Sectional Anatomy Ch. 7: Pelvis
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
the pelvic girdle consists of
sacrum, ilium, ischium, and pubis
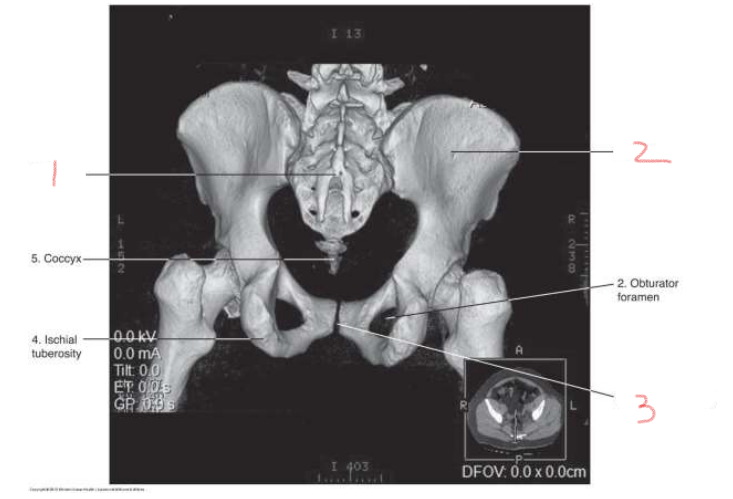
1
sacrum
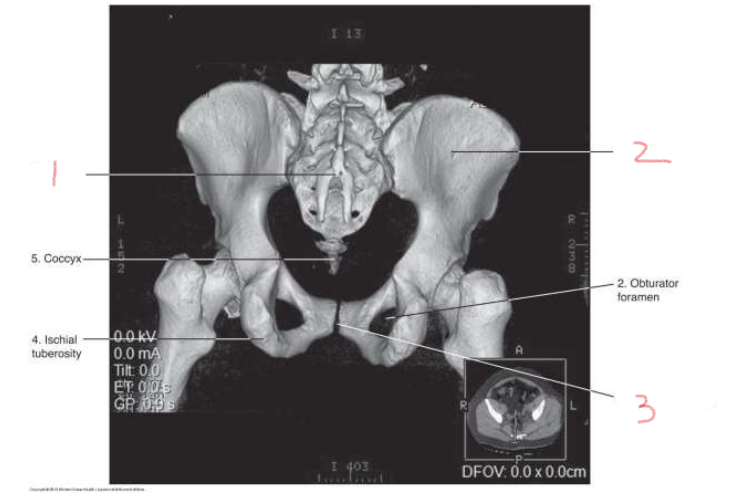
2
ilium
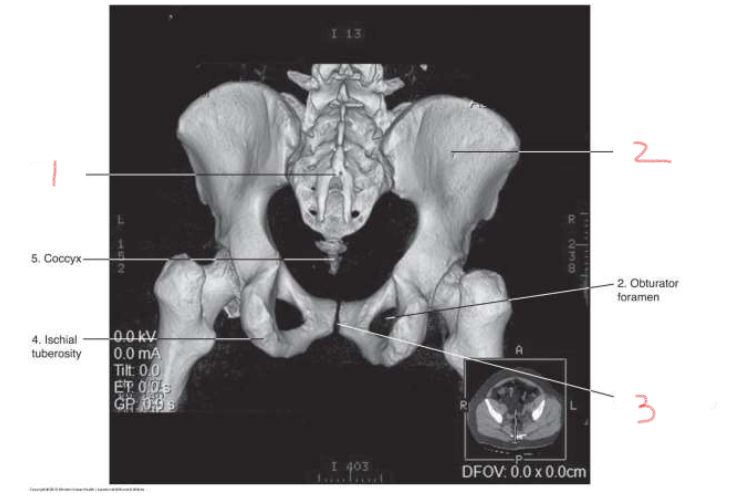
3
pubic symphysis
what forms the posterior portion of the pelvic girdle?
sacrum
what forms the lateral and anterior portions of the pelvic girdle?
ilium, sacrum, and ischium
most superior bone of the pelvic girdle
ilium
top of the ilium
iliac crest
where are the anterior superior spine and anterior inferior spine located?
directly superior to the pubic tubercle
what is the pubic symphysis
the cartilaginous joint between the two pubis bones
what notches does the ischium have?
greater and lesser sciatic notch
what is between the greater and lesser sciatic notch
ischial spine
what is the bony region you’re sitting on?
ischial ramus
where does the femoral head sit?
acetabulum
what forms at the junction of 3 hip bones?
acetabulum
what forms between the pubis and ischium
obturator foramen
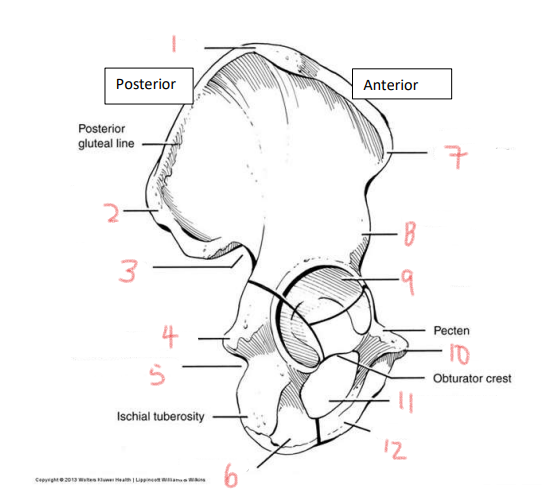
1
iliac crest
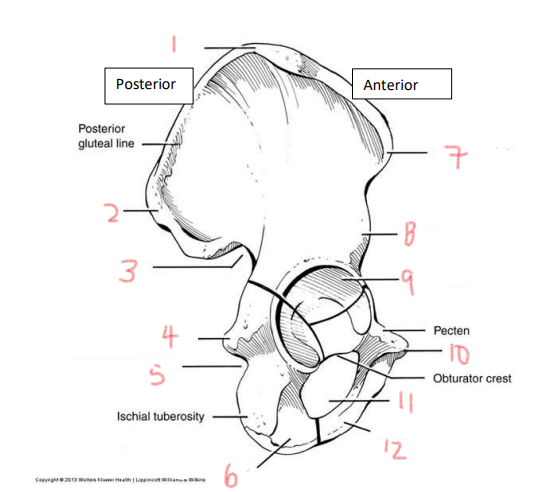
2
superior posterior spine
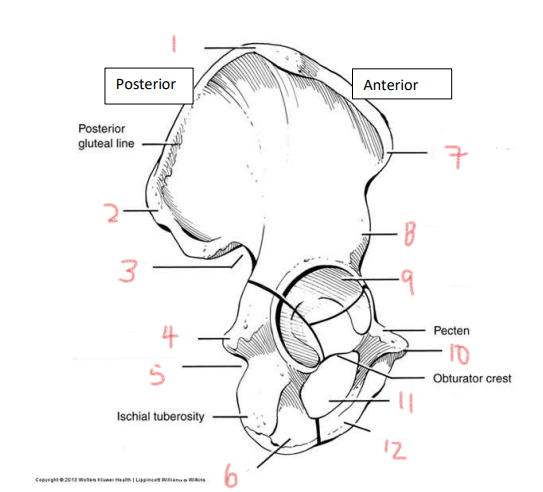
3
greater sciatic notch
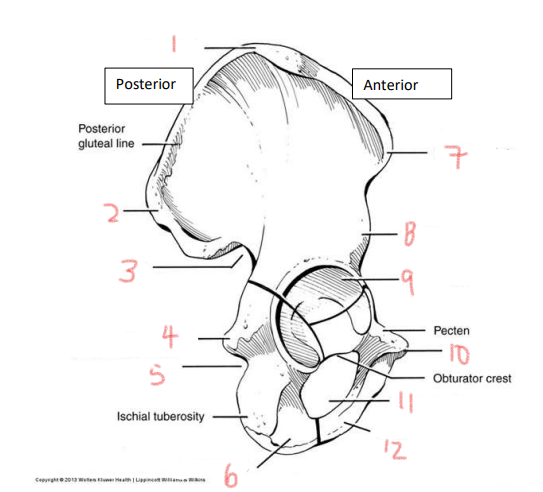
4
ischial spine
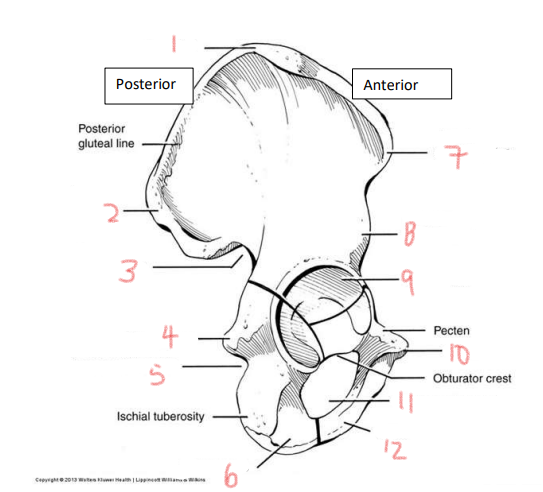
5
lesser sciatic notch
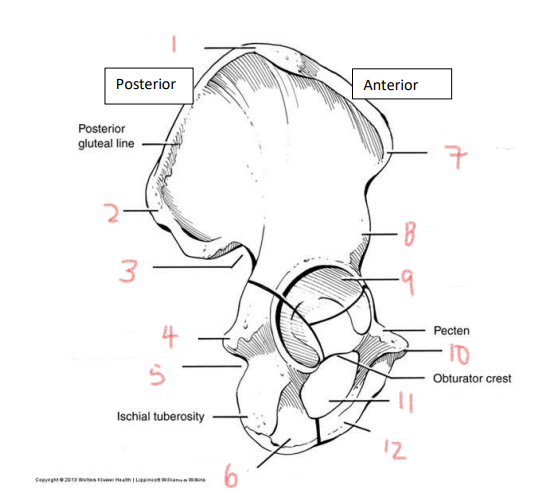
6
ischial ramus
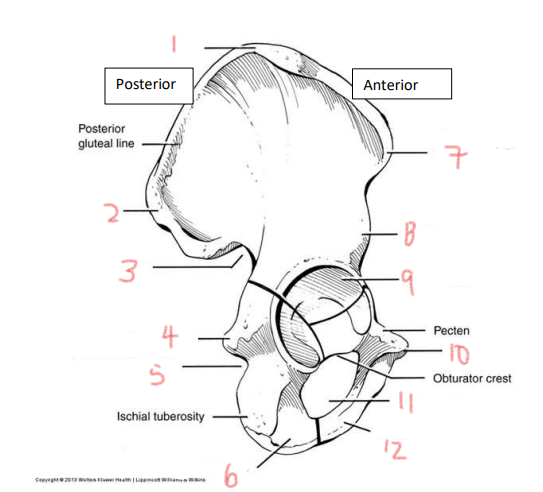
7
anterior superior spine
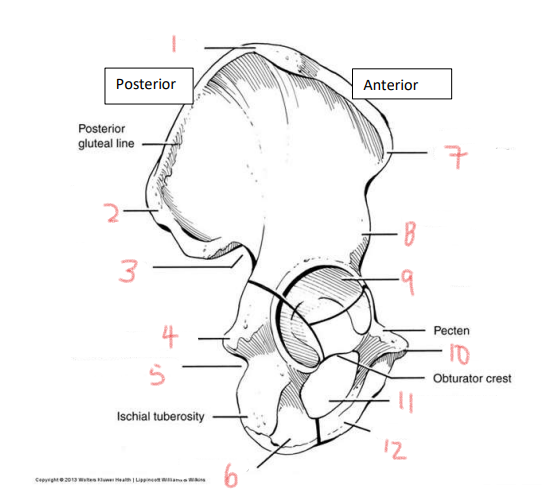
8
anterior inferior spine
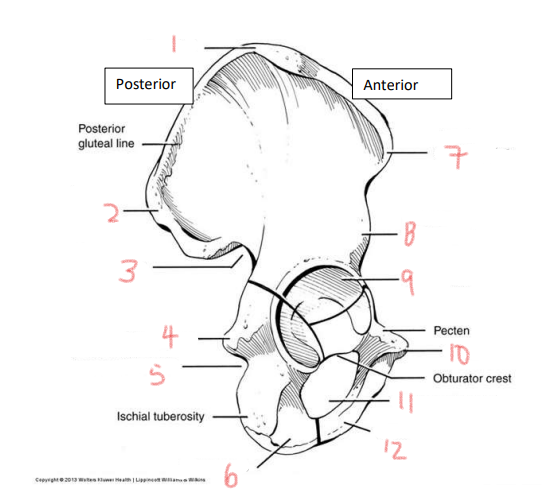
9
acetabulum
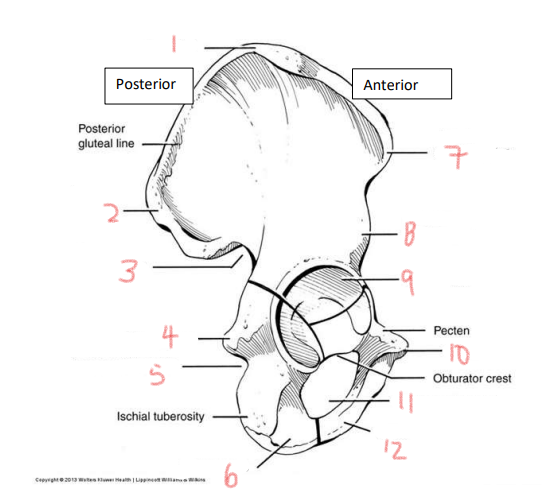
10
pubic tubercle
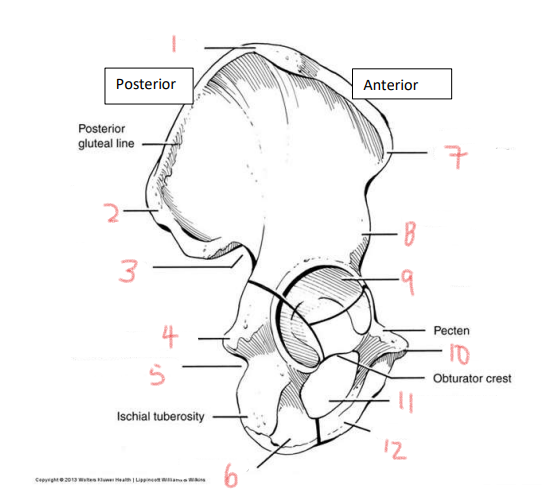
11
obturator foramen
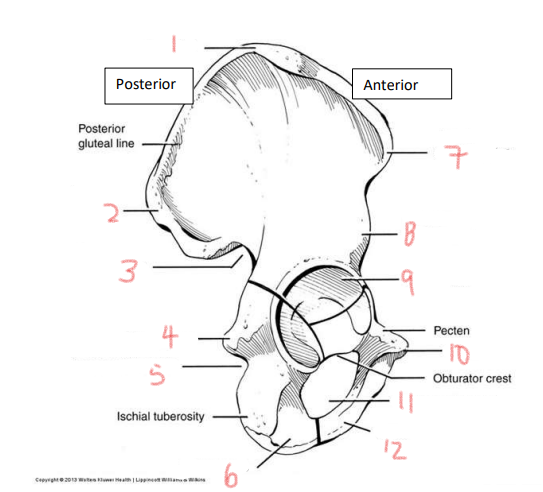
12
pubis
thigh bone
femur
longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in body
femur
what inserts into the acetabulum
head of femur
the joint of the acetabulum and femur is known as a
ball and socket joint
between the two trochanters
intertrochanteric crest
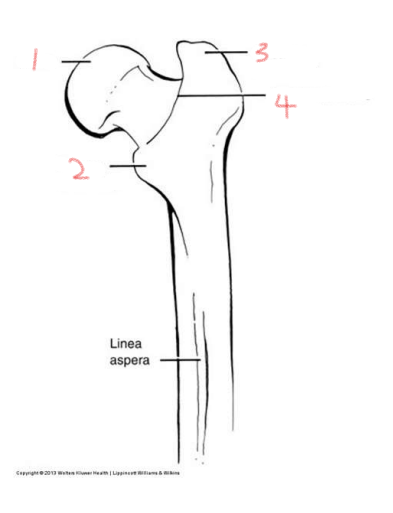
1
head
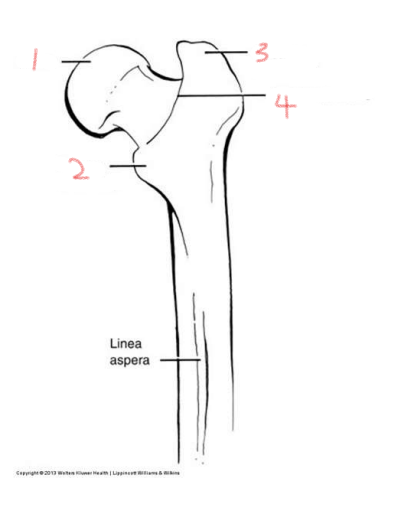
2
lesser trochanter
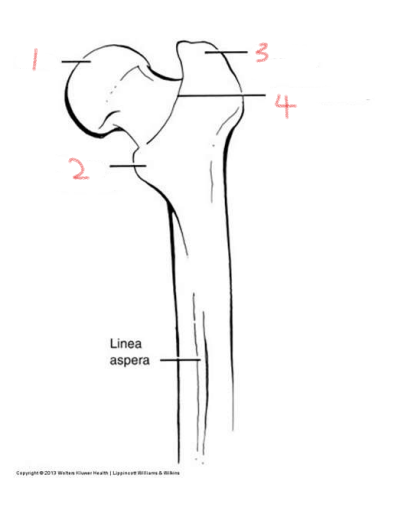
3
greater trochanter
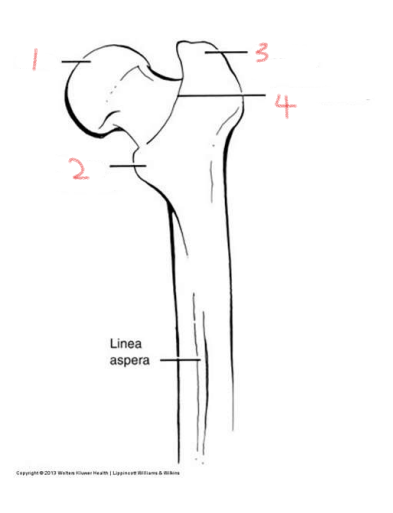
4
intertrochanteric crest
common iliac arteries bifurcate into the —-, at the level —-
internal and external iliac arteries; roughly L4
the external iliac arteries bifurcate into the
femoral arteries
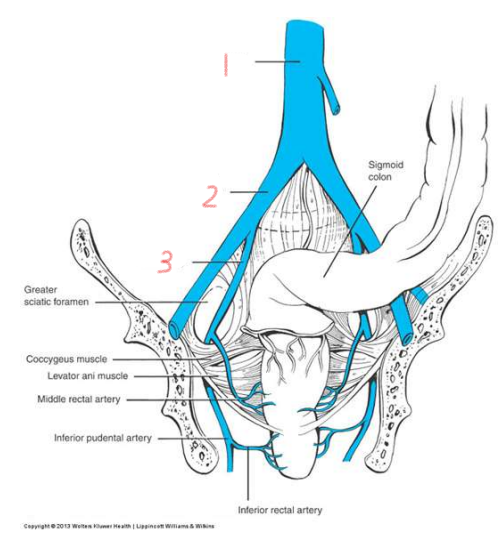
1
aorta
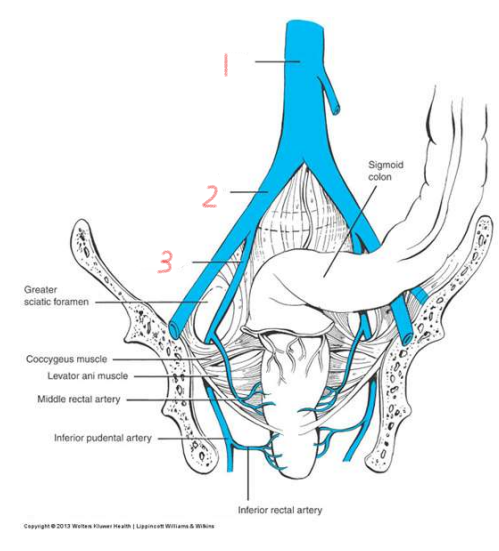
2
common iliac artery
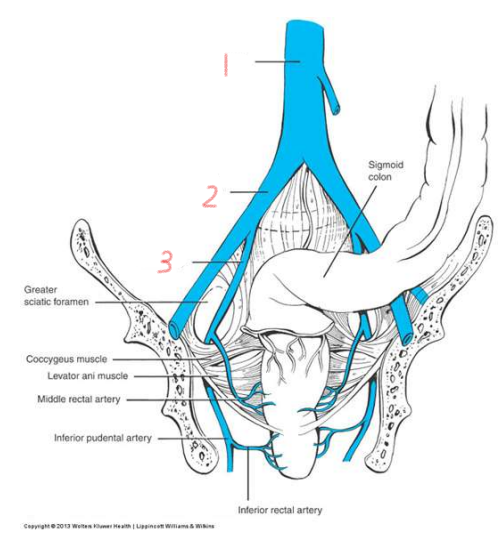
3
internal iliac artery
bladder is posterior to the — in the male urogenital system
pubis
what is posterior to the bladder in the male urogenital system
rectum
immediately inferior to the bladder in the male urogenital system
prostate gland
job of the bladder
collect and hold urine
urethra starts in the —, passes through the —, and extends through the —
bladder, prostate, penis
two structures made of erectile tissue
corpus spongiosum and corpus cavernosum
site of sperm production
testis
sperm maturates as it travels through the —
ductus deferens
what provides nutrients to sperm
seminal vesicles
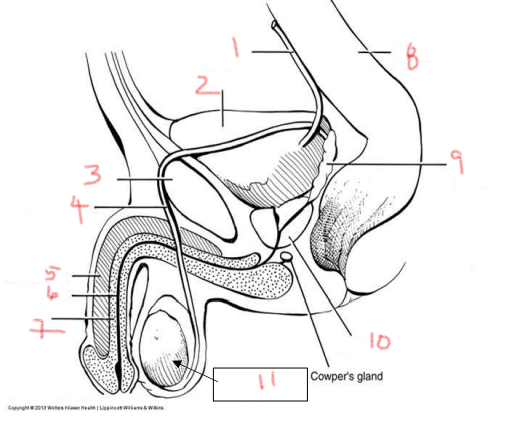
1
ureter
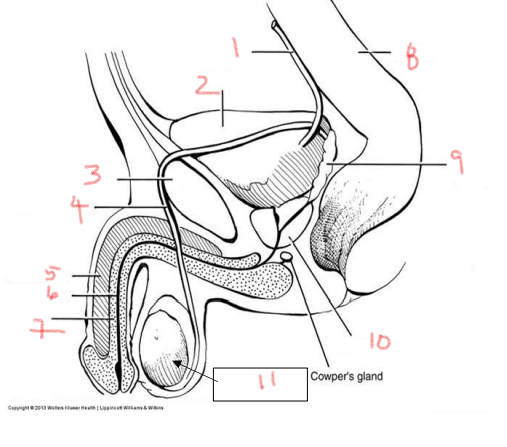
2
bladder
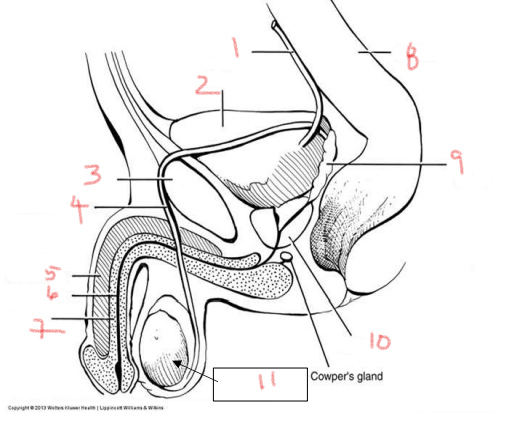
3
pubis
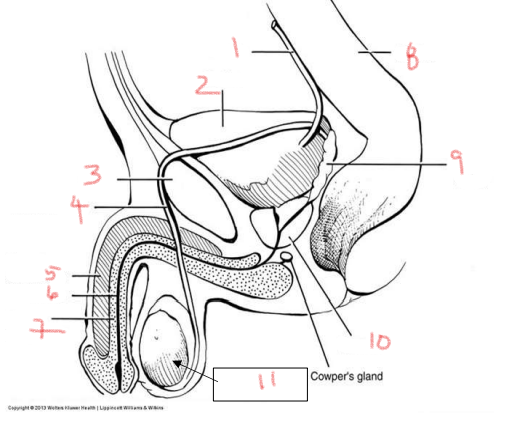
4
ductus deferens
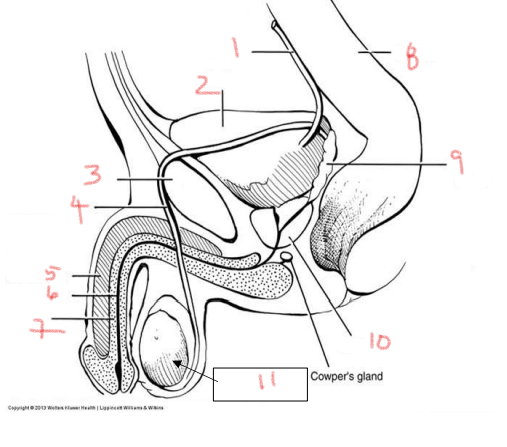
5
corpus cavernosum
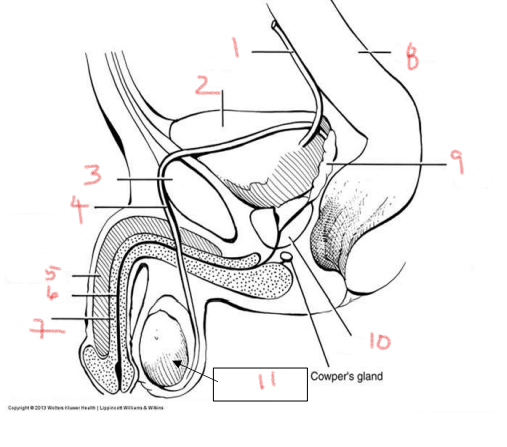
6
urethra
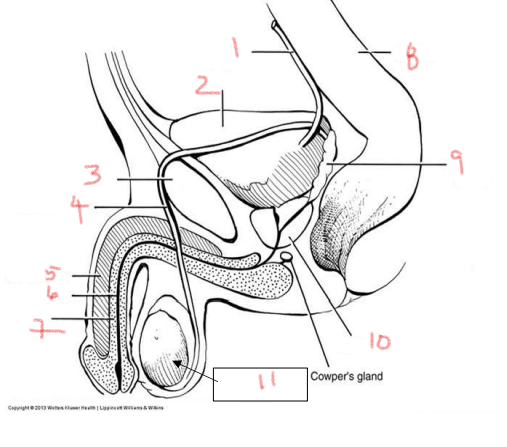
7
corpus spongiosum
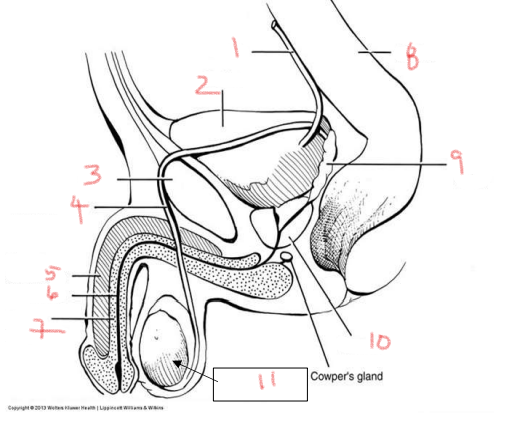
8
rectum
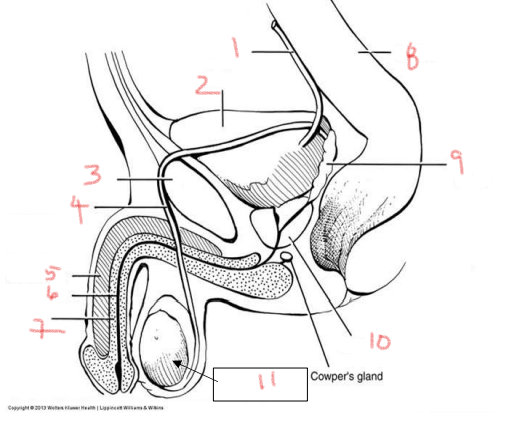
9
seminal vesicle
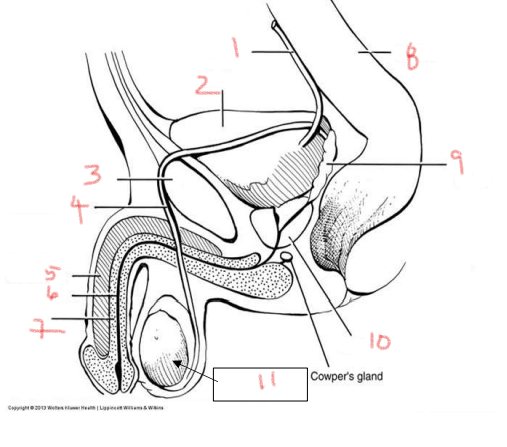
10
prostate
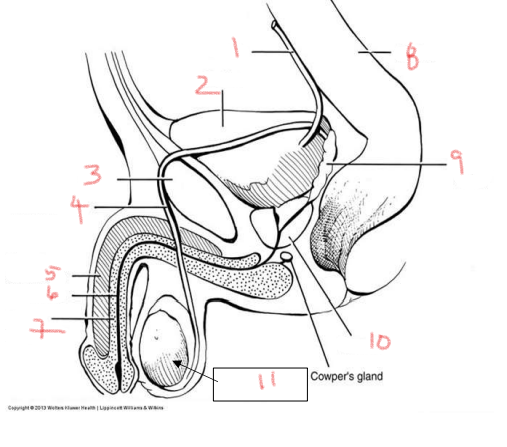
11
testis
urethra is shorter in men or women
women
directly posterior to urethra in the female urogenital system
vaginal cavity
opening into the uterus
cervix
uterus located between:
urinary bladder and rectum
three parts of uterus
cervix
body
fundus
largest part of the uterus
body
dome-shaped region found above uterine tubes
fundus
recess that forms due to the cervix protruding into the vaginal cavity
fornix
what produce ova
ovaries
what do ova travel through to get to the uterine wall
oviducts
adnexal area contains the
ovaries, oviduct, and various ligaments
pouch between the uterus and rectum
rectouterine pouch
how is the rectouterine pouch formed
lining of the peritoneum falling into the space
the peritoneum extends across the upper surface of the uterus, folds and forms the —
broad ligament
another name for broad ligament
mesometrium
job of broad ligament
attach and support all various structures within it to the pelvic walls
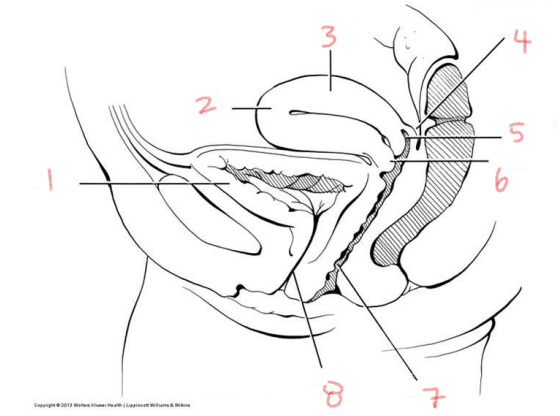
1
bladder
2
fundus of uterus
3
body of uterus
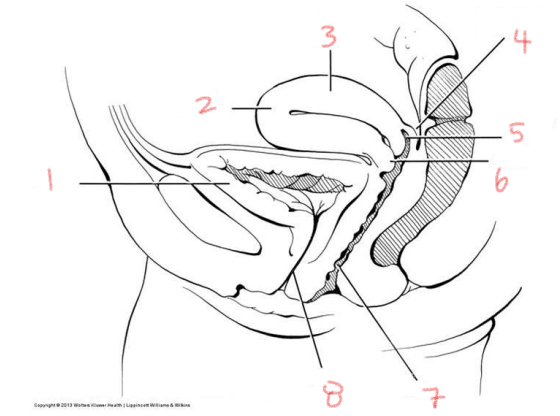
4
rectouterine pouch
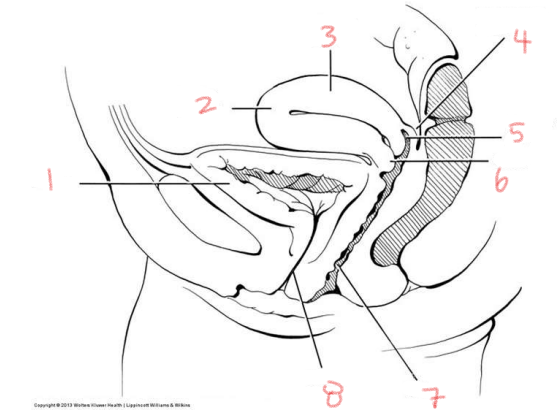
5
posterior fornix
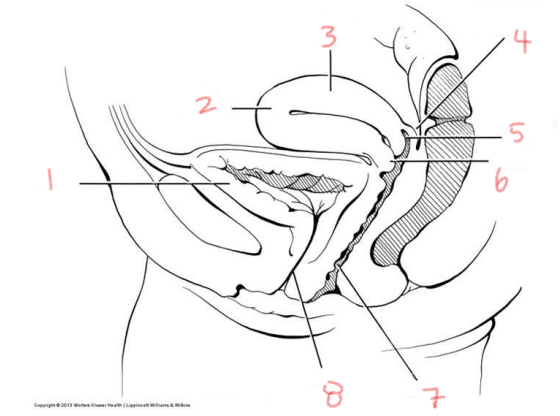
6
cervix
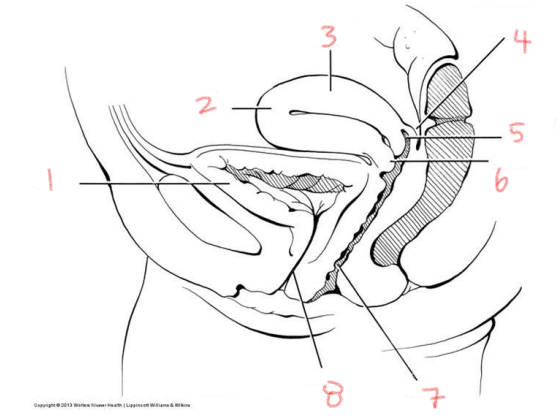
7
vagina
8
urethra
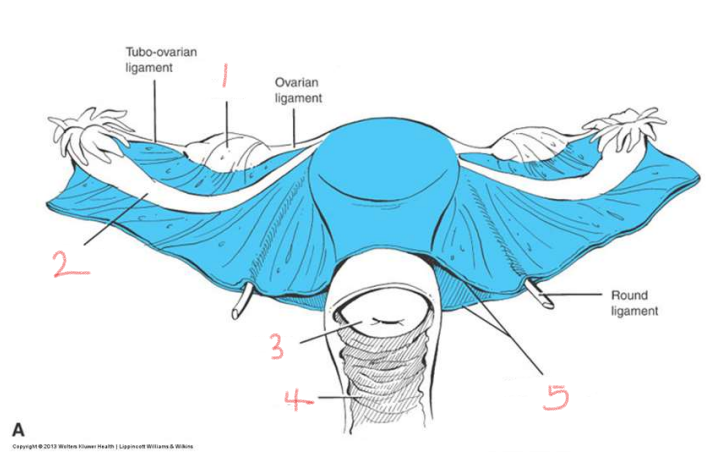
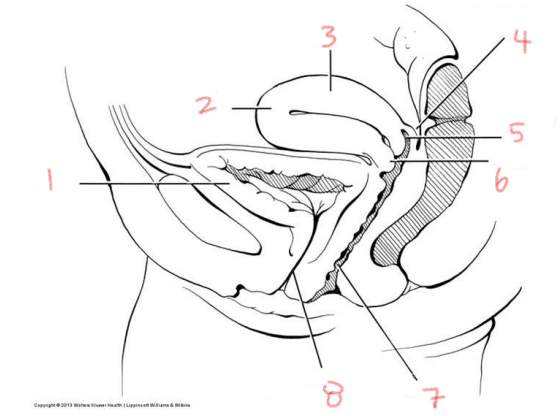
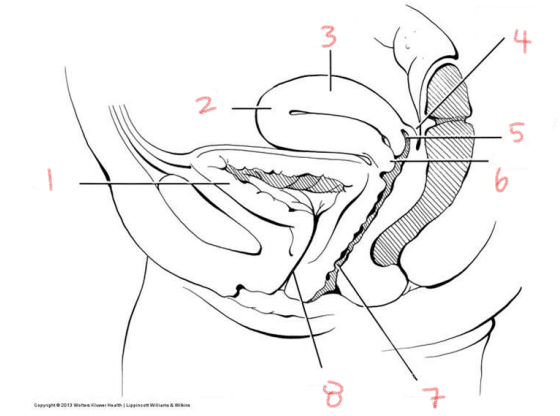
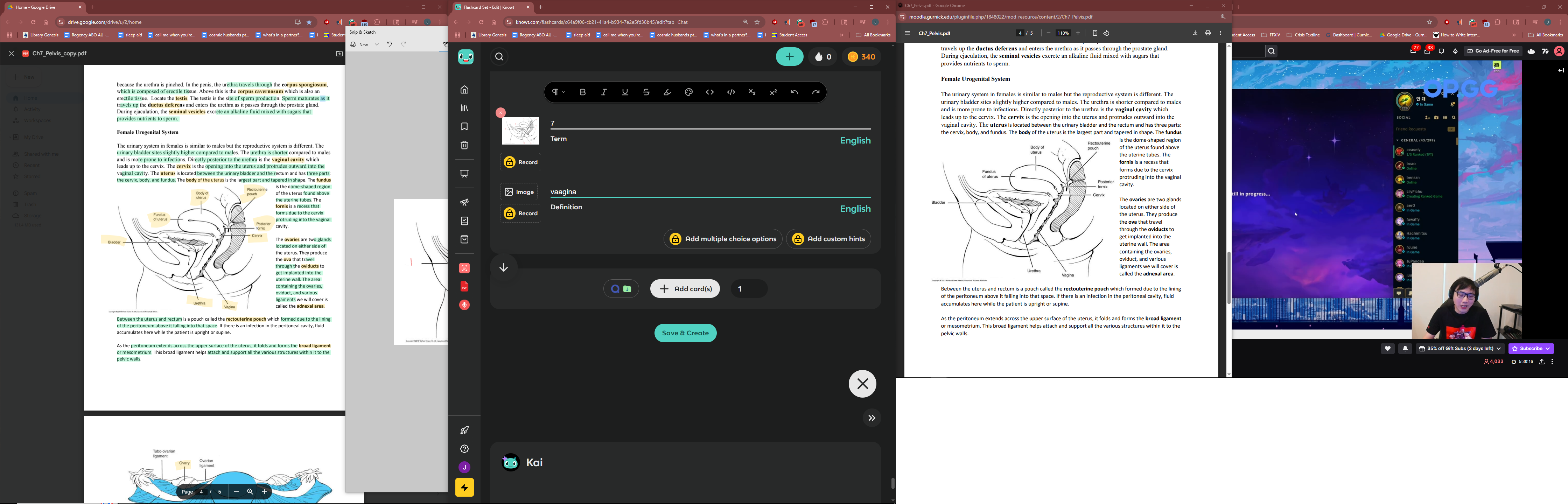
1
ovary
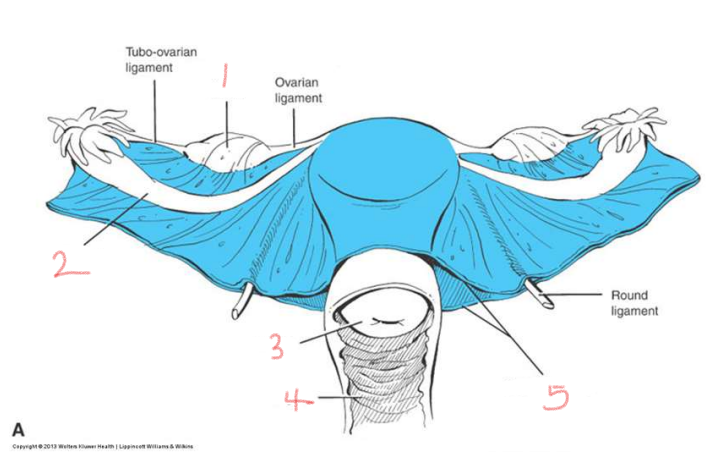
2
oviduct
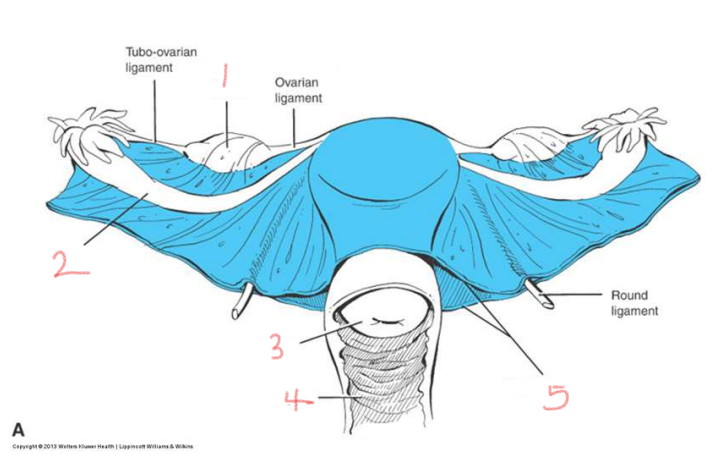
3
cervix
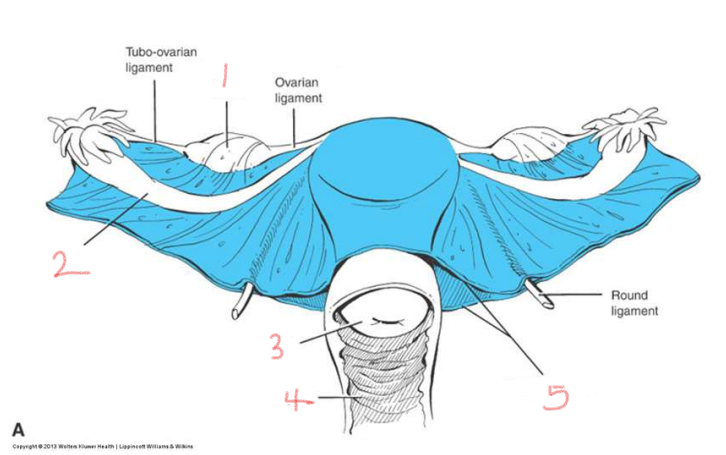
4
vagina
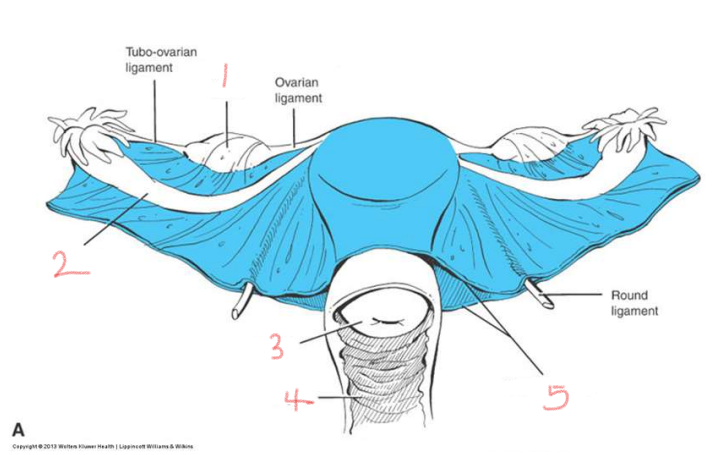
5
broad ligament