PTE 754: exam 3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
name the organs that make up the GI system.
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), large intestine (cecum, colon, rectum), and anus
name the organs that act as the “support” group for the GI system via controlling secretions.
liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
the GI system is known to have a “little brain.” what does that mean?
little brain = the enteric nervous system (ENS) a vast, independent network of over 100 million nerve cells lining the GI tract; it regulates digestion, including motility, enzyme secretion, and nutrient absorption
while the GI system has a “little brain,” it still works through the autonomic nervous system. describe that nervous system’s role on the GI system.
parasympathetic: rest and digest → facilitate GI
sympathetic: fight or flight → inhibit GI
GI organ overview
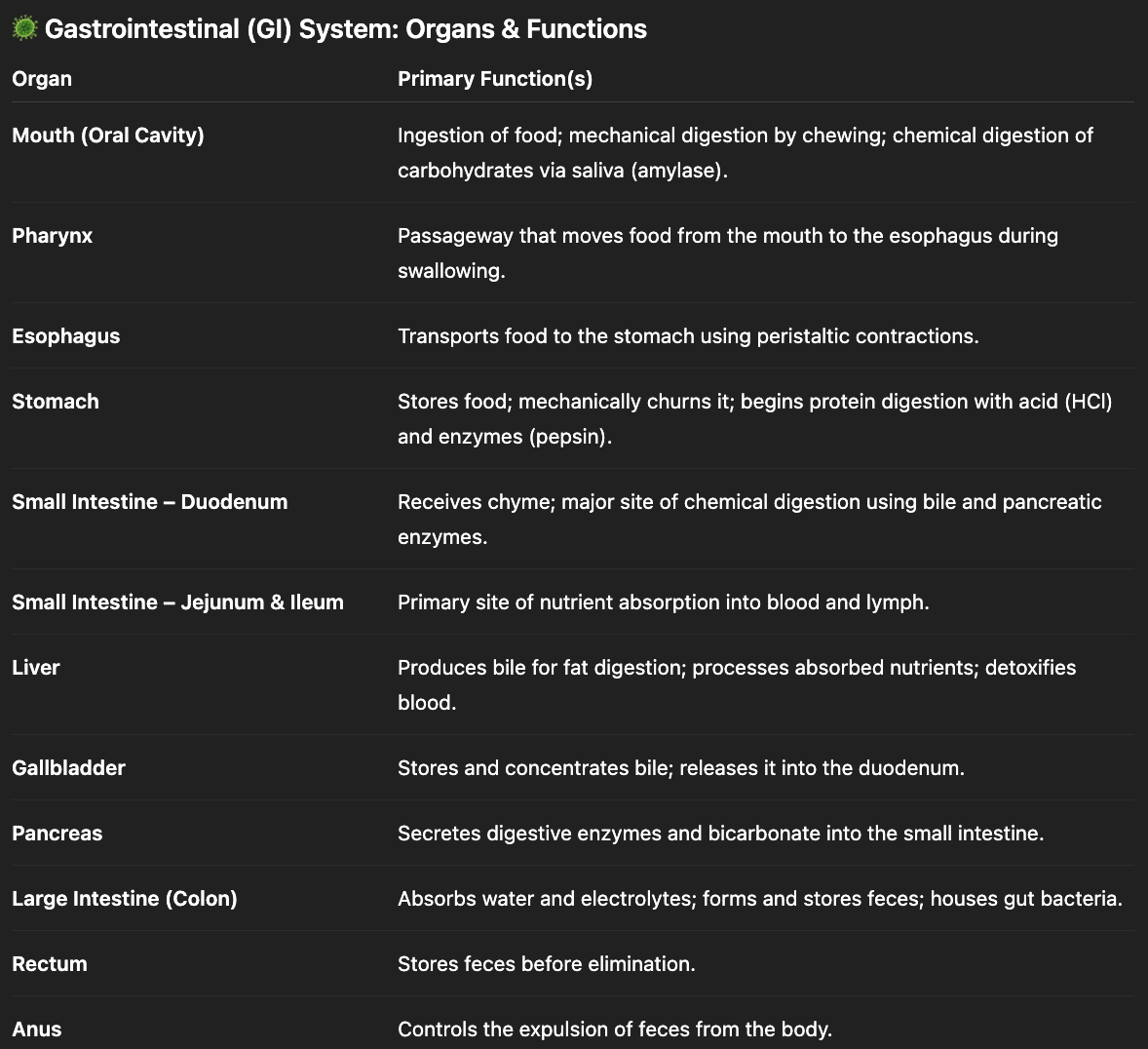
what are the GI’s functions?
portal for food
mixes food with secretions
absorption of nutrients
expels residue and debris
innate and adaptive immunological function
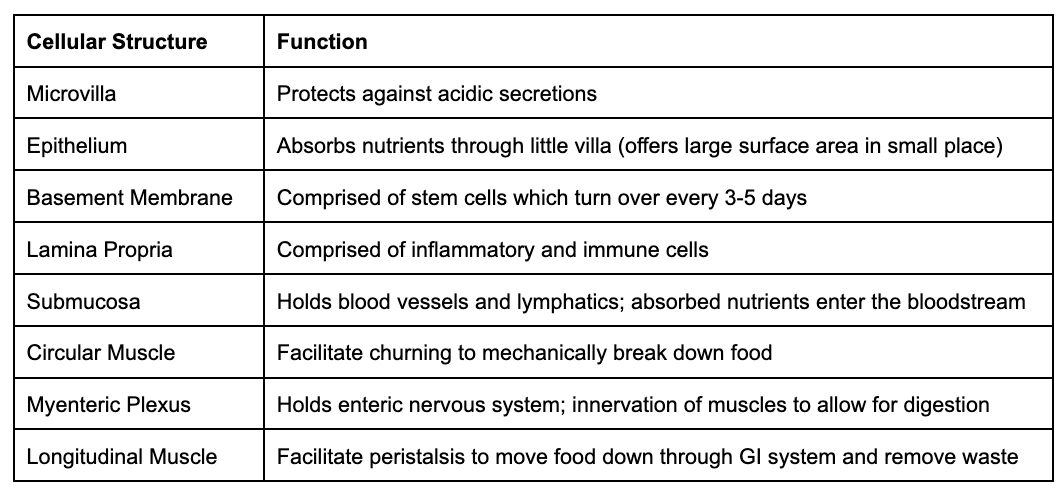
list the cellular layers of the GI tract from inside to outside.
microvilla → epithelium → basement membrane → lamina propria → muscularis mucosa → submucosa → circular muscle → myenteric plexus → longitudinal muscle → mesothelium
functions of the GI cellular layers
what are the four phase of digestion?
oral
gastric
intestinal
defecation
the oral phase of digestion is within the mouth. what are the two components of this phase?
chewing
swallowing
what occurs during the chewing component of the oral phase?
lubricates food through saliva, amylase breaks down starch (carbs), and mechanical chewing chops food in smaller pieces
the secretion of saliva needed for chewing is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. what are the two types of saliva produced in response to the ANS?
PSNS: watery saliva
SNS: viscous saliva
what occurs during the swallowing component of the oral phase?
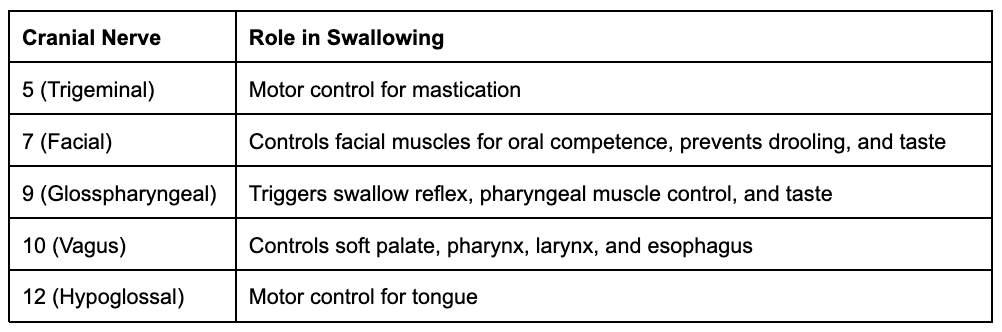
its a reflexive response that transmits sensory impulses to an area at the medulla-pons and then motor impulses of various cranial nerves contracts various muscles (CN 5, 7, 9, 10, 12)
functions of the CNs within the oral phase