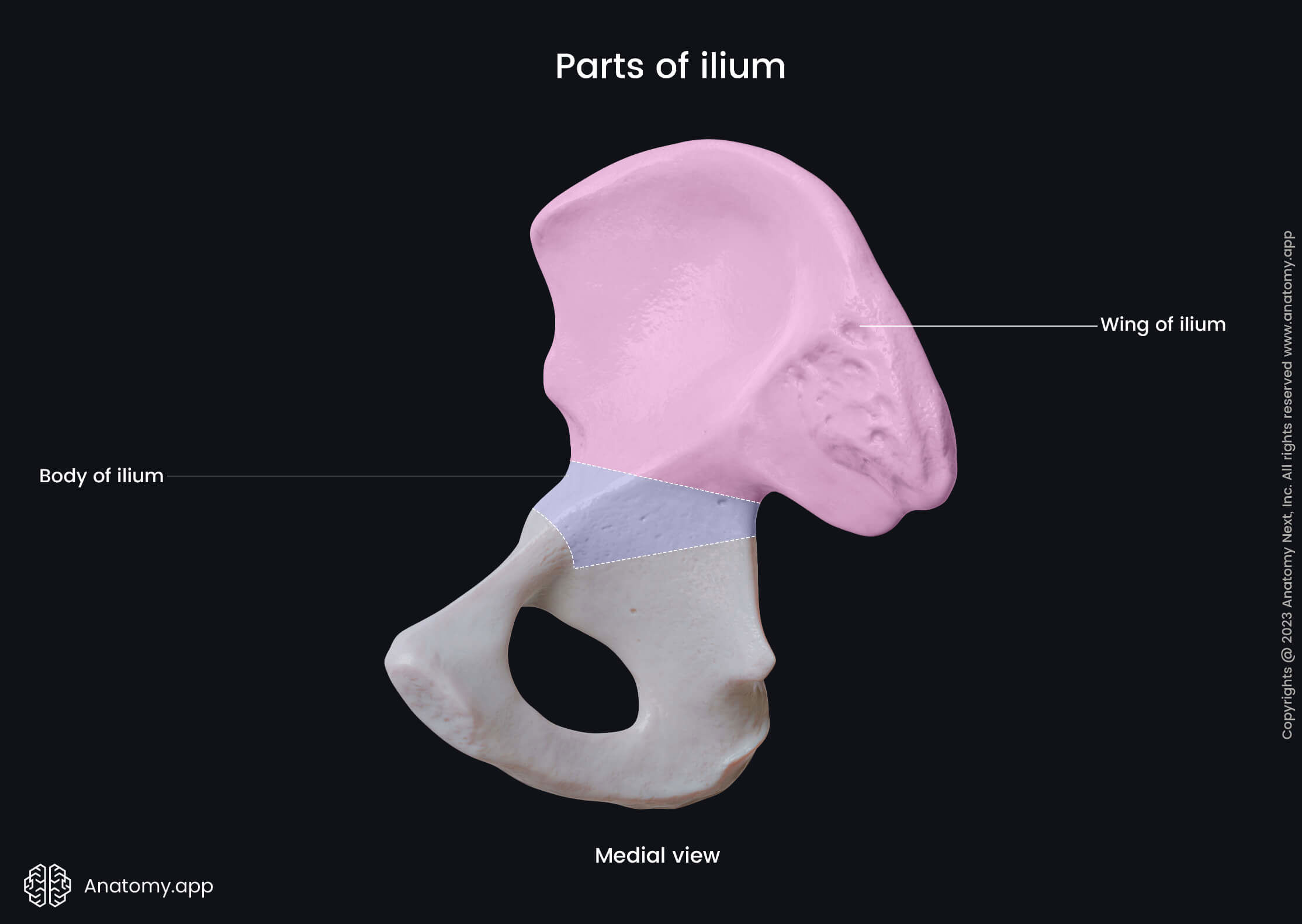
What is the broad, wing-like part of the ilium
Ala
What are the three borders of the ala
Superior, anterior, and posterior borders
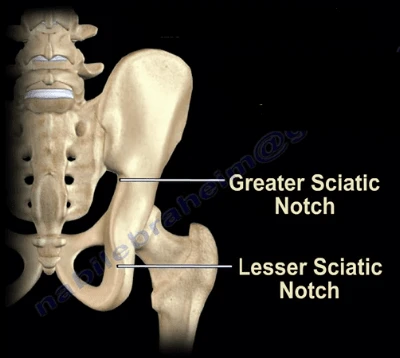
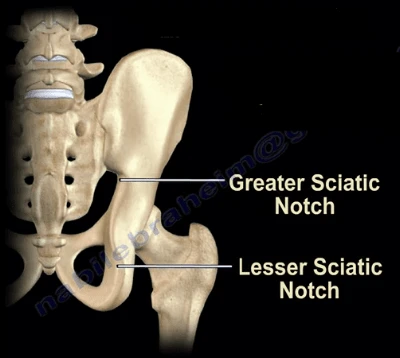
What is the large notch on the posterior ilium for the passage of the sciatic nerve
Greater sciatic notch
What is the posterior-inferior portion of the hip bone
Ischium
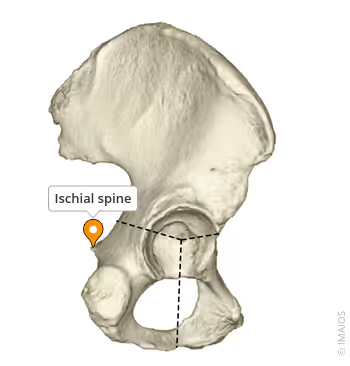
What is the pointed projection on the posterior border of the ischium
Ischial spine
What is the main central portion of the ischium
Body of ischium
What is the portion of the ischium that joins with the pubis to form the inferior part of the obturator foramen
Inferior ramus of ischium

What is the small notch located just below the ischial spine
Lesser sciatic notch
What is the anterior portion of the hip bone
Pubis
What is the main central portion of the pubis
Body of pubis
What is the superior branch of the pubis that contributes to the acetabulum
Superior ramus of pubis
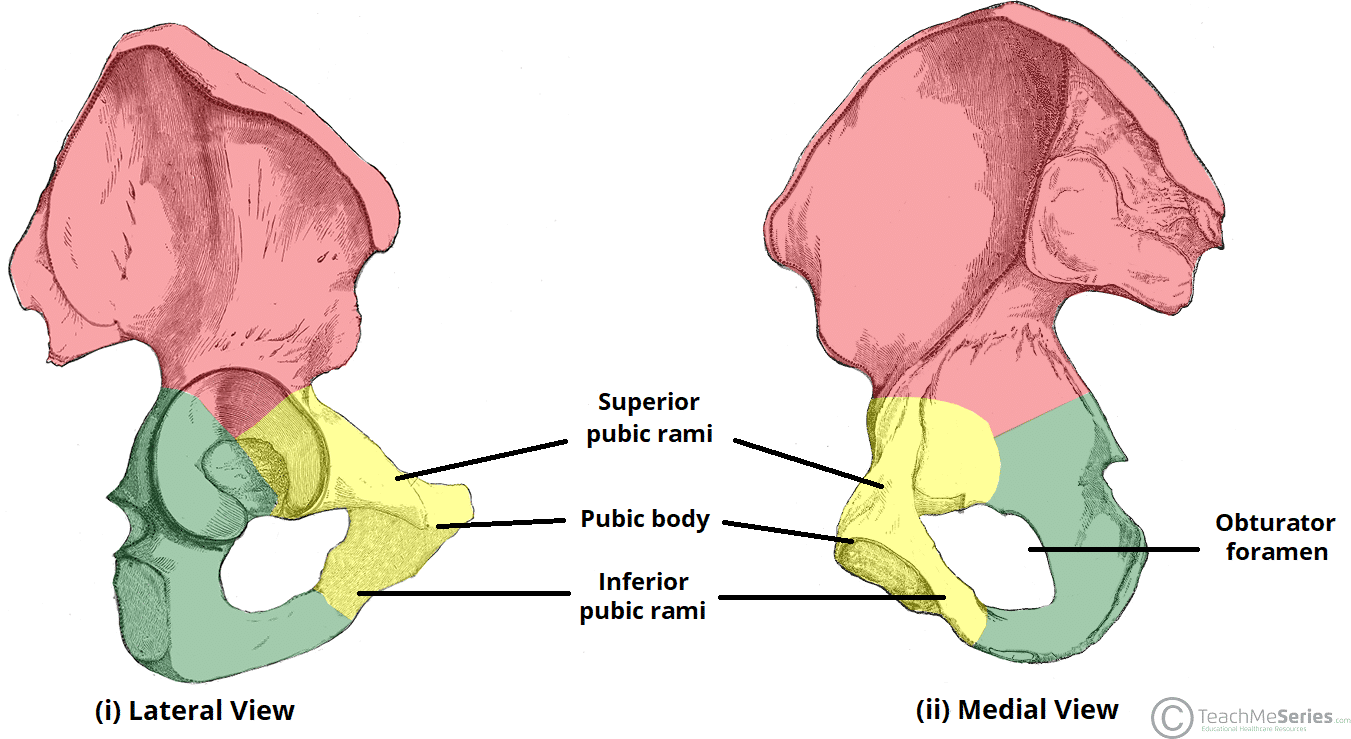
What is the inferior branch of the pubis that forms the lower boundary of the obturator foramen
Inferior ramus of pubis

What is the large opening formed by the ischium and pubis
Obturator foramen
What two bones compose the obturator foramen
Ischium and pubis
What is the deep socket in the pelvis that articulates with the femoral head
Acetabulum
What is the cartilaginous joint at the midline of the pelvis formed by the pubic bones
Symphysis pubis
What is the synovial joint connecting the sacrum to the ilium
Sacroiliac (SI) joint
What is the ball-and-socket joint between the femoral head and the acetabulum
Hip joint
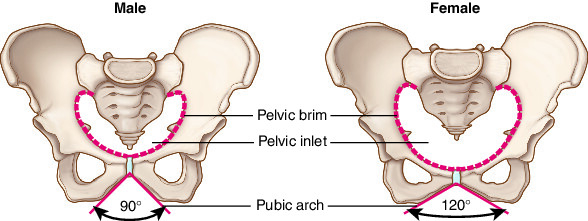
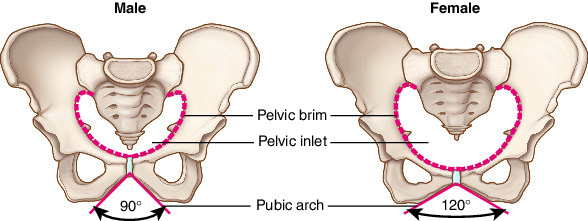
How does the female pelvis differ from the male pelvis
Wider, shallower, larger pelvic inlet and outlet, lighter bones
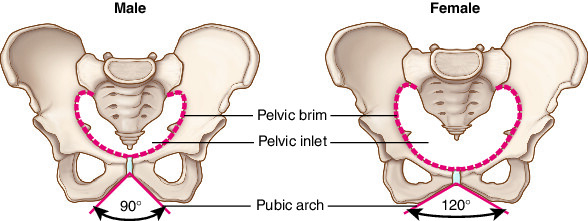
How does the male pelvis differ from the female pelvis
Narrower, deeper, smaller pelvic inlet and outlet, heavier bones
How is the bony pelvis divided into false (greater) pelvis and true (lesser) pelvis
Divided by the pelvic brim
What is the area of the pelvis located above the pelvic brim
False (greater) pelvis

What is the area of the pelvis located below the pelvic brim
True (lesser) pelvis
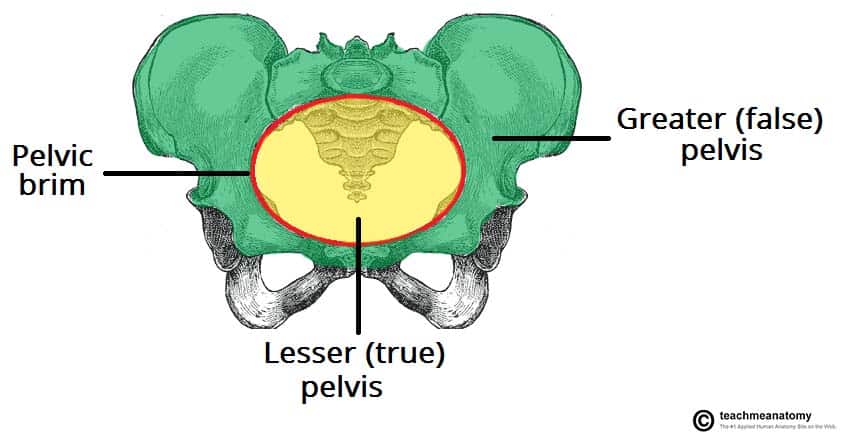
What is the superior opening of the true pelvis
Pelvic inlet
What is the inferior opening of the true pelvis
Pelvic outlet
What type of injury involves a break in the proximal femur
Hip fracture
What type of injury occurs when the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum
Hip dislocation
What type of injury involves one or more breaks in the pelvic bones
Pelvic fractures
What type of fracture is evaluated with Judet radiographs
Acetabulum fractures
What type of fracture is evaluated with inlet and outlet radiographs
Rami fractures
Why do fractures of one section of the pelvis often lead to fractures in another section
Because the pelvic ring is continuous, stress in one area often transmits to another
What are the two common sites of fracture in elderly of the femur?
Femoral neck
Intertrochanteric crest
What kind of joint is the hip joint
Synovial ball and socket joint
The intertrochanteric ___ is on the anterior aspect
Intertrochanteric line
The intertrochanteric ___ is on the posterior aspect
Intertrochanteric crest
What are the other names for the hip bone?
Os coxae
Innominate
What makes up the Acetabulum?
Ilium 2/5
Ischium 2/5
Pubis 1/5
What part of the ilium ends in the sciatic notch
Posterior inferior iliac spine
What are the four prominent processes of the ilium?
Anterior superior iliac spine
Anterior inferior iliac spine
Posterior superior iliac spine
Posterior inferior iliac spine
What is the greater sciatic notch between?
Between the Posterior inferior iliac spine and the ischial spine
What forms the obturator foramen?
The ischial ramus with the inferior ramus of pubis
What are the three things that make up the pubis?
Body
Superior ramus
Inferior ramus

What kind of joints are Sacroiliac (SI) joints?
Irregular, gliding
What kind of joint is the pubic symphysis joint?
Cartilaginous, slightly movable joint

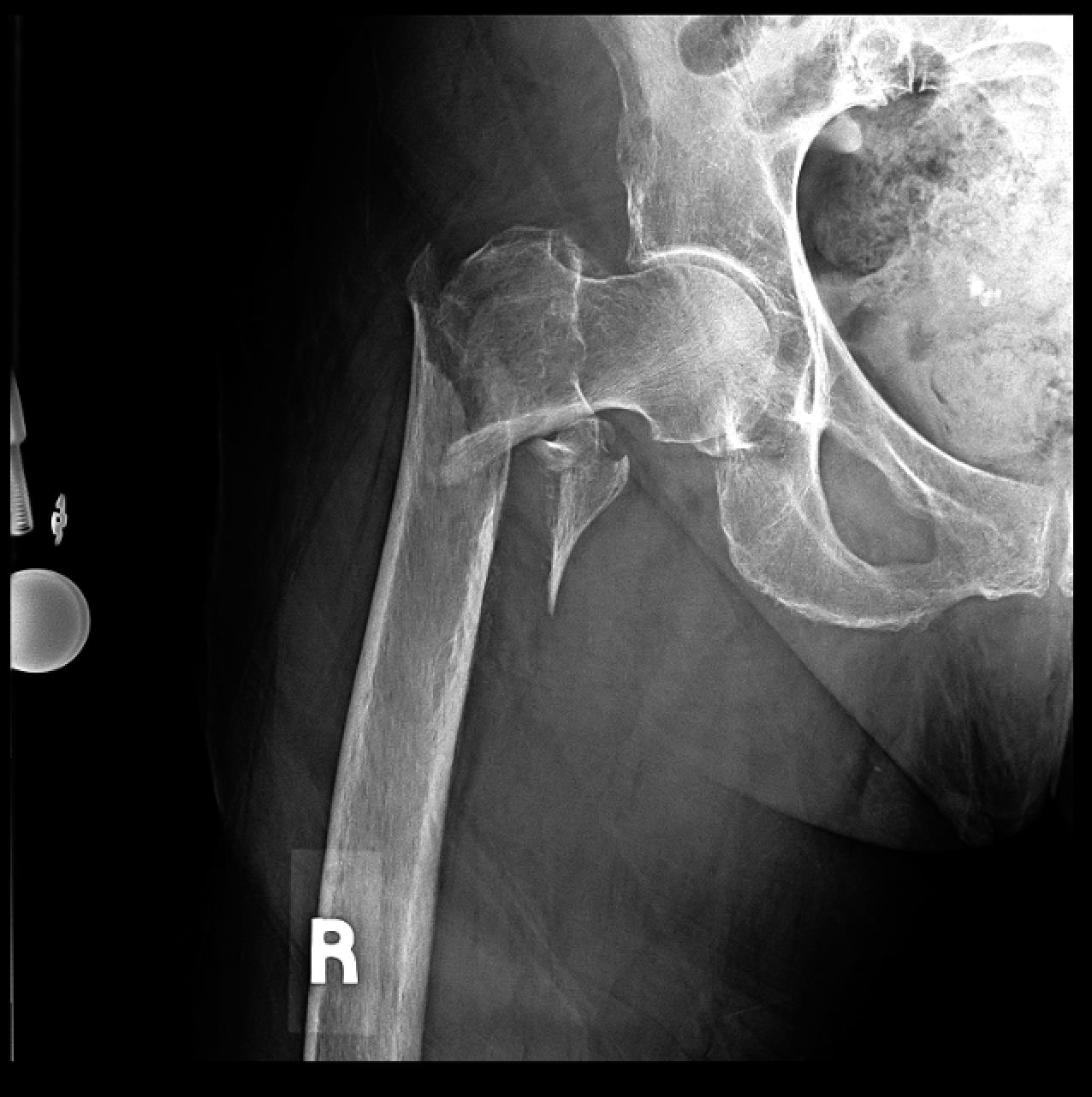
What kind of fracture is this?
Subtrochanteric fracture
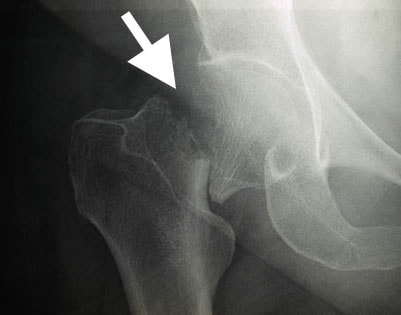
What kind of fracture is this?
Intertrochanteric fracture
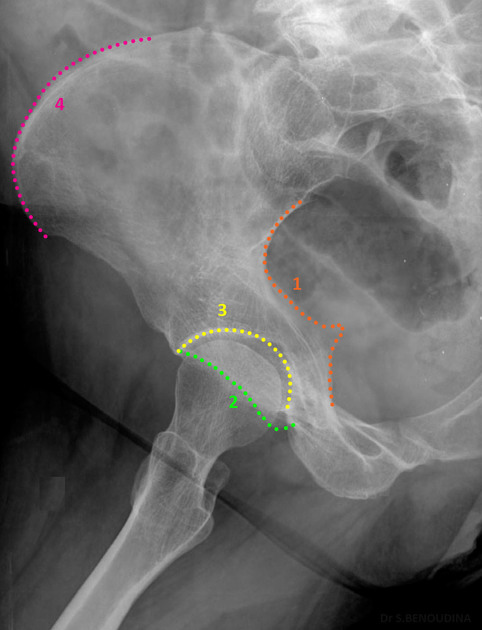
What kind of fracture is this?
Intracapsular fracture
What kind of dislocation of the hip is more common?
Posterior dislocation
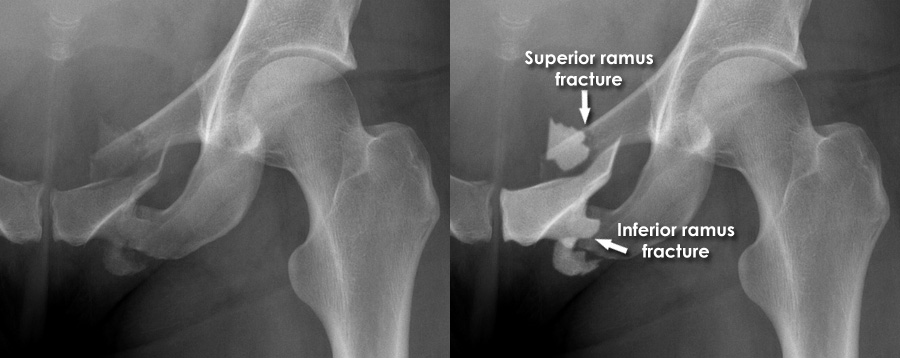
What view do you need to see a acetabulum fracture?
Judet
What view do you need to see a rami fracture?
Outlet
What is the anterior portion of the pelvis?
iliopubic column
What is the posterior portion of the pelvis?
ilioischial column
AP pelvis part position
Medially rotate feet 15–20°
AP pelvis central ray
Top of IR 1½ inches above iliac crest
AP pelvis structures visualized
Entire pelvis; femoral heads and necks; trochanters; iliac crests; proximal femur
AP low pelvis (bilateral hips) part position
Medially rotate feet 15–20°
AP low pelvis (bilateral hips) central ray
Top of IR at level of CREST
AP hip part position
No pelvic rotation; medially rotate lower limb and foot 15–20°
AP hip central ray
Perpendicular to femoral neck
AP hip structures visualized
Ilium; acetabulum; femoral head and neck; trochanters; pubic symphysis
AP oblique hip frog leg part position
Flex affected hip and knee, abduct thigh, bring knee up and drop it down to its side as much as possible
AP oblique hip frog leg central ray
Center at femoral neck
AP oblique hip frog leg structures visualized
Lesser trochanter on medial side of femur, Pelvis with no rotation
Lateral hip Lauenstein patient position
Supine, rotated toward affected side 35 degrees
Lateral hip Lauenstein part position
Flex affected knee; thigh raised toward hip; femoral neck centered
Lateral hip Lauenstein structures visualized
Proximal femur; acetabulum
Axiolateral hip cross table part position
Flex knee and hip of unaffected limb to place thigh vertical, rest unaffected leg and foot on a support, no rotation of pelvis
Axiolateral hip cross table central ray
Horizontal and perpendicular to long axis of femoral neck
Axiolateral hip cross table structures visualized
Head, acetabulum, neck, trochanters
AP oblique acetabulum Judet patient position
RPO or LPO
AP oblique acetabulum Judet part position
elevate patient 45° with support
Judet affected hip position, Affected hip up = ____ oblique, affected hip down = ___ oblique
Internal, external
AP oblique acetabulum Judet central ray
2 inches medial to elevated ASIS
AP oblique acetabulum Judet structures visualized
Entire pelvis; acetabulum
AP axial pelvic outlet part position
MSP centered to midline of grid
AP axial pelvic outlet central ray
Men: 20–35° cephalic; Women: 30–45° cephalic; enters midline 2 inches below ASIS, with change in SID
AP axial pelvic outlet structures visualized
Pubic and ischial rami
AP axial pelvic inlet part position
MSP centered to midline
AP axial pelvic inlet central ray
35–40° caudal; enters midline at level of ASIS
AP axial pelvic inlet structures visualized
Entire pelvic ring
AP axial SI joints Ferguson part position
Supine
AP axial SI joints Ferguson central ray
30° cephalic (male); 35° cephalic (female); enters 2 inches below ASIS MSP
AP axial SI joints Ferguson structures visualized
Lumbosacral joint; symmetric sacroiliac joints
Posterior oblique SI joints part position
25–30° posterior oblique with support
Posterior oblique SI joints central ray
1 inch medial to elevated ASIS
Posterior oblique SI joints structures visualized
SI joint farthest from IR; open joint space
Why are Judet views performed?
To visualize the acetabulum
Why are pelvic outlet views performed?
To visualize the rami
Why are pelvic inlet views performed?
To visualize the pelvic ring

What view is this?
AP Pelvis
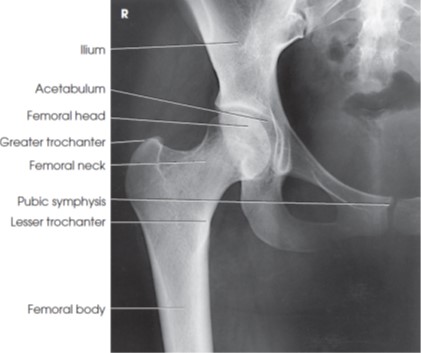
What view is this?
AP Hip
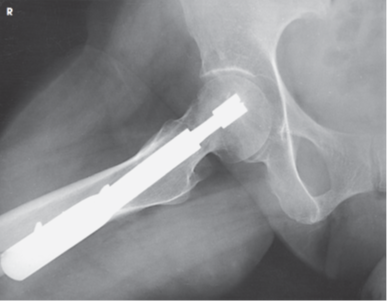
What view is this?
AP Oblique “Frog Leg”