anatomy lab 3
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
osmosis, transport, & cellular structures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What are the levels of structural organization from smallest to largest?
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ systems, organismal
What is the level of hierarchy from smallest to largest?
Atoms, molecules, macromolecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
Microscopic
Cannot be seen with the naked eye
Macroscopic
Can be seen with the naked eye
Cell
The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms
Nucleus
Houses the genome. Replication and transcription take place here
Nuclear envelope
Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Nuclear pore
Channels found in the nuclear envelope to allow for selective transport
Chromatin
Forms chromosomes and is housed in the nucleus
Nucleolus
In the middle of the nucleus. Houses ribosomal synthesis
Cytosol
The gel in a cell
Cytoplasm
All the components of a cell
Plasma membrane
A membrane that protects the interior of the cell and is selectively permeable
Golgi apparatus
Sorts and packages proteins
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Has ribosomes attached. Modifies proteins after production and transports them to the Golgi and other locations
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Does not have ribosomes attached. Synthesizes lipids, detoxifies drugs, breaks down glycogen
Centrosome
Tubular structures. Regulates cell motility and creates the spindle fibers during mitosis
Endocytic vesicle
Used for endocytosis
Free ribosome
Ribosomes floating around the cell. Synthesize all other proteins encoded by the genome
Lysosome
Contains hydrolase (digestive enzymes) that digest intracellular waste
Cilium
Tiny hairlike structures that can provide movement for the cell
Microvilli
Helps to absorb nutrients in the cell by increasing surface area
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration. Produces ATP
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis
Peroxisome
Oxidates fatty acids, a major source of metabolic energy. Synthesizes cholesterol/bile
Cellular extensions
Protruding parts of the cell used for motility or to increase surface area
DNA
Found in the nucleus. Contains genetic material, directs protein synthesis, and replicates before division
Transcription
Occurs in the nucleus. DNA information is encoded in mRNA
Translation
Occurs in the cytoplasm. mRNA’s information is decoded and used to assemble polypeptides
What are the functions of proteins?
Structural framework, movement, catalysis, transport, regulation, body defense, etc
Primary structure
Sequence of amino acids, forms a polypeptide chain
Secondary structure
Primary chain forms alpha helices and beta pleated sheets due to hydrogen bonding of R groups
Tertiary structure
Forms a globular protein by intramolecular bonding
Quaternary structure
Two or more tertiary proteins combine to form a functional protein
Integral proteins
A permanent membrane protein
Transmembrane proteins
A type of integral protein that spans the entirety of the membrane
Channel proteins
Used for facilitated diffusion of larger, polar molecules
Aquaporins
Diffuse water across the membrane
What can increase the rate of diffusion?
Temperature, particle size, and the concentration gradient
Diffusion
The tendency of molecules to move down their concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached
Osmosis
The diffusion of a solvent through a selectively permeable membrane until equilibrium is reached
Tonicity
The ability of the solution to change the shape of cells by altering the internal water volume
Hypotonic
Swells, possibly lyses
Isotonic
Remains the same
Hypertonic
Shrinks (crenates)
Cytosine (pyrimidine)
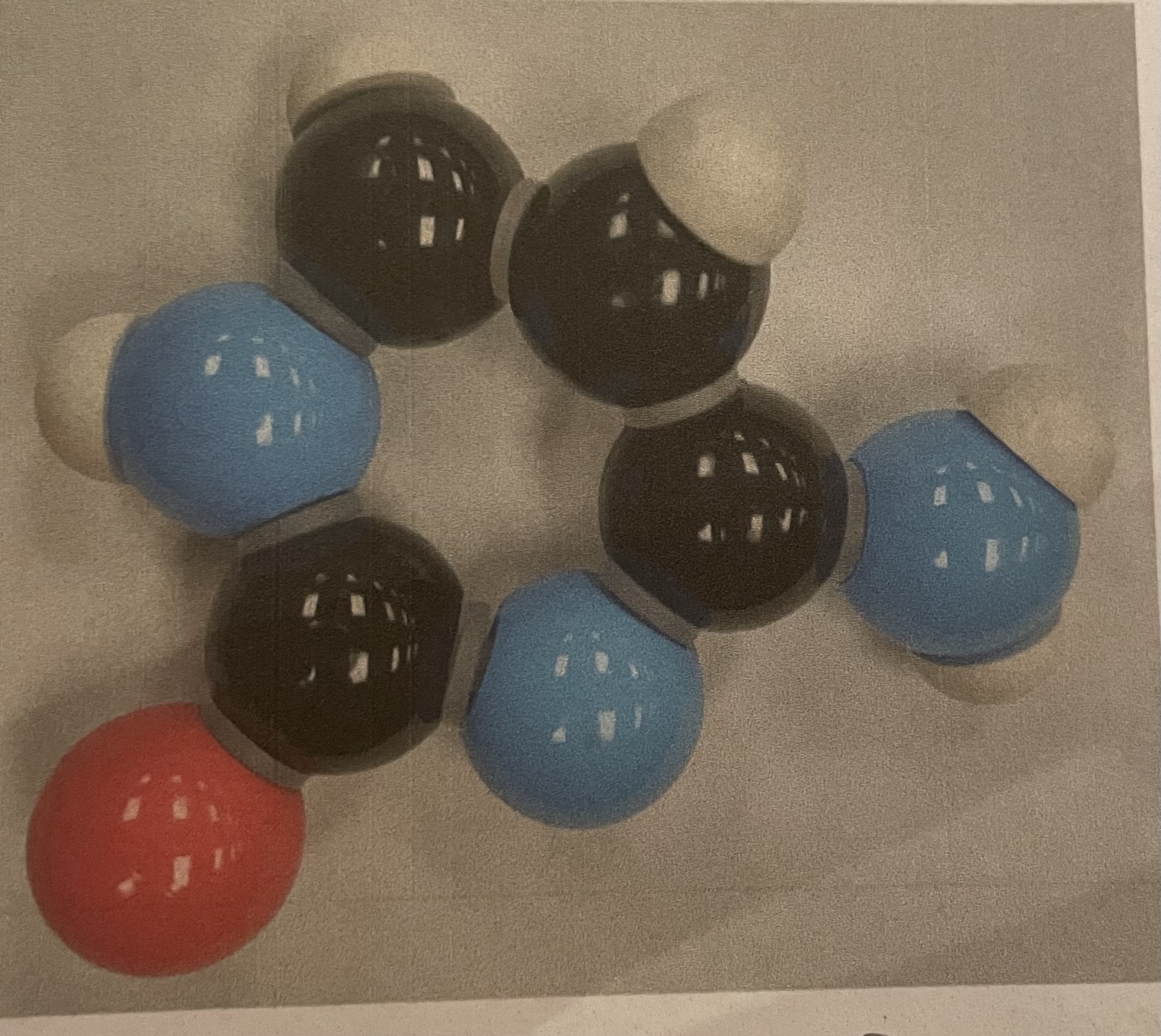

ATP
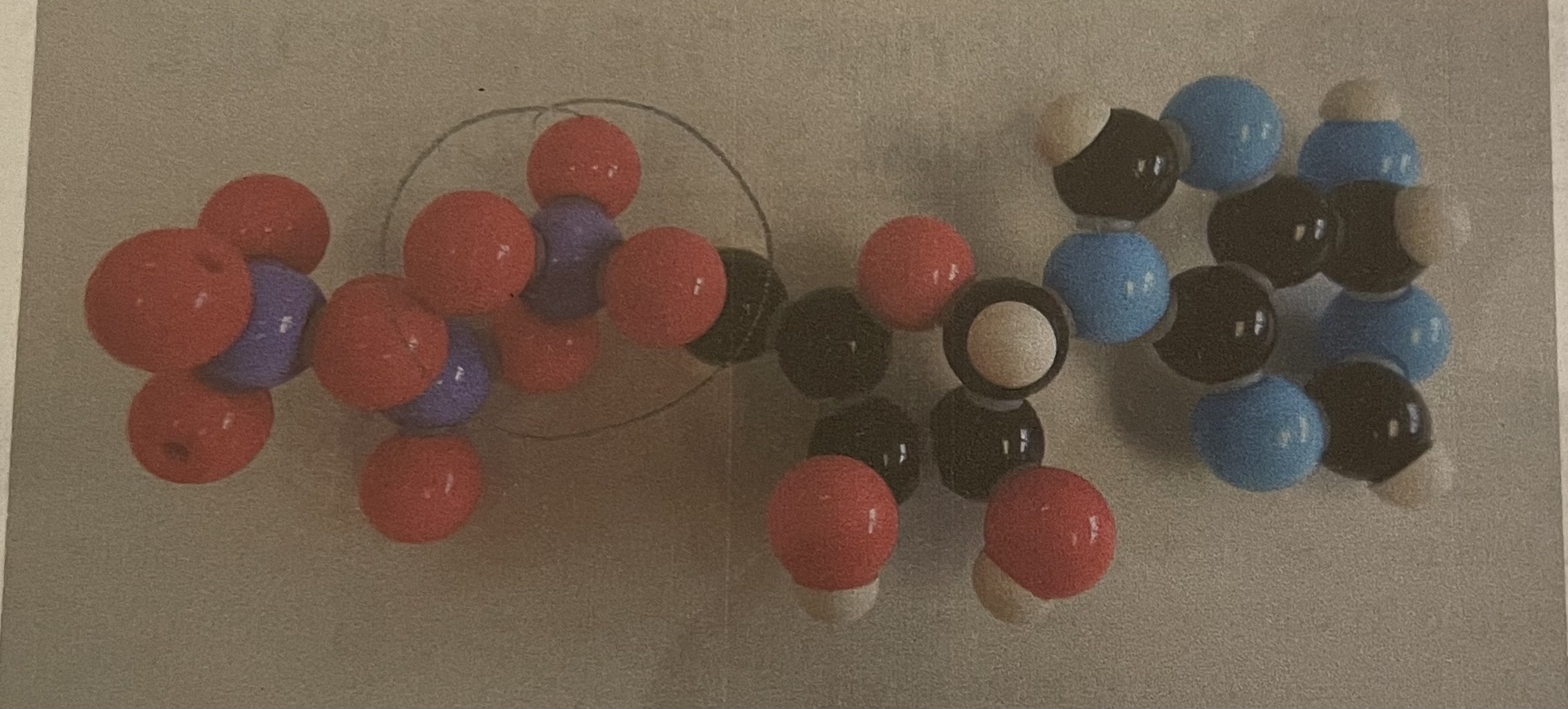
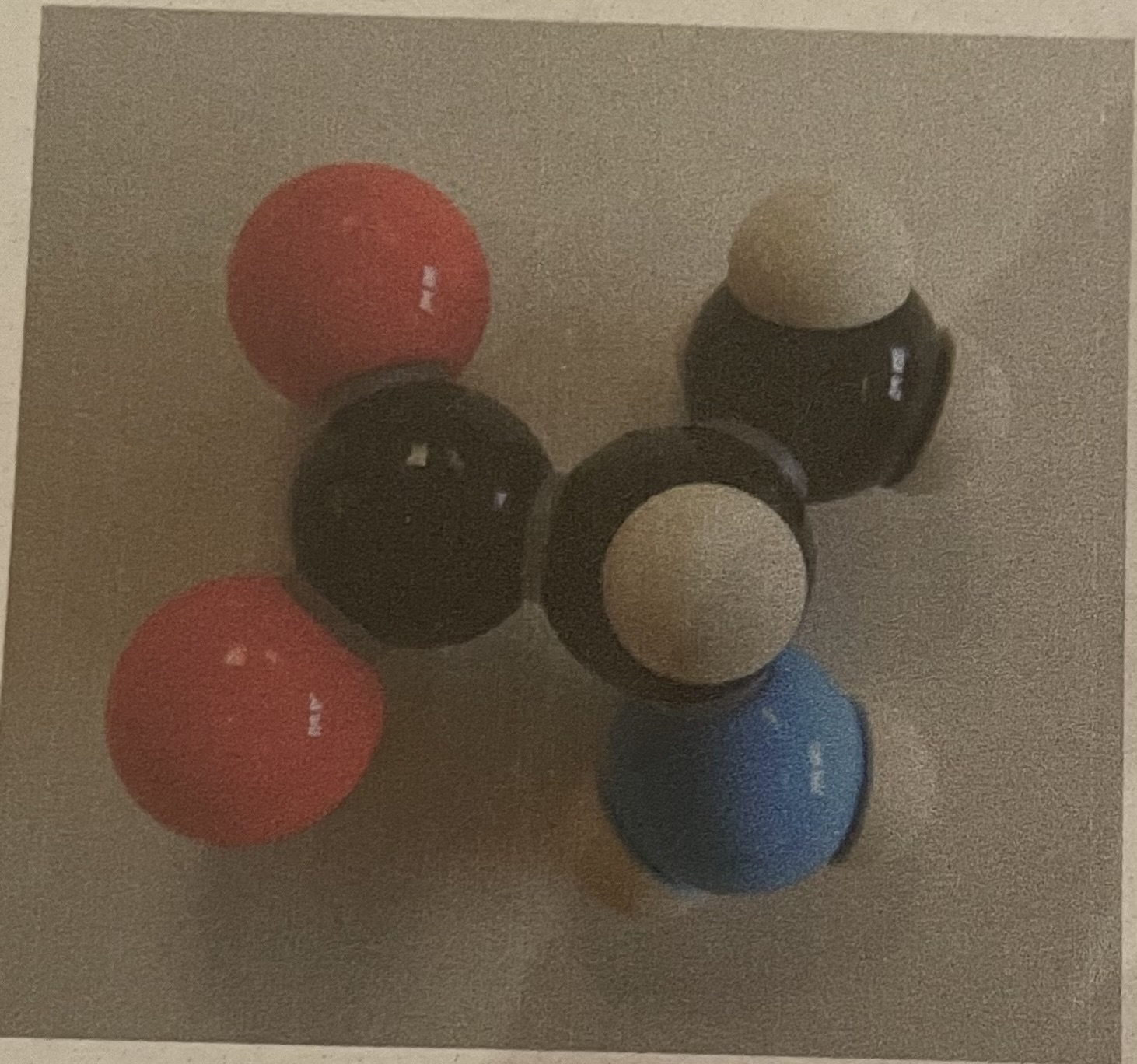
Alanine

Fatty acid

Fructose
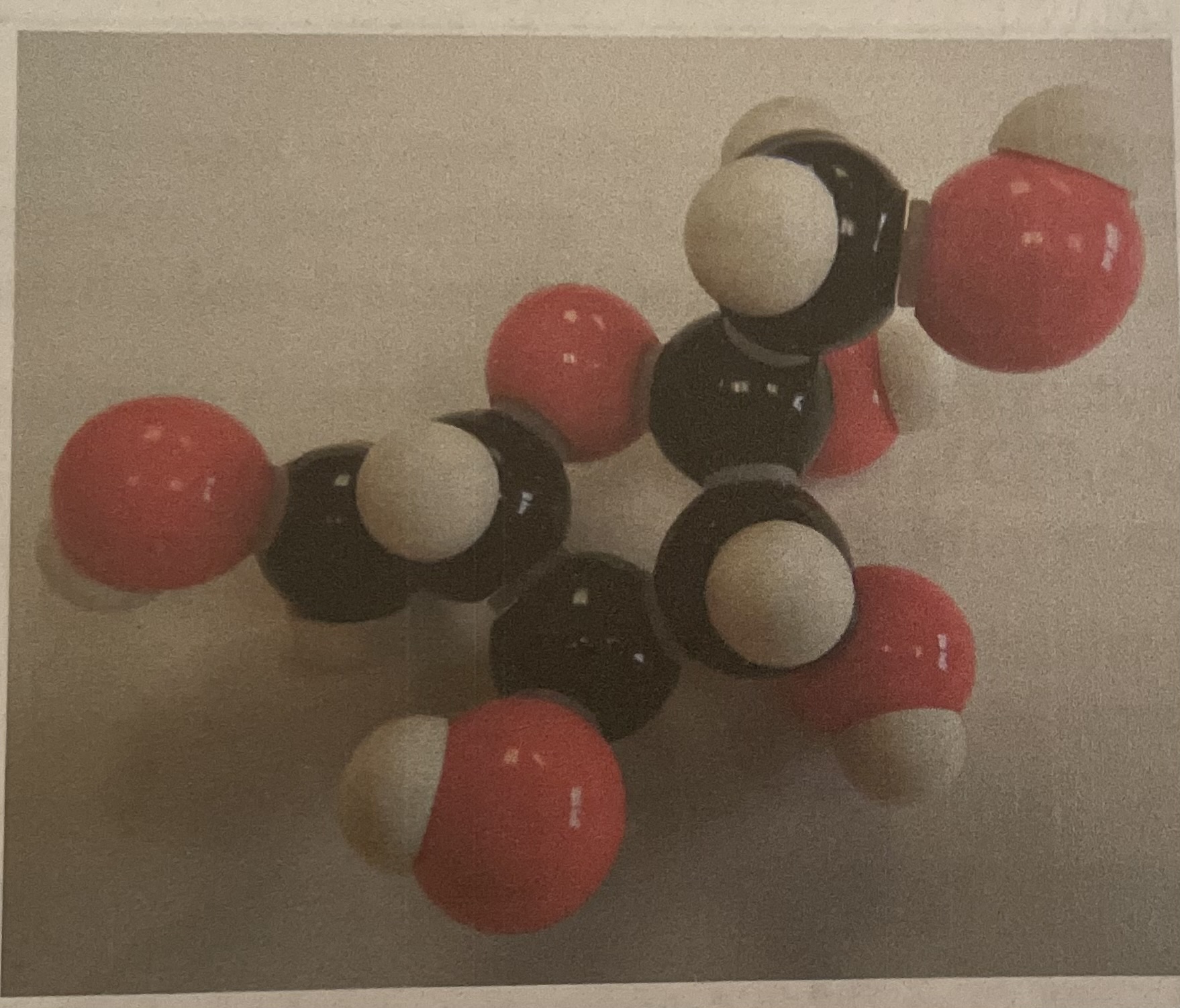
Glucose
Dipeptide (ala-gly)
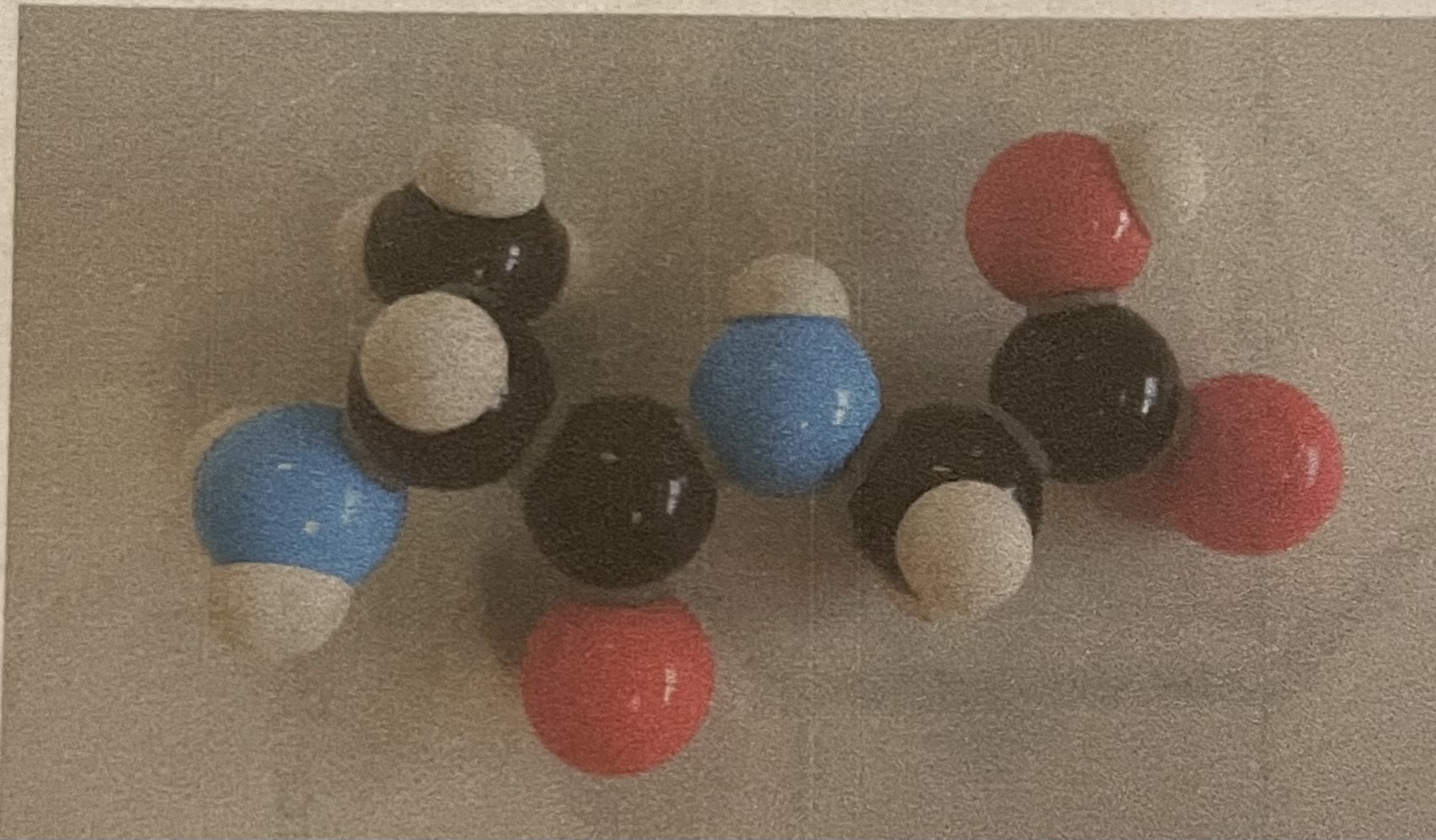

Thymine (pyrimidine)
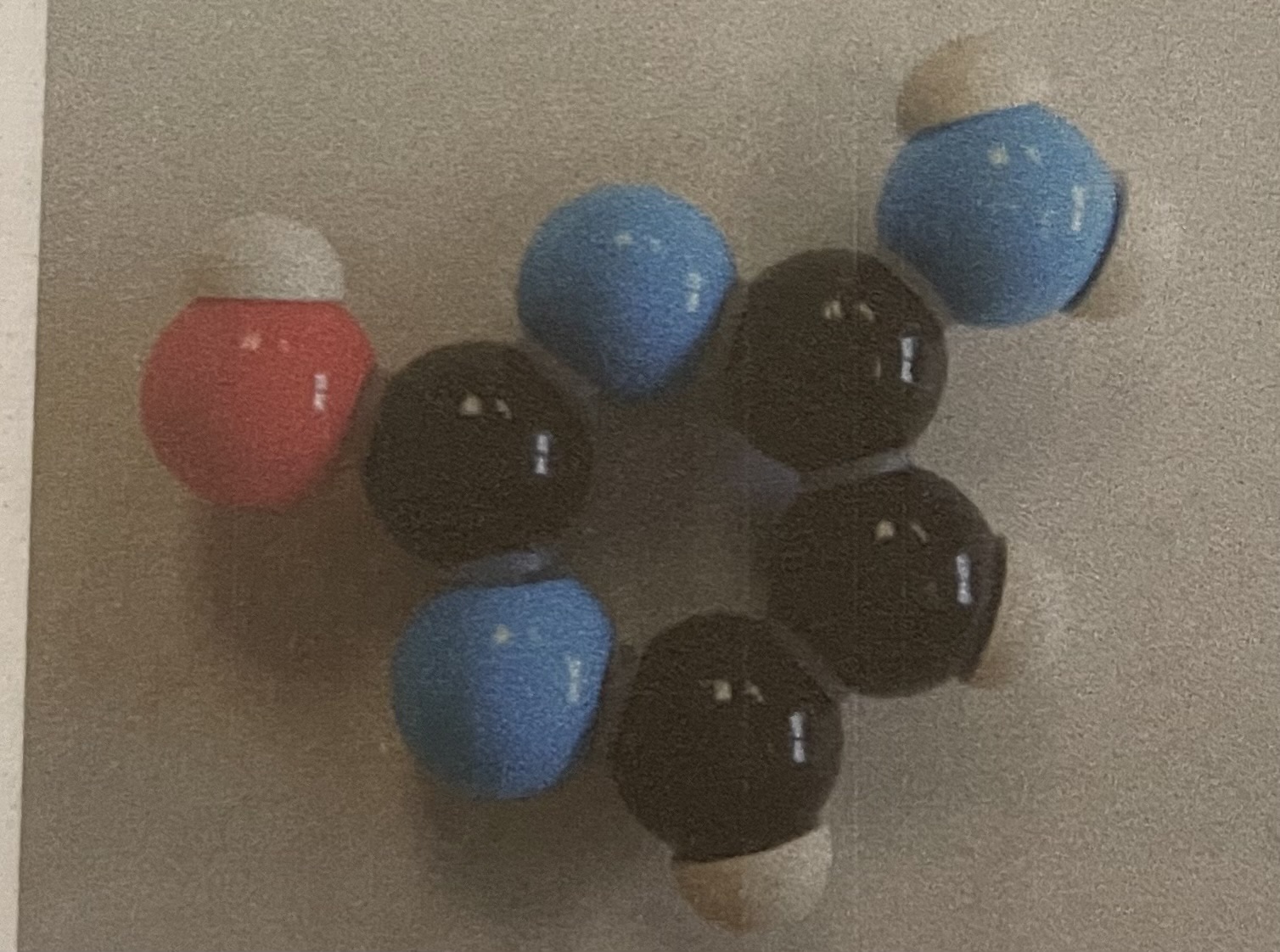

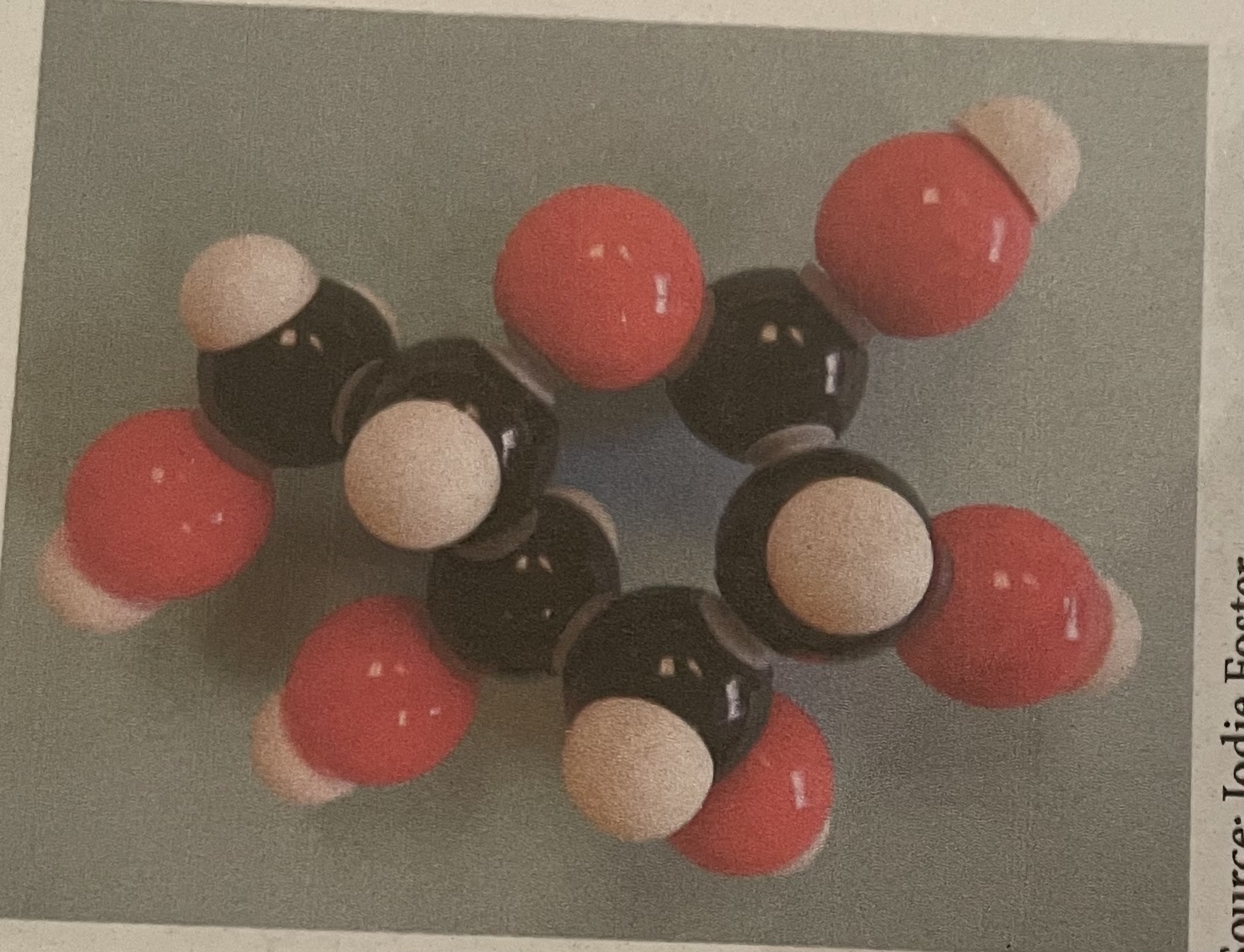
Maltose
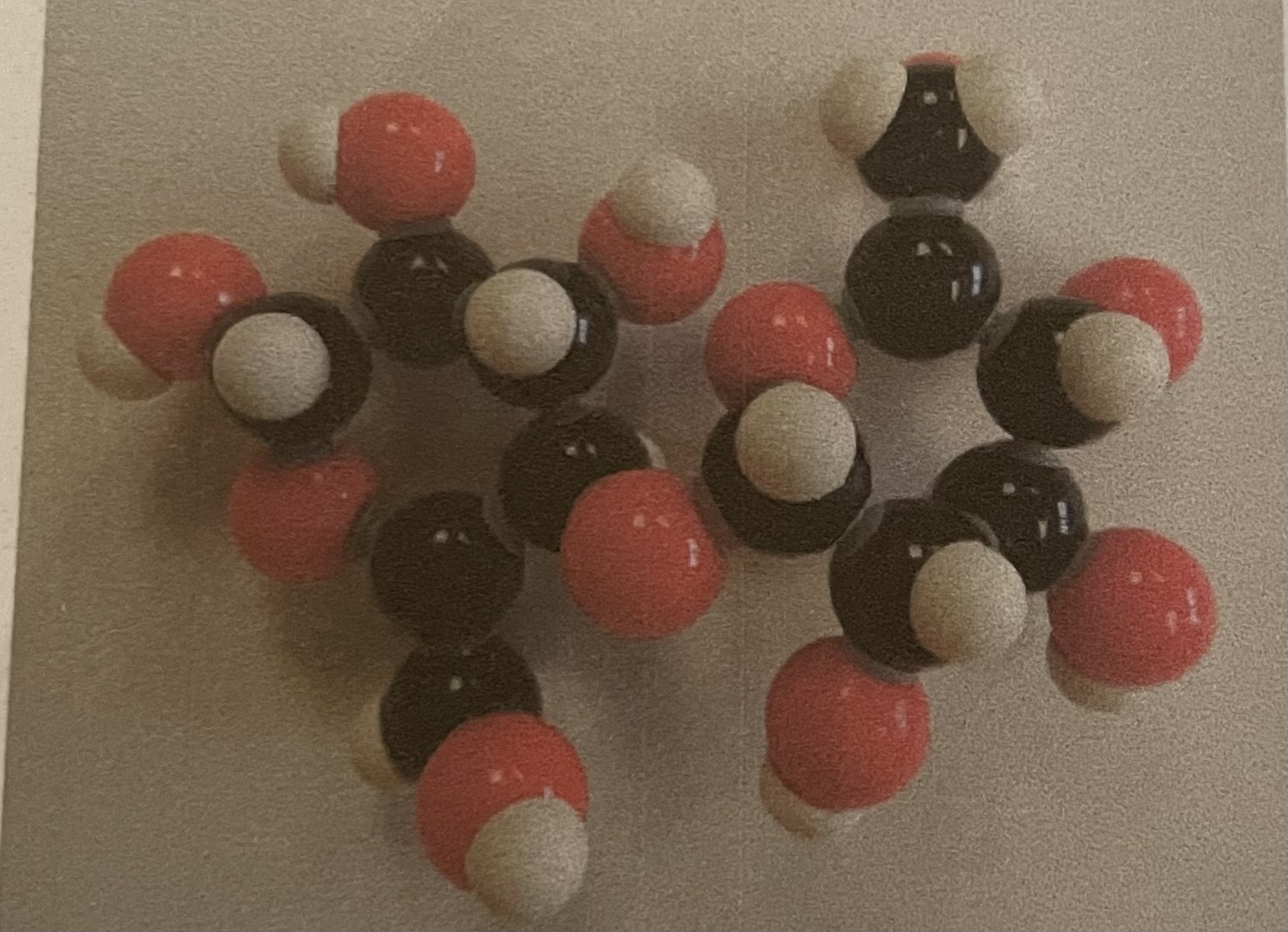

Purine (alanine)
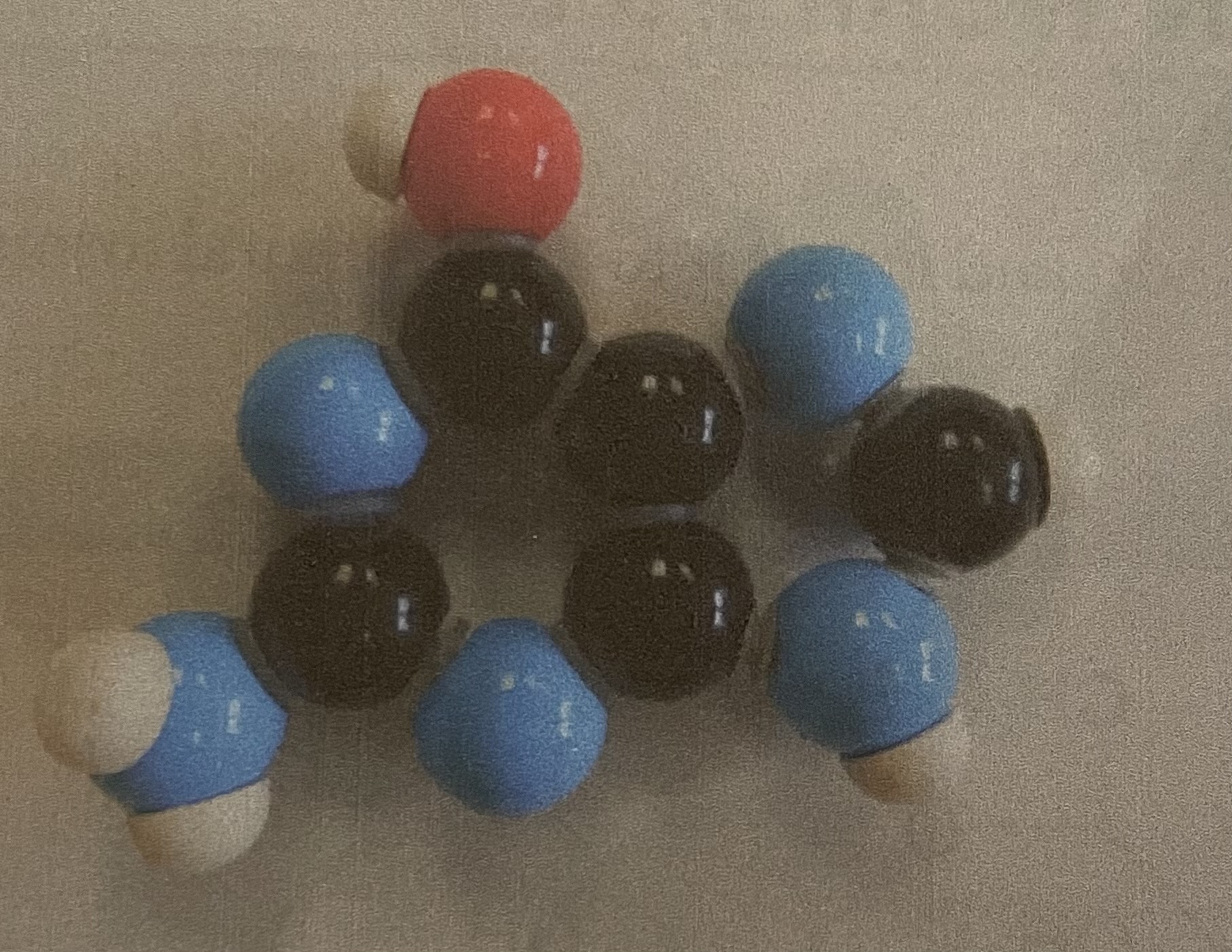
Glycine
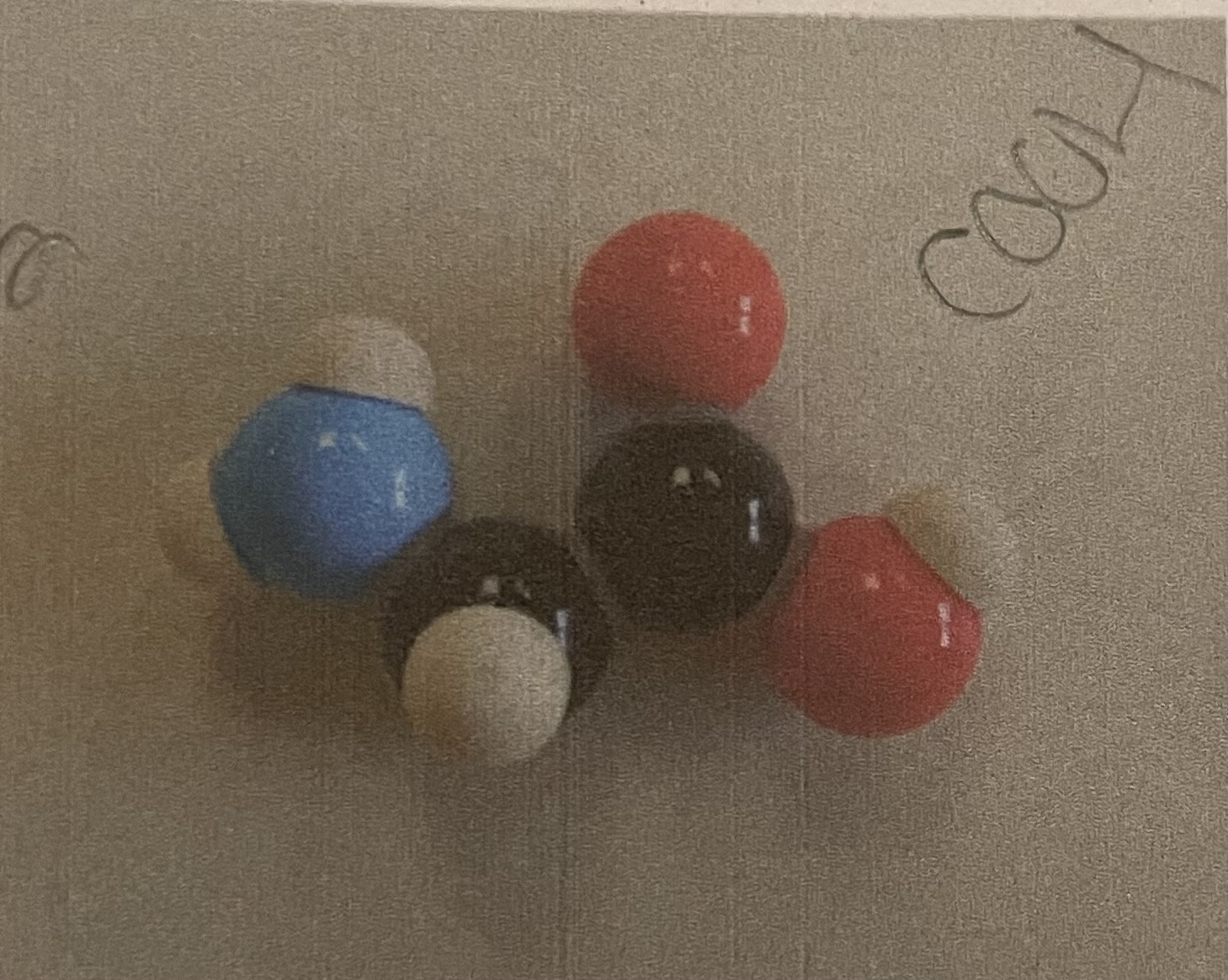

Cysteine
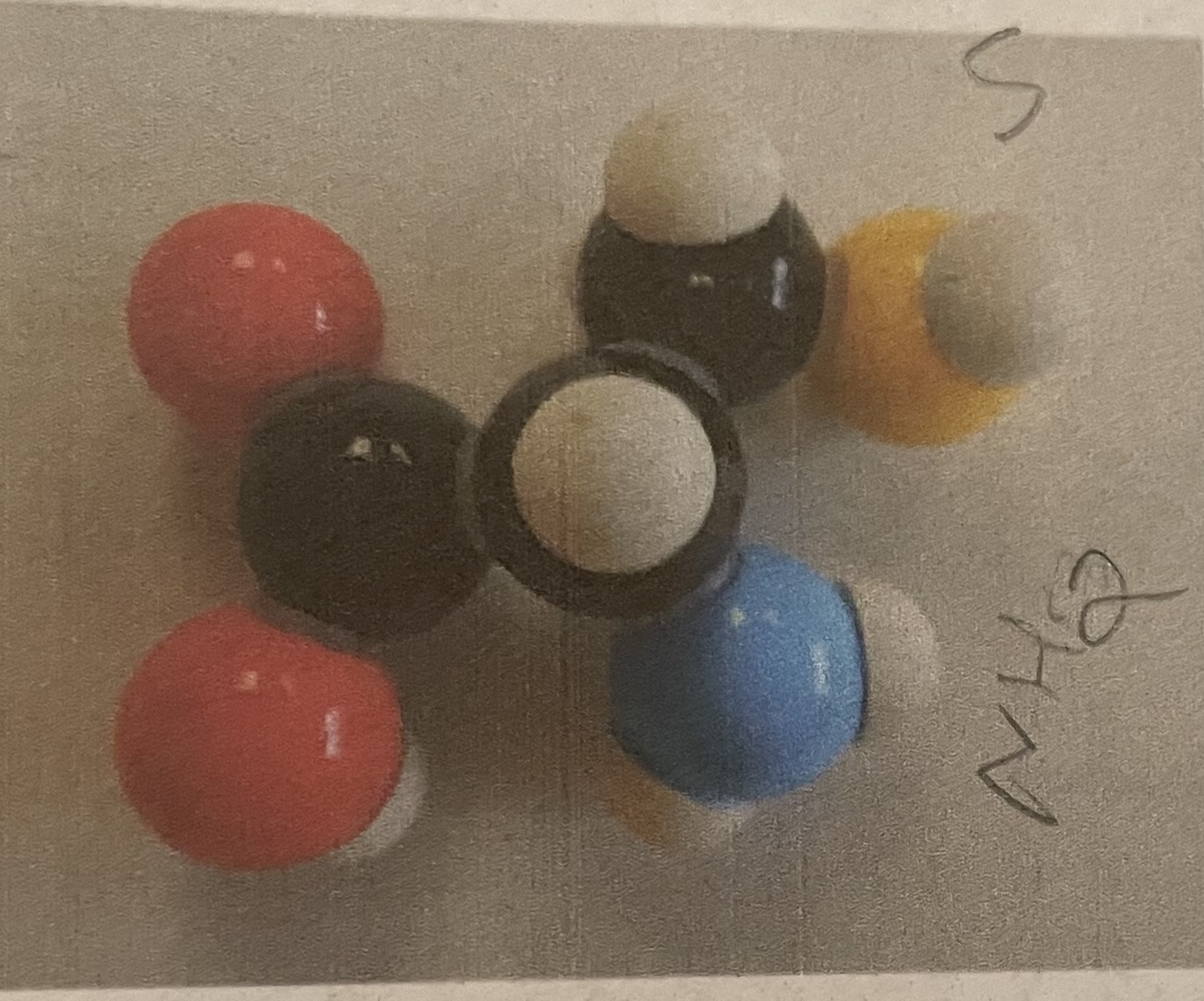
Alanine (purine)
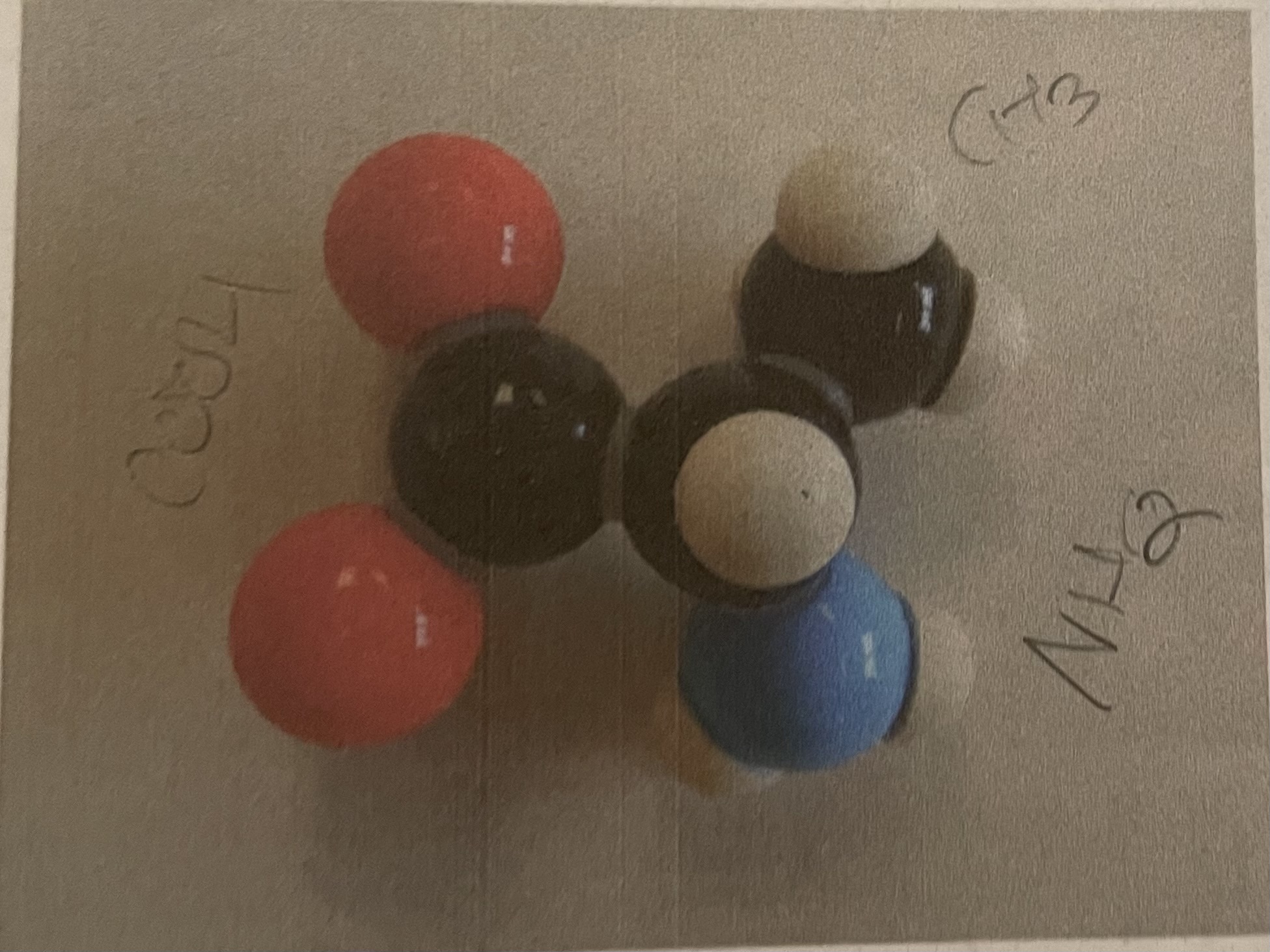
What is the difference between a pyrimidine and a purine?
Purine has 2 rings, pyrimidine has 1
What are the colors for carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus?
Black, red, white, blue, yellow, purple
Which bases are pyrimidines?
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil
Which bases are purines?
Guanine and adenine
How many hydrogen bonds are between adenine and thymine?
2
How many hydrogen bonds are between cytosine and guanine?
3
How can you identify glycine?
R group is a single hydrogen
How can you identify cysteine?
Presence of sulfur (yellow)
How can you identify alanine?
R group is CH3