Ecology (Science Olympiad)
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
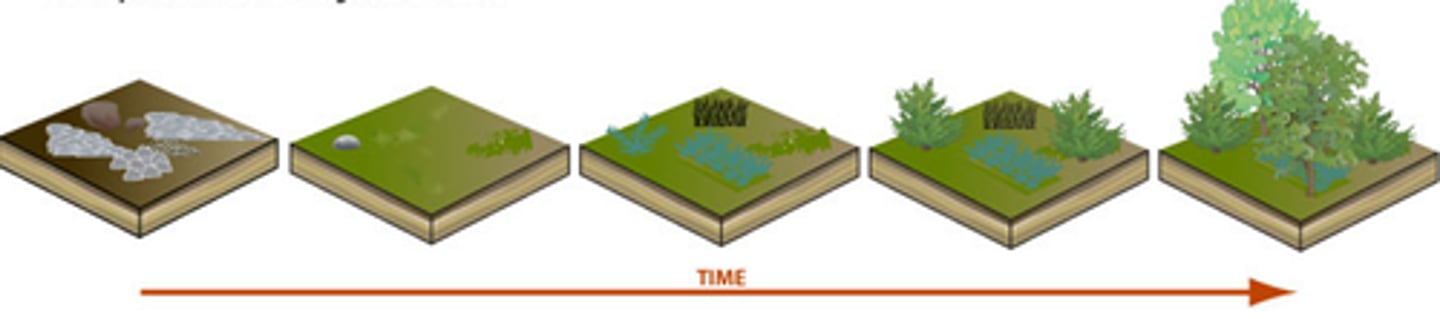
Succession
The replacement of one community by another, developing toward a climax
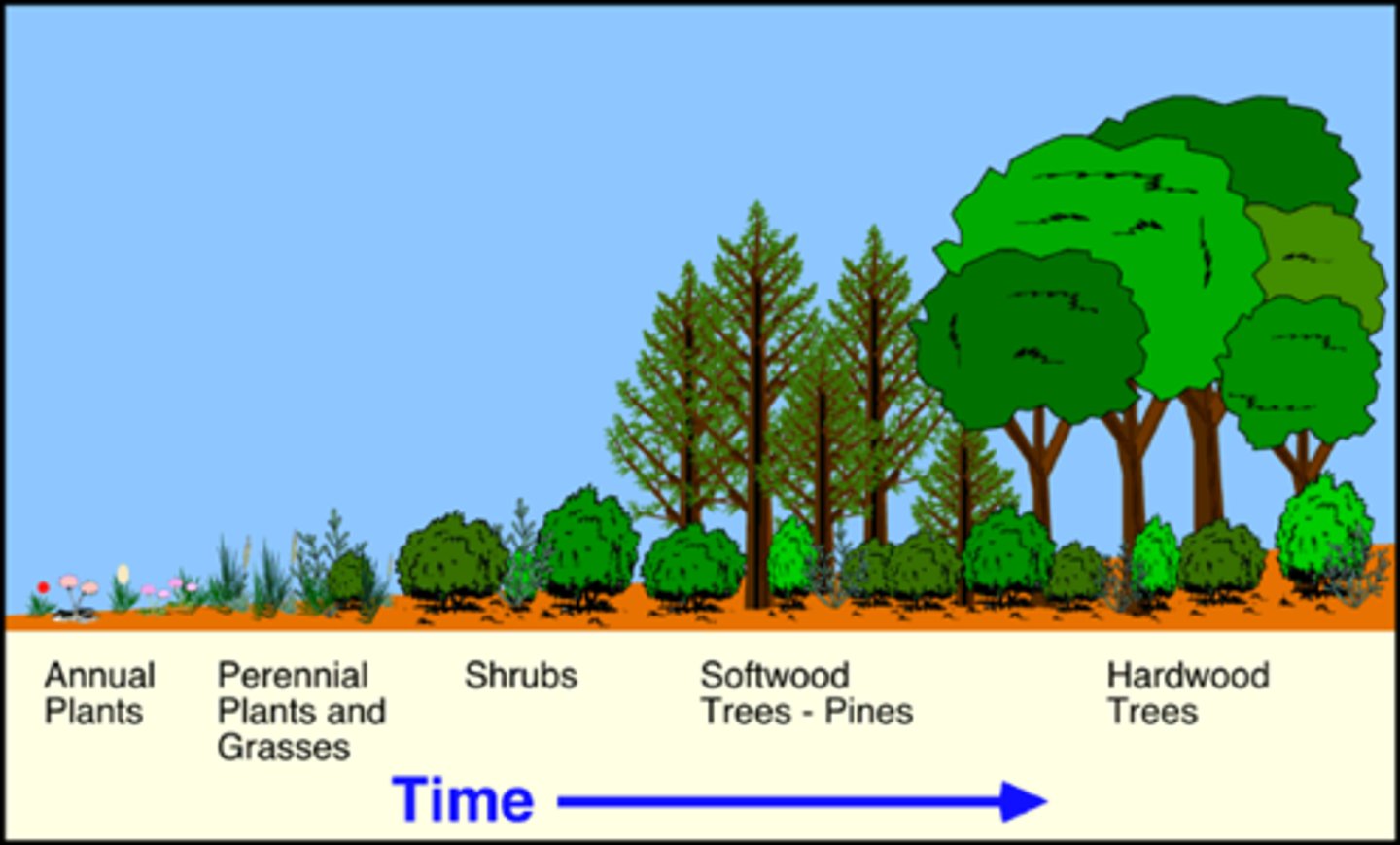
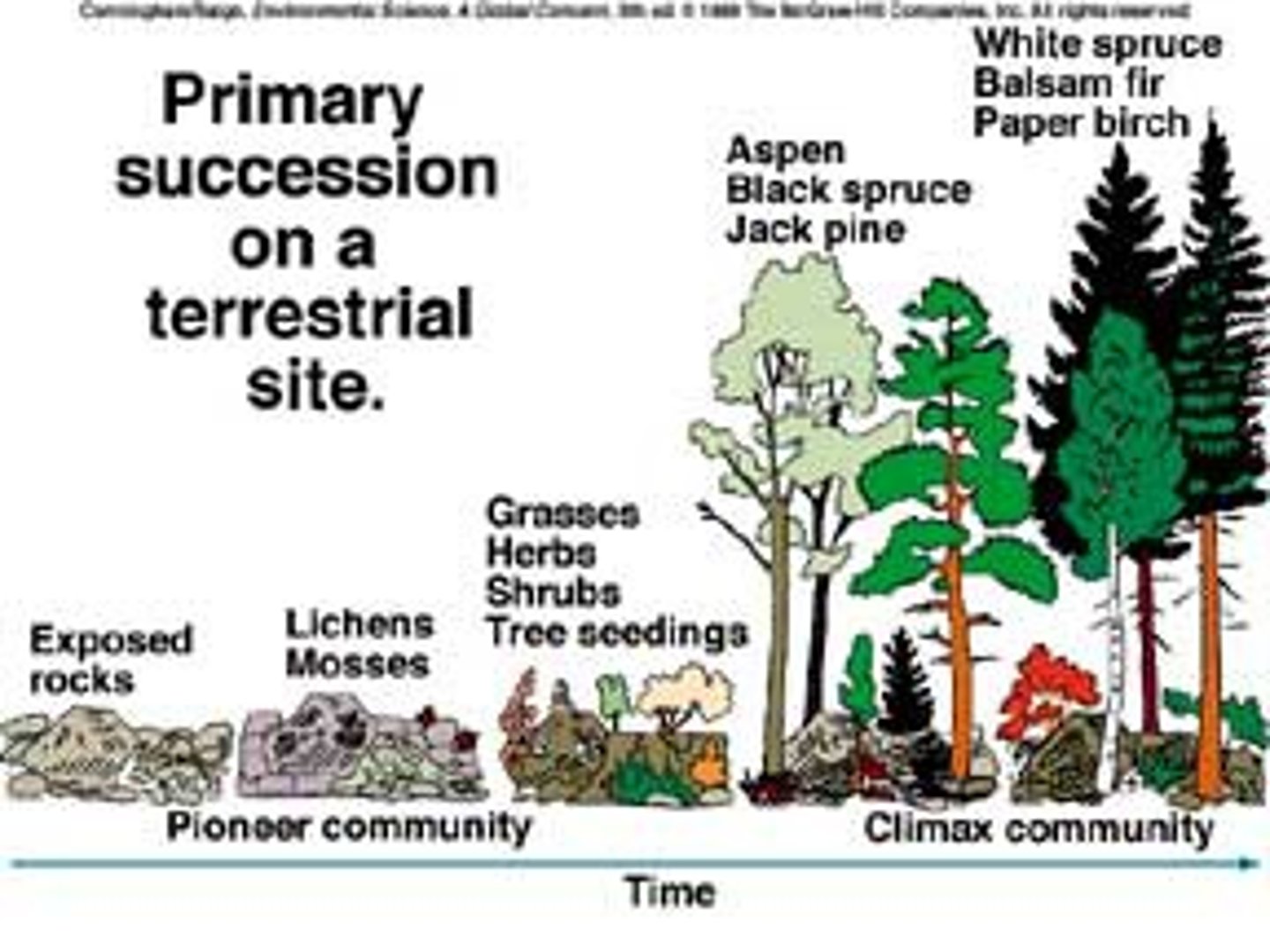
Primary Succession
Succession starting with no soil
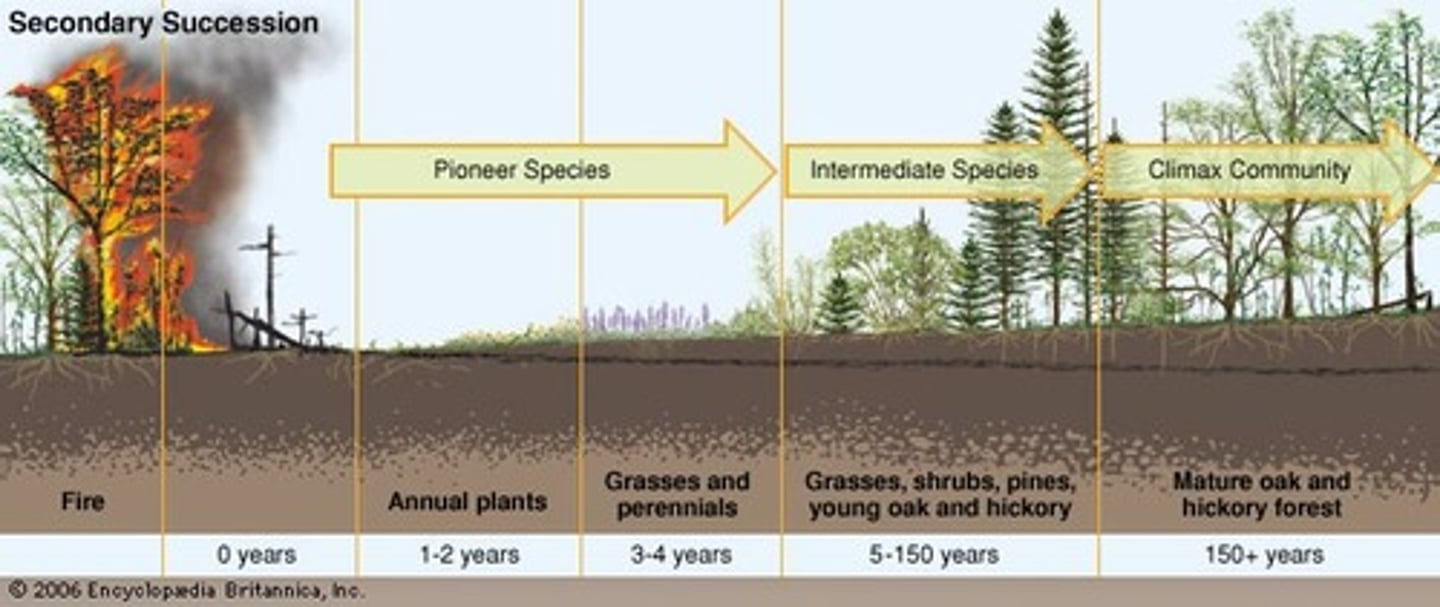
Secondary Succession
Succession starting with soil but no vegetation
Extinction
When a species has no more living members
Natural Selection
The differential survival and reproduction of organisms with genetic characteristics that enable them to better utilize environmental resources
Stabilizing Selection
A type of natural selection in which genetic diversity decreases as the population stabilizes on a particular trait
Disruptive Selection
Disruptive selection is a type of natural selection that simultaneously favors individuals at both extremes of the distribution.
Directional Selection
In population genetics, directional selection occurs when natural selection favors a single allele and therefore allele frequency continuously shift in one direction.
Artificial Selection
The process in which breeders choose the traits they want
Limiting Factors
A factor that limits a population's growth; i.e. resources, shelter, food and disease
Biodiversity
The number and variety of organisms within one region (biome)
Type 1 graphs
Type I organisms have lower mortality rate at low ages which gradually increases with age. (ex. Humans, most large mammals)
Type 2 graphs
Type II organisms have mortality rates that stay the same throughout life. (ex. birds, some lizards)
Type 3 graphs
Type III organisms have the largest mortality rates at birth. (fish, oysters, frogs)
Exponential Growth
Occurs when the growth rate remains the same while the population grows. It creates a J shaped curve.
Logistic Growth
Occurs when the growth rate decreases as the population grows due to density-dependent factors (factors increasing mortality rate as population grows such as predation rates, competition, and disease). This creates an S-shaped curve. It is the most common type of population growth.
Greenhouse Effect
When heat is stuck in the atmosphere due to greenhouse gases and Earth is warmed
Invasive Species
A species that has moved into an area and reproduced so aggressively that it has replaced some of the original species.
Acid Rain
rainfall made sufficiently acidic by atmospheric pollution
Wet deposition
acidic rain, fog, and snow
Dry deposition
acidic gases and particles
causes of Acid Rain
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Environment
the surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal, or plant lives
Biotic Factors
Living components of an ecosystem.
Population
Group of individuals of the same species occupying a common geographical area
Community
Two or more populations of different species occupying the same geographical area.
Population Ecology
The study if how populations interact with their eniornment
Population Size
Number of the individuals making up its gene pool
Population Density
Number of individuals per unit of area or volume
population growth formula
G is growth, r is rate of increase, N is number of individuals. Used to represent population growth mathematically.
K- selected organism:
put most of their energy into growth
Detritivores
decomposers which eat detritus
Logistic growth
a population that at will first rapidly grow but as they near the carrying capacity they will level off
interaction types
Neutral, Commensalism, Mutualism, Parasitism, Predation
Gross Product: Gross primary productivity =
the rate at which the primary producers capture and store energy per unit time. since the primary producers expend energy during respiration the net primary productivity is considerably lower than the gross productivity
Age Structure
pre-reproductive, reproductive, and post-reproductive
Density dependent factors
the growth that is affected by the density of individuals
Density-independent factors
the growth that is not affected by the density of individuals
Potential niche
no competitors and unlimited resources
Niche
the biotic and abiotic resources used by an organism
Realized niche
fundamental niche that a species actually occupies in nature
Climax community
a stable, self-perpetuating array of species in equilibrium with one another and their habitat
Pioneer community
a community that contains the first organisms to occupy an area
Transitional communities
a community that comes and goes
Biotic potential
the maximum growth rate of a population given unlimited resources and space and lack of competition and predators
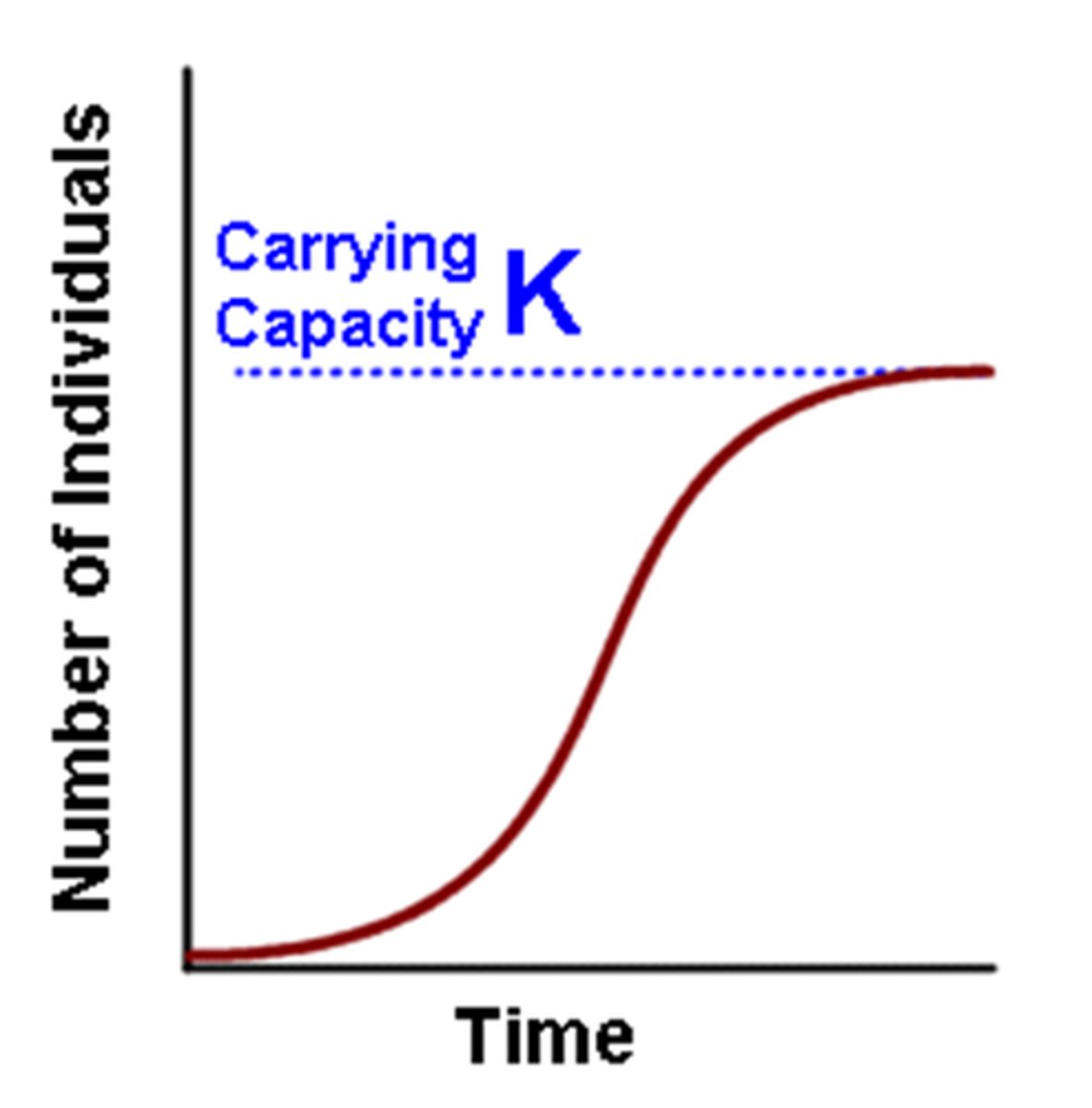
Carrying capacity
maximum number of individuals of a species or population a given environment can sustain.
Habitat
the physical place where an organism lives, e.g. a pine forest or fresh water lake
Gause's law
all who use same resource can't coexist
Resource partitioning
the resources are divided, and species w/ same need are living together
Climate is dependent upon several factors, name them
Solar radiation
The earth's daily rotation
The earth's rotation around the sun
The distributions of continents and oceans
Ecology
How organisms interact with one another and with their environment. The environment consists of living and nonliving components.
What is a growth curve?
A growth curve is the pattern that a population's numbers follow
Zero population growth
Designates a near balance of births and deaths
Exponential growth
If birth and death rates of a population remain constant they can be combined into one variable, r=net reproduction per individual per unit time(rate of increase)
10%
The amount of energy transferred from one trophic level to another.

Abiotic factors
Non-living parts of an environment (ex. sun, temperature)
Autotroph/Producer
An organism that makes its own food through photosynthesis.

Biome
The largest division of the biosphere which includes large regions with similar biotic components and similar abiotic components.
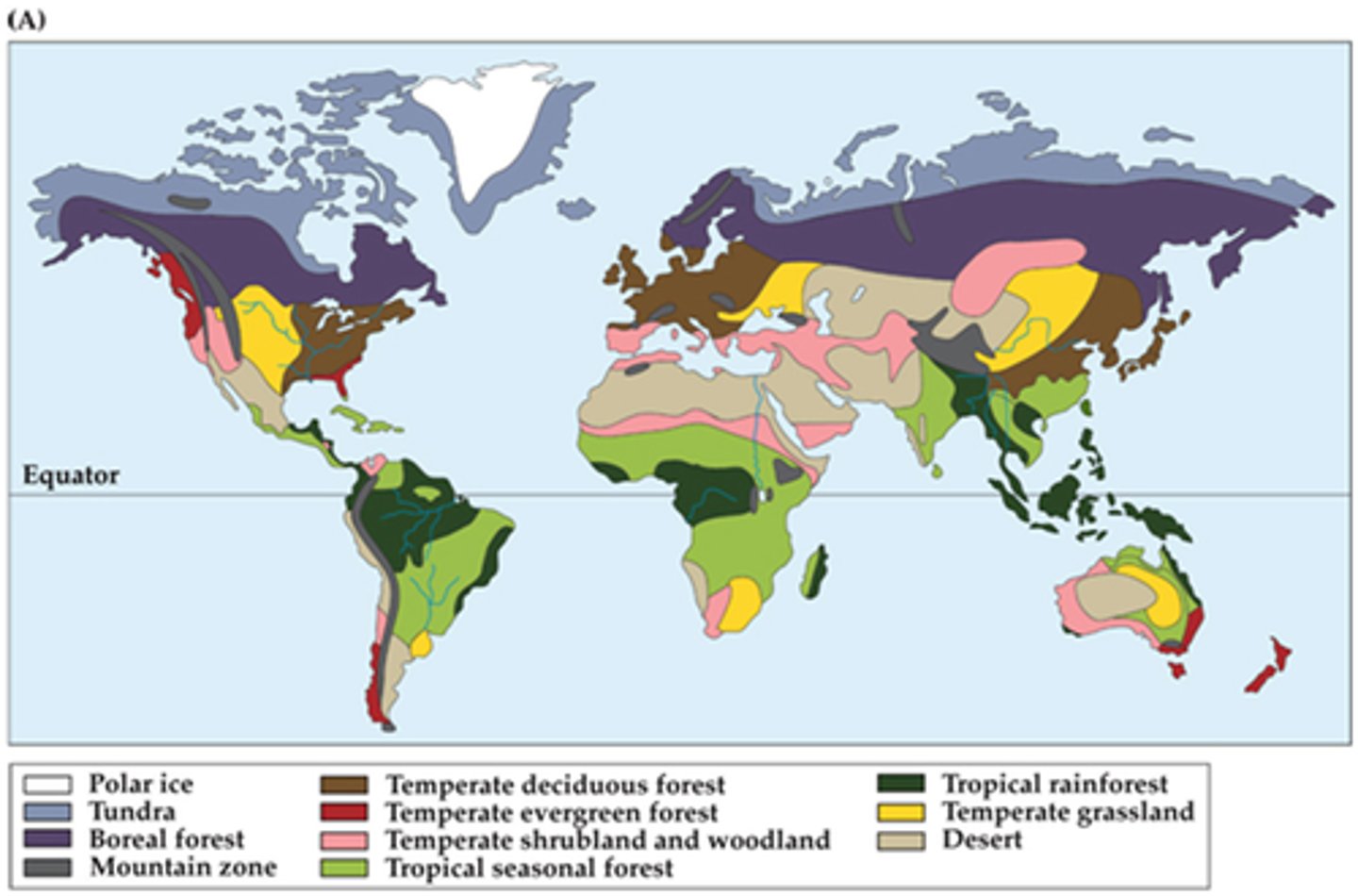
Biosphere
The thin layer of air, land, and water on or near Earth's surface in which all living things on Earth exist. Atmosphere, Lithosphere, and Hydrosphere.
Biotic factors
Living parts of an environment (ex. fungi, animals)

Carnivore
An organism that obtains energy by eating only animals.

Carrying Capacity
Size of a population during the steady state region of a logistic growth curve. It represents the optimum number of organisms of a particular species that can be supported by a particular environment.
Cellular Respiration
Process that occurs at all trophic levels in which glucose and oxygen are broken down to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Commensalism
Type of symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is unaffected (ex. remora and shark)

Competitive Exclusion Principle
Two species cannot coexist if they are in the same niche.
Consumer/Heterotroph
An organism that acquires energy by feeding on other organisms.

Decomposer
An organism that feeds on and breaks down the remains of dead organisms and recycles those nutrients back into the environment; also known as detrivores.

Density-dependent limiting factors
Limiting factors that operate more strongly on large populations than on small ones (ex. competition, predation, parasitism, crowding, stress).

Density-independent limiting factors
Limiting factors that control population regardless of
how large the population is at the time (ex. natural disasters).

Ecological Niche
An organism's role in an ecosystem - includes things like diet, reproductive method, role in a food web, etc.

Ecological Succession
Process in which an existing community is gradually replaced by another community.
Ecology
The study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their environments.

Ecosystem
A part of a biome in which biotic and abiotic components interact.

Emigration
Leaving an environment.
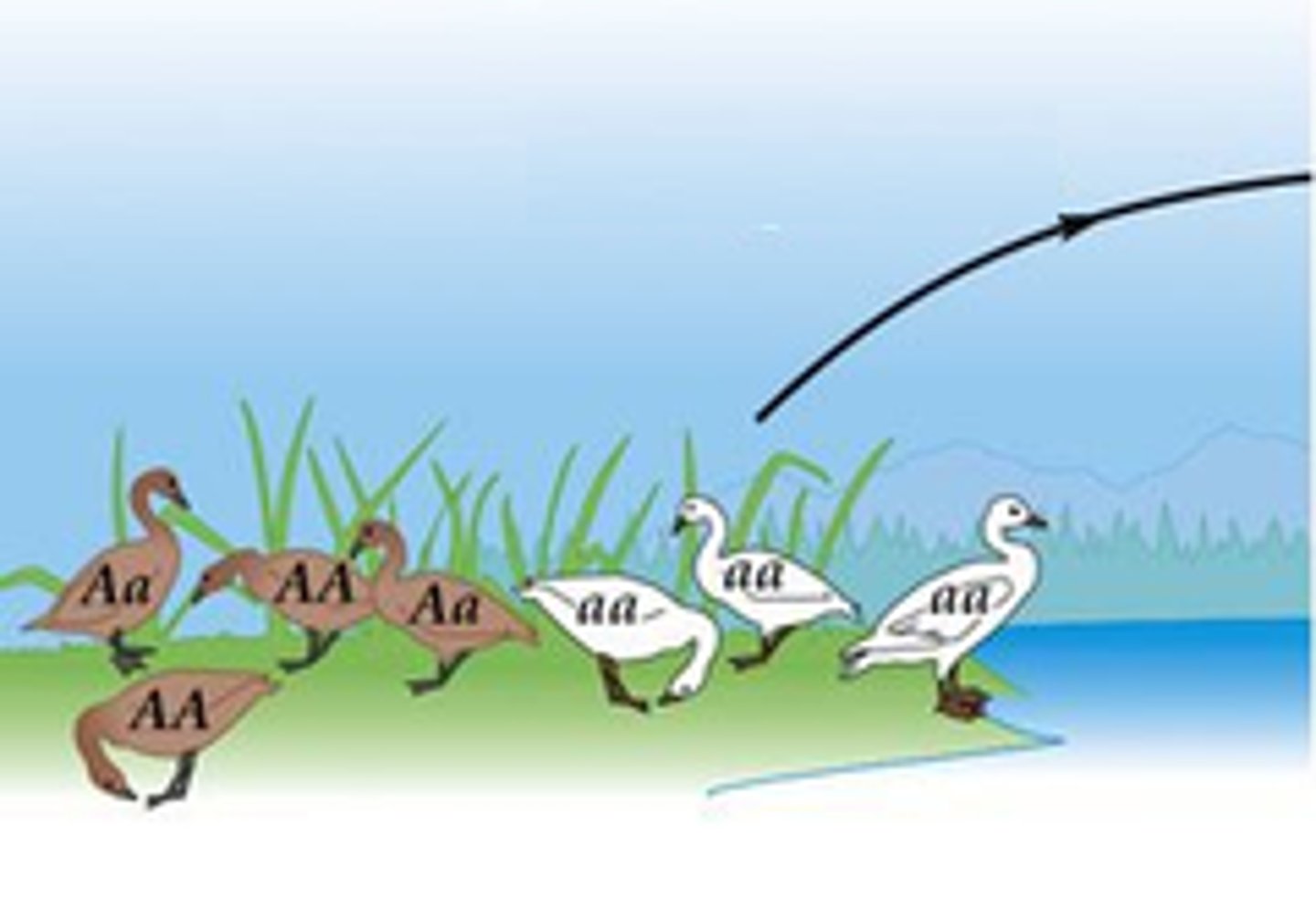
Generalists
Species with broad niches (ex. common crow). Environments with lots of this type have low diversity.

Herbivore
An organism that obtains energy by eating only plants.

Immigration
Entering an environment.
Logistic Growth
Growth typically experienced by populations. Five stages: 1) slow initial growth; 2) rapid exponential growth; 3) population growth begins to slow; 4) population slows even more still; 5) Population reaches steady state in which growth rate is zero.
Mortality
Death Rate
Mutualism
Type of symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit (ex. bacteria in our digestive tract, flowers and pollinators)

Natality
Birth rate.
Omnivore
An organism that obtains energy by eating both plants and animals.

Parasitism
Type of symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is harmed (ex. parasite and host, cuckoo and warbler)

Primary Consumer
An organism that feeds on producers.

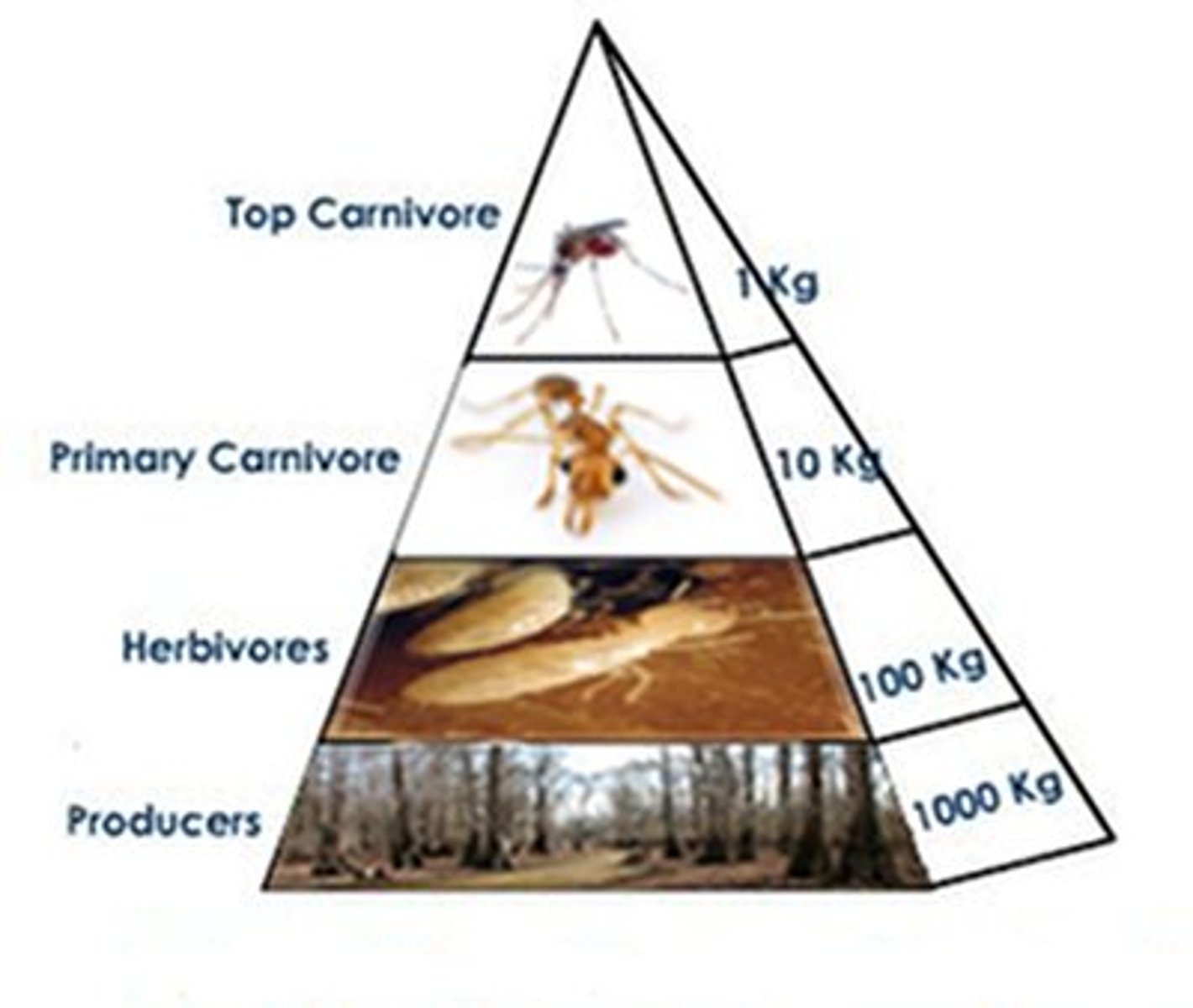
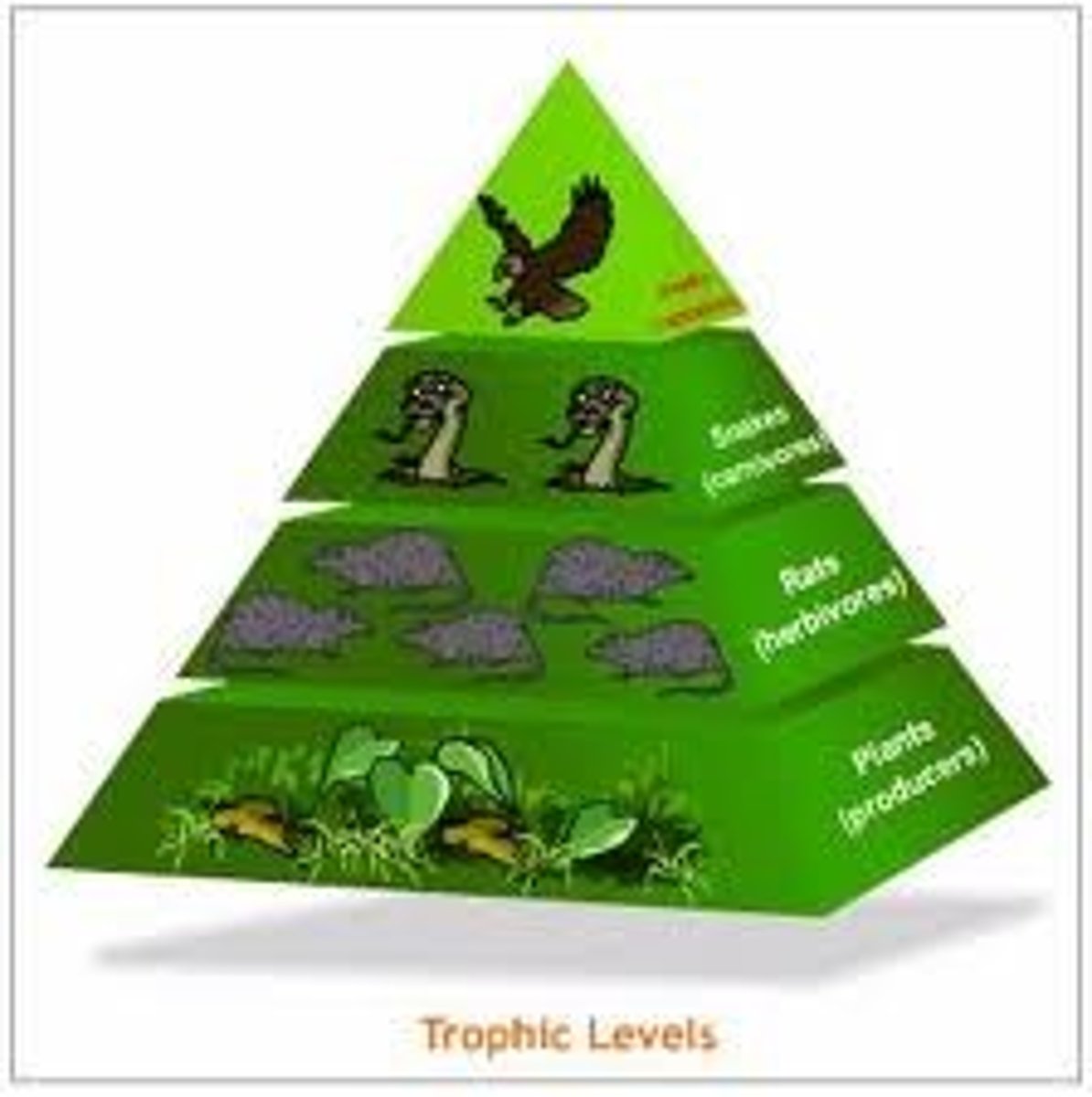
Pyramid of Biomass
A pyramid that illustrates the total mass of all the organisms in a trophic level.
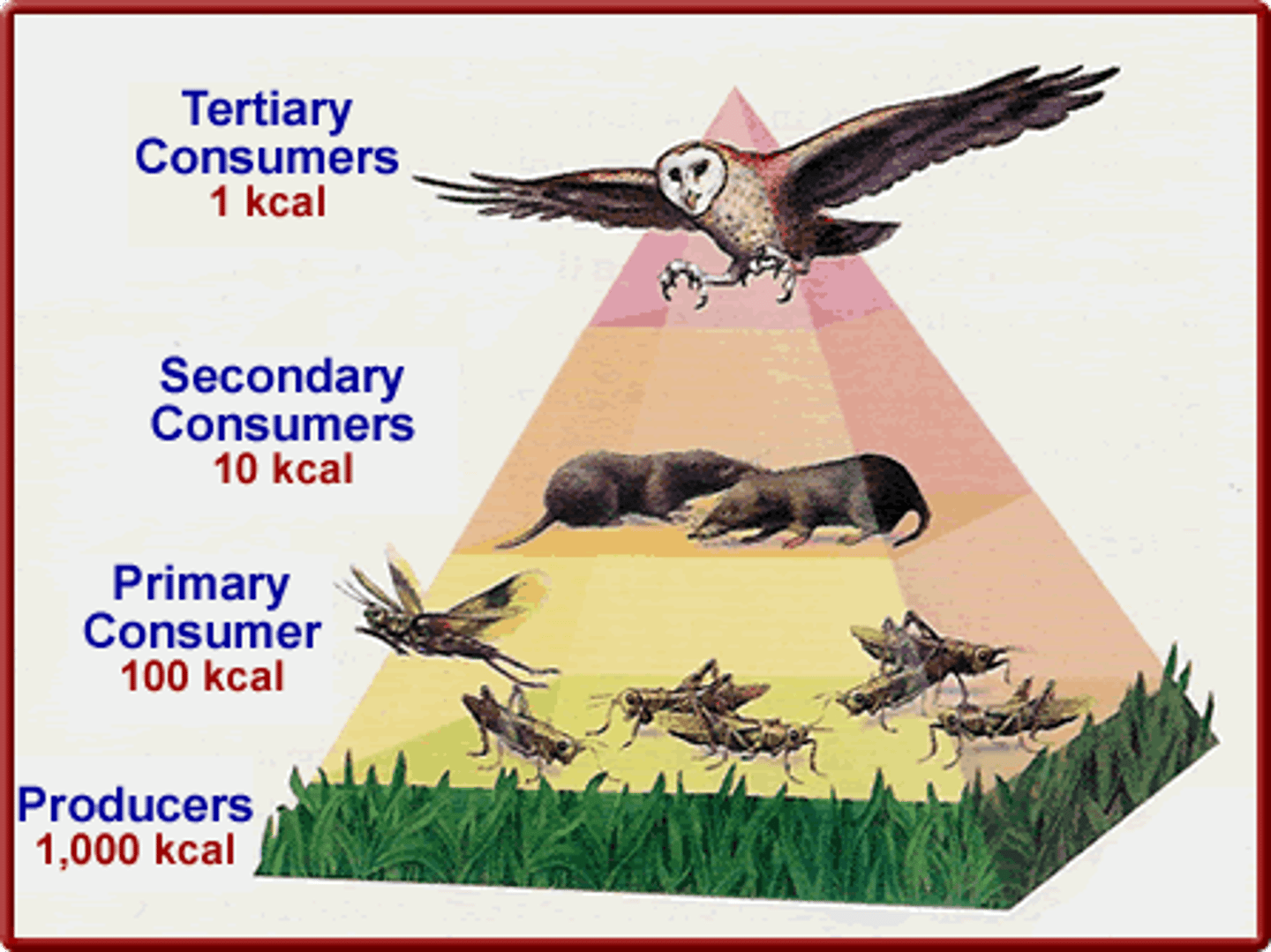
Pyramid of Energy
A pyramid that shows the total amount of energy available at each trophic level.
Secondary Consumer
An organism that eats primary consumers.

Specialists
Species with narrow niches (ex. anteater). Environments with lots of this type have high diversity.

Species
A group of closely related organisms that can reproduce with one another.

Steady State
Final stage in logistic growth in which birth rate = death rate.
Symbiosis
Relationship between two different species in which at least one species benefits.

Tertiary Consumer
An organism that eats secondary consumers.

Trophic level
A step in a food chain.
endothermal
organisms that maintain their own body heat internals usually through metabolism
ectothermal
organisms that rely on outside factors to maintain their body heat
homothermal
maintain a constant body temperature
Poikilotherm
body temperature fluctuates based on outside conditions
heterothems
characteristics of both homotherms and poikilotherms, they can switch between the two, usually occurs with animals that hibernate
cohort life table
recording the death of a group of individuals born at relatively the same time
static life table
recording the age of death of a group of individuals assuming they have they experienced the same events