Cell Chemistry, Nutrition, and Microbial Culture Techniques
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Nutrients
Supply of monomers (or precursors of) required by cells for growth
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts
Micronutrients
Nutrients required in trace amounts
Carbon
Required by ALL cells; typical bacterial cell is ~50% carbon (by dry weight); major element in ALL classes of macromolecules
Heterotrophs
Use organic carbon
Autotrophs
Use carbon dioxide (CO2)
Nitrogen
Typical bacterial cell is ~13% nitrogen (by dry weight); key element in proteins, nucleic acids, and many more cell constituents
Phosphorus (P)
Synthesis of nucleic acids and phospholipids
Sulfur (S)
Sulfur-containing amino acids (cysteine and methionine); vitamins (e.g., thiamine, biotin, lipoic acid) and coenzyme A
Potassium (K)
Required by enzymes for activity
Magnesium (Mg)
Stabilizes ribosomes, membranes, and nucleic acids; also required for many enzymes
Calcium (Ca)
Helps stabilize cell walls in microbes; plays key role in heat stability of endospores
Sodium (Na)
Required by some microbes (e.g., marine microbes)
Iron
Key component of cytochromes and FeS proteins involved in electron transport
Growth factors
Organic compounds required in small amounts by certain organisms; examples: vitamins, amino acids, purines, pyrimidines
Vitamins
Most commonly required growth factors; most function as coenzymes
Culture media
Nutrient solutions used to grow microbes in the laboratory
Defined media
Precise chemical composition is known
Minimal media
Nothing more than the essential compounds
Complex media
Composed of digests of chemically undefined substances (e.g., yeast and meat extracts)
Enriched media
Contain complex media plus additional nutrients
Selective media
Contain compounds that selectively inhibit growth of some microbes
Differential media
Contain an indicator (dye), detects particular chemical reactions
Pure culture
Culture containing only a single kind of microbe (species, strain even)
Contaminants
Unwanted (usually unknown) organisms in a culture
Solid media
Prepared by addition of a gelling agent (agar or gelatin)
Streak plate
Technique where isolated colonies are obtained at the end of the streak
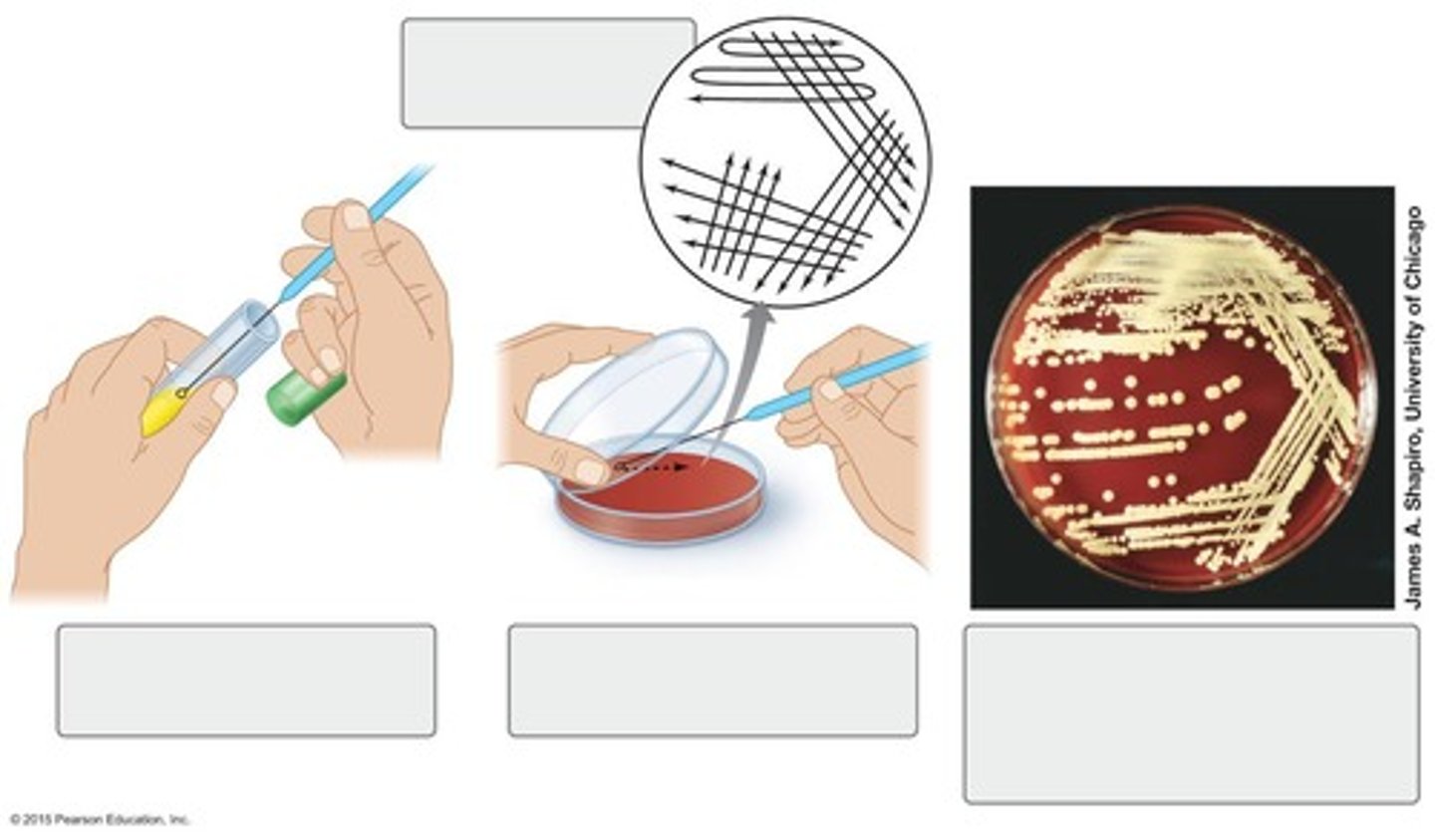
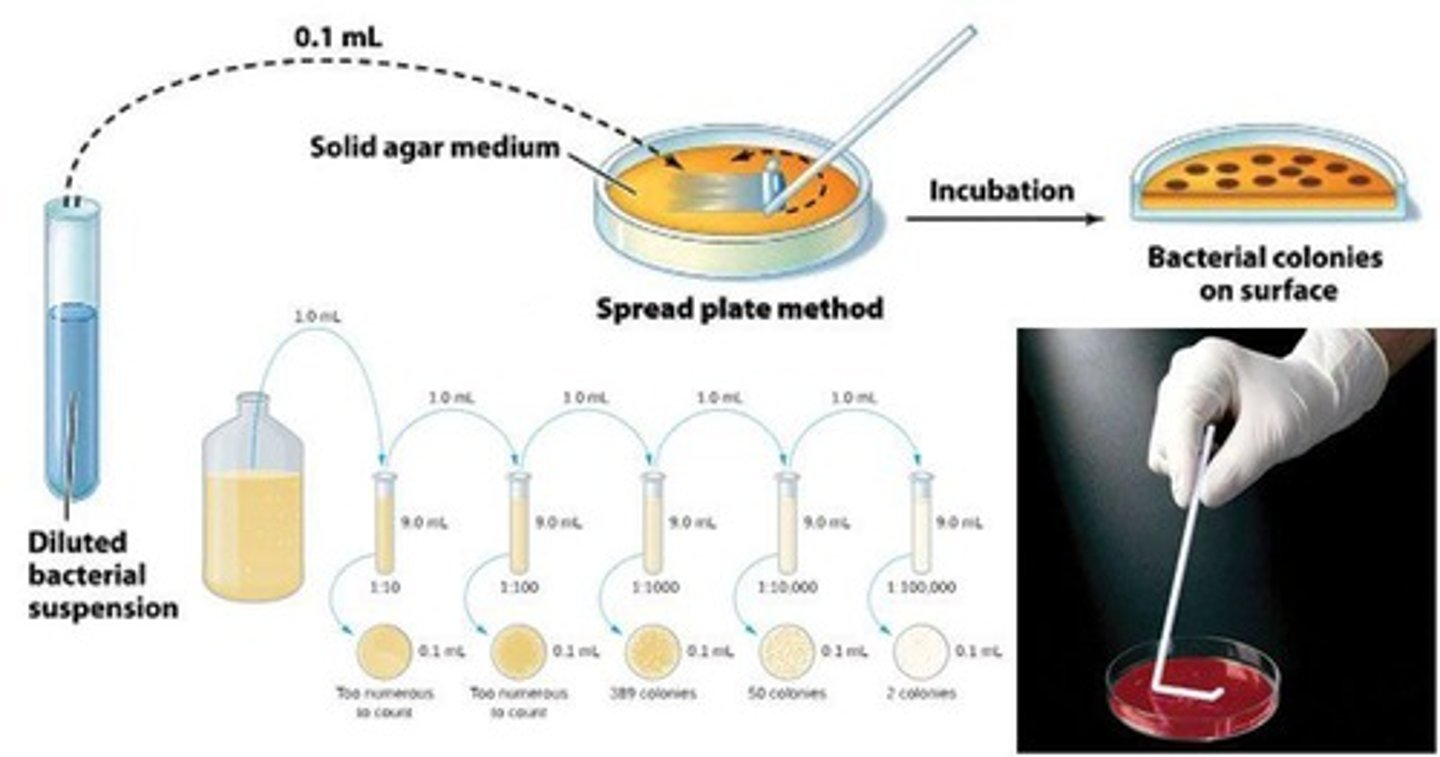
Spread Plate
CFU = # colonies/dilution factor * plating factor
Metabolism
The sum total of all of the chemical reactions that occur in a cell
Catabolic reactions (catabolism)
Energy-releasing metabolic reactions
Chemorganotrophs
Microorganisms that obtain energy from organic compounds
Chemolithotrophs
Microorganisms that obtain energy from inorganic compounds
Phototrophs
Microorganisms that obtain energy from light
Heterotrophs
Microorganisms that obtain carbon from organic sources
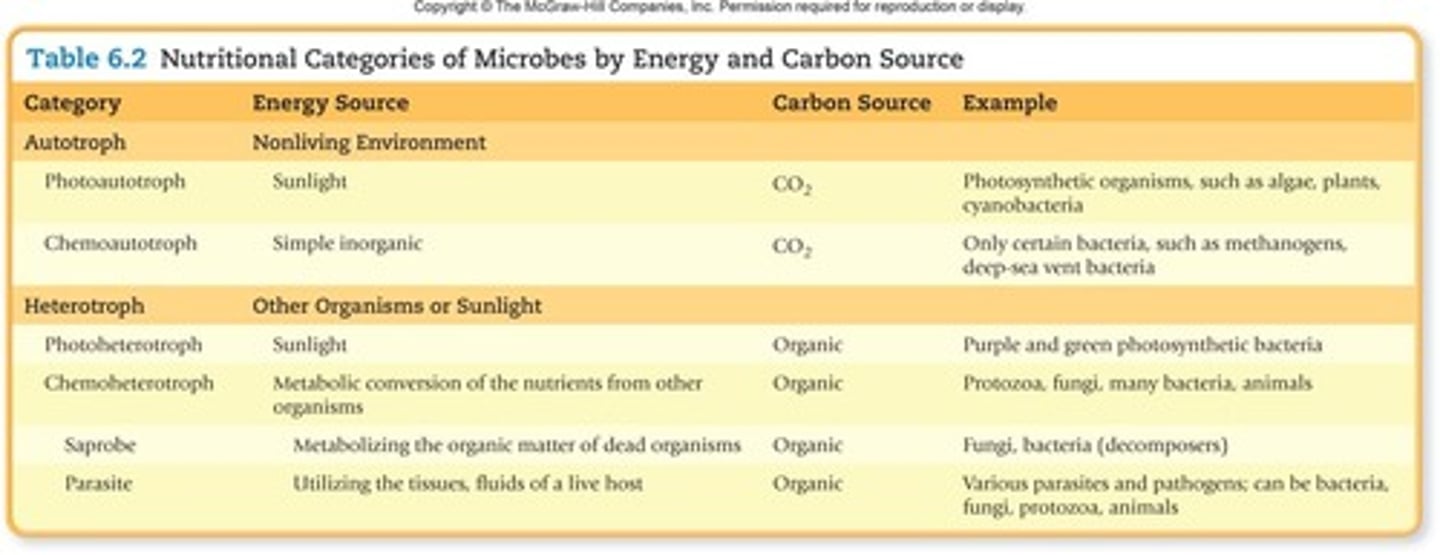
Autotrophs
Microorganisms that obtain carbon from inorganic sources