The Muscular System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Define some of the functions of the muscular system
- Balance
- Posture
- Respiration (autonomic nervous system)
- Movement
- Thermoregulation
- Heartbeat
Name the different types of muscle
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
Describe the properties of skeletal muscle
striated
elongated cells
multinucleated cells
voluntary
Describe the properties of Cardiac muscle
striated
branched cells
1-3 central nuclei
involuntary
List the properties of smooth muscle:
nonstriated
single central nucleus
involuntary
walls of hollow organs or blood vessles
function: lines smooth organs, redirection of blood to skin
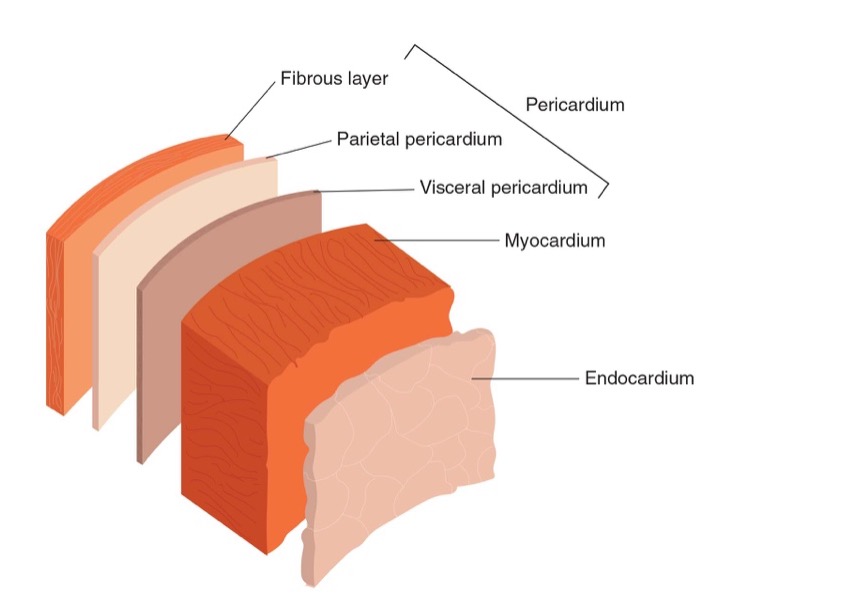
Describe the components of cardiac muscle
Pericardium: dense fibrous tissue avoid heart becoming overstretched
Myocardium: doing most of work in heart. contains actin and myosin. Responsible for forceful contractions. Left ventricle has largest myocardium (thickness of myocardium depends on activity)
Endocardium (inner layer forms inner lining of heart). Single layer of epithelial cells. Provides smoothness to reduce friction = easy bloodflow. Located in blood vessels and hollow organs
List the different types of connective tissue that holds the muscle bundle together
Epimysin
Perimysin (contains bundles called fasciculi)
Endomysium
Myofibril
Contains basic contractile elements of the muscle fiber
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane surrounding the MF. Inside contains sarcoplasma (like gelatine, transports nutrients like protiens/ minerals/ fats)
T Tubules (aka transverse tubules)
Provide ‘pathways’ through the fibre - as transport network which allows comms through the muscle and between fibers. Vital for electrical impulses to pass through muscle fiber.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Longitudinal network of tubules.
Stores Ca2+
parallel to myofibril. Provides structural stability.
Plays role in depolarisation of electrical signals across muscle.
Nucleus
Control centre of the cell. Cellular regeneration, regrowth, repair.
Mitochondria
Energy centre of the cell.
Sarcomere
Basic contractile structures
make the muscle have light and dark areas (striations)
Myofilaments
Actin
Myosin
Z-line / Z-disk
Start and end of sarcomere. Individual sarcomeres either arranged in parallel or series. Denoted by Z-line.
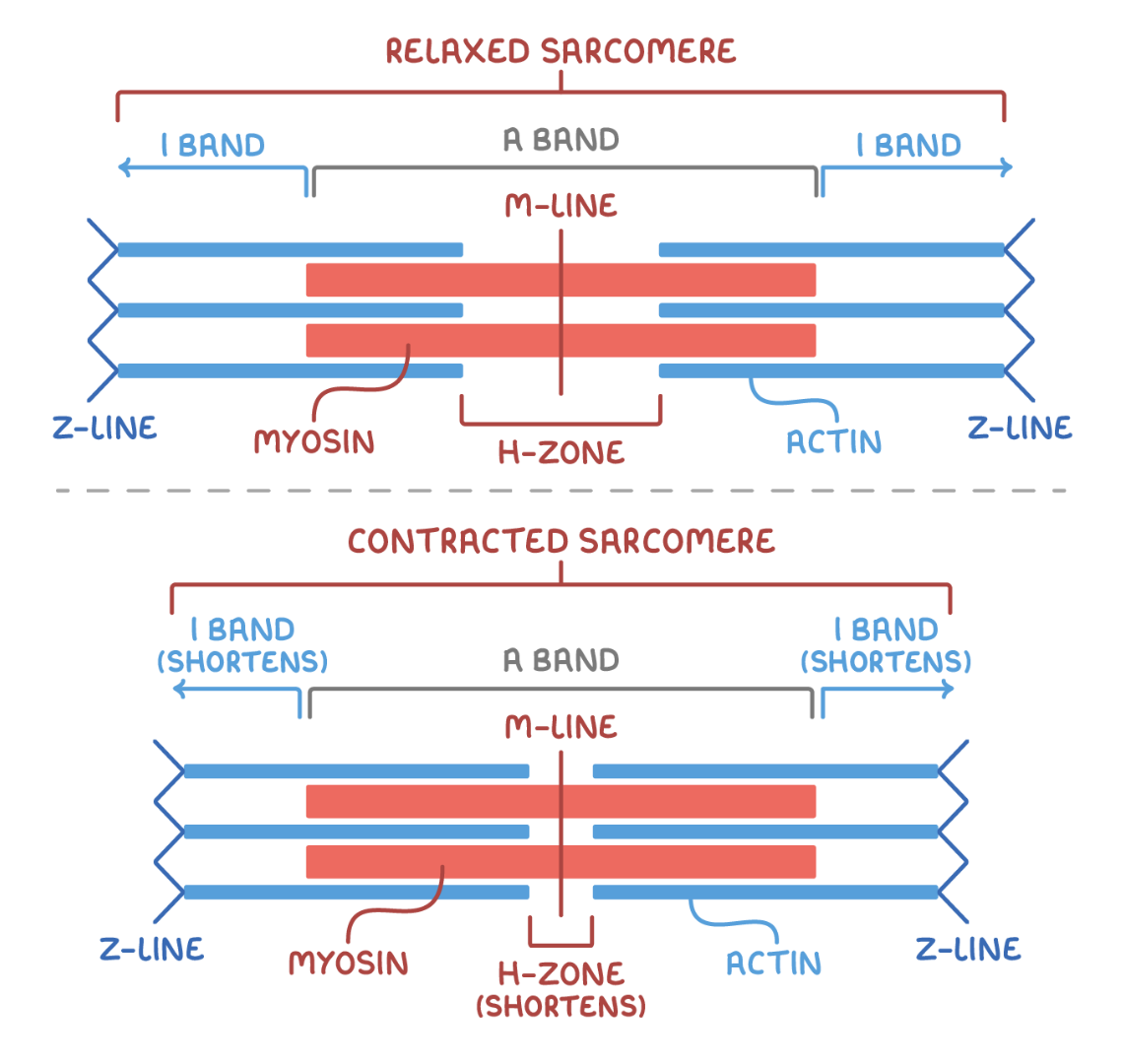
M-line
Line of protein in centre of sarcomere. No actin filaments present.
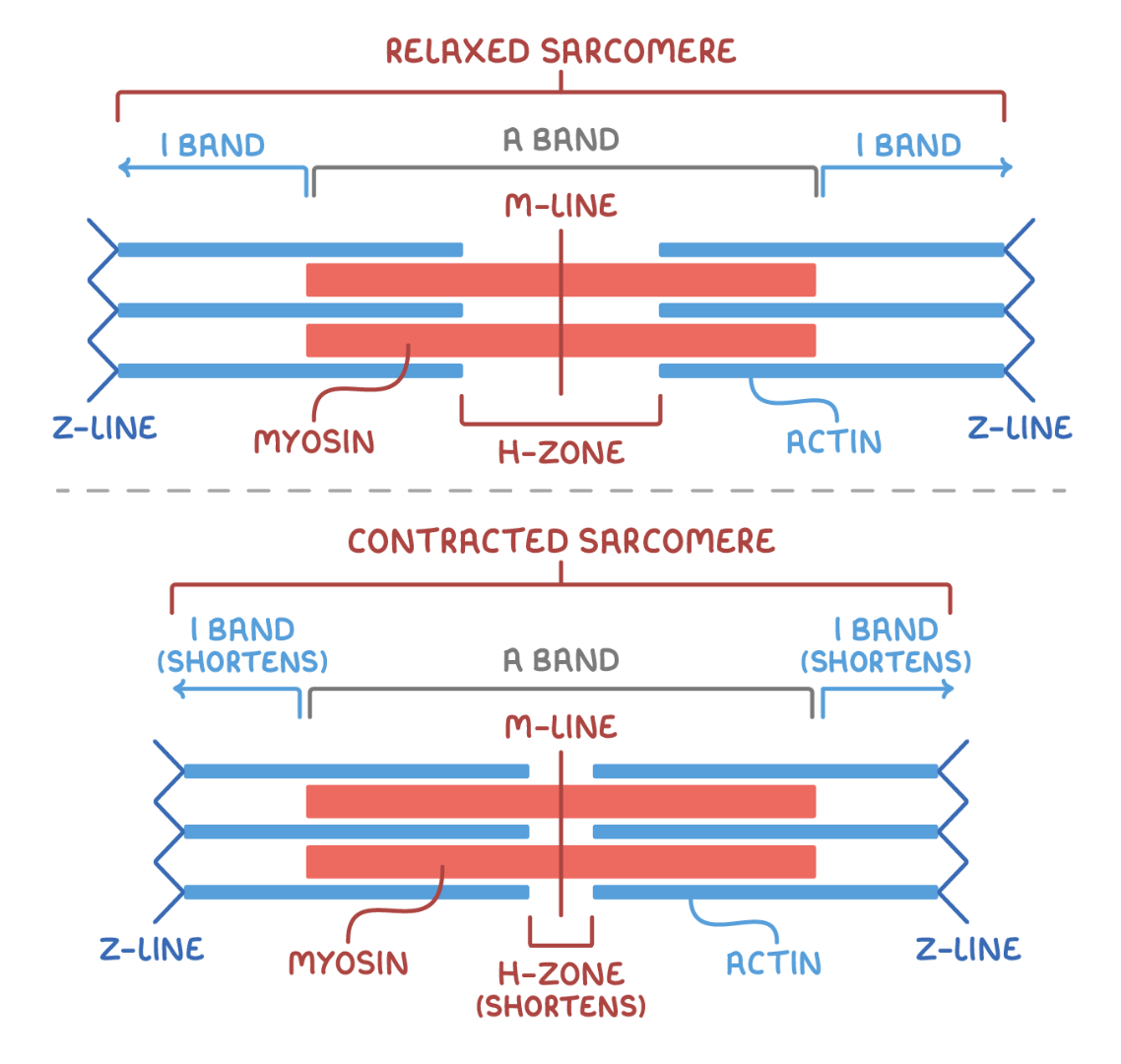
A band
Area containing thick myosin filaments. Dark region. Located at center. Both actin and myosin overlapping.
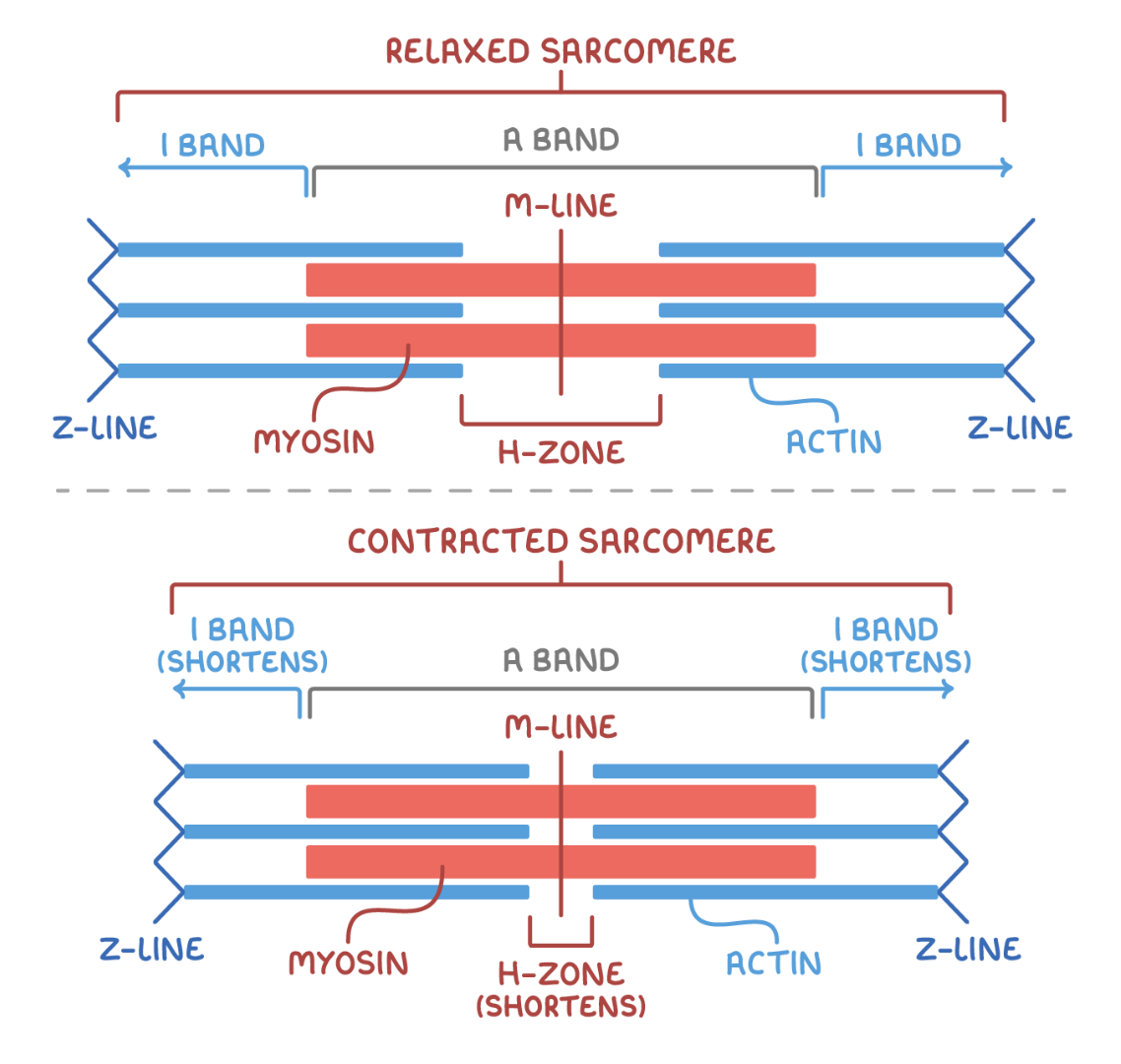
I-band
Area containing only thin actin filaments
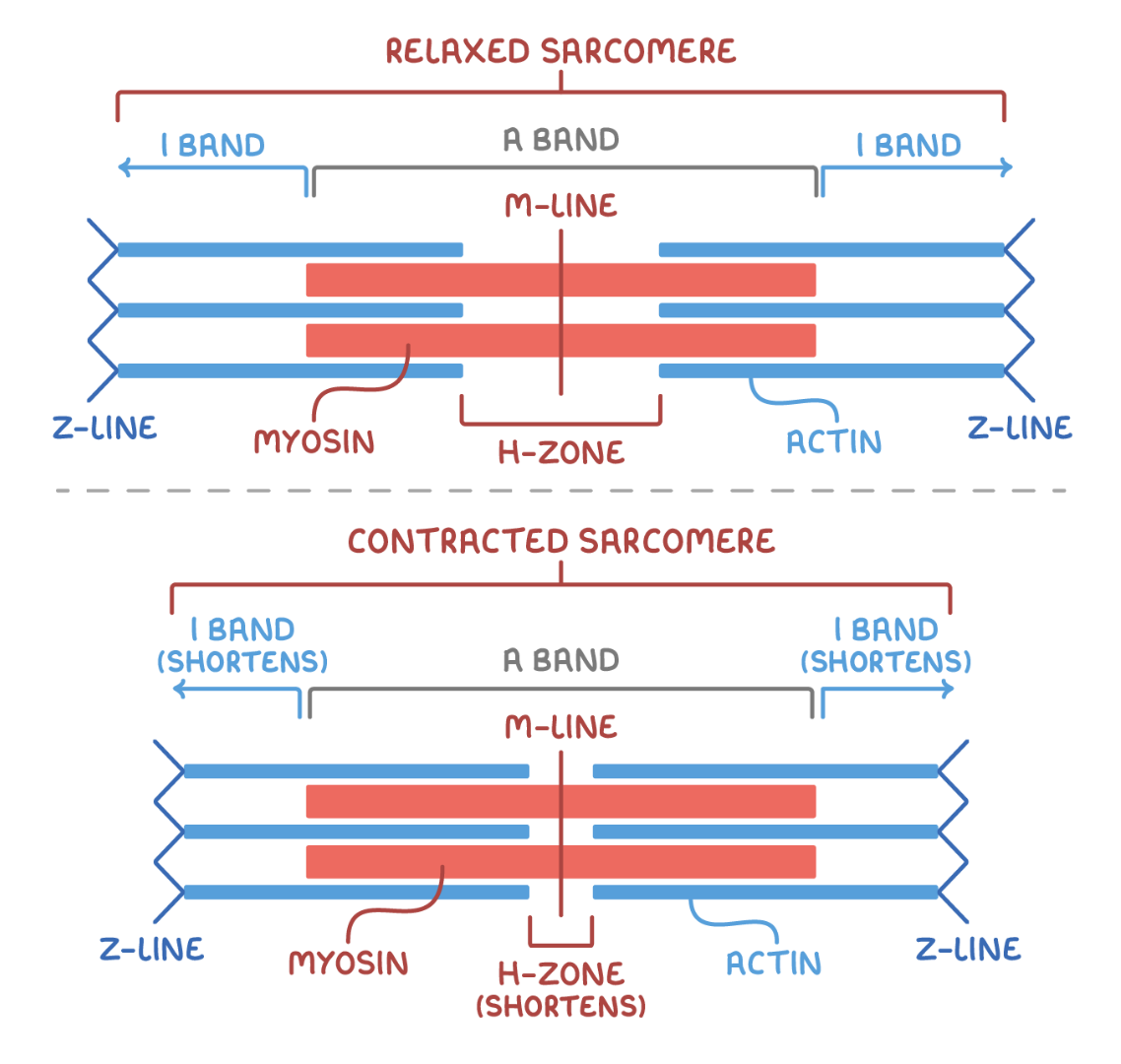
H zone
Gap between the ends of adjacent actin filaments. Within the A band. The dark line. a protein which provides attachment area for actin filaments.
Which structures on neurons help propagate the signal along?
nodes of Ranvier
Myelin sheath (de-myelination = disease damages myelin sheath = electrical signal disrupted)
Why are neurons described as excitable?
They are transducers! They receive a range of stimuli which need to be converted into specific types of signals
Fascicle
a bundle of structures, such as nerve or muscle fibres
Describe the process of stimulating a muscle contraction
at rest, the motorneuron is polarised (negatively charged to -70mV) to create potential difference