Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
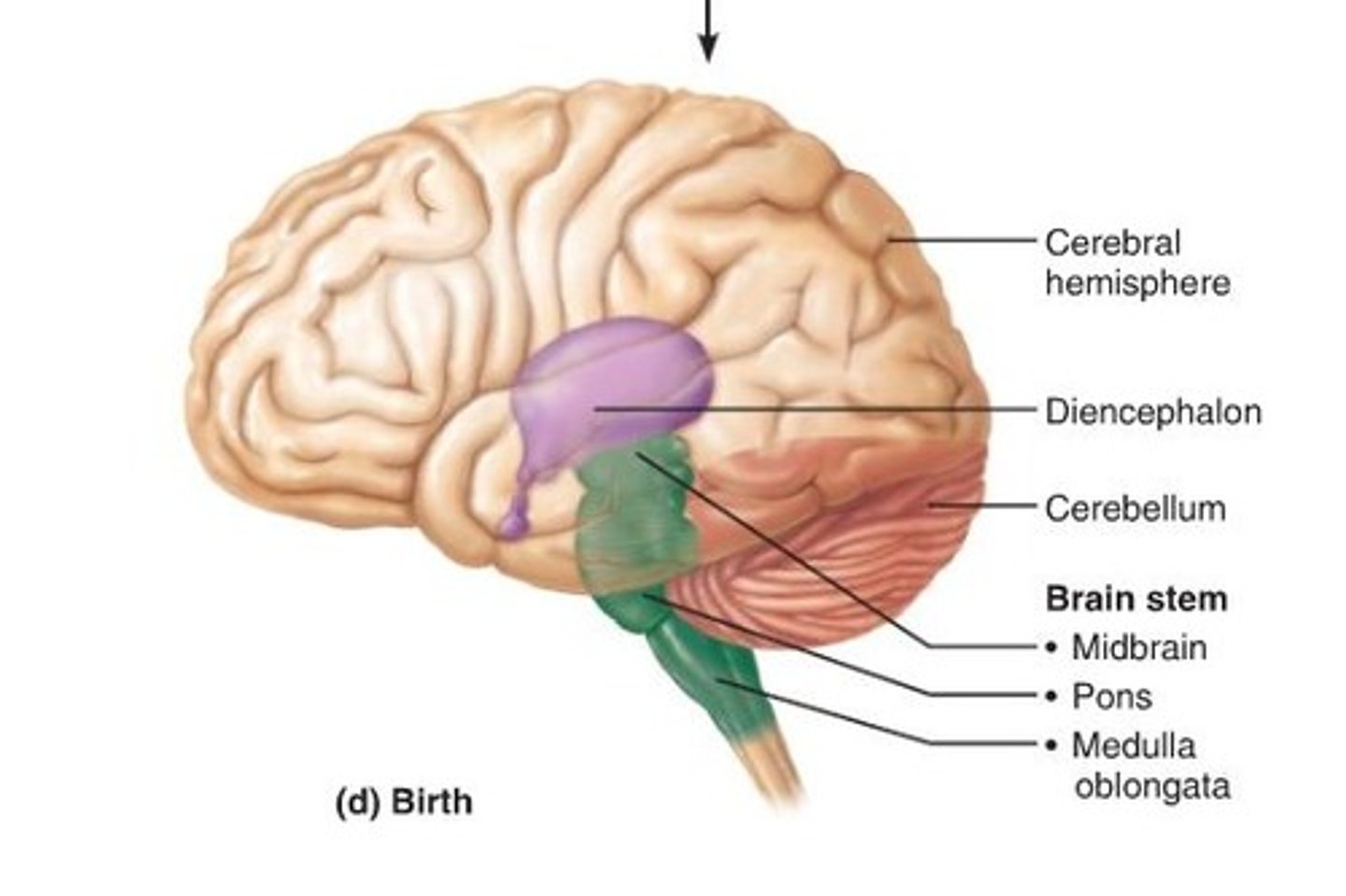
Cerebrum
-Largest portion.
-2 half globes called cerebral hemispheres.
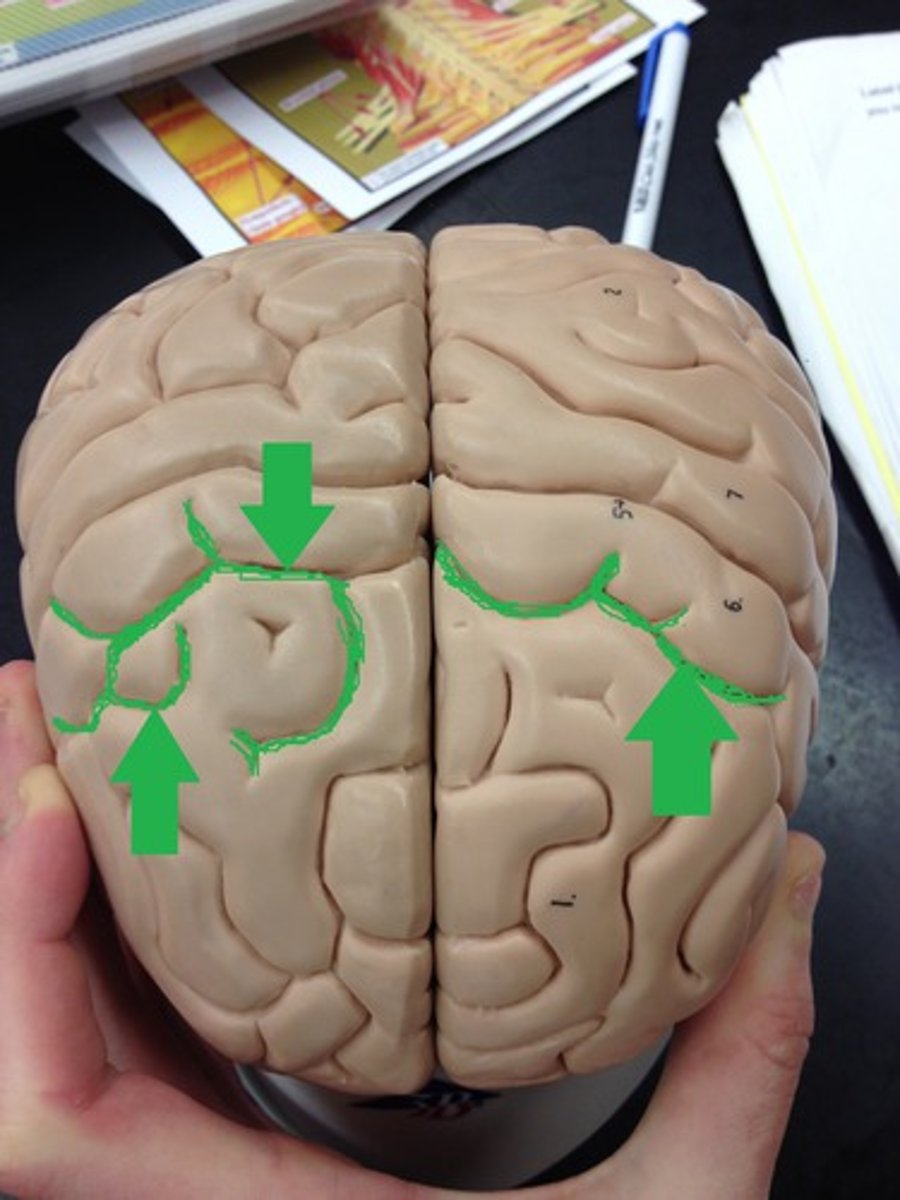
Longitudinal fissure
divides the 2 half globes of the cerebrum

Gyri
thick folds that mark the cerebrum
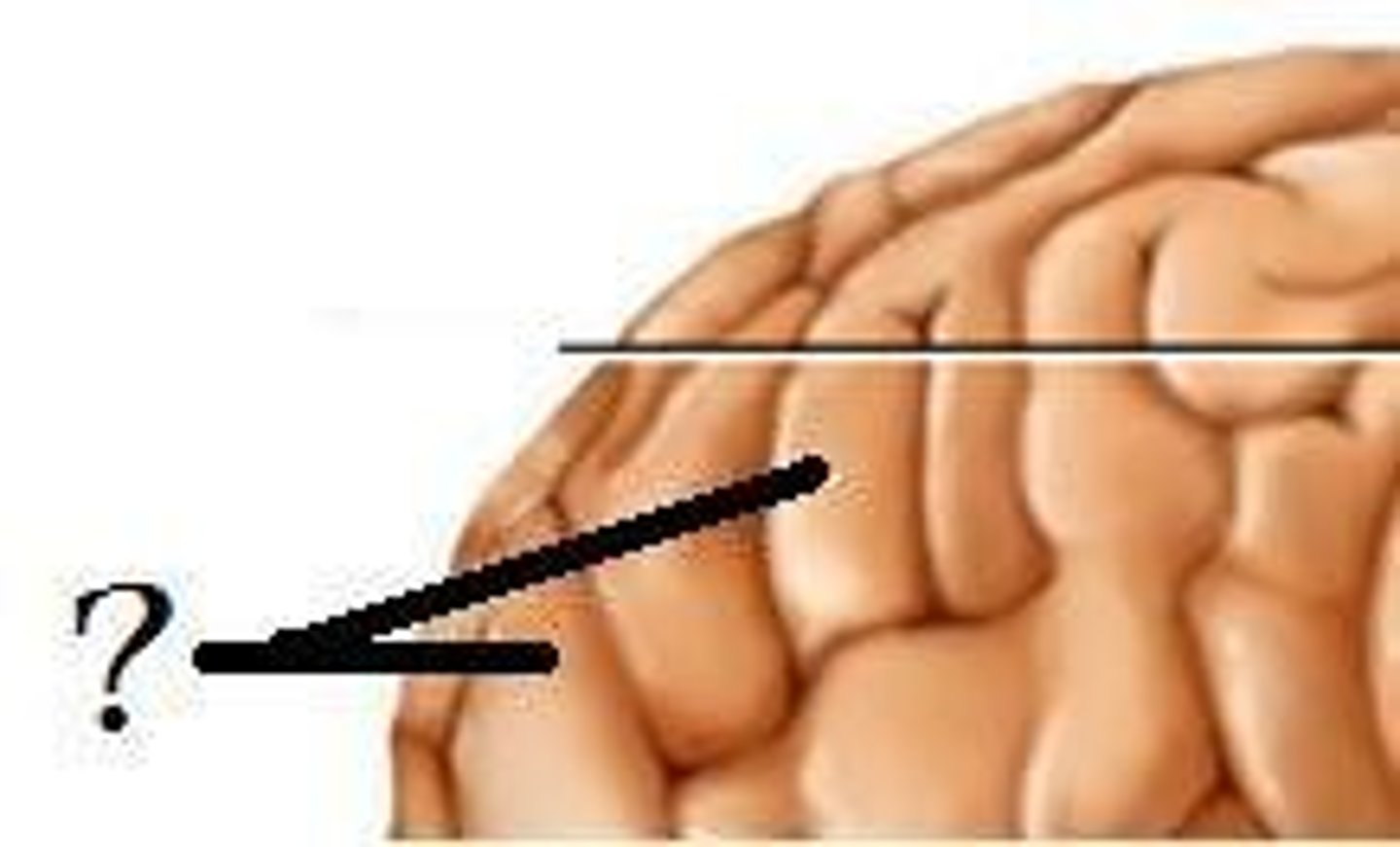
Sulci
shallow grooves that mark the cerebrum
Corpus Callosum
a thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the cerebral hemispheres
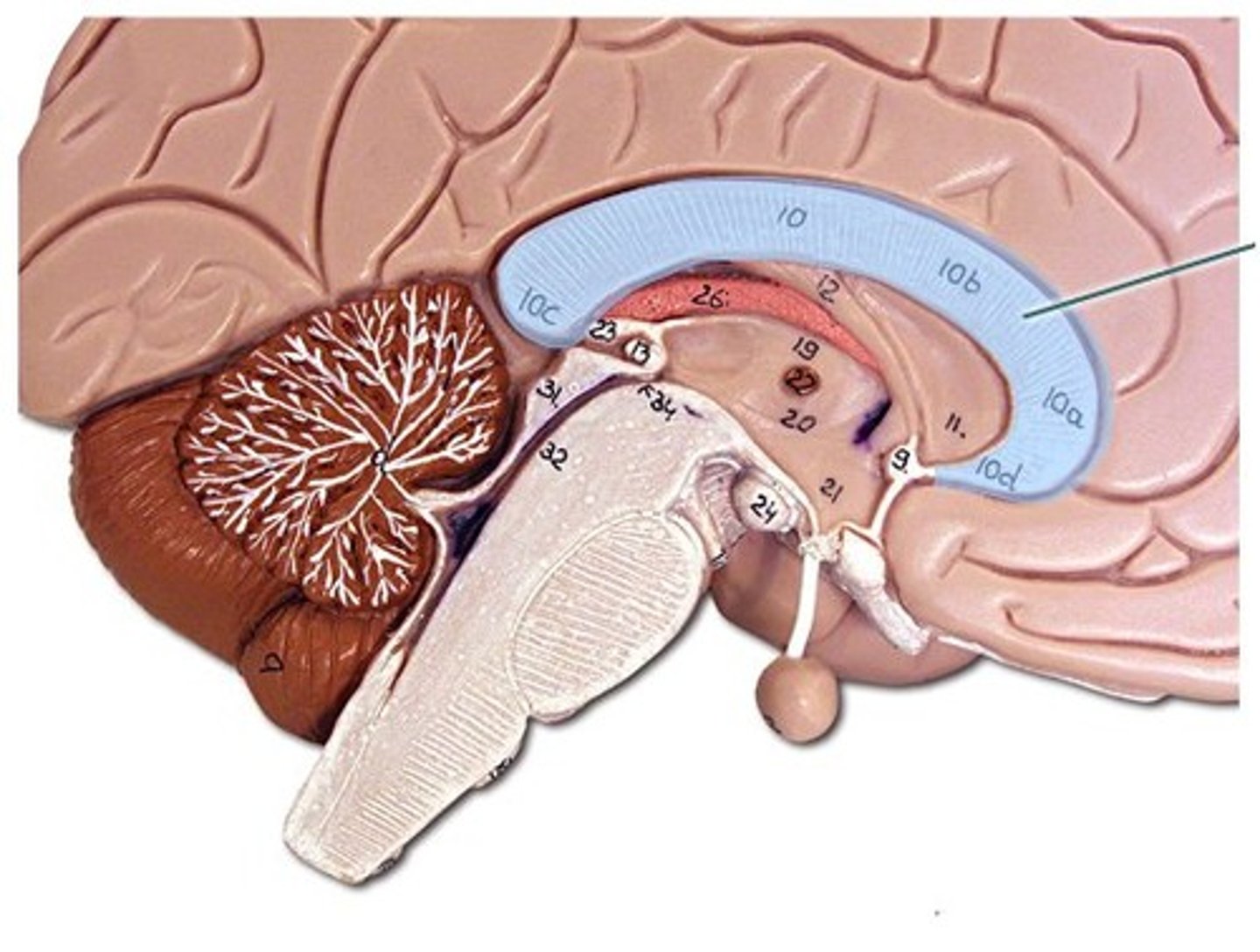
Cerebellum
-2nd largest part of the total brain and contains 50% of neurons.
-2 of them separated by transverse cerebral fissure.
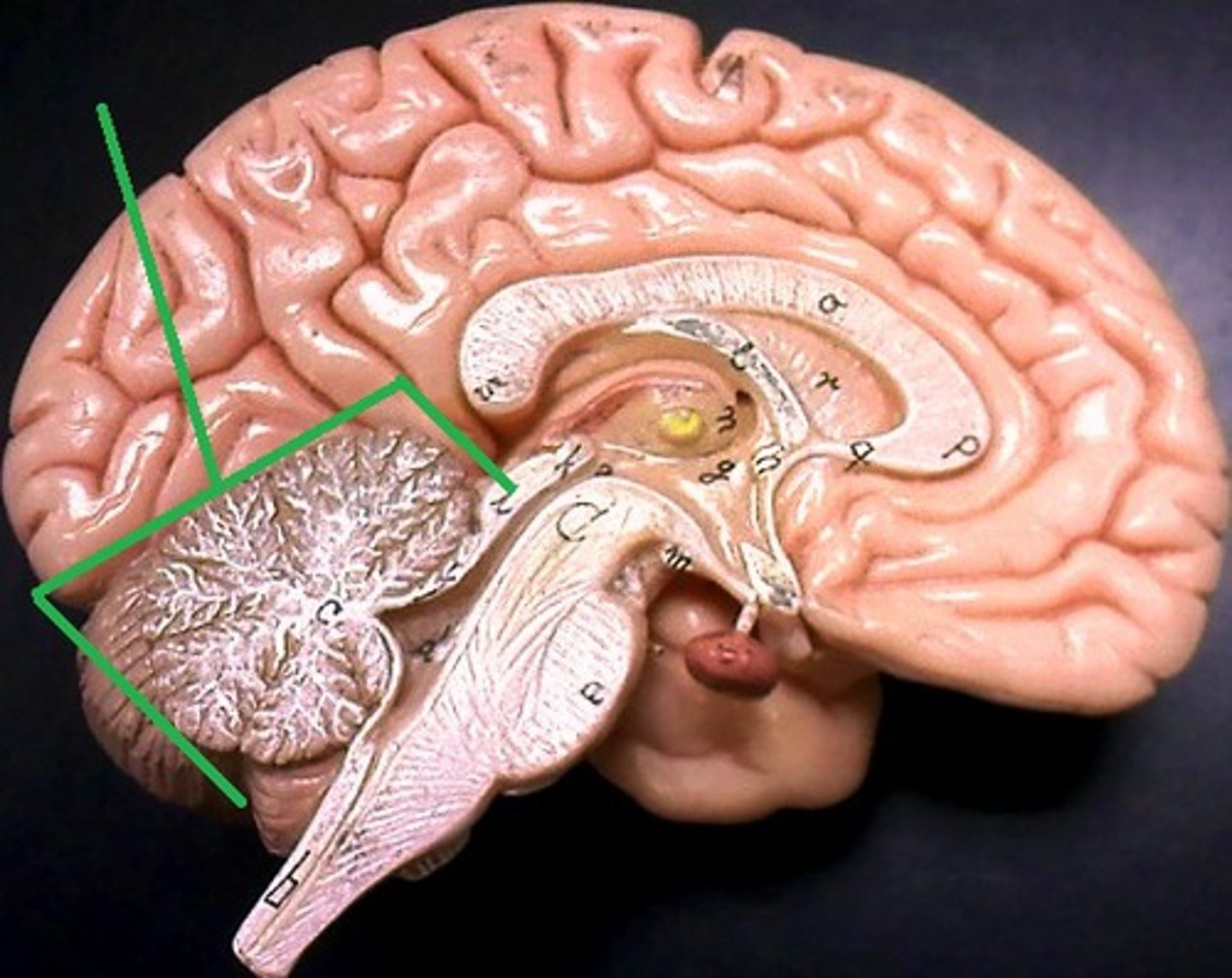
Brain stem
-everything else.
-major components: diencephalon, midbrain, pons, medulla oblangata.
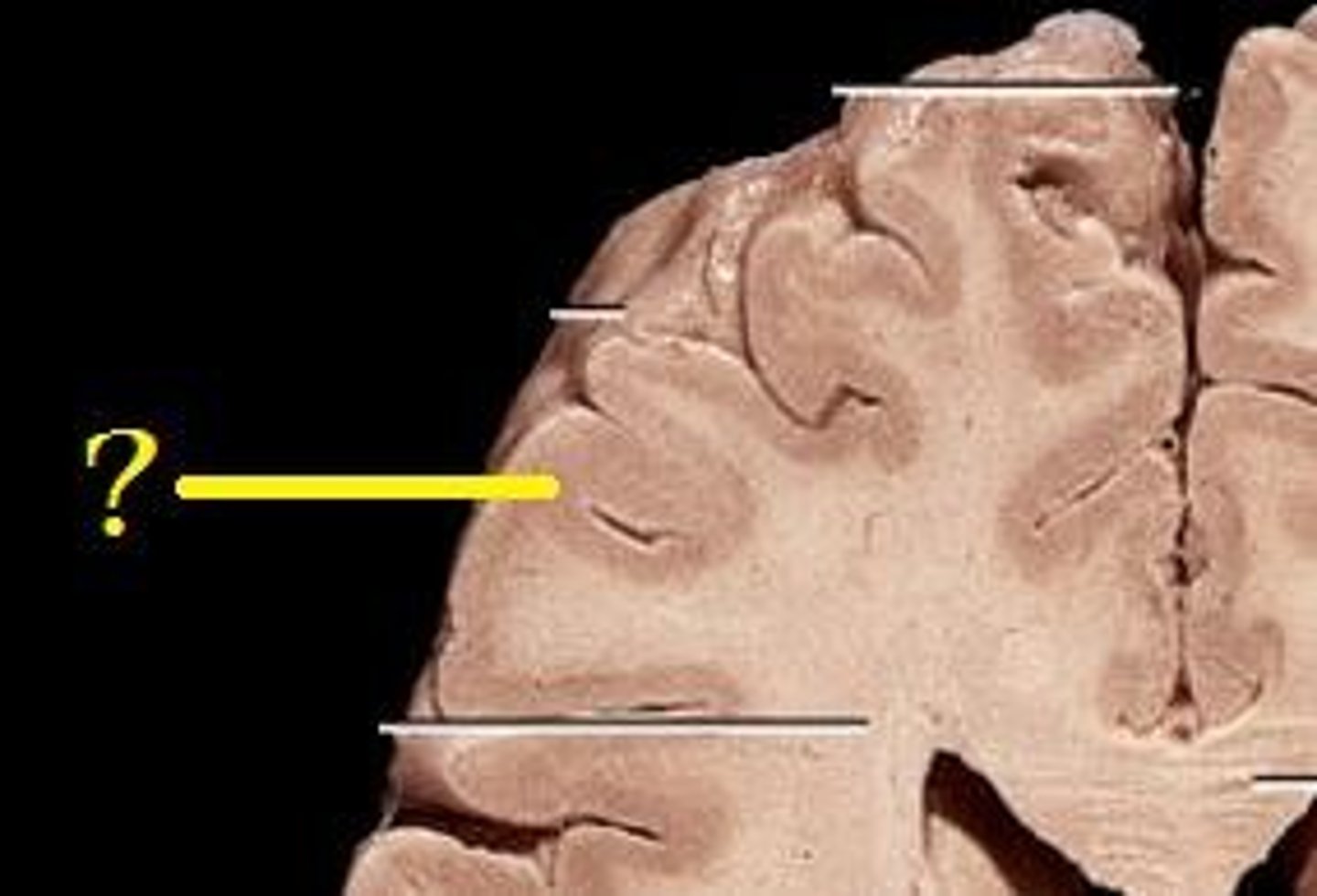
Gray Matter
-neurosomas, dendrites, and synapses (same as spinal cord).
-intergration: the thinking part (receives signals).
-outer portion.
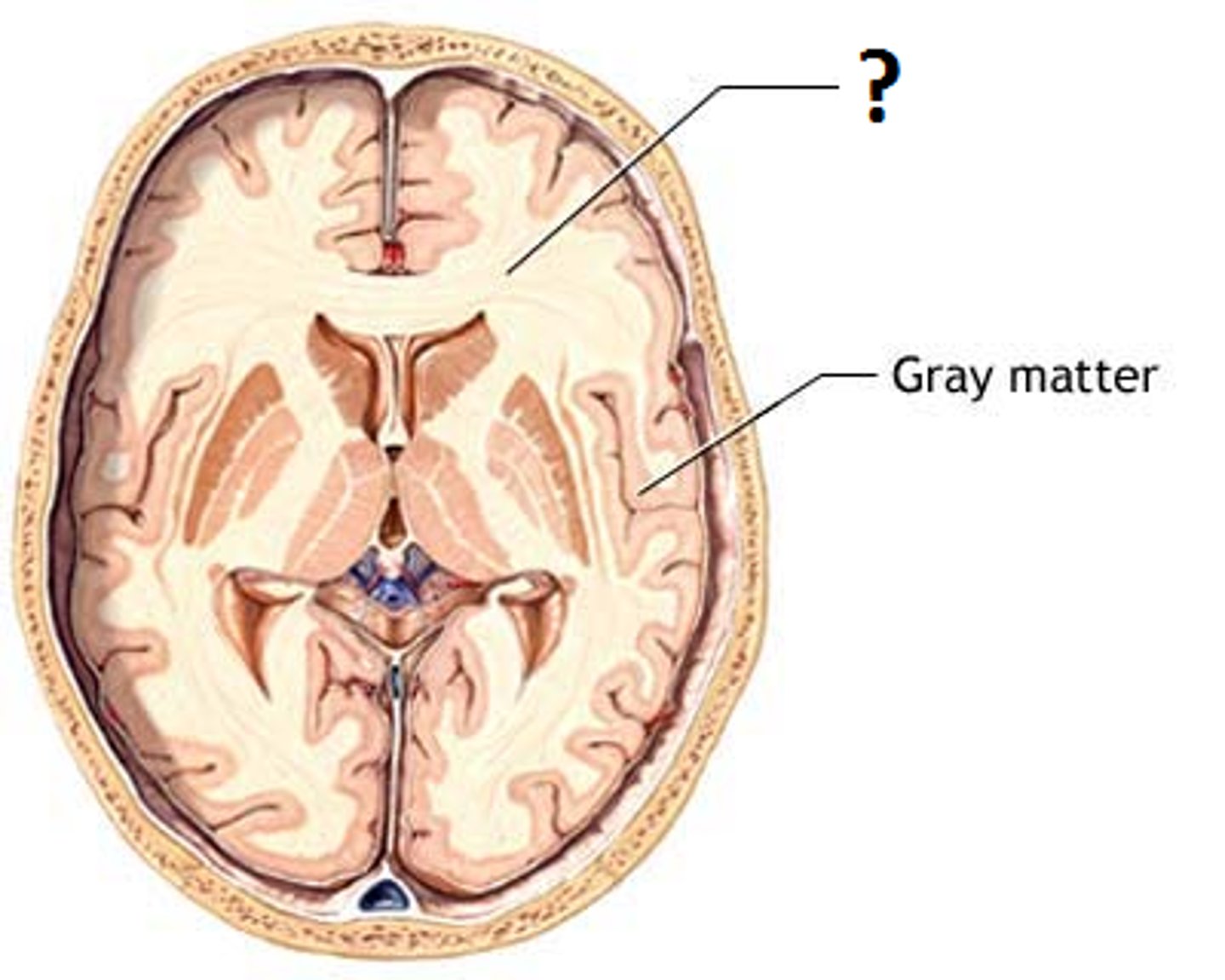
White Matter
-bundles of axon.
-sends/moves signals.
-lies deep to cortical gray matter (opposite relation in the spinal cord).
Dura Mater
-superficial.
-pressed closely against the cranial bones but not attached.
Arachnoid mater
-middle.
-Transparent membrane over brain surface.
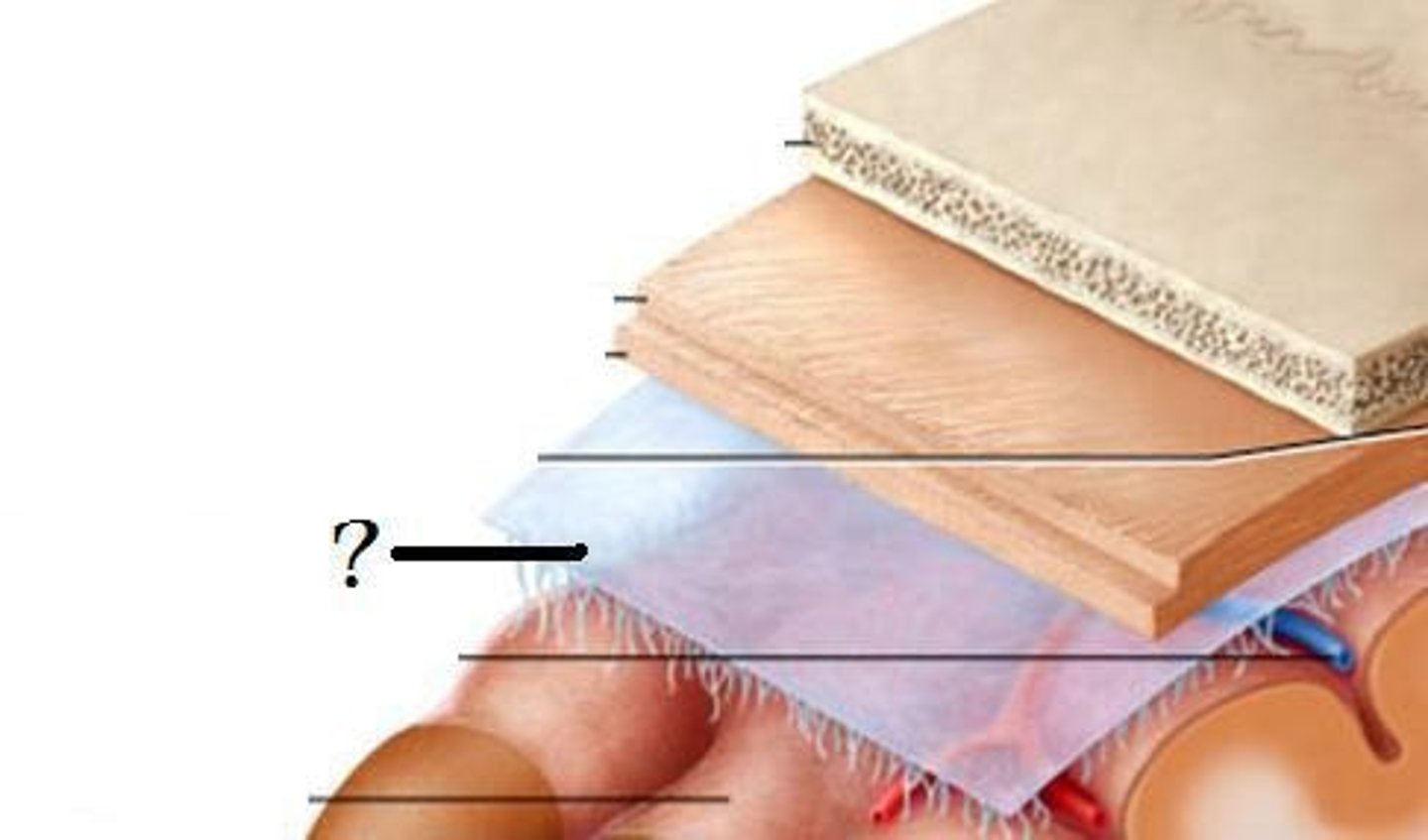
Pia mater
-deep.
-Very thin and follows the contours of the brain.
-not usually visible without a microscope.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
fluid in the brain.
3 Functions of CSF
-buoyancy (helps it float in the middle).
-protection.
-chemical stability.
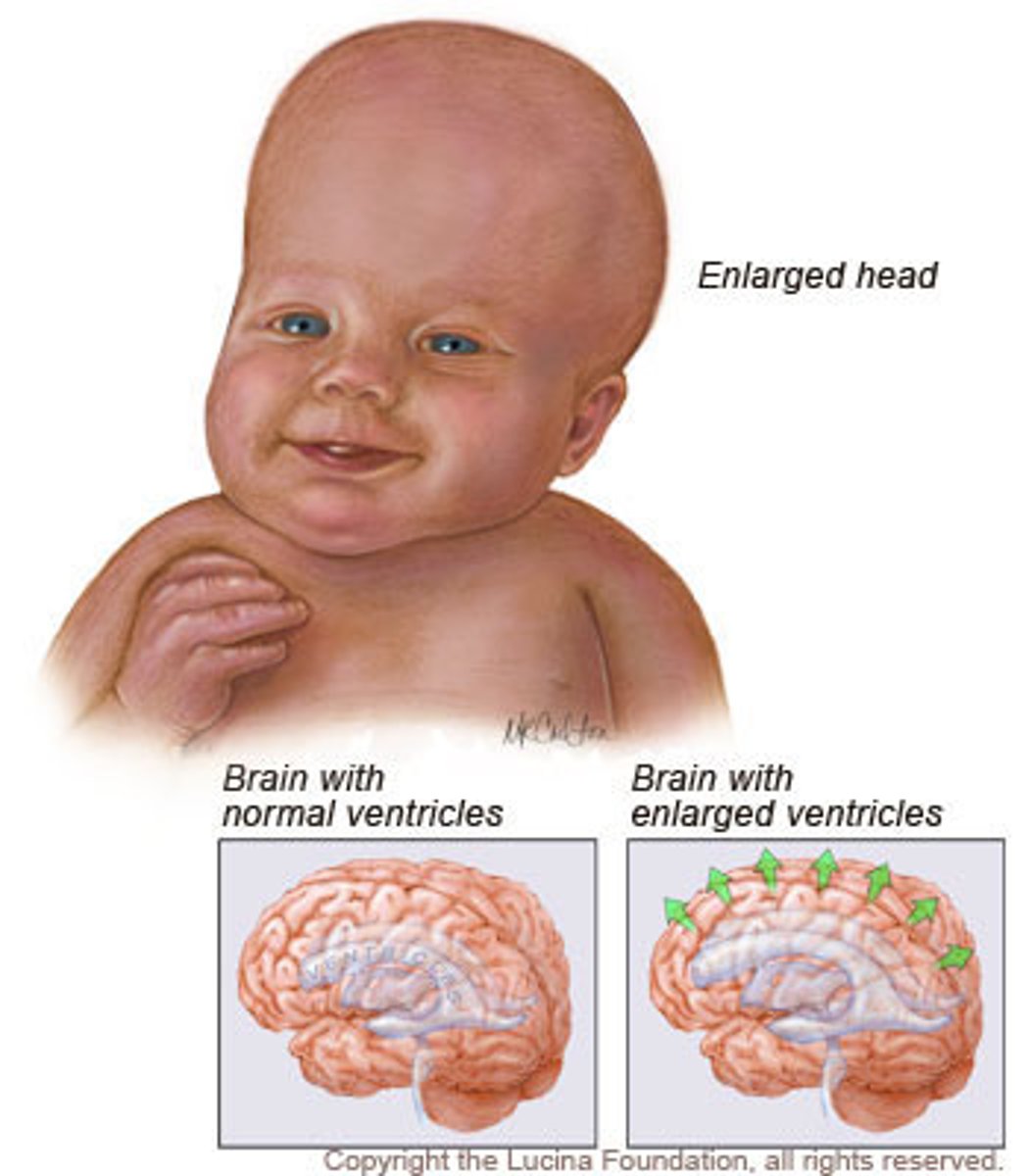
Hydrocephalus
abnormal accumulation of CSF in the brain from a blockage in its route of flow.
-can be fatal.
-in a fetus or infact, the entire head can swell due to unfused cranial bones.
-treated by placement of a shunt.
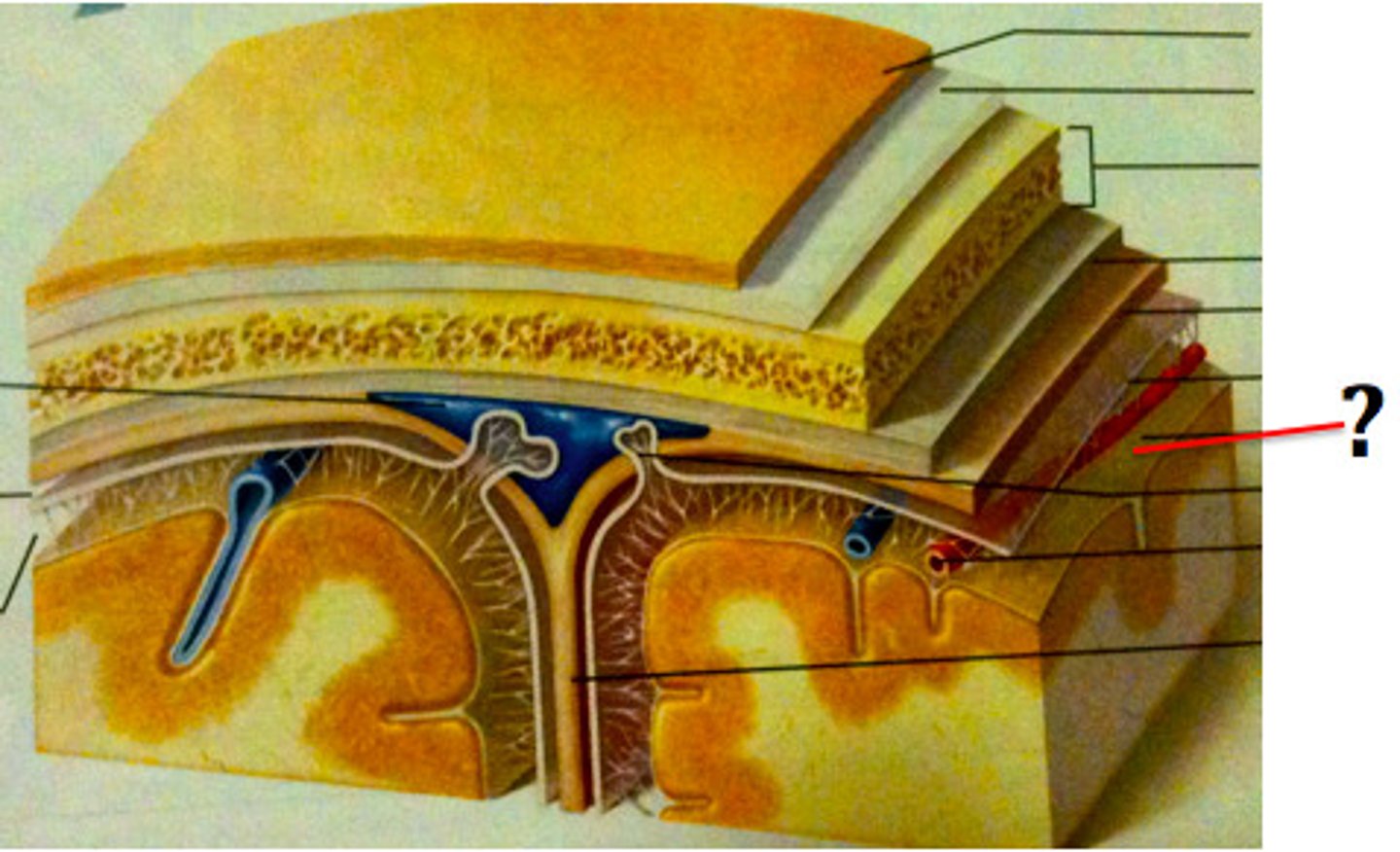
Blood-brain barrier (BBB)
Barrier between blood and brain.
-consists of a tight junction between endothelial cells that form the capillary walls.
-highly permeable to: H20, glucose, 02, C02, alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, and anesthetics.
Regions of the Brainstem
from rostral to caudal:
-diencephalon,
-midbrain.
-pons.
-medulla oblongata.
(-spine)
Reticular Formation
gray matter than run vertically through all levels of the brain stem.
Reticular Formation Functions
-somatic motor control.
-cardiovascular control.
-pain.
-sleep and consciousness.
-habituation (ignore constant stimuli).
Hindbrain
-medulla oblongata.
-pons.
-cerebellum.
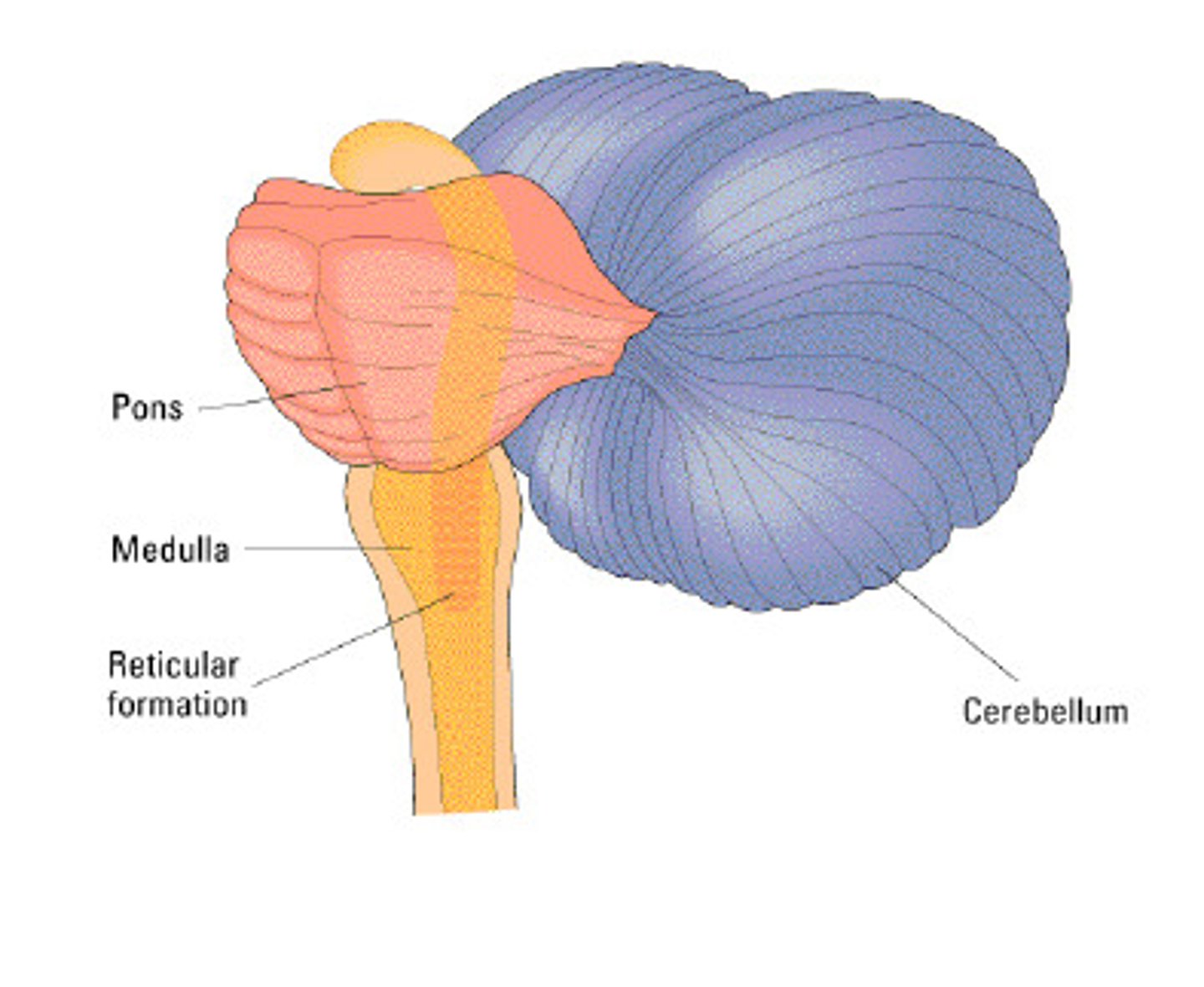
Medulla Oblongata
contains:
-Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
-Vagus nerve (X)
-Accessory nerve (XI)
-Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
The Pons
contains:
-Trigeminal nerve (V)
-Abducens nerve (VI)
-Facial nerve (VII)
-Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
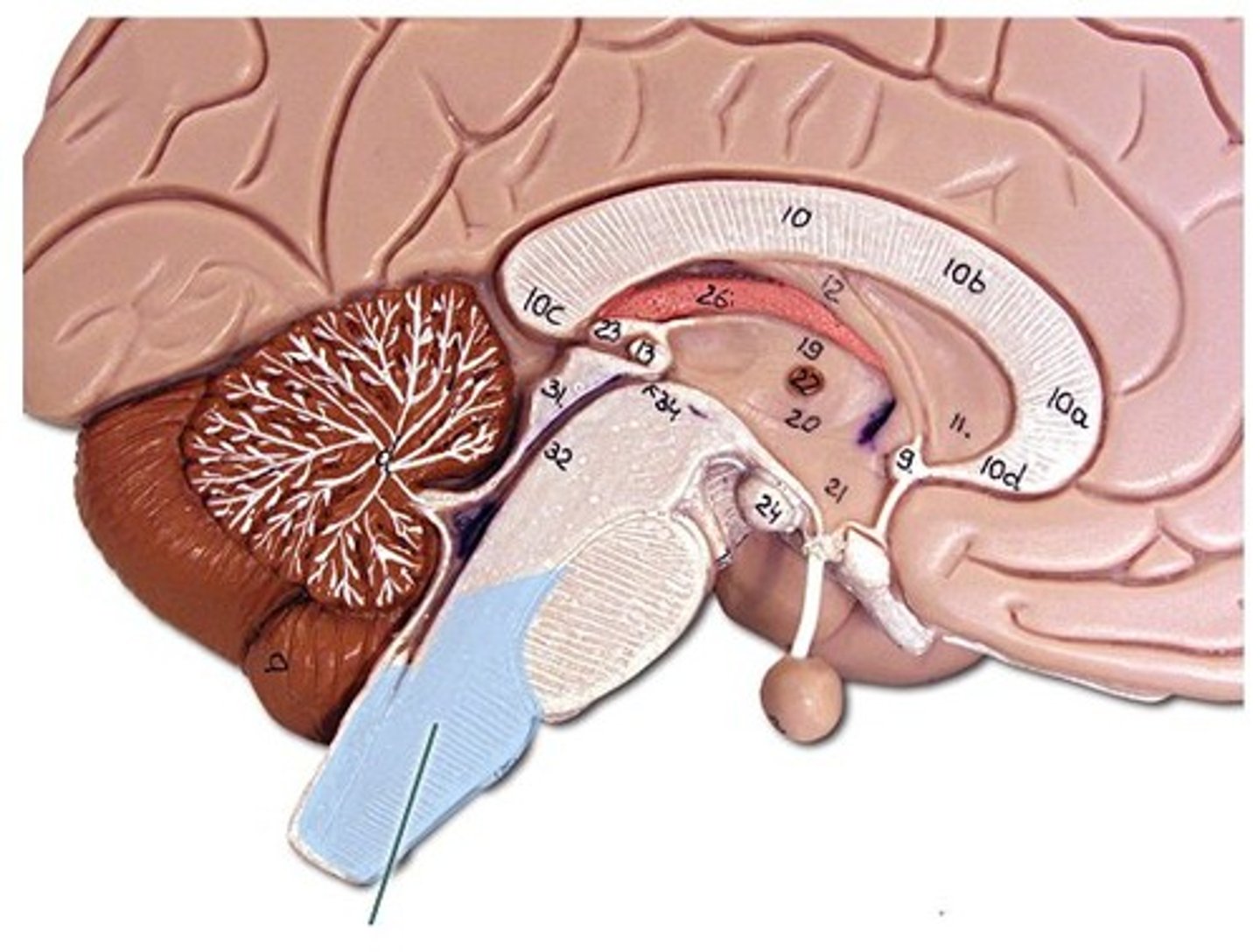
The Midbrain
contains:
-Oculomotor nerve (III)
-Trochlear nerve (IV)
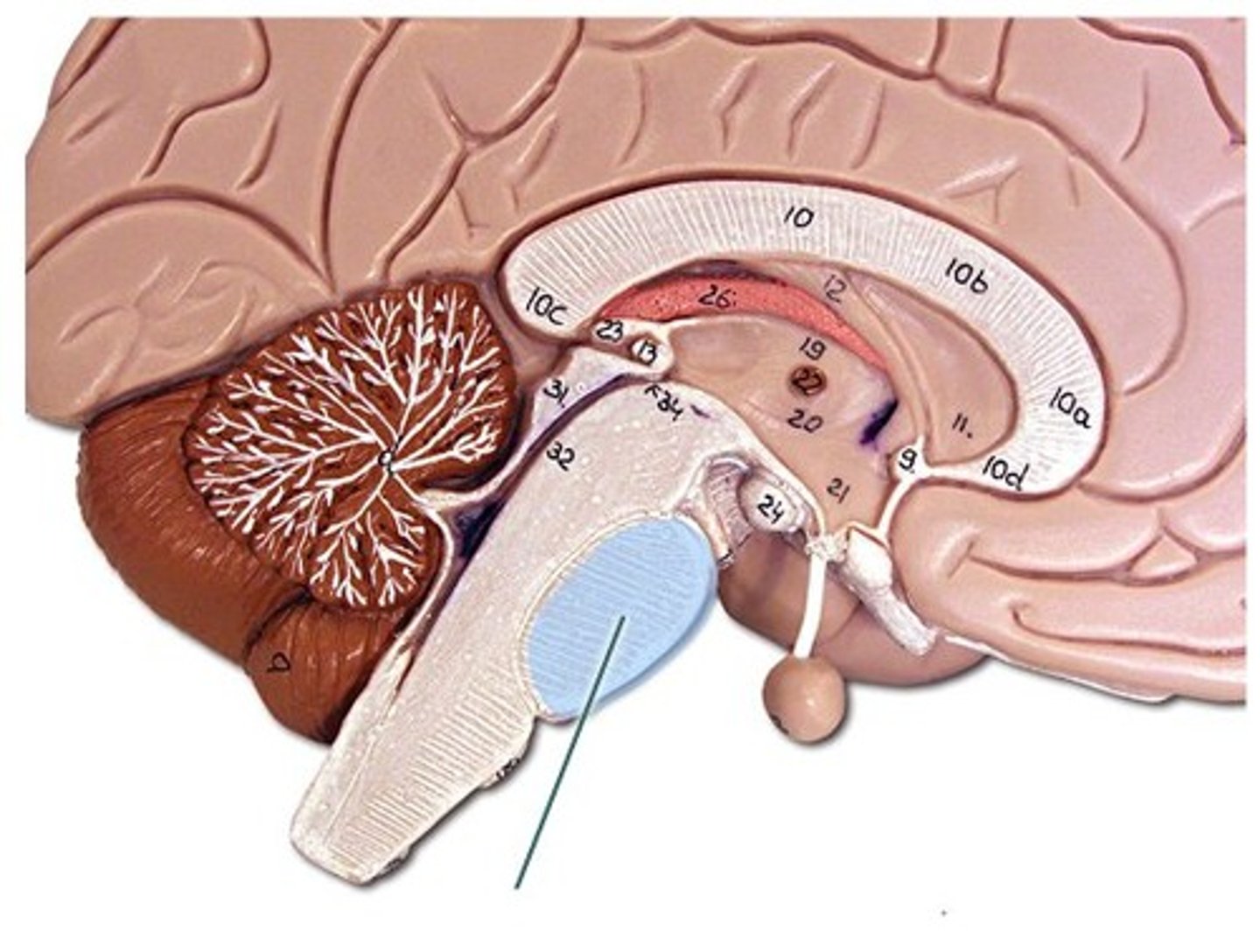
Cerebellum functions
-motor muscle contractions and coordination.
-Evaluation of sensory input.
-timekeeping center (predicting movement of objects etc.)
-hearing.
Forebrain
-diencephalon.
-telencephalon (or cerebrum).
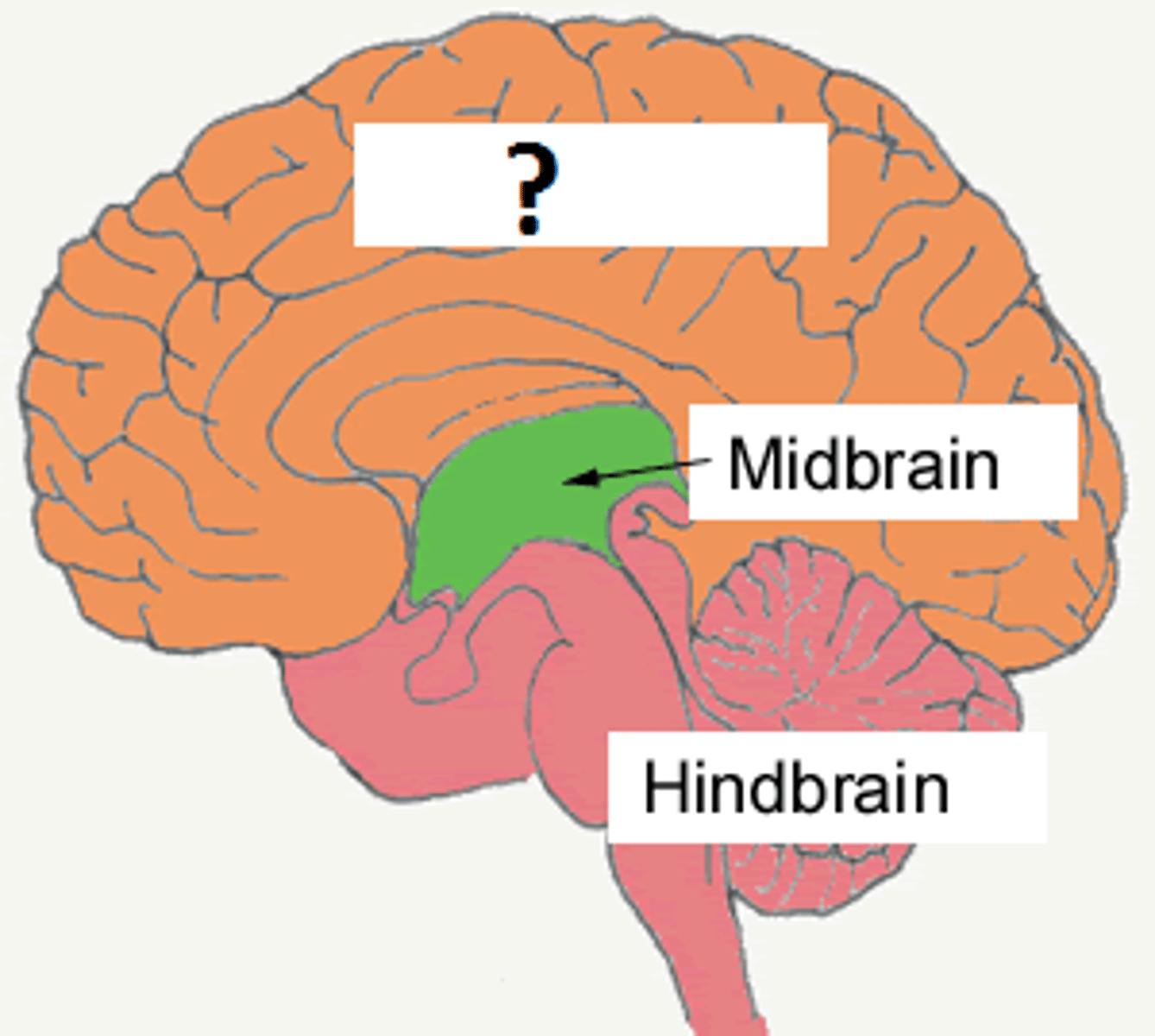
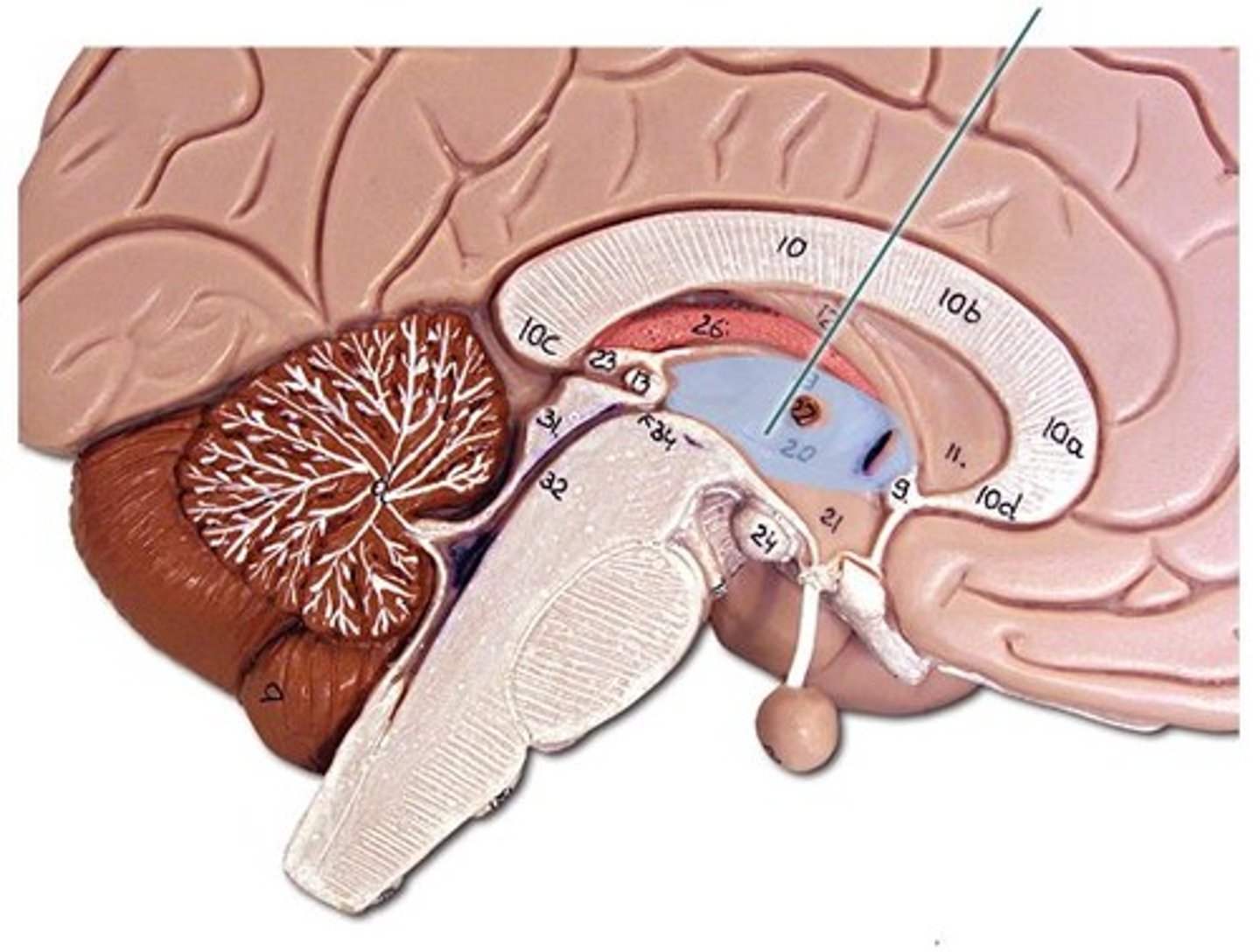
Diencephalon
-thalamus.
-hypothalamus.
-epithalamus.
Thalamus
-largest part of the diencephalon.
-the gateway to the cerebral cortex (nearly all input passes through).
functions:
-motor control.
-memory.
-emotional functions.
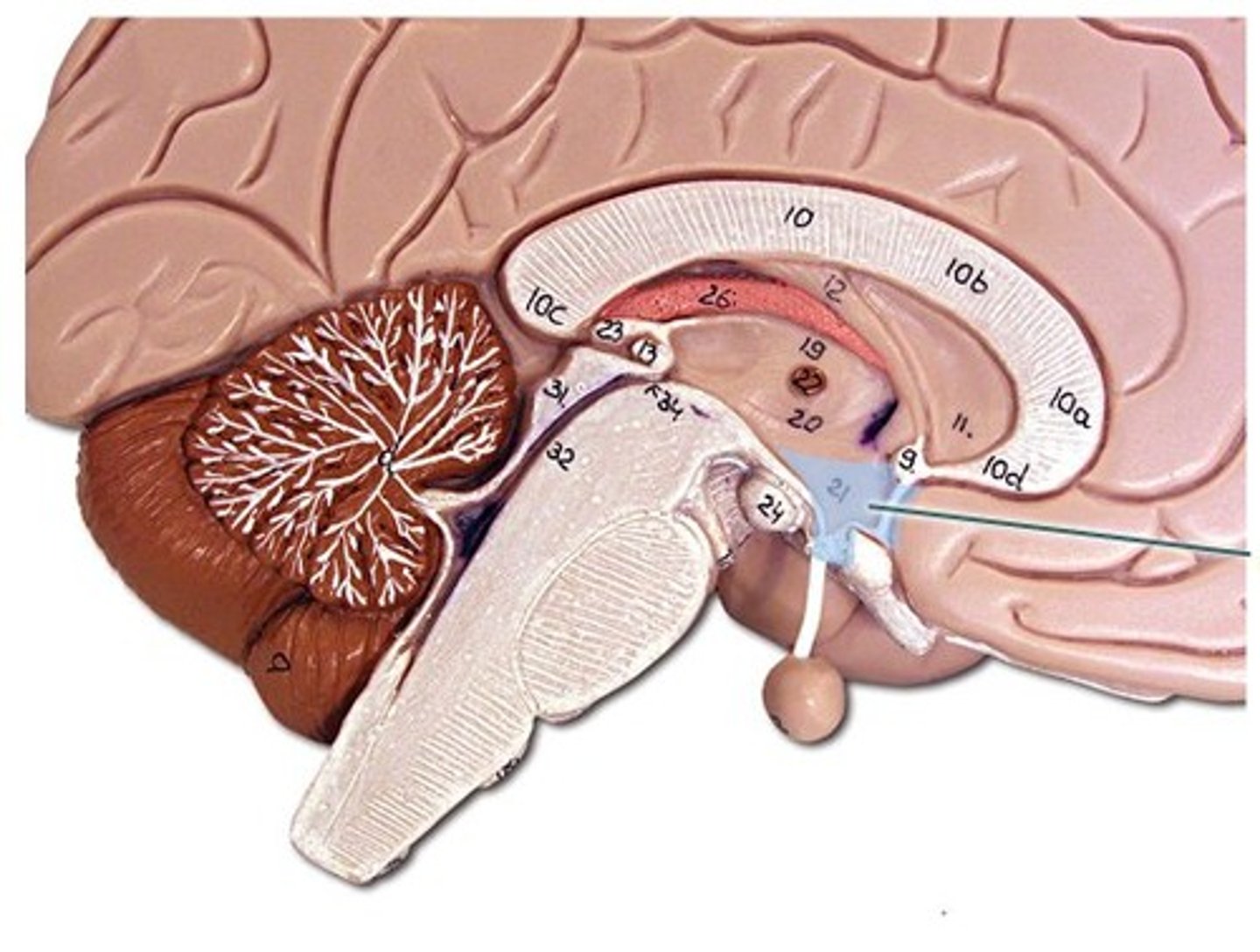
Hypothalamus
-control center of the endocrine and ANS.
-attached to the pituitary gland.
functions:
-hormone secretion.
-autonomic effects (integrating center).
-thermoregulation.
-food and water intake.
-sleep and circadian rhythms.
-memory.
-emotional behavior.
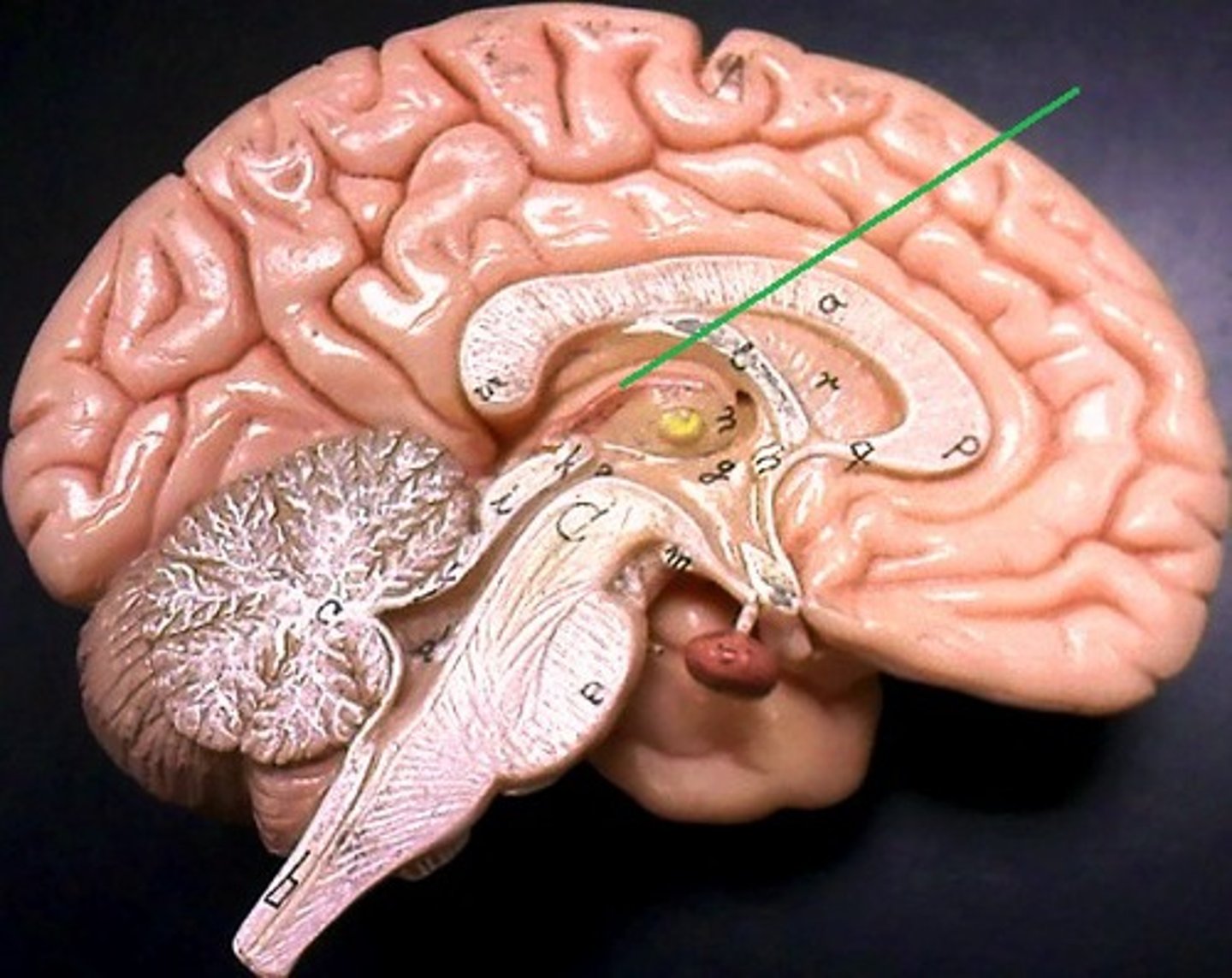
Epithalamus
-composed primarily of the pineal gland.
-primary function is to produce melatonin.
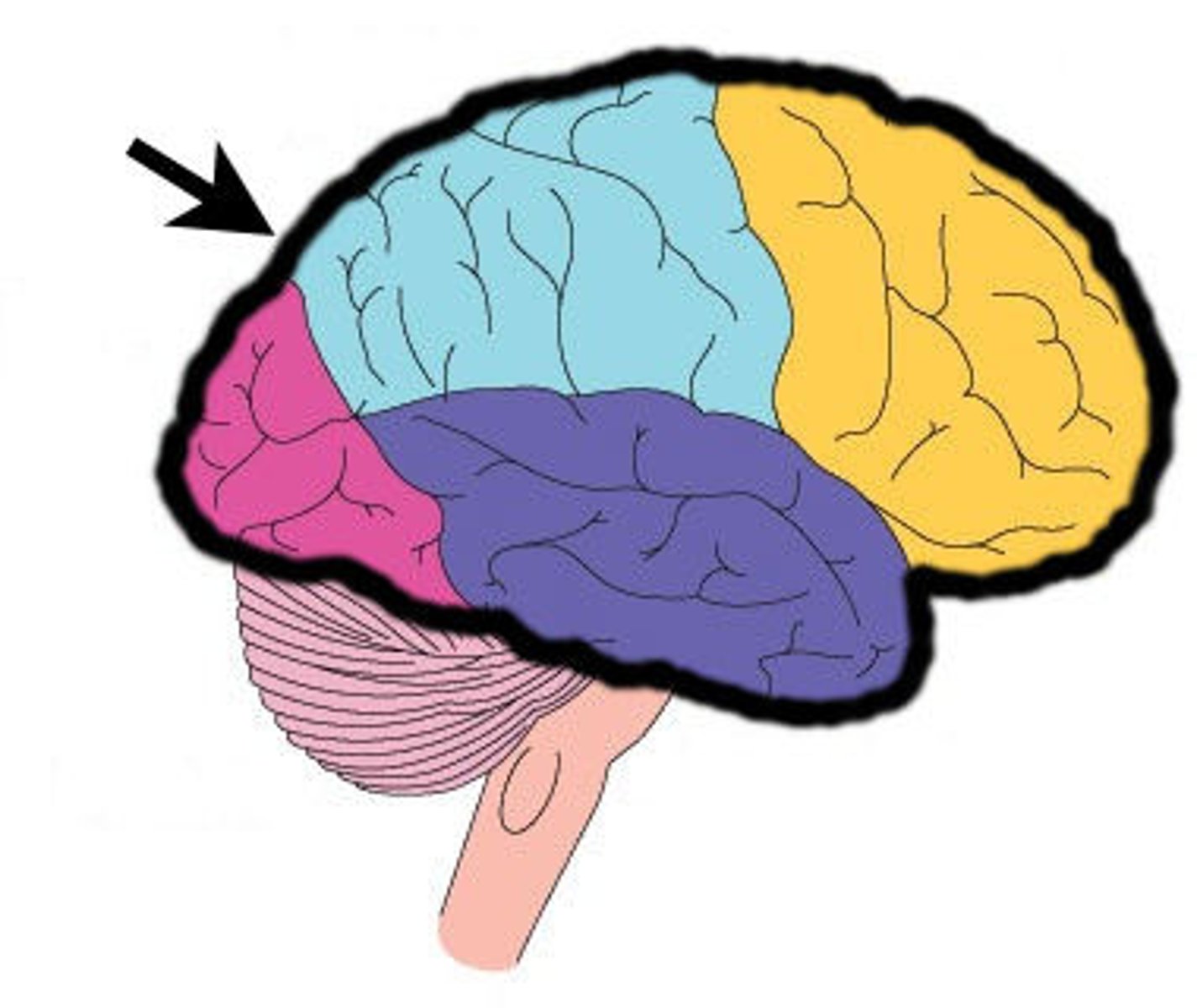
General Anatomy of the Cerebrum
-frontal lobe.
-insula.
-parietal lobe.
-temporal lobe.
-occipital lobe.
Cerebral White Matter
has 3 kinds of tracts:
-projection tracts: extend vertically; carries information between the brain and body.
-commissural tracts: cross between hemispheres.
-association tracts: connect different regions of the same hemisphere (inside one).
Neural Integration
-cerebral cortex.
-basal nuclei.
-limbic system.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
-monitors electrical activity called brain waves.
-4 types: alpha, beta, theta, delta.
Alpha waves
awake and resting with eyes closed and mind wandering.
Beta waves
eyes open and performing mental tasks.
Theta waves
sleepy children or drowsy light sleeping adults.
Delta waves
deep sleep in adults.
Sleep
-temporary state of unconsciousness.
-restorative effect: brain glycogen and ATP levels increase in non-REM.
-memories strengthened in REM.
Stage 1 of sleep
Feel drowsy, close eyes, begin to relax.
-Alpha waves
Stage 2 of sleep
Pass into light sleep.
-Theta waves.
Stage 3 of sleep
Moderate to deep sleep.
-theta and delta waves appear.
Stage 4 of sleep
called slow-wave sleep (SWS): high-amplitude delta waves.
Information Management
-Learning.
-Memory.
-Forgetting.
Declarative memory
inability to describe past events.
Amnesia
defects in declarative memory
Anterograde amnesia
unable to store new information
Retrograde amnesia
person cannot recall things known before the injury.
Cerebral Lateralization
difference in the function of the cerebral hemispheres.
Left Hemisphere
usually the categorical hemisphere.
-math and sciences.
Right hemisphere
usually the representational hemisphere.
-musical and artistic skill.
Epilepsy
sudden, massive discharge of neurons.
Migraine headaches
recurring headaches often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and aversion of light.
Schizophrenia
disorder involving delusions, hallucinations, inappropriate emotional response to situations, incoherent speech and withdrawal from society.
Bell palsy
paralysis of the facial muscles on one side resulting in distortion of facial features.