Topic 6 - People and Team Management
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro to Business UC3M
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What are the three main components of the management role?
Goal Setting - Identification of mission and formulation of goals in an environmental context
Developing Plans - choices between alternative plans of action to reach the goals
Implementation - execution of the plan throughout the rest of the management process
Where do organizational goals derive from
Goals are derived from the mission of the business organization
What are the three levels organizational goals/ plans from top to bottom?
Mission and long-term strategic goals (top management)
Tactical functional goals (middle management)
Operational goals (low management/first line supervisers
Define strategic plans/goals and provide examples
Strategic plans focus on the organization as a whole (not specific functions) and refer to a period of more than 5 years. Examples include:
Corporate strategies: Internationalization, innovation, diversification
Business strategies: low cost differentiation
What are operational plans/goals?
Operational plans refer to a period no longer than one year. They deal with day-to-day activities and allocation of resources.
Technical skills refer to…(Managerial skills)
Low management
Ability to understand how things operate
Interpersonal skills refers to…(Managerial skills)
Middle management
the ability to interact with people at work successfully
Conceptual skills refer to… (Managerial skills)
Top management
Ability to see the firm as a whole
According to Mintzberg’s Managerial roles what falls under interpersonal roles?
The Figurehead: Symbolic leadership (social and legal events)
The Leader: Responsibility for motivating and encouraging employees, exercising their formal authority
The Liaison: build and maintain relationships
According to Mintzberg’s Managerial roles what falls under informational roles?
The Monitor: scans the environment for new information to collect
The Disseminator: passing on privileged information directly to other members in the organization
The Spokesperson: Sharing information with people outside the organization
According to Mintzberg’s Managerial roles what falls under decisional roles?
The Entrepreneur: Seeks to improve the unit by initiating projects; fosters creativity and innovation
The Disturbance Handler: manages organizational problems and crises
The Resource Allocator: Decides who gets what
The Negotiator: Represent the organization in negotiations
Fayols Five Managerial Functions: Forecasting and planning
Set objectives
Determine best course of action to achieve them
Involves: forecasting, setting goals, and deciding on the steps if necessary
Fayols Five Managerial Functions: Controlling
Monitoring progress toward goals
Comparing actual performance with plans
Making necessary adjustments
Fayols Five Managerial Functions: Organizing
Arranging resources (people, finances, materials) and tasks in a structured way to achieve the plan.
It includes creating a structure of roles and responsibilities.
Fayols Five Managerial Functions: Commanding /Leading
Directing and guiding employees to carry out their tasks effectively
Involves leadership, motivation, communication, and supervision
Fayols Five Managerial Functions: Coordinating
Ensuring all parts of the organization work together smoothly
Involves synchronizing activities and resolving conflicts
The Role of Management - eight steps that one goes to make a decision
Recognizing the problem or opportunity
Gathering information: identifying the critical factors
Considering alternative courses of action
Analyzing alternatives
Choosing an alternative
Implementing the decision
Evaluating the results
Implementing changes
What is Human Resources?
A firm’s employees, including workers and managers
What is Human Resource Management
The process of recruiting, selecting, training, appraising, and compensating employees. It is one of the basic functions that all managers perform
HR management sequence and solution
Motivation, leadership, and communication
Recruiting, selecting, and training
Performance appraisal systems, compensation, and incentive programs
What are Herzberg’s two factors
Motivators
Achievement
Recognition
Work itself
Responsibility
Advancement
Hygiene
Interpersonal relations
Company policy/administration
Supervision
Salary
Working conditions
What is the basic motivation cycle?
Needs —> Behaviors —> Either:
Satisfying a necessity OR
Frustration
What is the key principle for managers regarding employee motivation
Identify and recognize needs and desires from employees
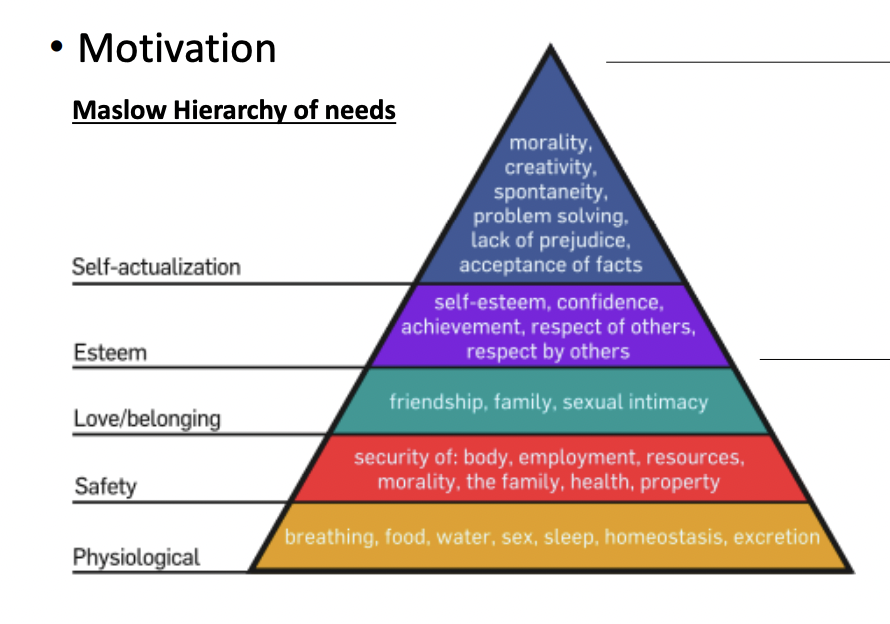
List Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs from bottom to top
Physiological needs (base)
Safety needs
Social needs (belonging/love)
Esteem needs
Self actualization (top)
What is leadership in terms of power?
Leadership is a way of power - the ability to affect behavior in a particular way
What are the three fundamental bases of power
Legitimate power
Reference power
Expert power
What is communication in a management context?
Communication is an information transmission process
What are the three types of organizational communication
Descendent (downward)
Ascendent (upward)
Crossed (horizontal/lateral)
What is recruiting?
Recruiting is the process of ensuring that a sufficient number of applicants apply for the job offer
What are the pros of internal recruiting
Career planning becomes possible; employees see a future within the firm
Assessment of applicants is easier
Lower cost of the recruitment process
What are the cons of internal recruiting
The business may stagnate (no new ideas)
Personal competition among colleagues (detriment of cooperation)
Not getting the best people
What are the four phases of the selection process?
Application - Response to advertisement, submission of job application
Shortlisting - Qualifying candidates are shortlisted, personalty/interest tests, reference checks
Interviews - Consider CV/test results/ background tests
Notify applications - Make an offer/ Reject/ Hold over
What two types of rewards does compensation include?
Extrinsic rewards - salary and benefits
Intrinsic rewards - achieving personal goals and more challenging job opportunities
What is direct compensation
Direct compensation is salary or wage
What is indirect compensation, with examples
Indirect compensation consists of benefits that an employee receives such as:
Holidays
Studies/education
Medical aid
Pension scheme
Insurances
What are three types of rewards that can be given to employees
Salary increase based on individual work performance
Financial bonuses for those that have performed exceptionally well
Paid holidays, overseas trips with all expenses paid
What does Harvard Business School’s Frank Cespedes say about rethinking sales compensation?
He says that the assertion that money is the only motivator, comp plans must be simple, and we pay for results and not process, is false and can be damaging / needs to be reexamined. Compensation is only one part of strategic sales performance management, without the link to a bigger plan even the best compensations plans won’t pay off.
Explain the organization structure in a business in terms of team management
arrange the HR of the firm so that their activities contribute to the firm’s goals
The purpose is to give each person a distinct task and to ensure that these tasks are coordinated in a way that the firm accomplishes its goals
Organization chart of a graphic representation of the organization structure
Describe the difference between formal and informal structure
Formal is defined by the management
Informal - informal contacts, communications, and ways of doing things that employees develop
Real structure falls somewhere in between
Factors that determine the organizational structure
Specialization = Horizontal (number of tasks), vertical (autonomy to one’s job)
Standardization
Formalization
Structural configuration = departmentalization (types), number of layers (hierarchical levels), span of control, size of administrative component
What are the types of formal structures
Strategic Apex (top management)
Middle Line (middle management)
Operating core (employees)
these are common parts in any formal organizational structure
Describe simple structure
Strategic apex is the key part of the structure (direct supervision)
Only strategic apex and operating core
Start-ups or very small business

What is functional departmentalization?
Functional departmentalization organizes the company by functions (e.g. Production, Marketing, Finance, HR, R&D) under general management
What are the advantages of functional departmentalization
Logical and widely used
Encourages specialization
Efficiency in performing tasks
Facilitates control of functions
What are the disadvantages of functional departmentalization
Problems arise in highly diversified companies or with great international development
What is departmentalization by business lines or product?
An organization structure where general management oversees separate divisions for Business A, Business B, Business C, and Business D, with each division potentially having its own functional departments
What are the advantages of product/business line departmentalization?
Facilitates specialization of personnel and material (efficiency)
Faster response to customer demands for each product
Leverages synergies within a business
What are the disadvantages of product/business line departmentalization
More control and coordination costs
Misses information “between” businesses
What is geographical departmentalization?
Organization structure where general management oversees divisions by geographical areas (Area A, Area B, Area C, Area D, etc.).
What are the advantages of geographical departmentalization?
Can respond more quickly to the demands of one zone or another
Leverages synergies within an area
What are the disadvantages of geographical departmentalization?
More control and coordination costs.
What is customer organization/departmentalization?
Organization structure that divides the company based on different customer segments or types.
What are the advantages of customer organization?What are the advantages of customer organization?
Better understanding of customer's needs
Improvement of customer satisfaction
Increased customer loyalty
More effective communication
What are the drawbacks of customer organization?
Possible duplication of resources
Greater organizational complexity
Higher cost
Risk of neglecting other important aspects
What is a matrix organizational structure?
A structure where employees report to both functional managers and project/product managers, creating dual reporting relationships.
What are the advantages of a matrix structure?
Enhanced collaboration
Efficient resource use
Flexibility and adaptability
Skill development
Improved decision-making
What are the drawbacks of a matrix structure?
Complex reporting relationships
Potential for conflict
Difficulty in performance evaluation
Higher overhead costs
What is a multidivisional structure?
A structure where functional departments exist within each business division or geographical area (rather than at the corporate level).
What factors should be considered when selecting the right plan during the planning phase?
Information about both internal and external environment should be used to select the right plan.
What does implementation involve in the management process?
Implementation involves putting the selected plan into operation by:
Organizing resources for the purpose
Leading subordinates
Exercising control
What is a key disadvantage of traditional hierarchical organizational structures?
Communication flows top-down, which can hurt engagement and collaboration; also, there is fierce competition for talent.
What advantage do flatter organizational structures provide?
They open up lines of communication and collaboration by removing layers, making it scalable for large organizations.
What is a disadvantage of flat organizational structures?
They often exist only on paper, with informal hierarchies or power structures still controlling decisions behind the scenes.
Why can informal hierarchies in flat organizations be harmful?
Power may concentrate in the hands of a few, creating cliques that are hard to challenge and lack transparency.
What accountability issues arise in flat organizations with no formal structure?
There are few checks and balances, unclear oversight, and no formal channels for reporting problems or abuses.
How can lack of formal structure affect employees’ job security?
Employees can be recruited with big promises but later discarded without clear reason, leaving them vulnerable to favoritism and punishment
What social risks can occur in organizations with minimal structure?
Increased risk of harassment and misconduct due to lack of supervision and clear policies.
What is the “tyranny of structurelessness” as described by Jo Freeman?
When no formal structure exists, strong personalities seize control, power goes unquestioned, and democracy disappears.
What is a Hierarchy organizational structure?
A traditional, linear structure where people follow clear leadership and authority.
Advantage: Good for straightforward, routine work that requires following orders.
Disadvantage: Can lead to fierce competition for talent and slow communication flows.
What is a Flatter organizational structure?
Reduces management layers to open communication and collaboration.
Advantage: Encourages better communication and is practical and scalable for large organizations.
Disadvantage: Requires strong tech support and mindset shift from managers that employees don’t have to “work at your company.”
What is.a Flat organizational structure?
Minimal or no formal management layers, often used by small to medium companies.
Advantage: Good for smaller companies and increases employee autonomy.
Disadvantage: Not practical for scaling and can lead to informal hierarchies based on personalities.
What are Flatarchies?
Temporary, hybrid structures combining flat and hierarchical elements, often used for projects or innovation teams.
Advantage: Flexible and can work for any size company, useful for specific initiatives.
Disadvantage: Can create isolated pockets of new structures, making it less consistent across the company.
What is a Holacratic organizational structure?
A system with no traditional managers; roles are distributed and self-managed, often seen in small to medium companies like Zappos.
Advantage: Supports employee autonomy and distributed decision-making.
Disadvantage: Difficult to implement in large companies and can face resistance from people used to traditional structures.