C1 : Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What does an atom contain? (3)
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
What is a radius of an atom?
1×10-10 m
Where is the nucleus located, what does it contain, what is its radius, what is its overall charge?
Located in the centre of the atom
It contains protons + neutrons
Its radius is 1 × 10-14 m
Its overall charge is positive because of the protons
Where are the electrons located in an atom?
In the shells which orbit the nucleus
What is the mass and charge of the 3 subatomic particles?
Protons
Mass → 1
Charge → +1
Neutrons
Mass → 1
Charge → 0
Electrons
Mass → Very small
Charge → -1
What is the overall charge of atoms + why?
Neutral
Because they have the same number of protons and electrons which balance each other out
What is an ion + what overall charge would an atom have if lost or gained?
An atom with an unbalanced number of electrons
Lost electrons → + charge
Gained electrons → - charge
What are atoms represented by?
A chemical symbol
What is a molecule?
two or more elements chemically bonded together
What is an element?
One type of atom only
What is an isotope?
Element with a different number of neutrons
What is the equation for relative atomic mass?

What is a compound?
Substances made up of 2 or more elements chemically joined together
During a chemical reaction what is a formed?
At least one new substance
Do compounds have the exact same properties as their original elements?
No
What are compounds represented by + give an example?
Formulas e.g. CO2
What are the 2 ways a chemical equation can be written?
Word equation
Symbol equation

What does the purple + the green represent?
Purple → Reactants
Green → Products

Balance this equation

What is a mixture?
Different elements or compounds not chemically joined together
What does it mean if a substance is soluble?
It can dissolve in a liquid
What does mean if a substance is insoluble?
It can’t be dissolved in a liquid
What are the 4 physical separation techniques?
Chromatography
Filtration
Crystallisation
Distillation
What is chromatography used to separate?
inks and dyes
Explain how to do chromatography (7)
Draw a line near the bottom of a sheet of filter paper, use a pencil (pencil is insoluble and won’t dissolve in the solvent)
Add a spot of ink to the pencil line and place the sheet in a beaker of solvent e.g. water or ethanol
Make sure the ink isn’t touching the solvent
The solvent should seep up the paper carrying the ink with it
Each different dye will move up the paper at different rates so the dyes will separate out, each dye will form a spot in a different place
If any of the dyes are insoluble then they will stay on thee baseline
Leave the paper to dry after the dyes have separated
What is separated using filtration?
Insoluble solid from liquids
Explain how to do filtration (4)
Get filter paper and fold it into a cone
Put the cone into a filter funnel
Put that into a beaker
Put the mixture in the funnel + wait till all the solids are in the paper and the liquid is in the beaker
What is evaporation used to separate?
Soluble salt from a solution (don’t do thermal decomposition)
Explain how to do evaporation (4)
Pour the solution into an evaporating dish
Slowly heat the solution, the solvent will evaporate and the solution will get more concentrated
Crystals will start to form
Keep heating the evaporating dish until all you have left is dry crystals
What is crystallisation used to separate?
Soluble salts from a solution
Explain how you would do crystallisation (5)
Pour the solution into an evaporating dish and gently heat the solution
The solvent will evaporate and the solution will get more concentrated
Once the some of the solvent has evaporated or when you see crystals start to form, remove the dish from the heat and leave the solution to cool
The salt should start to form crystals as it become insoluble in the cold, a highly concentrated solution
Filter the crystals out of the solution and leave them in a warm place to dry
What are the 2 types of distillation?
Simple distillation
Fractional distillation
What is simple distillation used to separate?
2 substances with very different boiling points
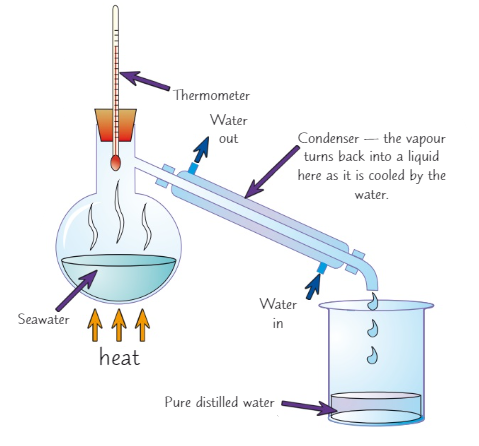
Explain how to do simple distillation (3)
Heat the solution, the part of the solution that has the lowest boiling point will evaporate first
The vapour is then cooled, condenses and is collected
The rest of the solution is left behind in the flask
What is fractional distillation used to separate?
A mixture of liquids with different boiling points
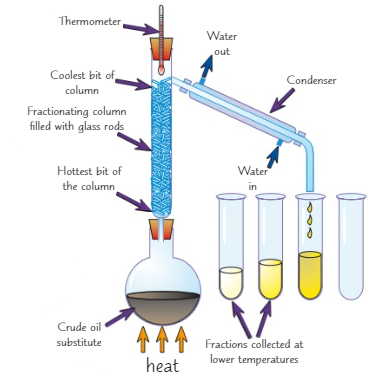
Explain how to do fractional distillation (6)
Put the mixture in a flask and put a fractionating column on top
Then start to heat the mixture
The different liquids will have different boiling points so they will evaporate at different temperatures
The liquid with the lowest boiling point evaporated first, it will reach the top of the column
Liquids with higher boiling points might also start to evaporate but the column cooler at the top so it will condense
When the first liquid has been collected raise the temperature until the next one reaches the top and so on and so forth
Explain the history of the atom (give the date, the person and the discovery) (5)
19th century ~ John Dalton → atoms are solid spheres
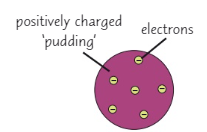
1879 ~ J J Thompson → plum pudding model
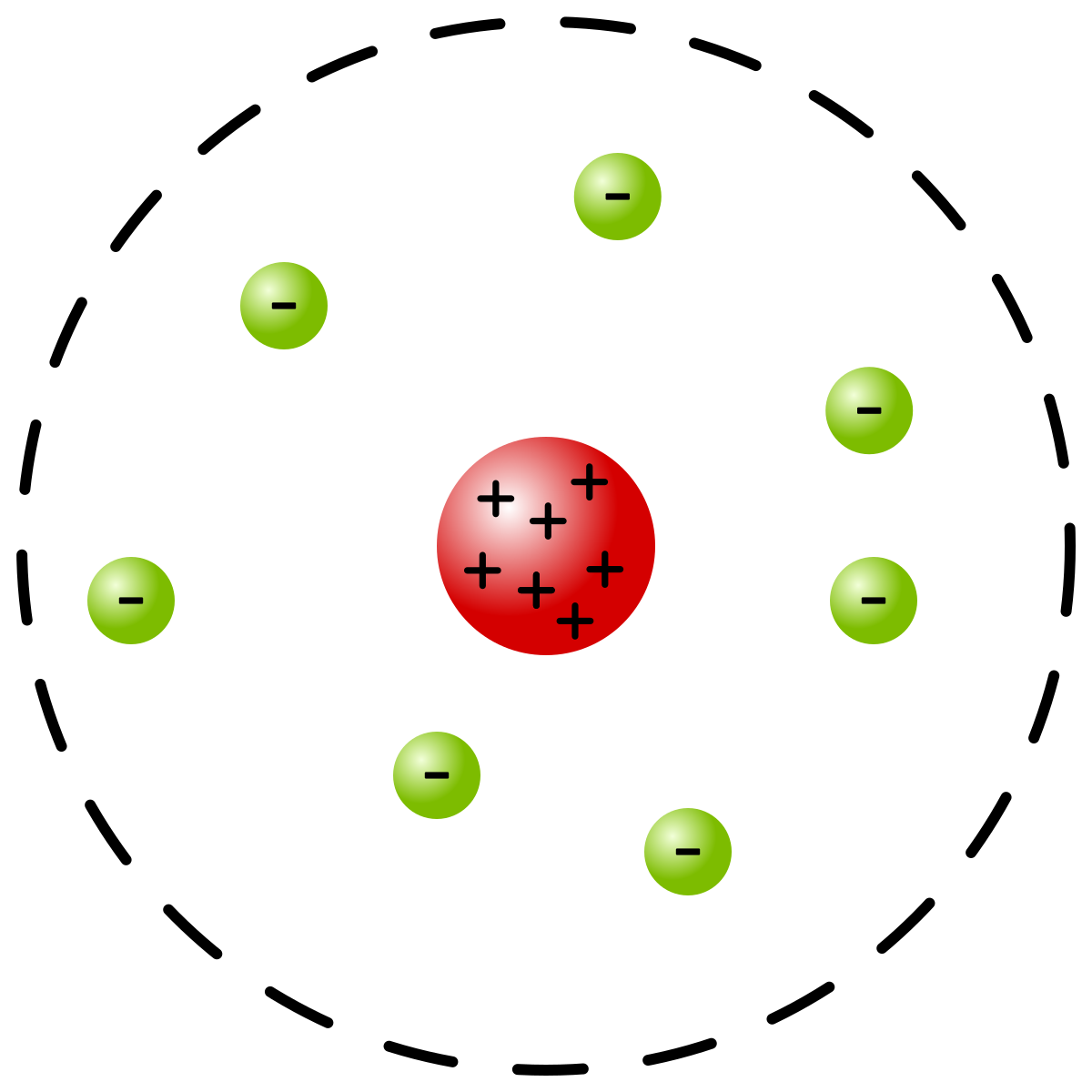
1909 ~ Earnest Rutherford → alpha scattering experiment + nuclear model
Niels Bohr → electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells, each shell being a fixed distance
James Chadwick → neutrons
Describe the plum pudding model
A ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded into it
Describe the alpha particle scattering experiment (3)
Positively charged alpha particles were thrown at an extremely thin sheet of gold
From the plum pudding model the particles were expected to pass straight through the sheet of gold or be only slightly deflected
However even though most of them did go through, more were deflected than expected and some came right back
What did the alpha particle scattering experiment conclude? (3)
That the mass of an atom was concentrated at the centre (nucleus)
The nucleus was charged
The atom was mostly empty space
Describe the nuclear model (2)
A tiny positively charged nucleus at the centre in which most of the mass is concentrated
A cloud of negative electrons surround this nucleus
Why did Niels Bohr suggest that electrons orbited the nucleus?
Because the electrons would be attracted the the nucleus and the atom would collapse
How many electrons are allowed on the first shell?
2
How many electrons are allowed on the 2 + the rest of the shells?
8
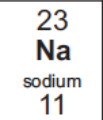
Draw the electronic structure of sodium
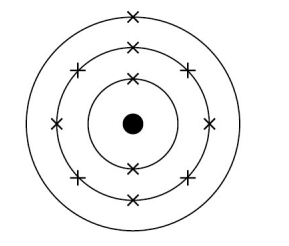
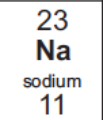
Write the electronic configuration of sodium
2,8,1
What 3 ways were elements arranged in the early 1800s?
Physical properties
Chemical properties
Atomic weight
Who made the table of elements, when did he make + how did he arrange it?
1869 ~ Dimitri Mendeleev → He left gaps for elements that hadn’t been discovered + he ordered it atomic weight
How is the modern periodic table arranged?
In order of increasing atomic number
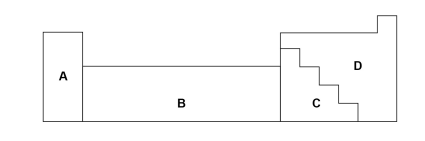
Where letter represents metals?
A,B,C
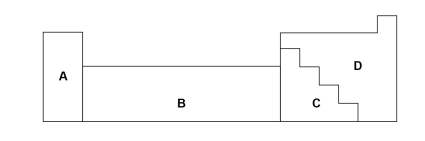
Where letter represents non-metals?
D
What do the periods on the periodic table tell you?
Number of shells
What do the groups on the periodic table tell you?
Number of electrons on the outer shell
How do elements in each group behave?
Similarly
What type of elements form positive ions + which ones don’t?
Metals form positive ions + non-metals don’t
Why do atoms react?
To form a full outer shell
What are the properties of metals? (7)(sscchhm)
Strong
Malleable
Conduct heat
Conduct electricity
High melting points
High boiling points
Shiny
What are the properties of non-metals? (5)
Dull
Brittle
Aren’t solid at room temperature (some of them)
Don’t conduct electricity
Low density
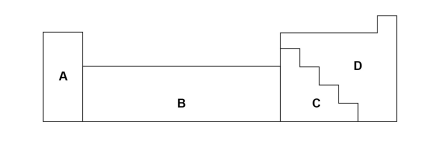
Which letter represents the transition metals?
B
What are the properties of transition metals? (15)
Less reactive than group 1 + 2 (more useful)
Hard
Ductile
Sonorous
Used as catalyst
Forms ions with multiple charges
High densities
Form coloured compounds
Shiny (lustrous)
Malleable
Strong
Conducts heat
Conducts electricity
High melting points
High boiling points
When are transition metals used as catalysts? (2)
Iron catalyst used in the Haber process for making ammonia
Nickel catalyst used in making margarine
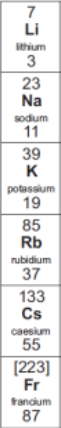
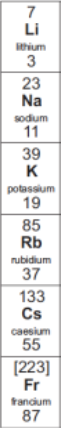
What are group 1 elements called?
Alkali metals
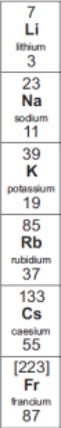
How many electrons in their outer shells do group 1 elements have?
1
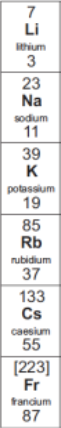
What are the properties of alkali metals? (4)
Soft
Low density
Form 1+ ions
Form ionic compounds
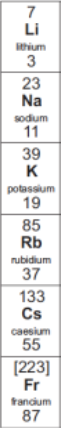
What is the trend of the alkali metals as you go down the group? (2)
More reactive
Melting + boiling points decrease
Why are the group 1 elements more reactive when you go down the group?
The outer electron is lost more easily as the attraction between the electron and the nucleus decreases because the electron is further away from the nucleus
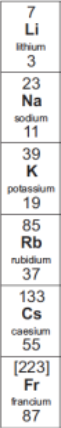
How do group 1 elements react with water + what do they produce?
They react vigorously
They produce hydrogen gas + metal hydroxides (compounds that dissolve in water to produce alkaline solutions)
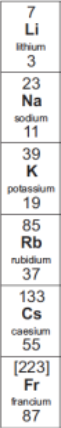
How do group 1 elements react with chlorine + what do they form?
They react vigorously
They form white metal chloride salts
How do group 1 elements react with oxygen + what do they form?
They react vigorously
They from a metal oxide
What are the differences between alkali metals and transition metals in terms of their chemical properties and physical? (7)
Chemical Properties | Physical Properties | |
|---|---|---|
Alkali Metals |
|
|
Transition Metals |
|
|

What are the group 7 elements called?
Halogens

How many electrons on their outer shells do group 7 elements have?
7

How do group 7 elements exist?
As diatomic molecules

What are the properties of halogens? (2)
Form 1- ions when reacting with metals called halides
More reactive halogens can replace a less reactive halogen (displacement reaction)

What is the trend of the group 7 elements going down the group? (2)
Less reactive
Melting + boiling points increase
Why do group 7 elements become less reactive when going down the group?
Its harder to gain an extra electron, because the outer shell is further away from the nucleus

What are the group 0 elements called?
Noble gases
How many electrons do group 0 elements have in their outer shells?
8 + helium has 2 (all have a full outer shell)

What are the properties of noble gases? (3)
Inert → don’t react with anything
Exist as monotonic gases → single atoms
Non-flammable

What is the trend of the noble gases as you go down the group?
Increased boiling points (more intermolecular forces to overcome)