WCHS Mr. Alasti PLTW HBS Human Body Systems 2.1 Unit Test
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What two systems of the body are involved in communication, response, & function regulation?
Nervous & endocrine systems
What kind of signals does the nervous system use?
Electrical signals
What kind of signals does the endocrine system use?
Chemical signals (hormones)
What are the two subsystems of the nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS) & peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What parts of the body does the CNS contain?
Brain & spinal cord
What parts of the body does the PNS contain?
A system of nerve cells that transmit information to and from the control center
How do the PNS & CNS work together?
To ensure that important information gets to your brain to be processed & interpreted & that the correct response is generated
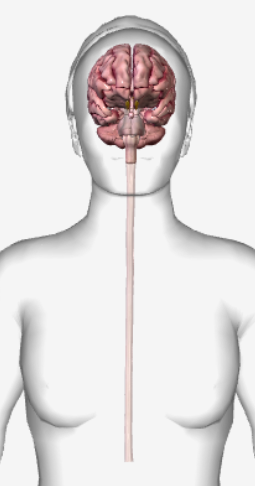
What subsystem of the nervous system is pictured?
CNS
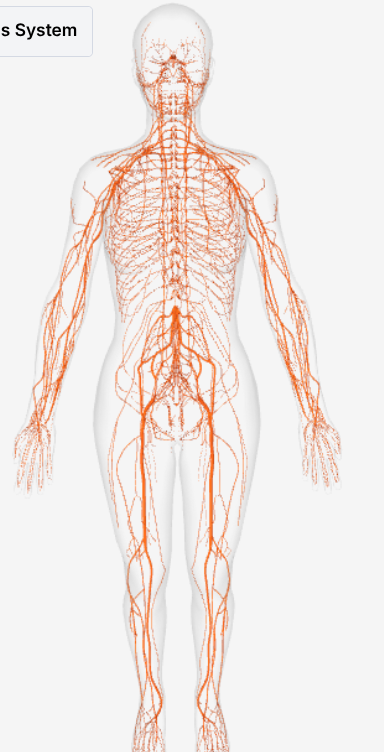
What subsystem of the nervous system is pictured?
PNS
What is the main organ of the nervous system?
The brain
What is the key to communication in the human body?
The brain
What are the 3 distinct structures of the brain?
Cerebrum (divided into 4 lobes)
Cerebellum
Brain stem
Cerebrum
Composed of right and left hemispheres & is the integrating center for memory, learning, emotions, & other highly complex functions of the CNS
Cerebellum
A large part of the brain, concerned especially with the coordination of muscles and the maintenance of bodily equilibrium, located between the brain stem and the back of the cerebrum
Brain stem
The part of the brain that is composed of the midbrain, pons, & medulla oblongata & connects the spinal cord with the forebrain & cerebrum
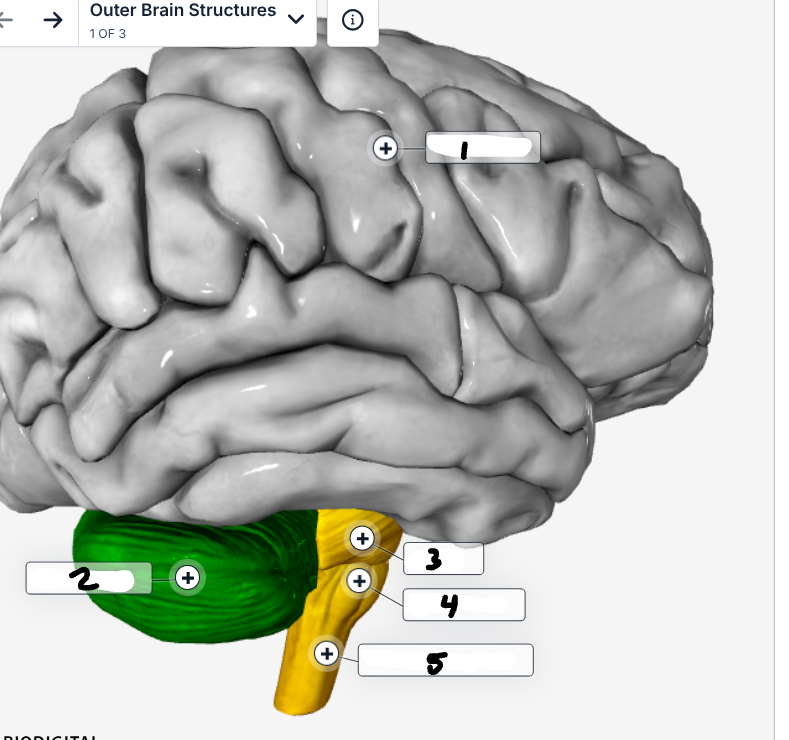
Label the image
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Pons
Brain stem
Medulla oblongata
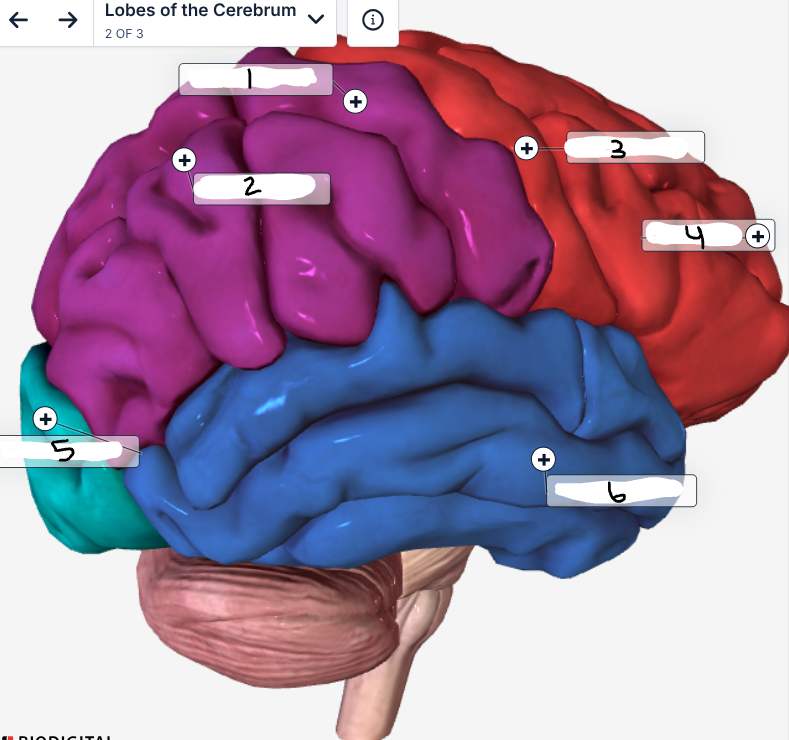
Label the image
Sensory cortex
Parietal lobe
Motor cortex
Frontal lobe
Occipital lobe
Temporal lobe
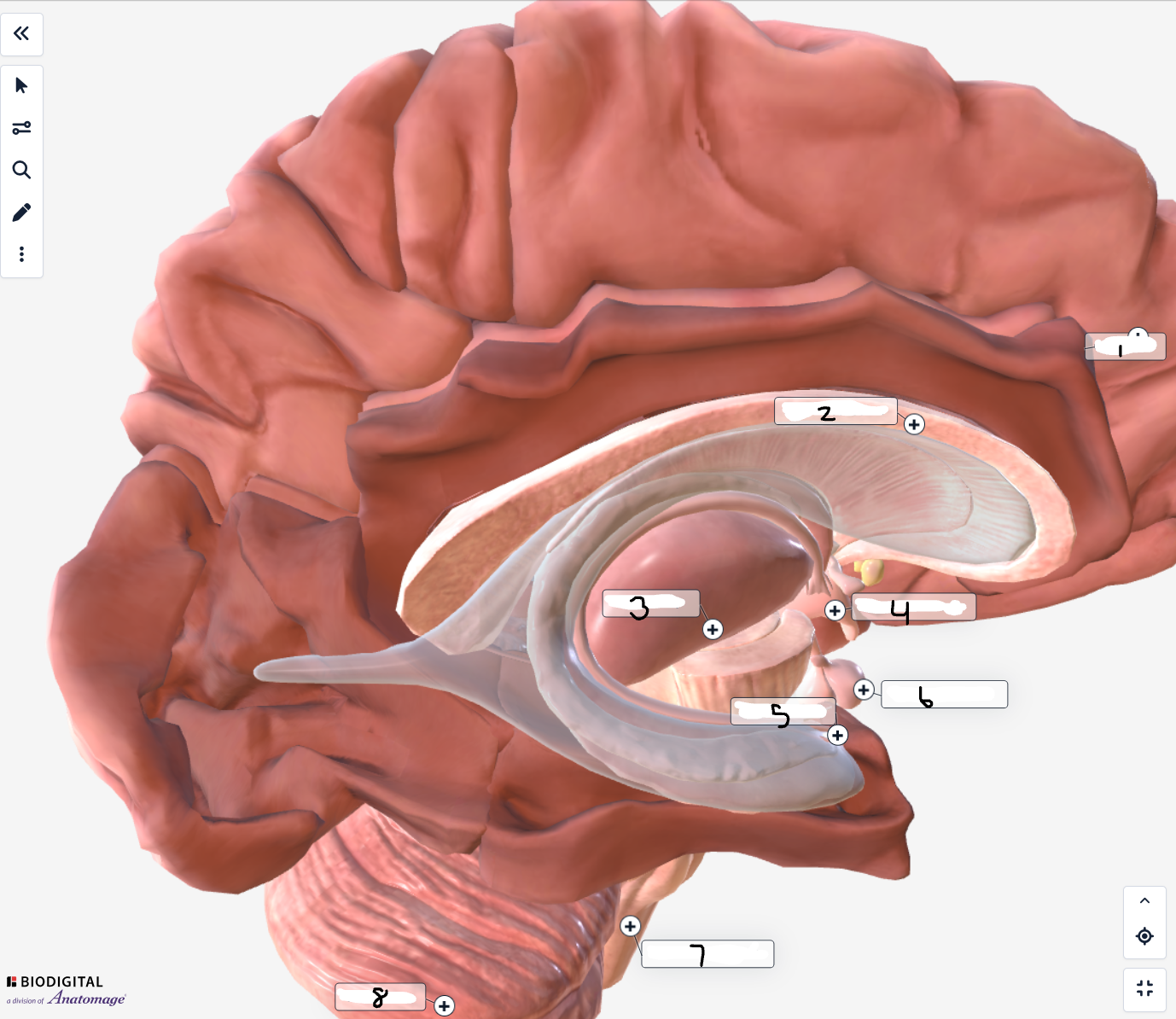
Label the image
Cerebrum
Corpus callosum
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Hippocampus
Pituitary gland
Pons
Cerebellum
Gyri
A ridge between anatomical grooves
Sulci
A shallow furrow on the surface of the brain separating adjacent gyri
Cerebral cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum, also known as “gray matter”
Olfactory Nerve
Relays information about the sense of smell
Optic Nerve
Relays information about the sense of sight
What do messages sent around the body help maintain?
Homeostasis
What kind of signal is an action potential?
Electrical signal
What kind of signal can a nerve generate and send?
An electrical signal (action potential)
Action Potential
A brief electrical impulse that travels along the axon of a neuron
How does an electrical signal travel down a neuron?
It travels down the axon and passed its message to the next neuron down the line
Ions
Small, electrically charged atoms or molecules (ex: sodium or potassium)
What impacts the overall charge of the inside and outside of the cell?
The number of ions
How is electricity created within a cell?
The sudden reversal of the overall charge of the cell
What does the sudden reversal of the overall charge of the cell produce?
A nerve impulse
What does a nerve impulse allow neurons to do?
It allows neurons to transmit electrical signals from one cell to the next
What are sodium and potassium channels designed to do?
To allow ions to move back and forth across the cell membrane, and they are specific to the ions that they transport
True or false: Channels such as potassium or sodium channels move ions in ONE specific direction, like a one way door
True
What direction does the potassium channel move ions?
Out of the cell
What direction does the sodium channel move ions?
Into the cell
What does the sodium potassium pump do?
Moves sodium & potassium ions back to the side where they started
Does the sodium potassium pump use energy to do its job?
Yes, in the form of ATP
How many of each ion does the sodium potassium pump move?
3 sodium ions out & 2 potassium ions in
Resting Potential
When the outside of the cell is more positively charged in comparison to the inside of the cell
What helps to maintain resting potential until the neuron receives a signal?
The sodium potassium pump
What happens when a neuron receives a signal?
Sodium channels along the membrane open, while the potassium channel stays closed, allowing sodium to rush into the cell, reversing the charge of the cell (inside is now more positive)
Depolarization
When the inside of the cell becomes more positive due to a rush of sodium particles, generating the electrical signal
What happens as depolarization occurs down the entire membrane of a neuron?
The action potential moves along the length of the axon, passing along the signal
Repolarization
The act of the cell returning to its resting potential (+ on the outside & - on the inside), when channel doors switch (potassium open & sodium shut), allowing potassium to move back out of the cell
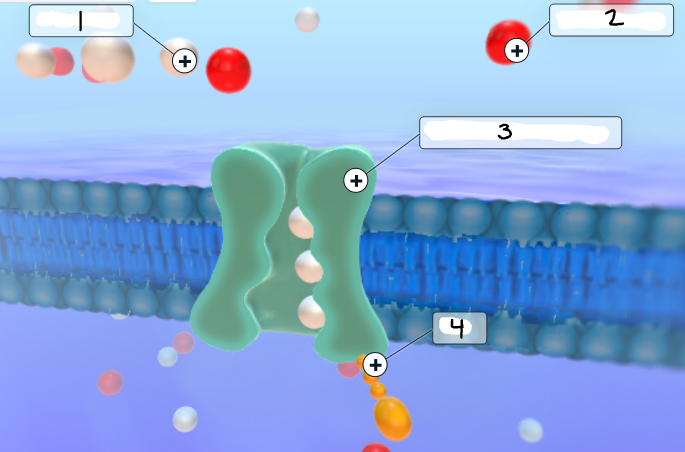
Label the image
Sodium ion
Potassium ion
Sodium-potassium pump
ATP
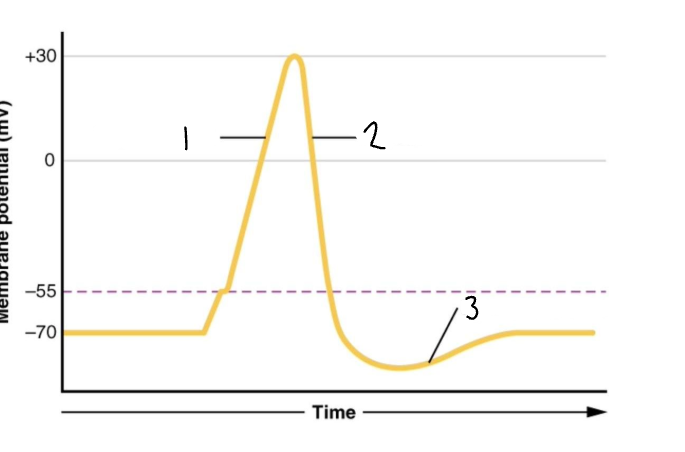
Label the graph
Depolarization
Repolarization
Hyperpolarization
Synaptic Cleft
The small space between the sending cell & the receiving cell
What could the receiving cell be when neurons send an action potential?
Another neuron, or a target cell such as a muscle or gland
What do the small sacs or vesicles within the axon terminals contain?
Chemical signals, called neurotransmitters
True or false: Different classes of neurons contain different types of neurotransmitters?
True
What allows you to sense, think, and respond?
The coordination of electrical & chemical signals
What happens when a nerve impulse arrives at the axon terminal?
It causes calcium ions to move into the cell through calcium channels, which are small gates within the cell membrane
When calcium ions move into cells, what does it allow the vesicles to do?
Fuse with the membrane & release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
What happens once neurotransmitters move across the synaptic cleft?
They bind to receptor proteins on the receiving cell, which are specific to the type of neurotransmitter that binds to them
What occurs when neurotransmitters bind to receptors?
The neurotransmitters activate specific ion channels in the cell membrane of the receiving cell, causing depolarization, making the receiving cell become a sending cell
What happens when a signal passes to a muscular gland?
The signal moves across the neuromuscular junction & activates muscle cells to generate contraction
Reflex
An automatic response to a stimulus that doesn’t reach the level of consciousness
Reaction
A thoughtful response to external stimuli in which the brain processes the nerve impulse before reacting
Reaction Time
The time it takes for your brain to receive and process input, interpret the information, and control muscle movement to produce a reaction
Is it possible to improve your reaction time or reflexes?
Reaction time
Differential Diagnosis
A list of all potential diseases, disorders, or conditions that could be causing a patient’s symptoms
Give examples of voluntary actions of the nervous system, and what subsystem of the PNS controls them?
The somatic system controls things like walking, running, writing, typing, throwing a ball, speaking, etc.
Give examples of involuntary actions of the nervous system, and what subsystem of the PNS controls them?
The autonomic system controls things like your heart beating, breathing, digestion of food, sweating, pupil dilation or constriction, etc.
What part of the brain controls vision?
Occipital
What part of the brain controls muscle coordination?
Cerebellum
What part of the brain controls breathing?
Medulla oblongata
What part of the brain controls happiness?
Amygdala
What part of the brain controls language understanding?
Temporal lobe
What part of the brain controls thirst and hunger?
Hypothalamus
What part of the brain controls speech production?
Frontal lobe
What part of the brain controls movement?
Motor cortex
What part of the brain controls smell?
Frontal lobe
What part of the brain controls reasoning?
Frontal lobe
What part of the brain controls long-term memory?
Hippocampus
What part of the brain controls hearing?
Temporal lobe
What part of the brain controls bodily sensations (touch, temperature, & pain)?
Parietal lobe
What part of the brain controls taste?
Sensory cortex
What part of the brain controls blood pressure regulation?
Medulla oblongata
What part of the brain controls sleeping and waking?
Hypothalamus
What part of the brain controls balance?
Cerebellum
What part of the brain controls problem-solving?
Frontal lobe
What part of the brain controls stress?
Amygdala
What is another name for an interneuron?
Relay or association
What is the most common type of sensory neuron?
Psuedounipolar
What starts an action potential?
Depolarization, the reversal of charge typically from nerve impulses
What kind of rare sensory neurons are located in our face?
Bipolar
What are the most common type of neuron (specifically interneurons and motor neurons)?
Multipolar
What structures are located in the axon terminals? What is within those?
Vesicles; neurotransmitters
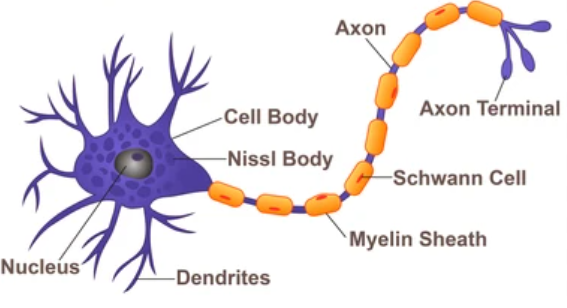
What kind of neuron is pictured?
Multipolar
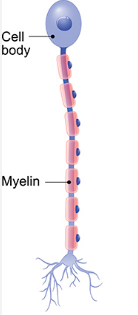
What kind of neuron is pictured?
Unipolar
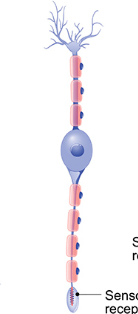
What kind of neuron is pictured?
Bipolar

What kind of neuron is pictured?
Psuedounipolar
Parkinson’s Disease
Caused by the death of dopamine-producing brain cells, crucial for smooth movement control. Parkinson’s causes tremors, stiffness, slow movement, and balance issues, affecting fine motor skills and coordination (PEOPLE ARE SELLING DOPE IN THE PARK)
Alzheimer’s Disease
A progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills, leading to loss of ability to perform daily tasks, personality changes, and behavioral issues (I FORGOT HOW TO SPELL ALZHEIMERS)
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
A chronic autoimmune disease that affects the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves because of the immune system attacking the myelin sheaths, which causes nerve signals to be disrupted (MYELIN SHEATHS)
Huntington’s Disease
A fatal, inherited brain disorder causing progressive breakdown of nerve cells, leading to uncontrollable movements, cognitive decline, and psychiatric problems (HUNTING BRAIN CELLS)
Epilepsy
A neurological disorder that disrupts rhythmic electrical impulse patterns that send messages. Instead of patterns, there are instead bursts of electrical energy between cells in one or more areas of the brain
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
A fatal progressive neurological disorder that destroys nerve cells controlling voluntary muscles, leading to weakness and paralysis (MOTOR NEURONS)