1&2: Wave Speed and Characteristics in SPH 3U1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Universal Wave Equation
The equation that relates wave speed, wavelength, and period, expressed as v = λ/T.
Period of a wave
The duration between successive crests measured by timing from a reference point.
Wavelength
The distance between successive crests of a wave.
Linear Density
The mass per unit distance of a string, calculated as µ = m/L.
Tension
The force exerted along a string, which affects how effectively the string transmits wave energy.
Factors Affecting Wave Speed
Elements such as intermolecular forces, temperature, linear density, and tension that influence the speed of a wave.
Wave Speed Formula
The formula v = √(FT/µ) used to calculate the speed of a wave on a string.
Vibration
The cyclical motion of an object about an equilibrium point (rest position), e.g. the pendulum in a clock.
Mechanical Wave
The transfer of energy through a material due to vibration.
Medium
The material through which a mechanical wave travels.
Net Motion
The displacement of a particle over a certain time interval; the difference between the particle's initial and final positions.
Transverse Wave
A wave in which the particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the flow of energy.
Longitudinal Wave
A wave in which particles vibrate parallel to the direction of the flow of energy.
Compressions
Region in a longitudinal wave in which the medium's particles are closer together.
Rarefactions
Region in a longitudinal wave in which the medium's particles are farther apart.
Sound
A form of energy produced by rapidly vibrating objects detectable to the human ear.
Amplitude
The maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium point.
Crest
The maximum point of a transverse wave.
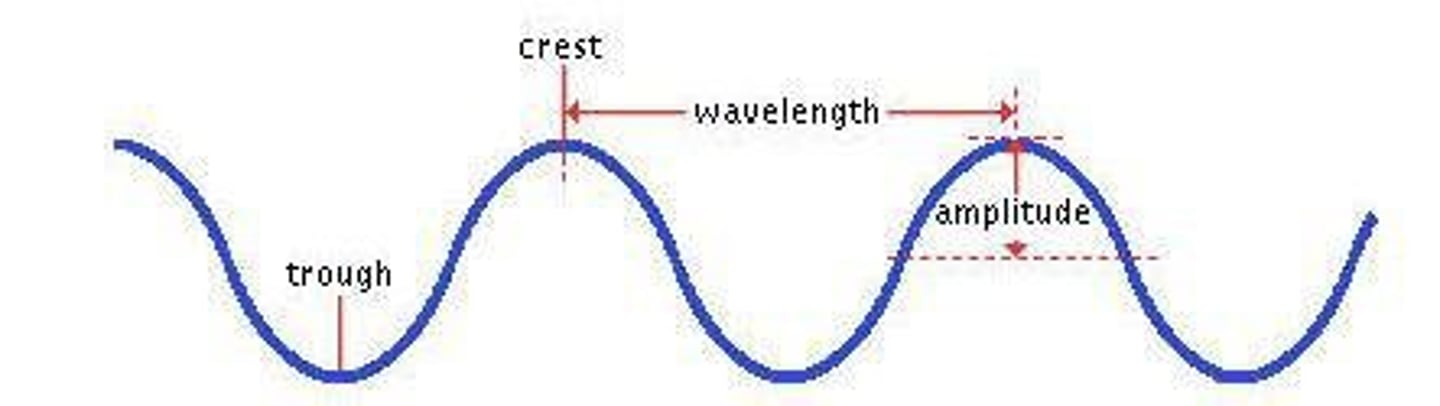
Trough
The minimum point on a transverse wave.
Wavelength (λ)
The distance between two similar points in successive identical cycles in a wave, such as from crest to crest or trough to trough.
Phase
In a continuous transverse or longitudinal wave, the x-coordinate of a unique point of the wave.
Phase Shift
A shift of an entire wave along the x-axis with respect to an otherwise identical wave.
In Phase
The state of two identical waves that have the same phase shift.
Out of Phase
The state of two identical waves that have different phase shifts.
Frequency (f)
The number of complete cycles that occur in a unit of time, usually 1 s; measured in hertz (Hz); 1 Hz = 1/s.
Period (T)
The time for a vibrating particle to complete one cycle.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
Motion that repeats itself at regular intervals.