HTHS 1110 Final Exam Weber State
1/318
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 9 and 10 wouldn't let me upload pictures noooo man.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
319 Terms
Free and encapsulated nerve endings serve which function of the integument?
a. dermatoglyphics (fingerprints)
b. immunologic defense
c. protection
d. sensory perception
e. thermoregulation
d. sensory perception
Keratin, lipid, and sebum help provide:
a. dermatoglyphics (fingerprints)
b. elasticity
c. immunologic defense
d. permeability barrier
e. sensory perception
d. permeability barrier
Which layer associated with the integument is made of loose connective tissue and lots of fat?
a. dense irregular connective tissue
b. dense regular connective tissue
c. dermis
d. epidermis
e. subcutaneous
e. subcutaneous
Sweat glands, blood vessel, and fat provide which function of the integument?
a. dermatoglyphics (fingerprints)
b. immunologic defense
c. protection
d. sensory perception
e. thermoregulation
e. thermoregulation
Which layer of the skin contains blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and glands?
a. dermis
b. epidermis
c. hair root layer
d. subcutaneous layer
a. dermis
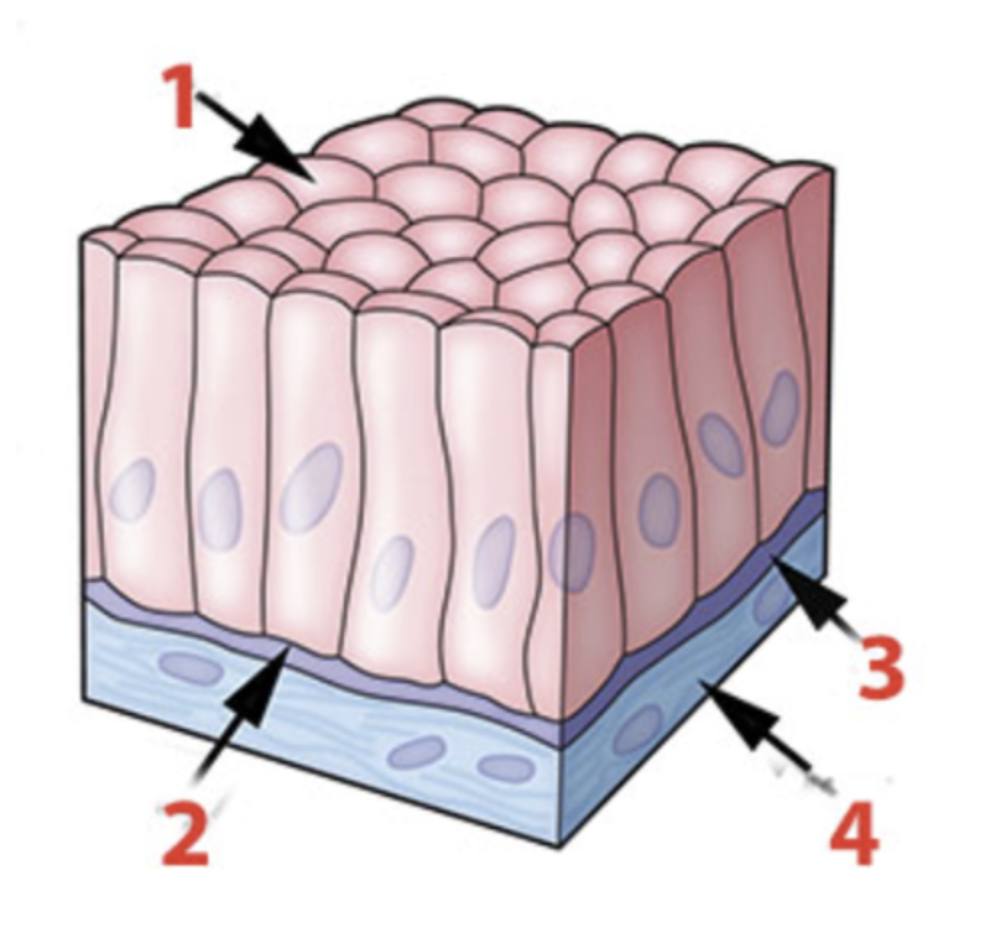
Identify the structure of the integument identified by the number 1?
a. dermis
b. epidermis
c. subcutaneous
b. epidermis
Identify the structure of the integument identified by number 3?
a. dermis
b. epidermis
c. subcutaneous
c. subcutaneous
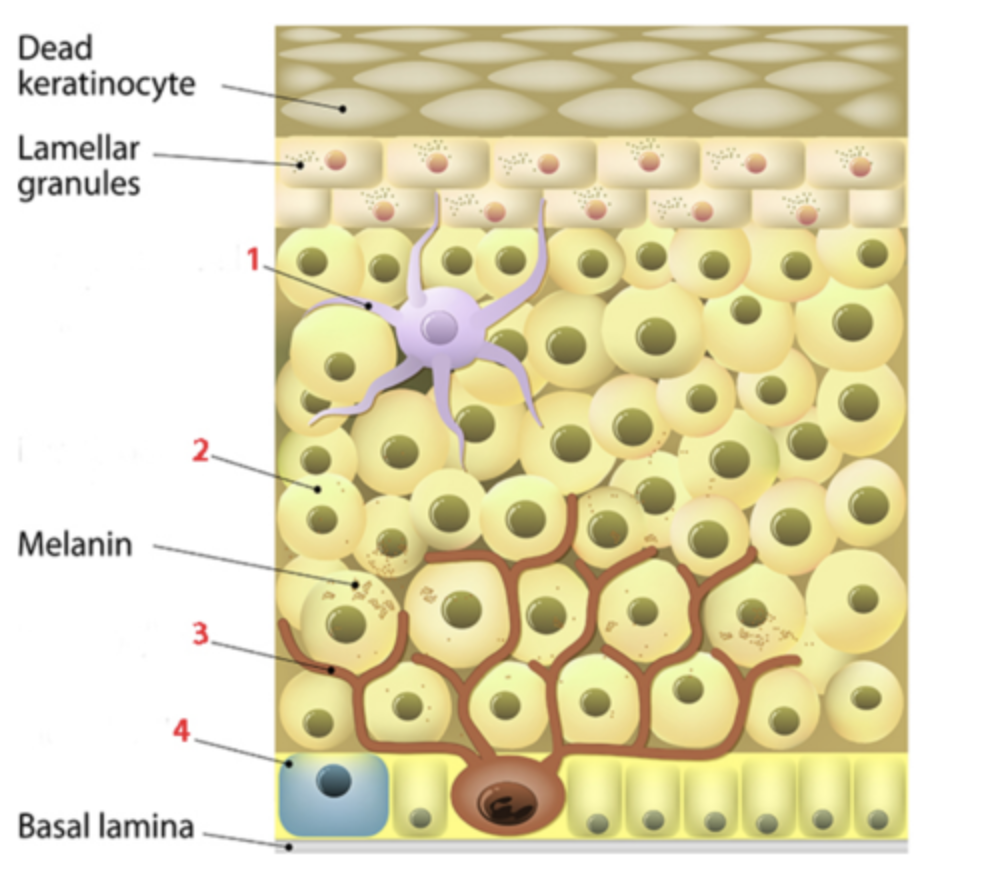
Identify the cell at number 4, which is a sensory cell in epidermis?
a. keratinocyte
b. Langerhans cell
c. melanocyte
d. Merkel cell
d. Merkel cell
Stratified squamous epithelium, along with keratin and melanin, provide which function of the integument?
a. dermatoglyphics (fingerprints)
b. immunologic defense
c. protection
d. sensory perception
e. thermoregulation
c. protection
Which layer of the integument is avascular?
a. dense irregular connective tissue
b. dense regular connective tissue
c. dermis
d. epidermis
e. subcutaneous
d. epidermis
The epidermal layer immediately superficial to the stratum basale is the:
a. stratum corneum
b. stratum granulosum
c. stratum lucidum
d. stratum spinosum
d. stratum spinosum
What cells in the epidermis manufacture pigment granules that give the skin its color?
a. keratinocytes
b. Langerhans cells
c. melanocytes
d. Merkel cells
c. melanocytes
Cells in the epidermis that function to destroy microbes are called ____________.
a. keratinocytes
b. Langerhans cells
c. melanocytes
d. Merkel cells
b. Langerhans cells
Which list has the layers of the epidermis in the connect order from deep to superficial?
a. DEEP︱stratum basale, stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum lucidum︱SUPERFICIAL
b. DEEP︱stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum corneum︱SUPERFICIAL
c. DEEP︱stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum︱SUPERFICIAL
d. DEEP︱stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale︱SUPERFICIAL
c. DEEP︱stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum︱SUPERFICIAL
Sudoriferous glands are more numerous in:
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum lucidum
d. thick skin
e. thin skin
d. thick skin
Thick skin is primarily located:
a. above the eyelids
b. everywhere except the palms, fingertips, and soles of the feet
c. in the palms, fingertips, and soles of the feet
d. in the umbilical regions
c. in the palms, fingertips, and soles of the feet
Hair follicles are present to:
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum lucidum
d. thick skin
e. thin skin
e. thin skin
Keratin and lamellar granules (lipids) in the epidermis function to _________ the tissue.
a. degrade
b. expand
c. shrink
d. waterproof
d. waterproof
What cells in the epidermis manufacture pigment granules that give the skin its color?
a. keratinocytes
b. Langerhans cells
c. melanocytes
d. Merkel cells
c. melanocytes
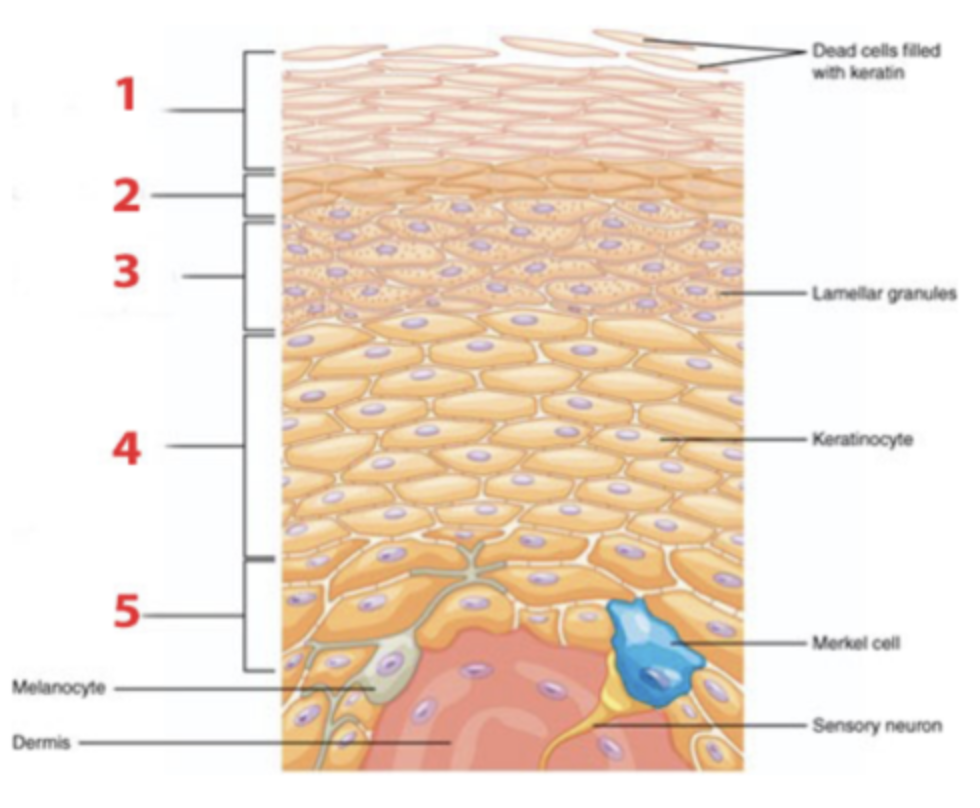
Which layer of the epidermis is identified by number 5?
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum granulosum
d. stratum lucidum
e. stratum spinosum
a. stratum basale
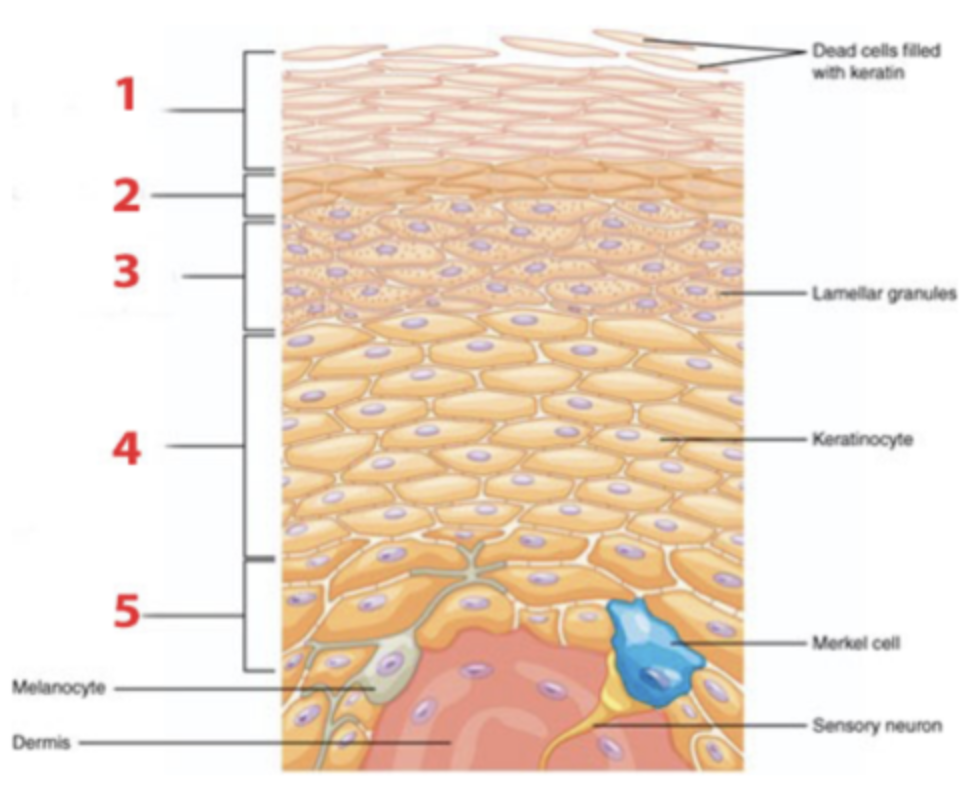
Cells in the epidermis that function as light-touch receptors are called ____________.
a. keratinocytes
b. Langerhans cells
c. melanocytes
d. Merkel cells
d. Merkel cells
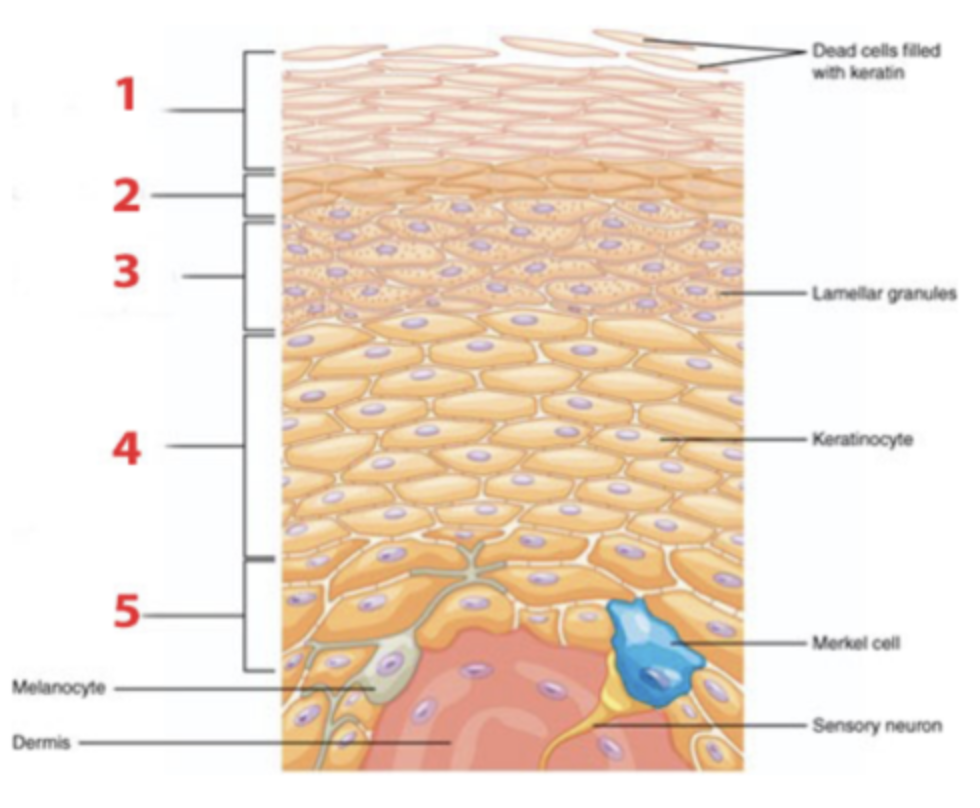
Which layer of the epidermis is identified by number 1?
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum granulosum
d. stratum lucidum
e. stratum spinosum
b. stratum corneum
Which layer of the epidermis is identified by number 2?
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum granulosum
d. stratum lucidum
e. stratum spinosum
d. stratum lucidum
Which layer of the
Which layer of the epidermis generates new keratinocytes by mitosis?
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum granulosum
d. stratum lucidum
e. stratum spinosum
a. stratum basale
The epidermal layer of thick skin immediately deep to the stratum corneum is the:
a. stratum basale
b. stratum granulosum
c. stratum lucidum
d. stratum spinosum
c. stratum lucidum
Lipids coating keratinocytes help make skin:
a. more sensitive
b. pigmented
c. structurally strong
d. waterproof
d. waterproof
Which epidermal layer is prominent in thick skin but not in thin skin?
a. stratum basale
b. stratum granulosum
c. stratum lucidum
d. stratum spinosum
d. stratum lucidum
Identify the cell at number 3, which is a pigment producing cell of the epidermis.
a. keratinocyte
b. Langerhans cell
c. melanocyte
d. Merkel cell
c. melanocyte
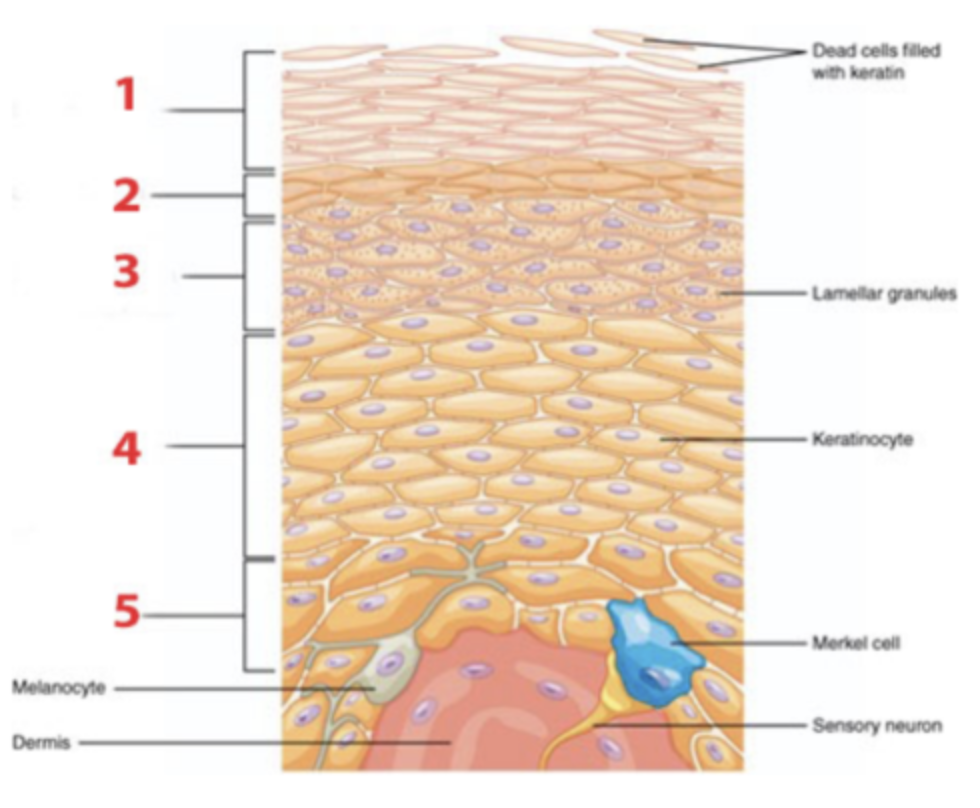
Which layer of the epidermis is identified by the number 4?
a. stratum basale
b. stratum corneum
c. stratum granulosum
d. stratum lucidum
e. stratum spinosum
e. stratum spinosum
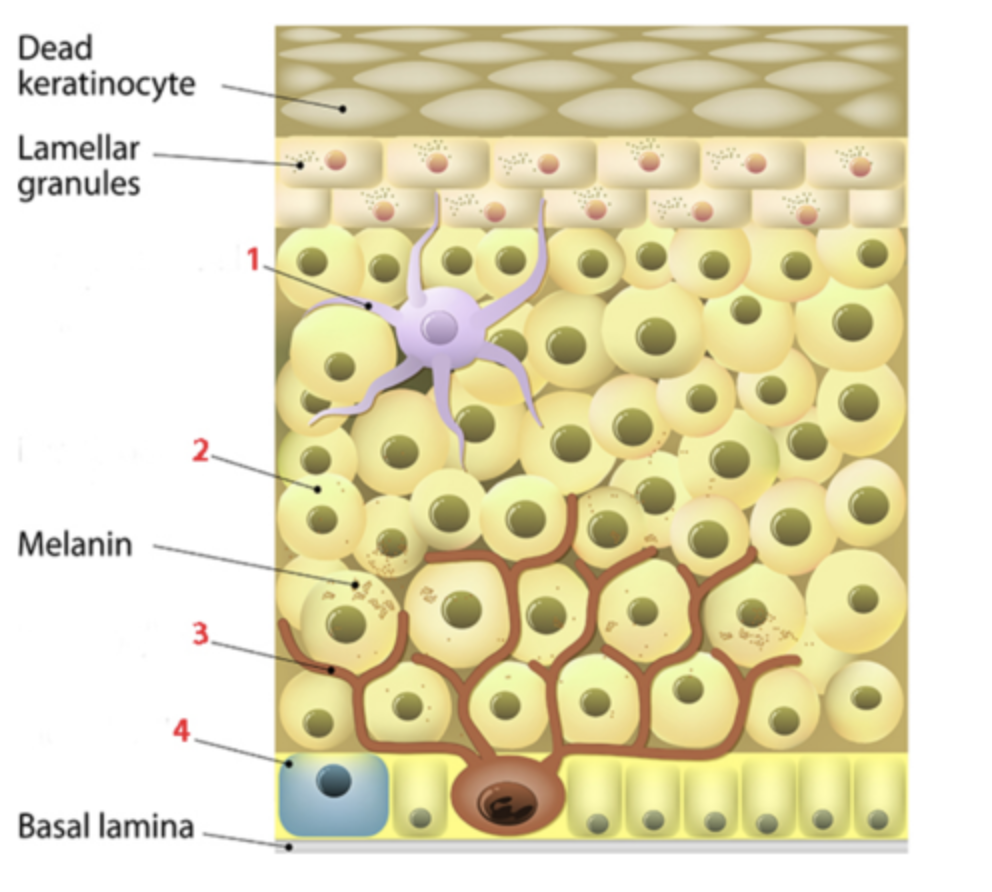
Which organelle found in melanocytes transfers the melanin pigments to keratinocytes?
a. carotenosomes
b. diffusion
c. hemoglobin
d. melanosomes
d. melanosomes
The pinkish color of skin is due to circulating __________.
a. bilirubin
b. carotene
c. hemoglobin
d. melanocytes
c. hemoglobin
Which of the following are pigments produced by melanocytes?
a. eumelanin and pheomelanin
b. eumelanin and hemoglobin
c. pheomelanin and carotene
d. pheomelanin and bilirubin
a. eumelanin and pheomelanin
Which epidermal skin pigment absorbs ultraviolet (UV) energy?
a. bilirubin
b. carotene
c. keratin
d. melanin
d. melanin
In which region of the dermis are the Meissner corpuscles and free nerve endings located?
a. adipose region
b. papillary region
c. reticular region
d. subcutaneous region
b. papillary region
Leather is made from the dermis of animals. Leather’s strength and flexibility is attributed to the prevalence of _______ fibers.
a. actin
b. collagen
c. integrin
d. keratin
b. collagen
Which structures provide tensile (stretching and pulling) strength to the dermis?
a. arrector pili muscles
b. sebaceous glands
c. sudoriferous glands
d. collagen and elastin fibers
d. collagen and elastin fibers______
___________ is the main physiological function of the subcutaneous layer compared to the epidermis and dermis.
a. Absorption
b. Healing and thermoregulation
c. Insulation
d. Protection
c. Insulation
Which of the following layers forms an insulation blanket to help maintain normal body temperature?
a. the dermal layer
b. the epidermal layer
c. the sensory layer
d. the subcutaneous layer
d. the subcutaneous layer
The subcutaneous layer serves as a storage depot for ___________.
a. carbohydrates
b. proteins
c. triglycerides and cholesterol
d. vitamins and minerals
c. triglycerides and cholesterol
____________ and ____________ pass through the areolar connective tissue of the subcutaneous layer.
a. Blood vessels; ligaments
b. Blood vessels; nerves
c. Blood vessels; tendons
d. Nerves; tnedons
b. Blood vessels; nerves
Eccrine and apocrine are both types of __________ glands.
a. endocrine
b. holocrine
c. sebaceous
d. sudoriferous
d. sudoriferous
The major function of sebaceous glands is to:
a. secrete an oil like substance, which helps to regulate body temperature
b. secrete an oil like substance, which serves to keep the skin and hair soft and pliable
c. secrete sweat, which can evaporate to help cool the body
d. secrete wax, which serves to trap foreign particles
b. secrete an oil like substance, which serves to keep the skin and hair soft and pliable
The excretory duct of ____________ terminates on the surface of the skin.
a. apocrine sweat glands
b. eccrine sweat glands
c. holocrine glands
d. sebaceous glands
b. eccrine sweat glands
This type of sweat glands is in highest concentration in the skin of the areolae, clitoris and labia minora.
a. apocrine
b. eccrine
c. holocrine
d. sebaceous
a. apocrine
This type of sudoriferous gland is especially active during emotional stress and sexual excitement.
a. apocrine sweat gland
b. eccrine swweat gland
c. endocrine gland
d. sebaceous gland
a. apocrine sweat gland
One of the main differences between apocrine sweat gland and eccrine sweat is that apocrine sweat contains ____________.
a. pheromones
b. salt
c. waste products
d. water
a. pheromones
What type of gland acts as effectors for thermoregulation?
a. endocrine
b. holocrine
c. sebaceous
d. sudoriferous
d. sudoriferous
What is the structure labeled “1”?
a. arrector pili muscle
b. hair matrix
c. hair shaft
d. inner root sheath
e. outer root sheath
c. hair shaft
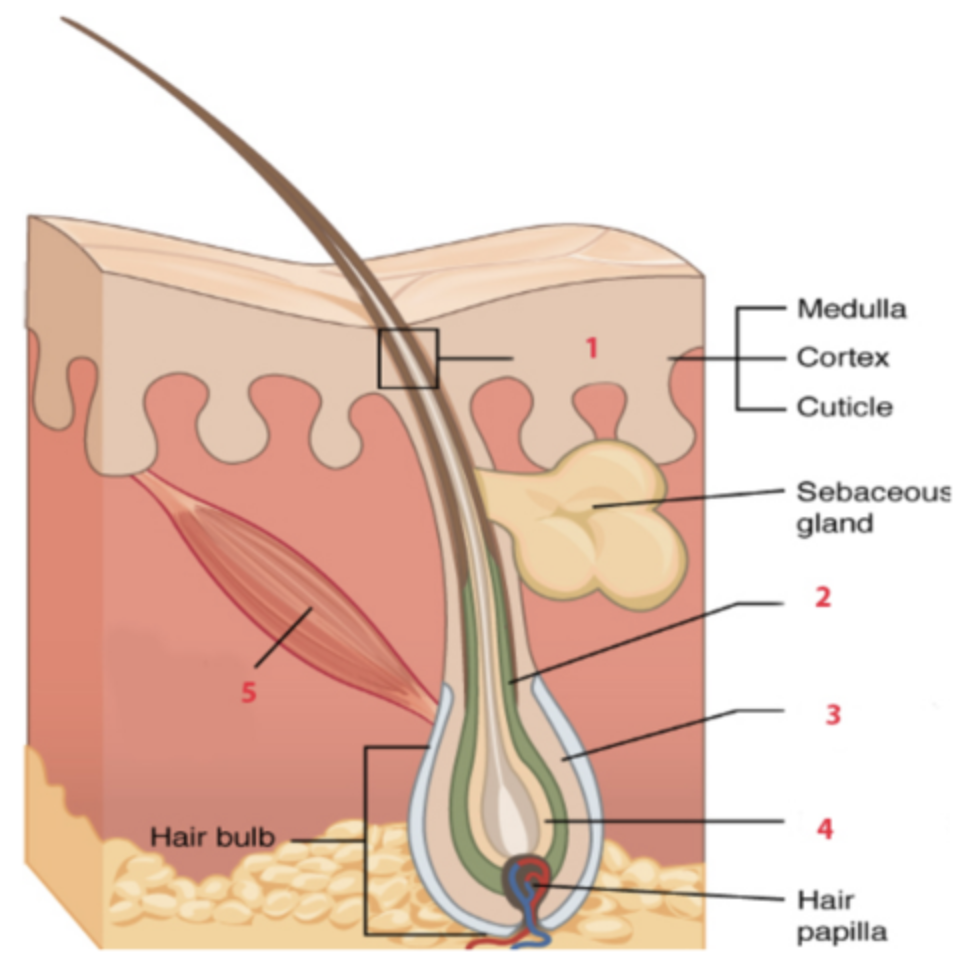
What is the structure labeled “4”?
a. hair shaft
b. inner root sheath
c. outer root sheath
d. hair matrix
e. arrector pili muscle
c. hair matrix
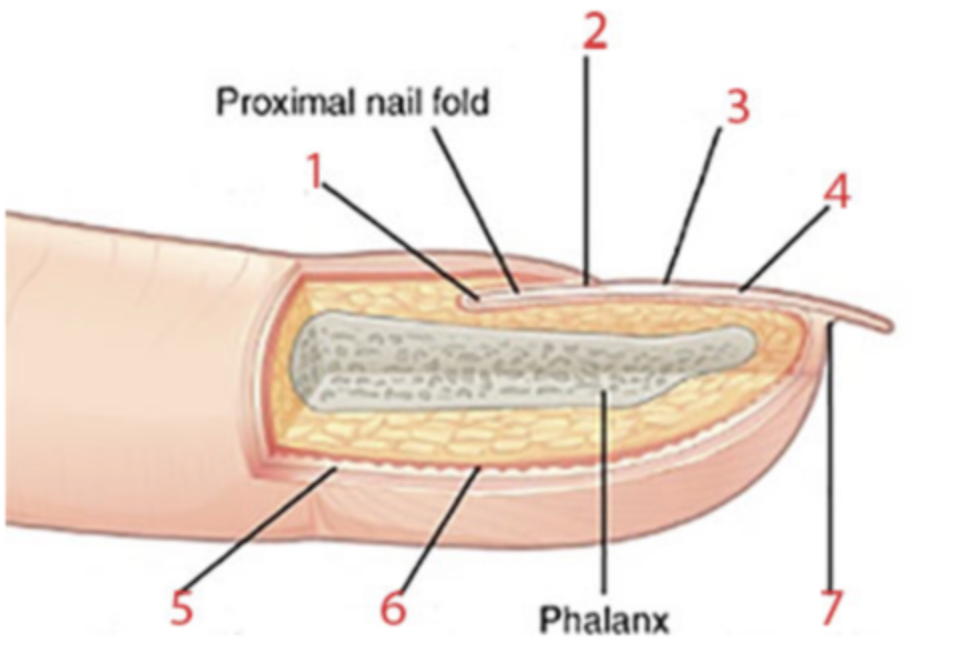
What nail structure is identified by the number 5?
a. dermis
b. epidermis
c. eponychium (cuticle)
d. hyponychium
e. lunula
f. nail body
g. nail root
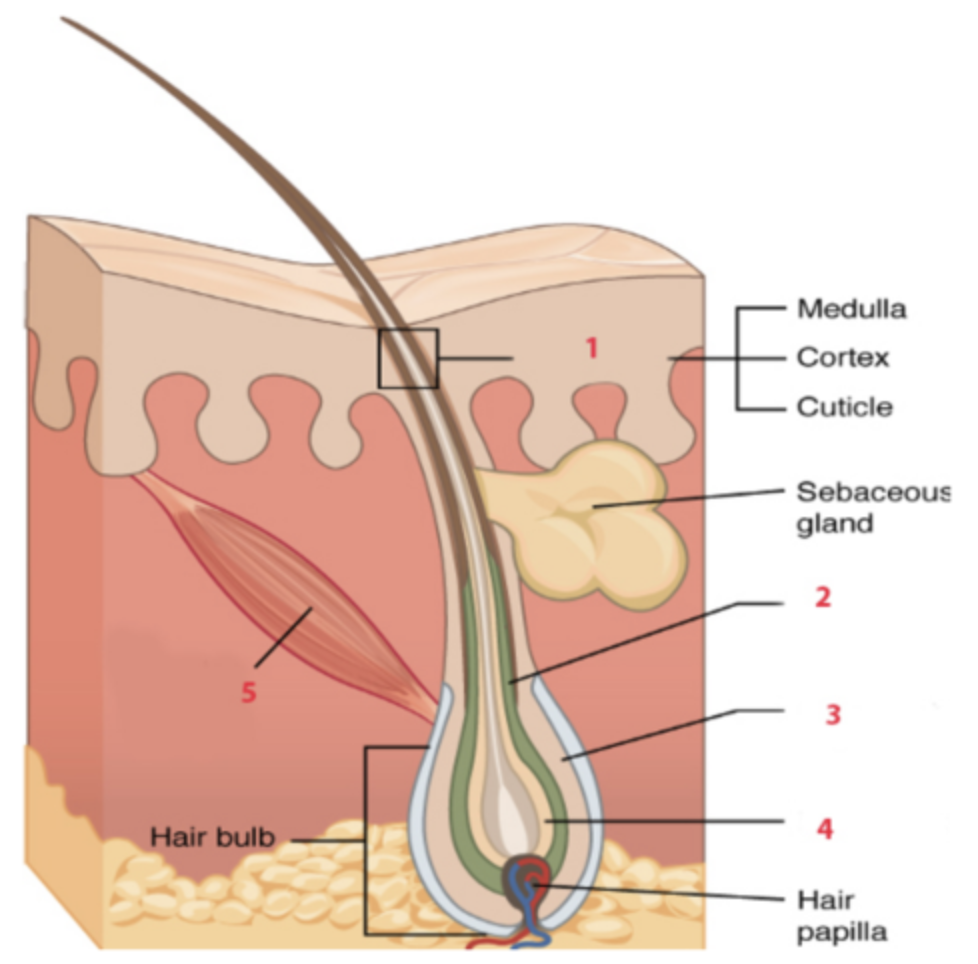
WHat is the structure labeled “3”?
a. arrector pili muscle
b. hair matrix
c. hair shaft
d. inner root sheath
e. outer root sheath
e. outer root sheath
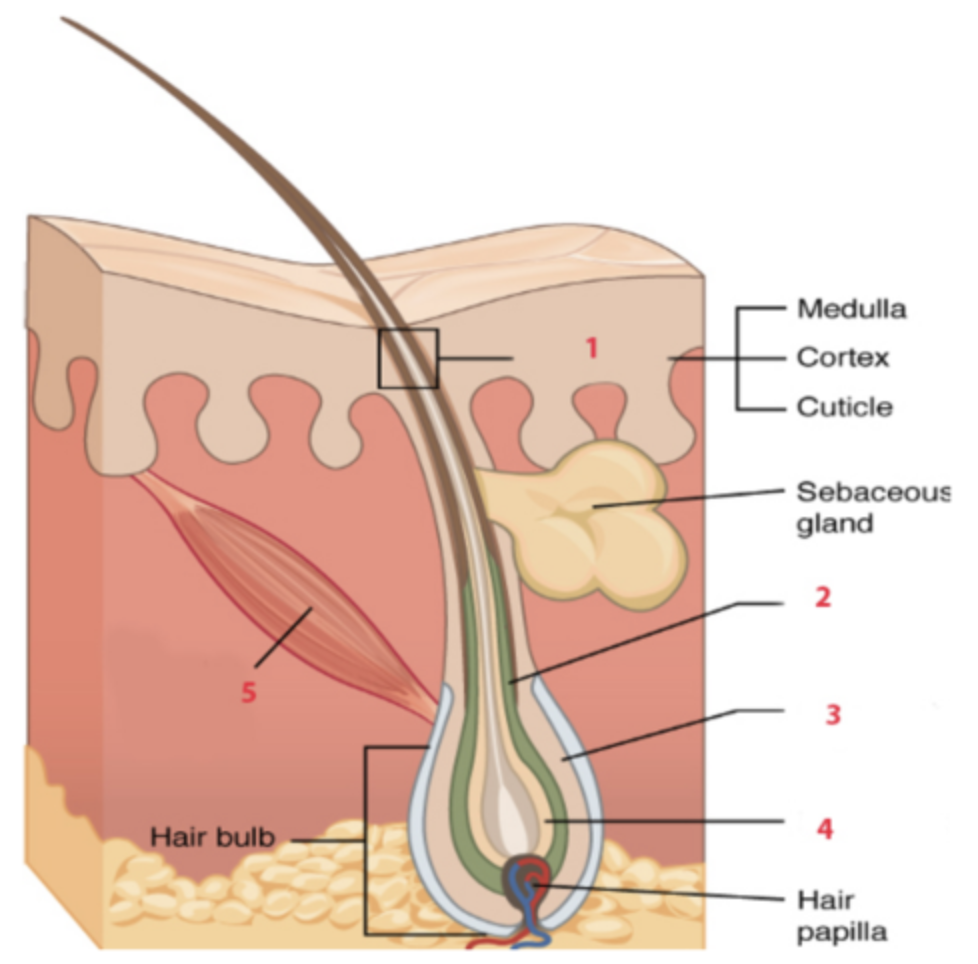
Which stage of the hair-growth cycle is characterized by rapidly dividing cells in the follicle that push the hair shaft up and out, causing the hair to become longer?
a. anagen stage
b. catagen stage
c. telogen stage
a. anagen stage
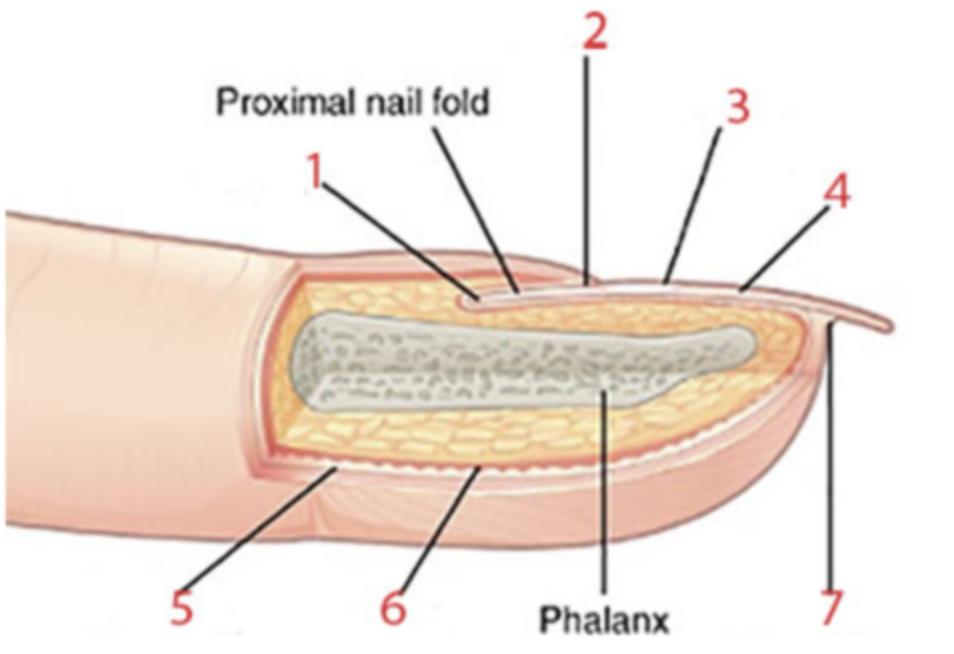
What nail structure is identified by the number 6?
a. dermis
b. epidermis
c. eponychium (cuticle)
d. hyponychium
e. lunula
f. nail body
g. nail root
a. dermis
The stage of the hair-growth cycle is the longest, and continues for two to six years.
a. anagen stage
b. catagen stage
c. telogen stage
a. anagen stage
The three layers of external hairs are, from innermost to outermost, are:
a. cortex, cuticle, medulla
b. cortex, medulla, cuticle
c. cuticle, cortex, medulla
d. cuticle, medulla, cortex
e. medulla, cortex, cuticle
f. medulla, cuticle, cortex
e. medulla, cortex, cuticle
A sign of peripheral vasoconstriction is _______________ skin.
a. orange
b. pale
c. pink or red
d. yellow
b. pale
To increase the core body temperatures, vessels in the dermis constrict. This is an example of __________ feedback.
a. keratin
b. negative
c. positive
d. vasodilatory
b. negative
To decrease the core body temperature, vessels in the dermis dilate. This is an example of ___________ feedback.
a. keratin
b. negative
c. positive
d. vasoconstrictive
b. negative
Nervous tissue:
a. conducts impulses to and from the central nervous system
b. facilitates movement of body parts and substances within the body
c. forms a covering to protect the body from the outside world
d. provides strength and holds organs together
a. conducts impulses to and from the central nervous system
Muscular tissue:
a. conducts impulses to and from the central nervous system
b. facilitates movement of body parts and substances within the body
c. forms a covering to protect the body from the outside world
d. provides strength and holds organs together
b. facilitates movement of body parts and substances within the body
The lumen of the gut tube is lined with:
a. connective tissue
b. epithelial tissue
c. muscular tissue
d. nervous tissue
b. epithelial tissue
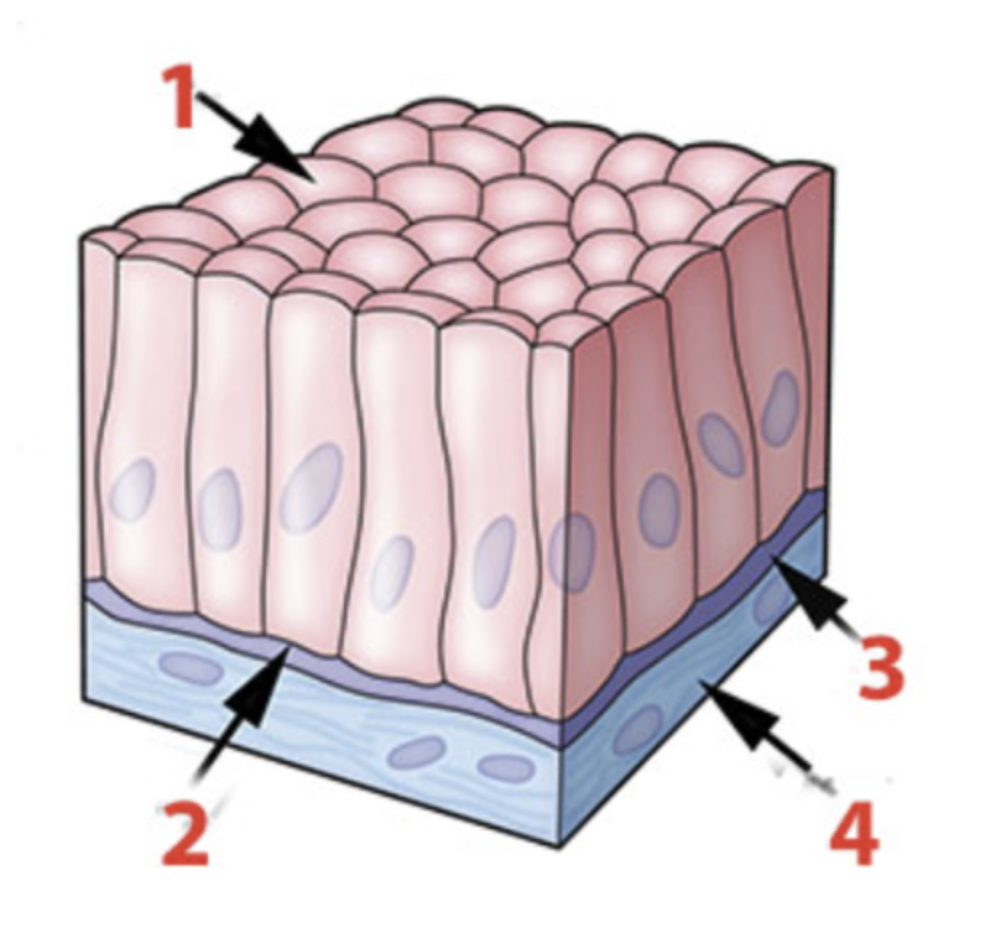
This epithelial tissue appears to be multilayered. However, all cells are in contact with the basal lamina.
a. Columnar
b. Cuboidal
c. Pseudostratified
d. Simple
e. Squamous
f. Stratified
c. Pseudostratified
What epithelial shape or arrangement is identified by the number 4?
a. columnar
b. cuboidal
c. round
d. squamous
d. squamous
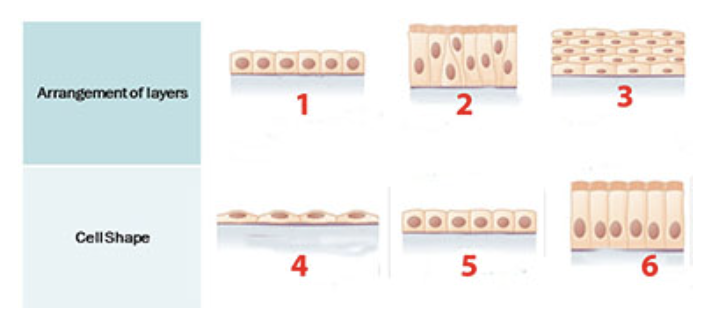
What surface of the epithelial cells is indicated by number 1?
a. apical
b. basal
c. basal lamina
d. connective tissue
e. reticular tissue
a. apical
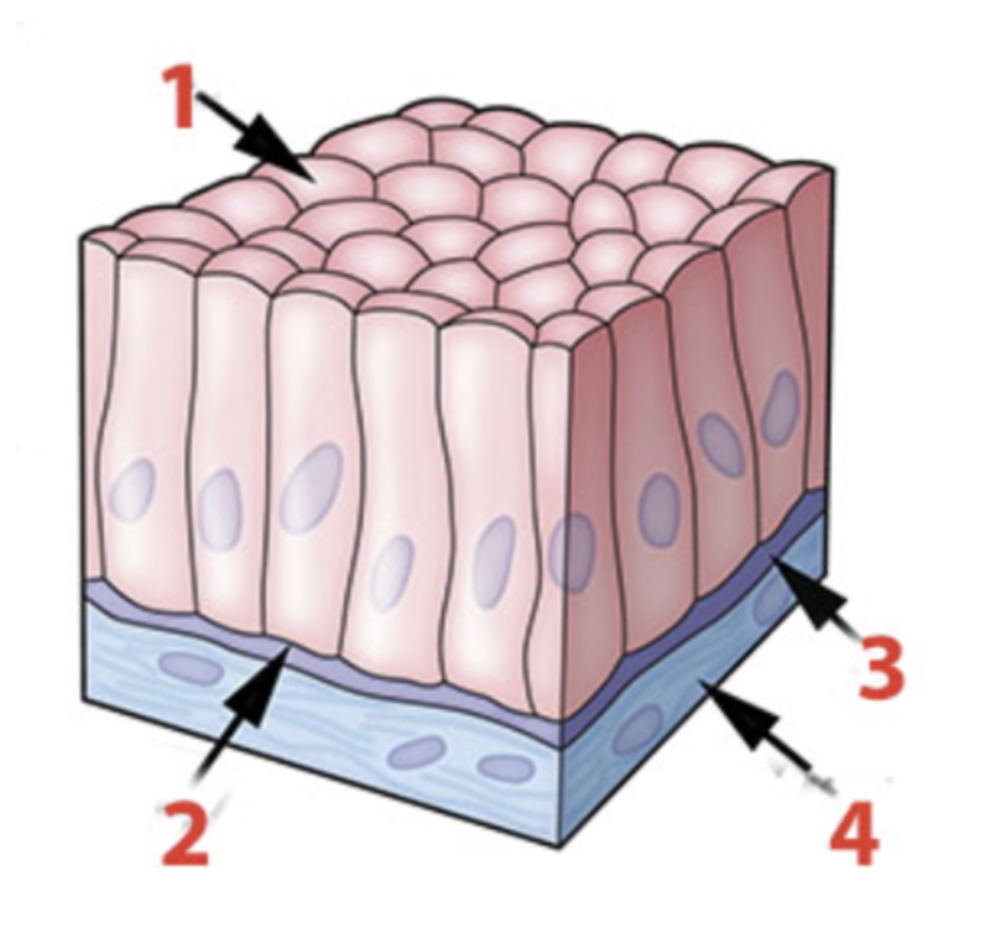
The terms simple, pseudostratified and stratified refer to whether all cells are in contact with:
a. a blood vessel
b. each other
c. the apical surface
d. the basement membrane
d. the basement membrane
______________ cells are epithelial cells that are as wide as they are tall.
a. Columnar
b. Cuboidal
c. Pseudostratified
d. Simple
e. Squamous
f. Stratified
b. Cuboidal
A simple cuboidal epithelium is shown in two places:
a. 1 and 2
b. 1 and 5
c. 2 and 5
d. 4 and 5
b. 1 and 5
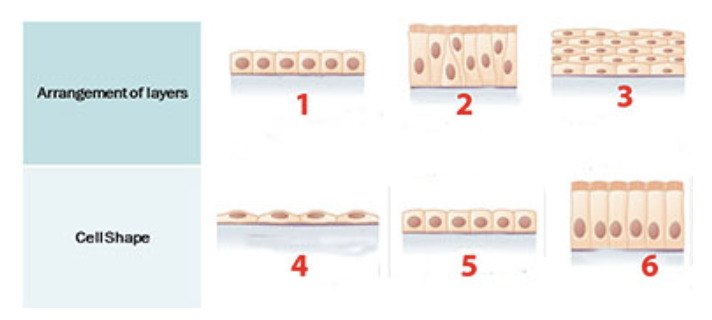
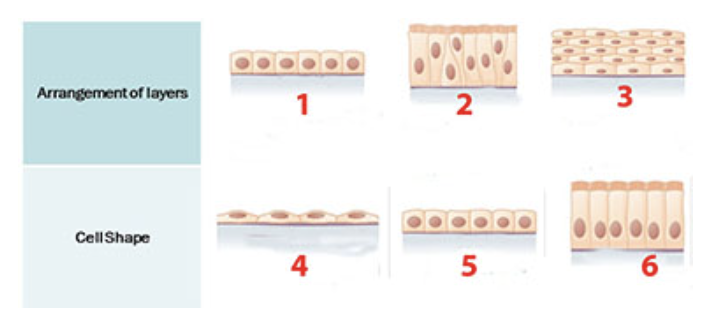
A stratified epithelium is shown at:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
f. 6
c. 3
_________________ are epithelial cells that are taller than they are wide.
a. Columnar
b. Cuboidal
c. Pseudostratified
d. Simple
e. Squamous
f. Stratified
a. Columnar
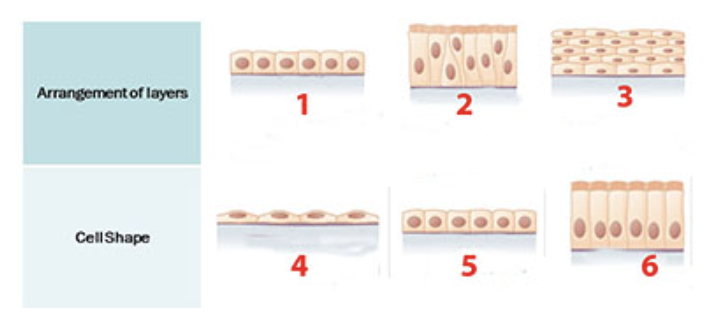
What epithelial shape or arrangement is identified by the number 6?
a. columnar
b. cuboidal
c. round
d. squamous
a. columnar
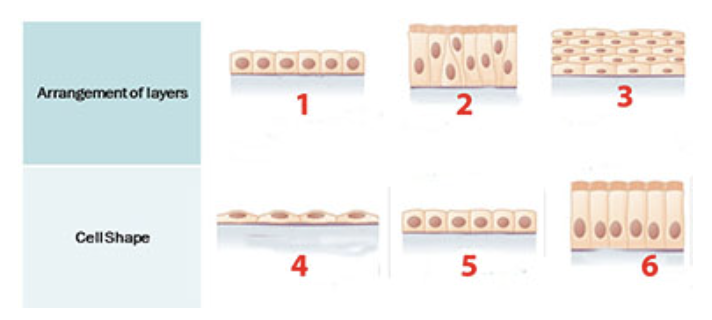
Much of the lining of the respiratory tract is a ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This type of epithelium is shown at:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
f. 6
b. 2
________________ cells are epithelial cells that are flat and resemble fish scales.
a. columnar
b. cuboidal
c. pseudostratified
d. simple
e. squamous
f. stratified
e. squamous
Many glands consist of a:
a. simple columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. transitional epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
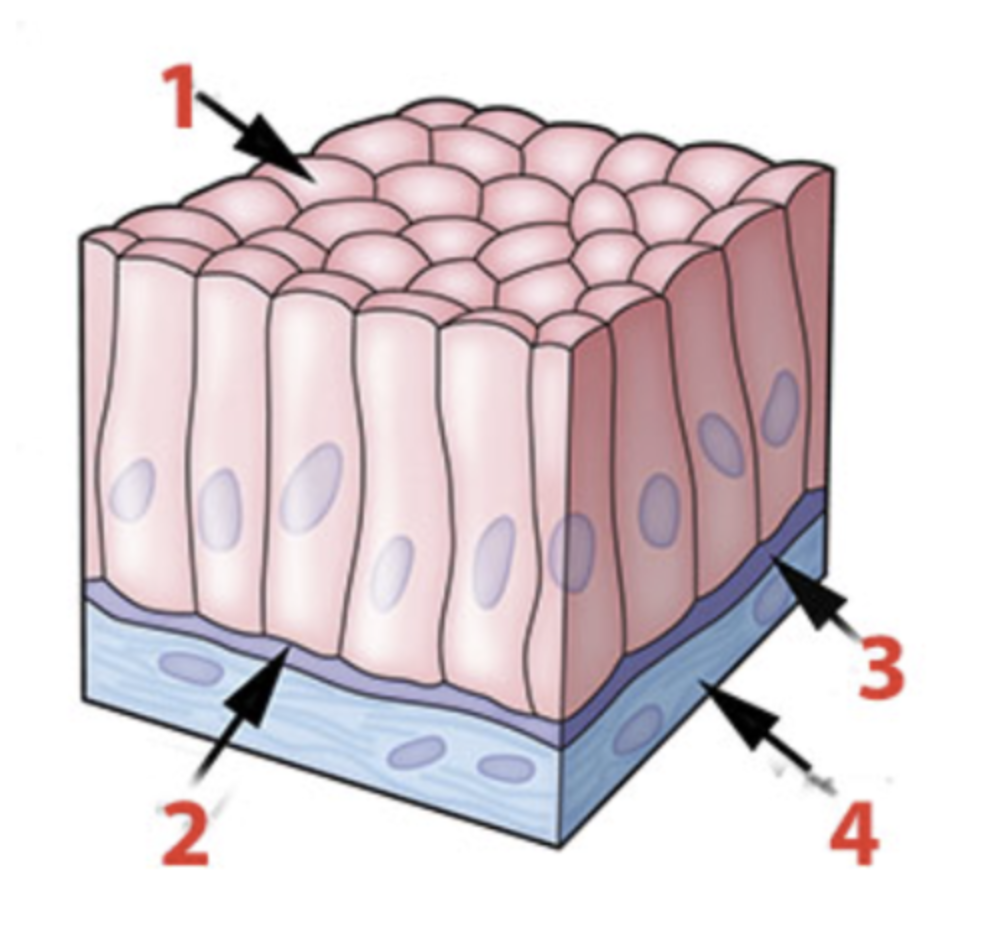
Blood vessels would be found in layer _____________?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
d. 4
Much of the urethra is lined with a multi-layered epithelium in which the cells on the apical surface are taller than they are wide. This is called a:
a. simple columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. stratified columnar epithelium
e. transitional epithelium
d. stratified columnar epithelium
This tissue has staggered nuclei making it appear to be stratified, but all of the cells are in contact with the basement membrane.
a. pseudostratified columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. stratified cuboidal epithelium
e. transitional epithelium
a. pseudostratified columnar epithelium
In a typical epithelium, the two layers of the basement membrane are the ____________ lamina and the ____________ lamina.
a. apical; basal
b. basal; reticular
c. columnar; stratified
d. squamous; transitional
b. basal; reticular
_______________ is an epithelial tissue in which all the cells are in a single layer.
a. columnar
b. cuboidal
c. pseudostratified
d. simple
e. squamous
f. stratified
d. simple
The single layer of thin, flat cells in this tissue facilitates gas exchange in the lungs and capillaries.
a. simple columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. stratified squamous epithelium
e. transitional epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
Transitional epithelium is found in lining organs and structures that:
a. absorb large amounts of nutrients
b. need mechanical protection
c. need to detoxify wastes
d. need to produce mucus
e. need to stretch
e. need to stretch
Blood vessels throughout the body are lined by endothelium, a type of:
a. simple columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. stratified squamous epithelium
e. transitional epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
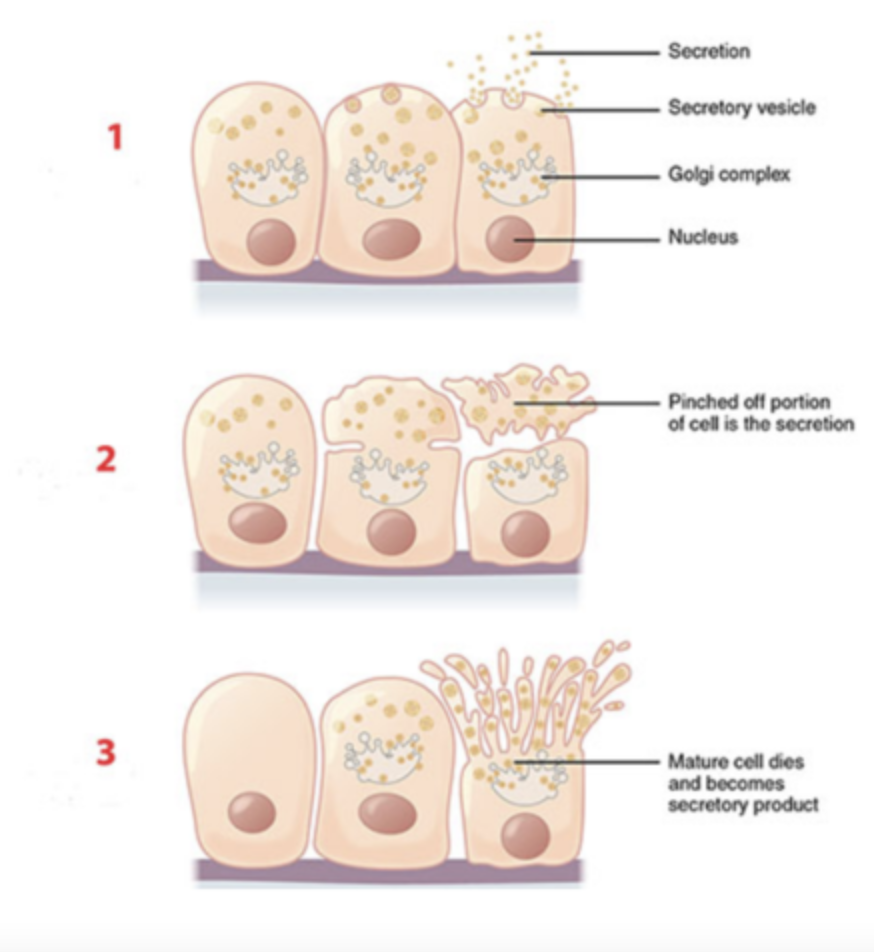
Apocrine exocrine glands release their products:
a. by cellular rupture
b. by pinching off the apical surface of the cell
c. through blood vessels
d. through vesicle-mediated exocytosis
b. by pinching off the apical surface of the cell
Microvili, cilia, and goblet cells are typical modifications of what type of tissue?
a. connective tissue
b. smooth muscle tissue
c. simple columnar epithelium
d. simple squamous epithelium
c. simple columnar epithelium
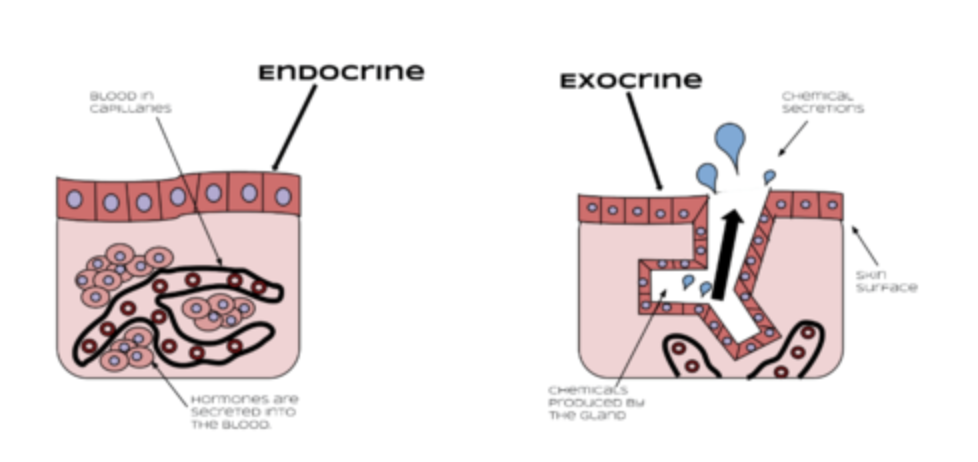
Which of the following describes an endocrine gland?
a. It consists primarily of connective tissue
b. It is only active during puberty
c. It releases its substances into the interstitial fluid, followed by the blood stream
d. It secretes its products into ducts that empty onto epithelium surfaces
c. It releases its substances into the interstitial fluid, followed by the blood stream
Which type of epithelial tissue forms the lining of the heart, blood and lymphatic vessels, and the air sacs of the lungs?
a. simple columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. stratified cuboidal epithelium
e. transitional epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
This tissue is found in sweat gland ducts and pancreatic ducts. It has multiple layers of cube shaped cells.
a. simple columnar epithelium
b. simple cuboidal epithelium
c. simple squamous epithelium
d. stratified cuboidal epithelium
e. transitional epithelium
d. stratified cuboidal
Image #1 is an example of a/an:
a. endocrine gland
b. exocrine gland
c. sweat gland
d. sudoriferous gland
a. endocrine gland
Which type of exocrine secretion is identified by the number 3?
a. apocrine secretion
b. holocrine secretion
c. merocrine secretion
d. tubular secretion
b. holocrine secretion
What is the primary function of the glandular epithelium?
a. absorption
b. covering
c. lining
d. secretion
d. secretion
Cells destroyed by this mode of secretion must be replaced by stem cells.
a. apocrine secretion
b. holocrine secretion
c. merocrine secretion
b. holocrine secretion
Triglycerides and cholesterol are stored in connective tissue. They are stored inside ____________.
a. adipocytes
b. chondrocytes
c. fibroblasts
d. white blood cells
a. adipocytes
Holocrine exocrine glands release their products:
a. by cellular rupture
b. by pinching off the apical surface of the cell
c. through blood vessels
d. through vesicle-mediated exocytosis
a. by cellular rupture
This protein forms the bulk of most connective tissues. It is a triple helix which provides strength. It comes in many different forms, called type I, type II, and so forth.
a. cadherin
b. collagen
c. elastin
d. fibronectin
e. integrin
b. collagen
Fibronectin, laminin, and proteoglycans are proteins in the ground substance. What is one function of these proteins?
a. allow tissues to resist stress in all directions
b. energy storage for the body
c. play an important role in the inflammatory response
d. provide a scaffolding for tissues
e. provide strength through a triple helix structure
d. provide a scaffolding for tissues
In all kinds of connective tissue the cells are:
a. closely packed with very little blood supply
b. found in single layers attached to a collagen membrane
c. widely scattered within an abundant extracellular matrix
d. widely scattered without a nucleus
c. widely scattered within an abundant extracellular matrix