OU Nursing BIOS 1300 Lab Quiz 9 Review (Nervous Tissue and Central nervous System) (Purposegames for models linked as well)
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Btw there is one slide's worth of a model missing slide 18/60 for lab discussion #9, but otherwise should hopefully be most the rest. Also every purposegames I made of the other models are tagged in this study set
https://www.purposegames.com/game/bios-1300-spinal-cord-labelling
https://www.purposegames.com/game/xy1vjjUvqcK
https://www.purposegames.com/game/brain-stuffn-such
https://www.purposegames.com/game/OHDroUcZ7Rv
https://www.purposegames.com/game/another-brain-model
https://www.purposegames.com/game/neuron-division
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
On a basic level how does the nervous system work?
1) Monitor
environmental
changes (inside and
outside body)
*Afferent
2) Process and interpret
input and decide
what to do.
*Brain/cord
3) Cause a response;
activate (action)
organs (muscles and
glands)
*Efferent
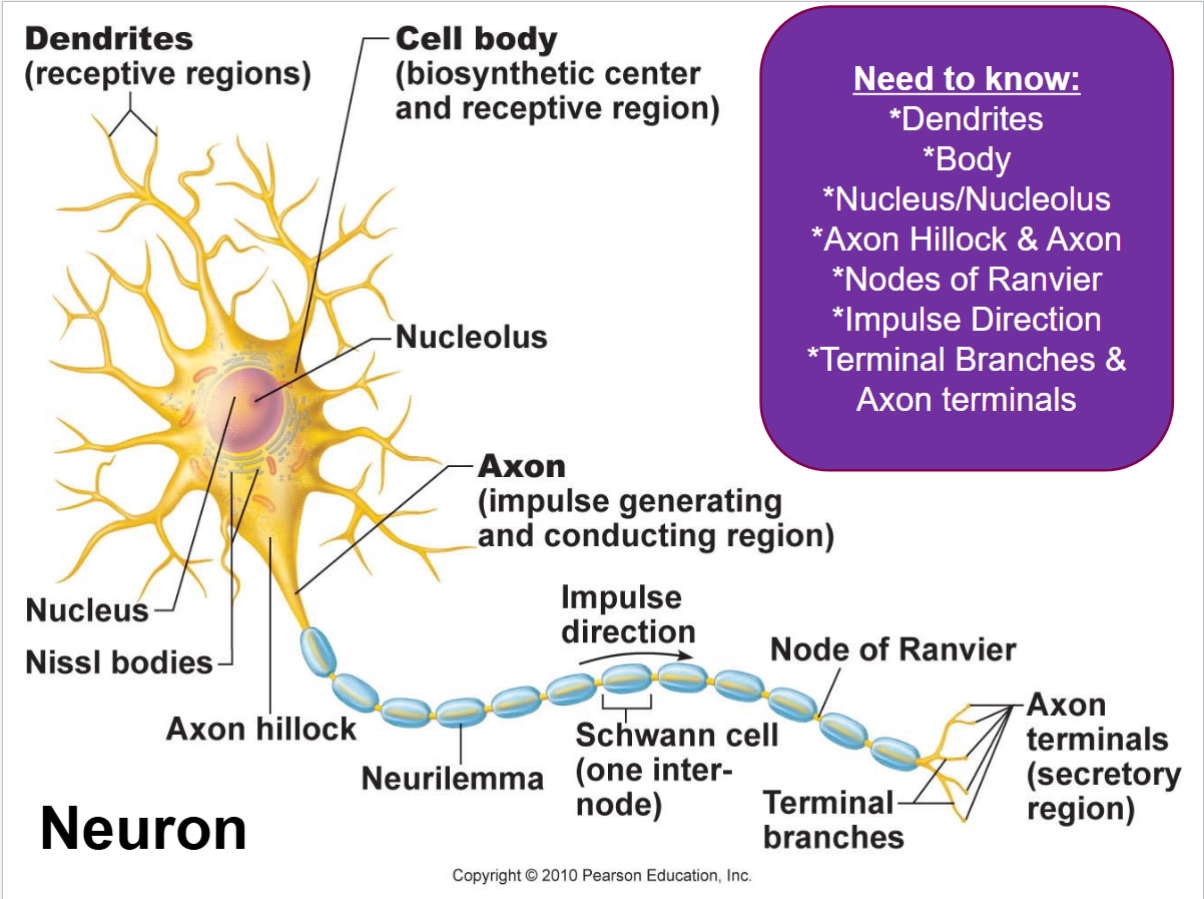
Know where everything is for the whole diagram of a neuron
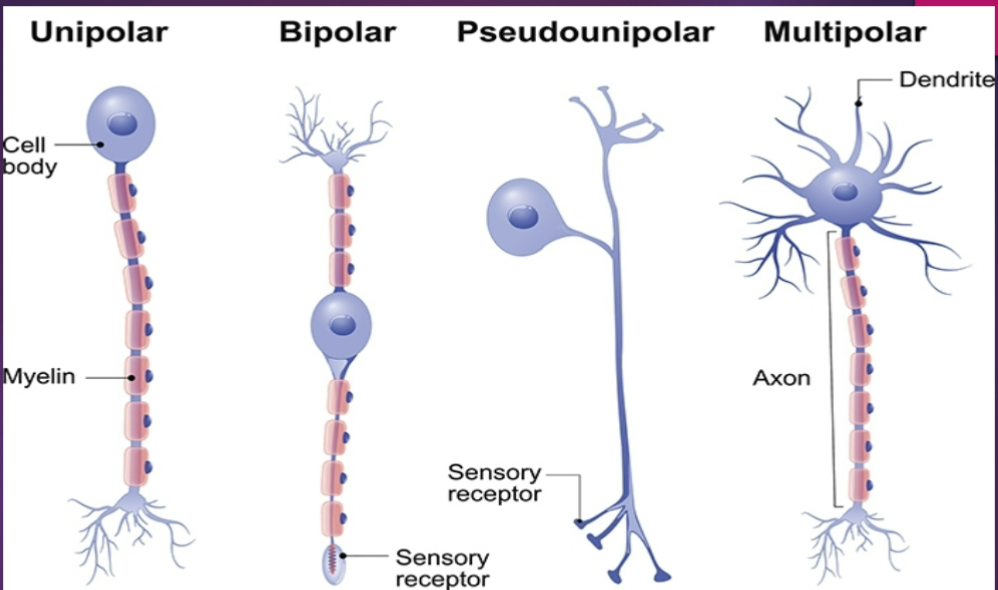
What are the four different types of neurons?
Unipolar, Bipolar, Psuedounipolar, Multipolar
Multiple Sclerosis
Autoimmune disorder
causing destruction of myelin
sheaths in CNS
sheaths become scars or
plaques
1/2 million people in the
United States and rising
appears between ages 20
and 40
females twice as often as
males
Symptoms include muscular
weakness, abnormal
sensations or double vision
and an intention tremor
Remissions & relapses result
in progressive, cumulative
loss of function
Multiple Sclerosis
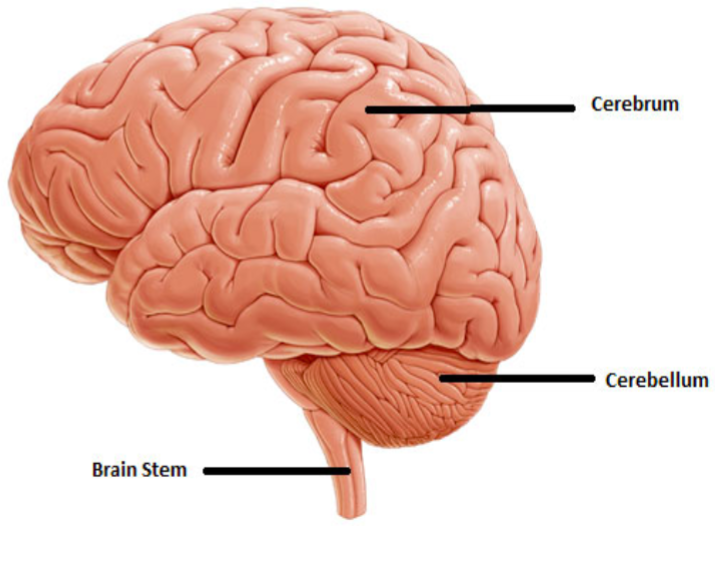
Gross Anatomy of the brain (3 parts)
1) Cerebrum– “thinking”
—Conscious thought
2)Cerebellum– Coordinated movement
3) Brain Stem– “unconscious”
—Autonomic function
White Matter vs Gray Matter
White matter = myelinated processes (white in color)
Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons
and neuroglia (gray color)
In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white
matter
In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters
called nuclei inside the CNS
Gray vs White Matter
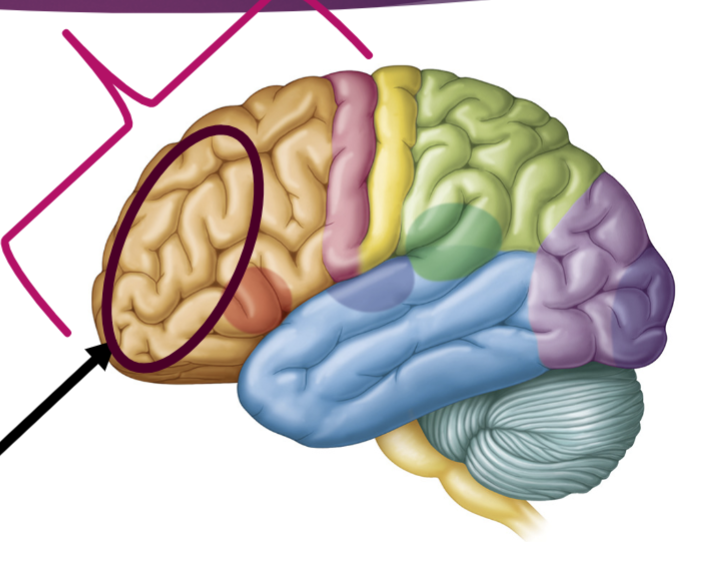
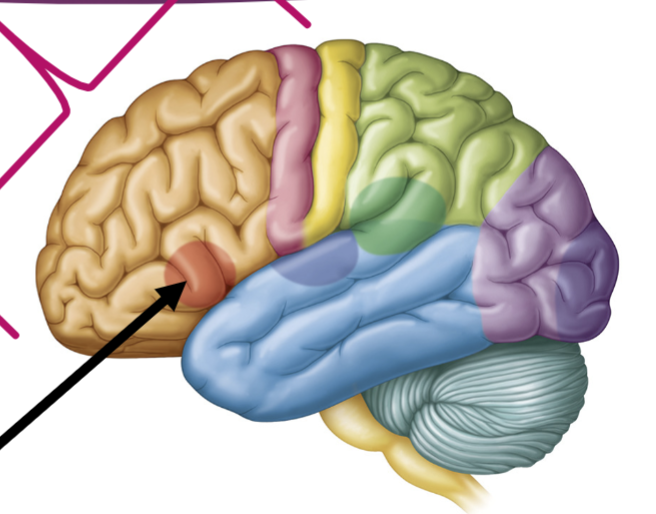
What is the arrow pointing to?
Prefrontal Cortex-(Tan w/in circle)
• Personality
• Decision Making
• Impulse Inhibitions
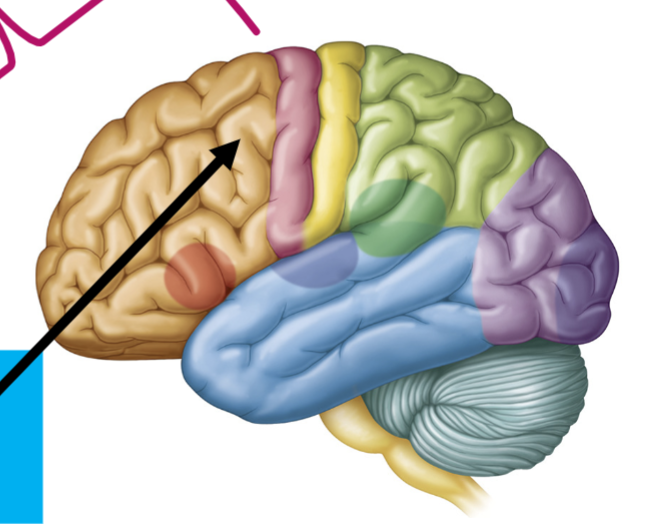
What is the arrow pointing to?
Primary Motor Cortex-(Red)
“voluntary motor commands”
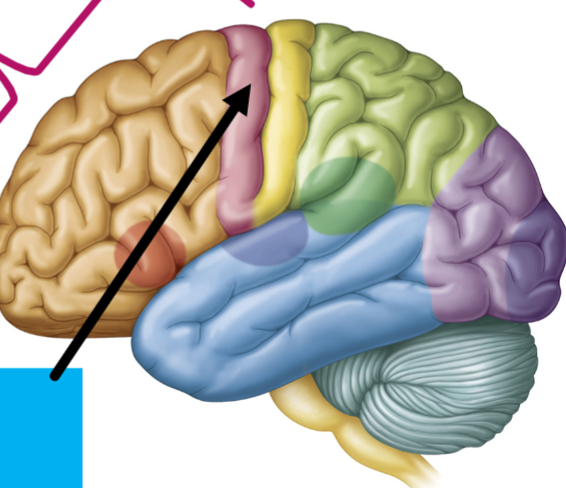
What is the arrow pointing to?
Premotor Cortex-(Tan)
“motor planning”
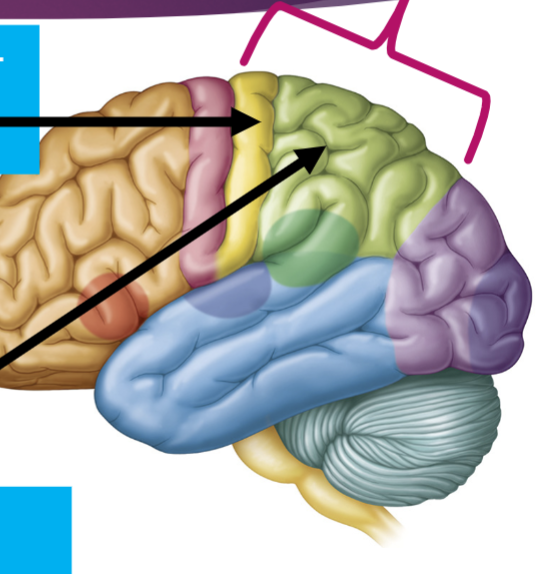
What is the arrow pointing to?
Broca’s Area-(Orange)
“Speech production”
What are the two arrow pointing to?
—Primary Somatosensory Cortex-(Yellow)
“Sensory receiving”
—Somatosensory Association Area-(Lime Green)
“Sensory Processing”
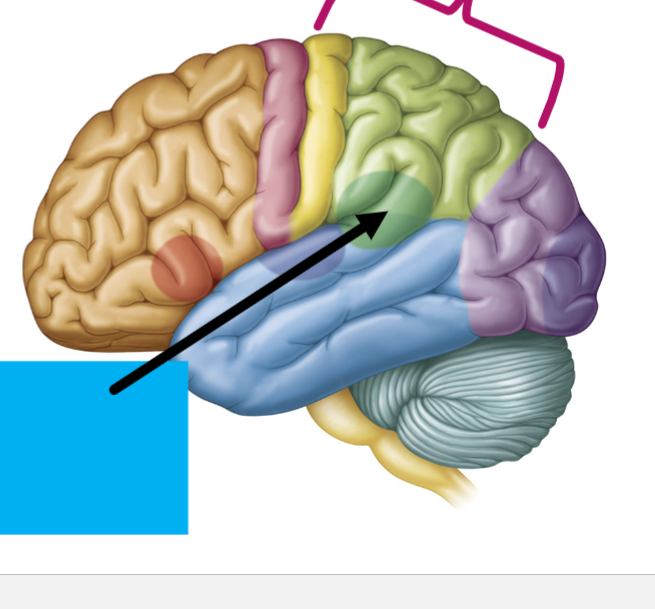
What is the arrow pointing to?
Wernicke’s Area-(Green)
“language interpretation”
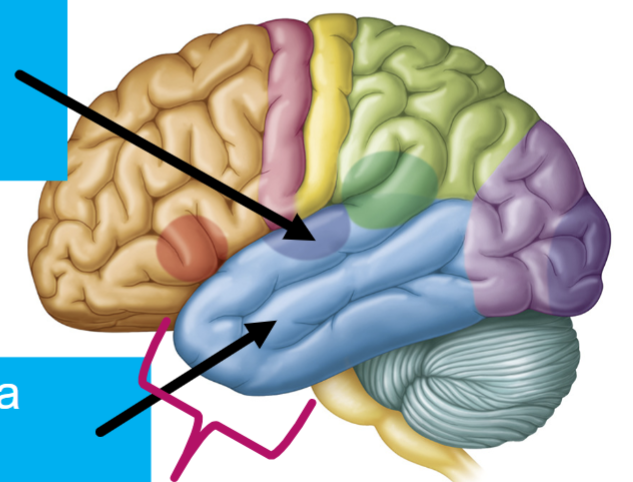
What are these two arrows pointing to?
—Primary Visual Cortex-(Dark purple)
Receiving Sensory Info
“visual perception”
—Visual Association Area-(Light purple)
Processing Visual Information
“image interpretation
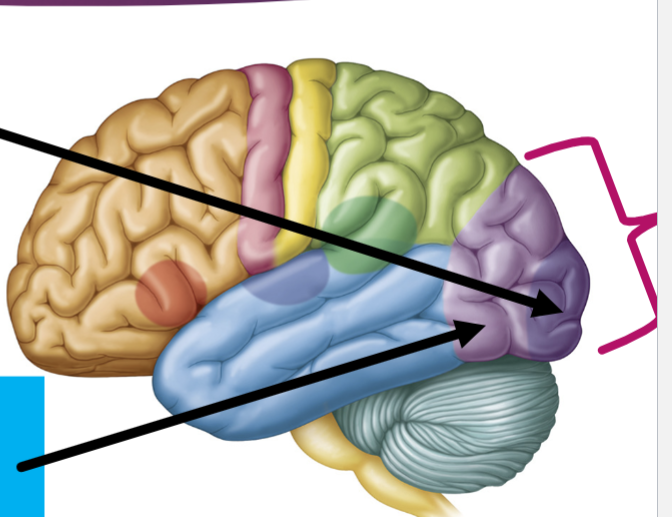
What are these two arrows pointing to?
—Primary Auditory Cortex-(Dark blue)
Receiving Auditory Info
”sound perception”
—Auditory Association Area-(Blue)
Processing Auditory Info
“sound interpretation”
Hydrocephalus
“Water on the Brain”
Congenital: @birth
Developmental defects
Genetic disorders
Acquired: later
Infections (ie.meningitis)
Bleeding in the brain
Tumors
Trauma
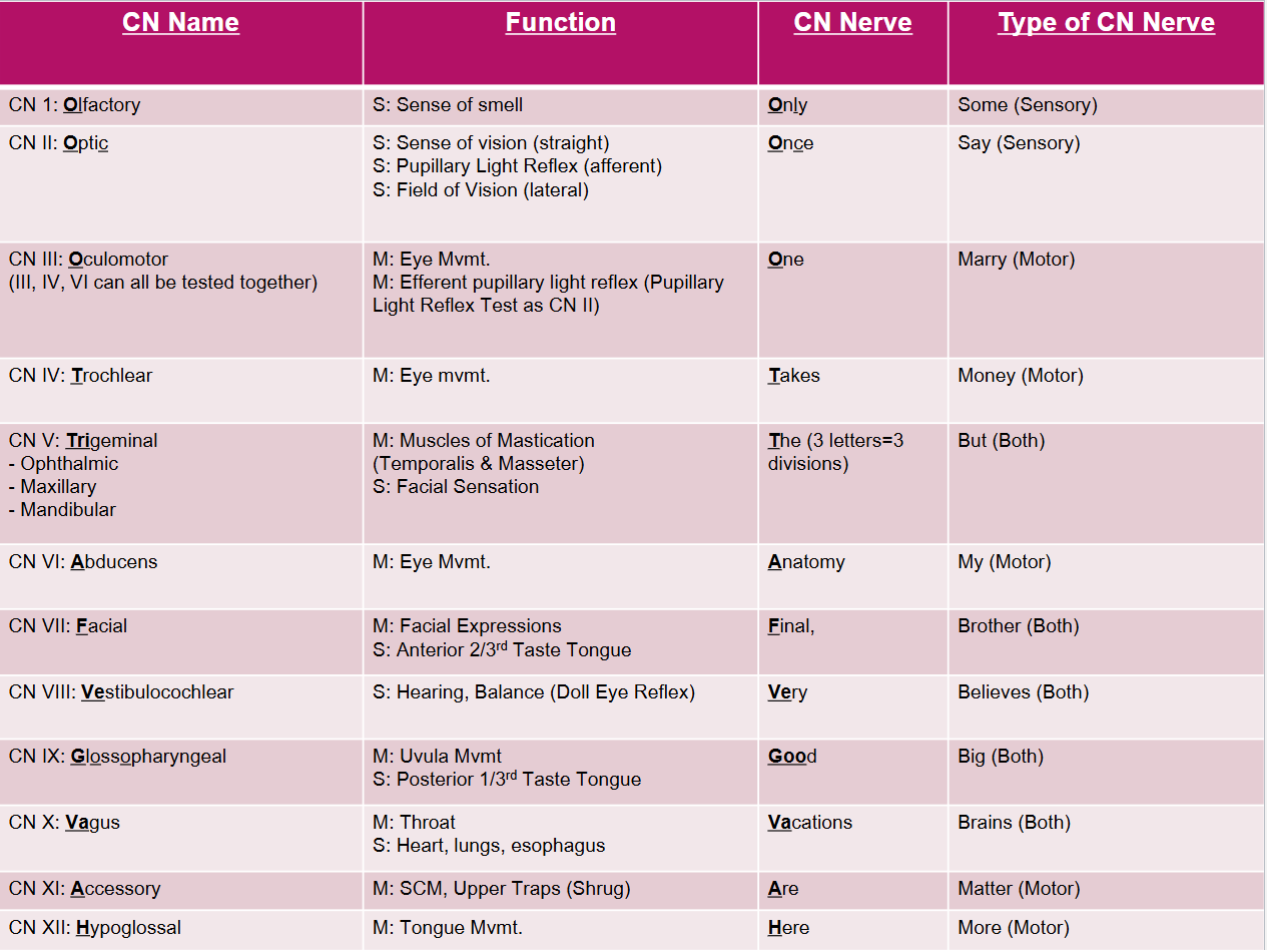
CN I: Olfactory
Sensory nerve of smell
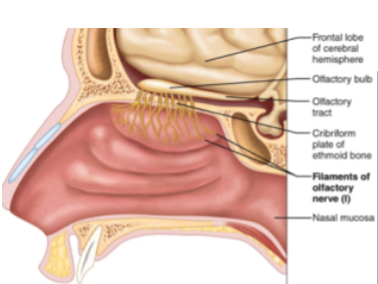
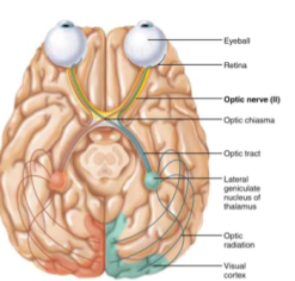
CN II: Optic
Sensory nerve of vision
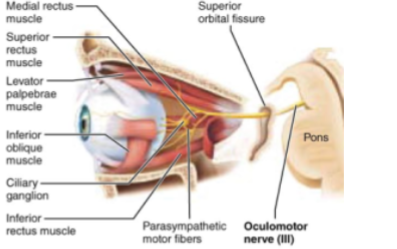
CN III: Oculomotor
Motor nerve of eye movement
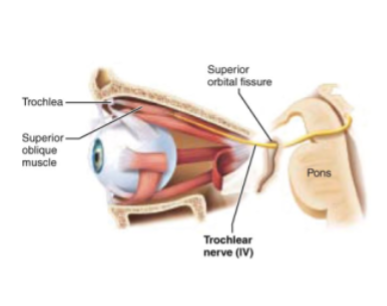
CN IV: Trochlear
Motor nerve of eye movement
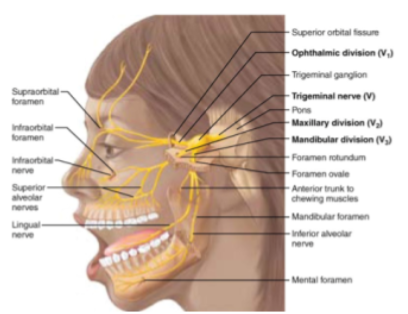
CN V: Trigeminal
—Motor nerve of chewing —Sensory nerve of forehead, scalp, and cheek
CN VI: Abducens
Motor nerve of eye movement
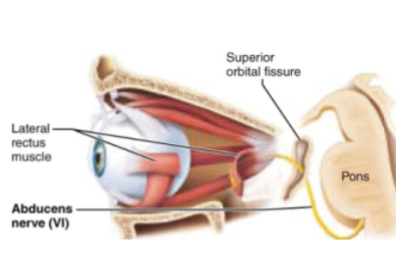
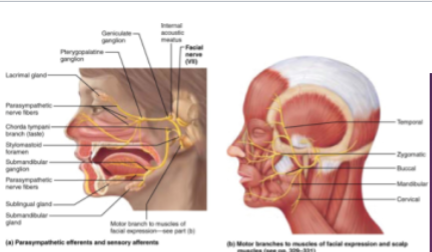
CN VII: Facial
—Motor nerve of face and scalp movement —Sensory nerve of taste and ear sensation
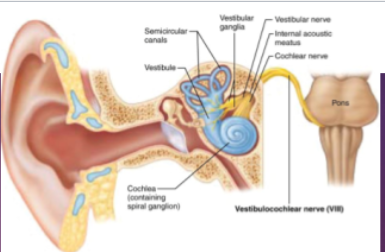
CN VIII: Vestibulocochlear
—Motor (efferent) nerve fibers adjust sensitivity of receptors —Sensory nerve of hearing and balance
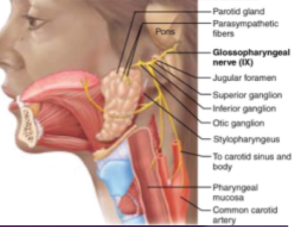
CN IX: Glossopharyngeal
—Motor nerve of throat movement —Sensory nerve of tongue and throat
CN X: Vagus
—Parasympathetic motor nerve fibers of peristalsis, blood pressure, heart rate —Sensory nerve of taste
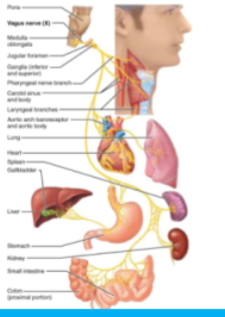
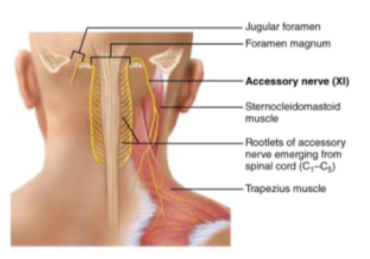
CN XI: Accessory
Motor nerve of swallowing and head & shoulder movements
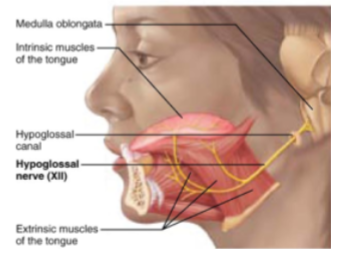
CN XII: Hypoglossal
Motor nerve of swallowing and speech
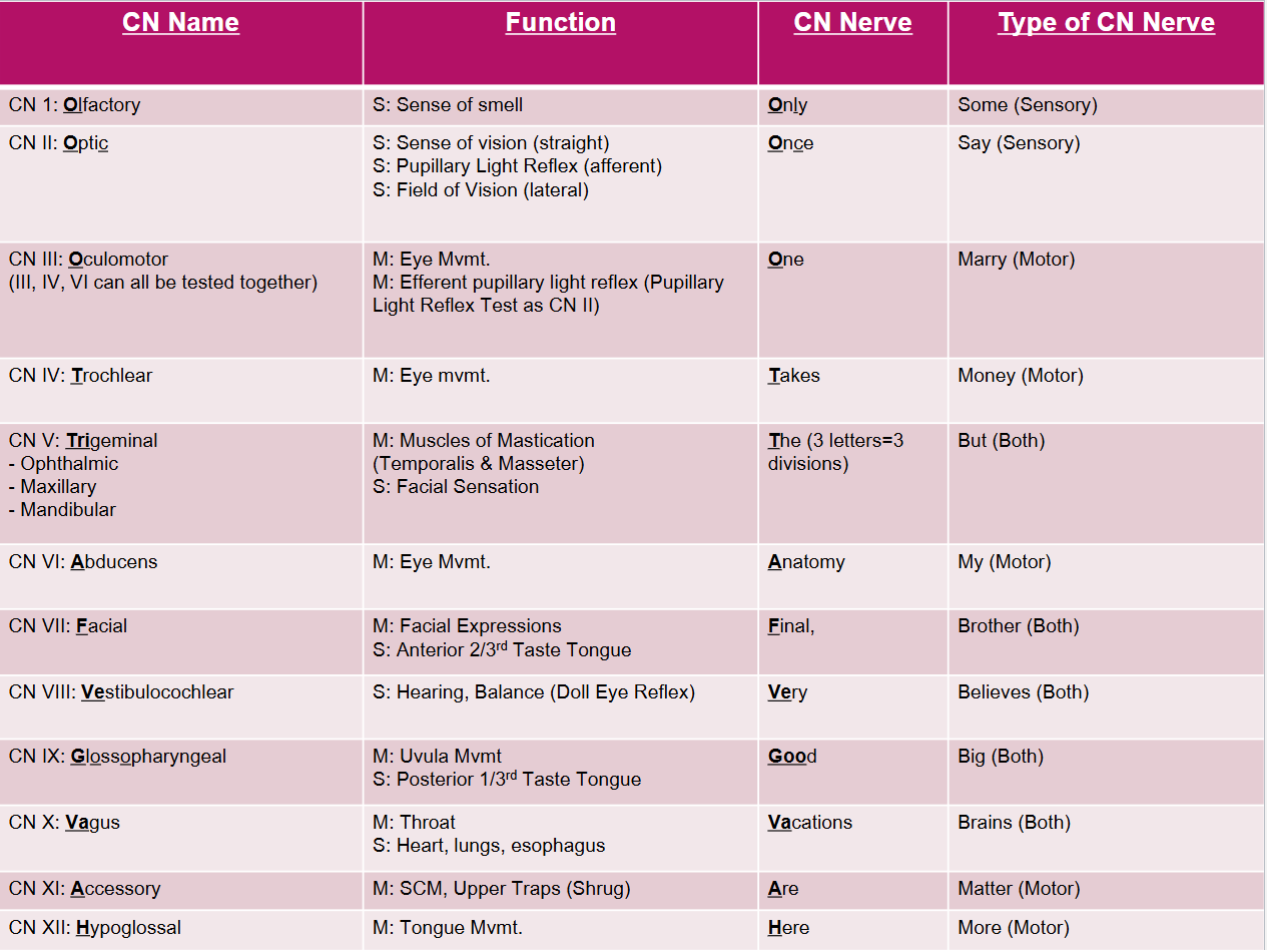
Not a question just a useful chart
Not a question just a useful chart
Lab Manuel Question #1: What structures make up the CNS?
Brain and Spinal Cord
Lab Manuel Question #2: What are the 3 parts of the brain?
Cerebrum, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem
Lab Manuel Question #3: What does CSF stand for?
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Lab Manuel Question #4: Which Brodmann’s Areas are the 2 parts of a conversation?
44 and 45 (Broca’s Area) NGL I looked this up but some also say 22 bc that’s Wernicke’s area too but no clue if its included*
Lab Manuel Question #5: Which 3 Cranial Nerves control the extraocular m. movements?
III, IV, & VI
Lab Manuel Question #6: Which lobe of the brain houses each other following? 1) Hearing? 2)Vision? 3)Sensation? 4)Motor Commands?
Hearing—Temporal Lobe Vision—Occipital Lobe Sensation: Parietal Lobe Motor Command: Frontal Lobe
Lab Manuel Question #7: What structure contains 200 million+ axons and is the communication between the brain’s hemispheres?
Corpus Callosum
Lab Manuel Question #8: The word for sensory information is…?
Afferent
Lab Manuel Question #9: What structure secretes CSF into the ventricular flow?
Choroid Plexus
Lab Manuel Question #10: Which Cranial Nerves are sensory only?
I & II
Lab Manuel Question #11: Which Cranial Nerves are motor only?
III, IV, VI, XI, & XII
Lab Manuel Question #12: Which Glial Cell creates the myelin sheath in the PNS?
Schwann Cells
Lab Manuel Question #13: Which Brodmann’s/functional area of the brain houses the personality?
prefrontal cortex
Lab Manuel Question #14: Where does the CSF travel after the third ventricle?
Cerebral Aqueduct
Lab Manuel Question #15: Folds of the cerebral cortex are called what?
Gyri (grooves are sulci)