Human Osteology Midterm
0.0(0)Studied by 31 people
Card Sorting
1/171
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:46 PM on 10/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1
New cards
Bones of the axial skeleton
-skull
-auditory ossicles
-hyoid bone
-vertebral column
-thoracic cage
-auditory ossicles
-hyoid bone
-vertebral column
-thoracic cage
2
New cards
bones of the appendicular skeleton
-scapula
-clavicle
-pelvic girdle
-humerus, radius, ulna, hand bones
-femur, fibula, tibia, foot bones
-clavicle
-pelvic girdle
-humerus, radius, ulna, hand bones
-femur, fibula, tibia, foot bones
3
New cards
Bone is an
organ
4
New cards
Physis
space between the metaphysis and epiphysis
-only in living individuals, seen in X-Rays
-only in living individuals, seen in X-Rays
5
New cards
Metaphysis
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet
6
New cards
Collagen in bone
type 2
7
New cards
Osteoblasts
build bone by secreting osteoid
8
New cards
osteoid
unmineralized bone matrix
9
New cards
Osteoclasts
clear away/break bone
-repair via remodelling
-repair via remodelling
10
New cards
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
-osteoblasts trapped in bone matrix
-osteoblasts trapped in bone matrix
11
New cards
Lacunae
pores that contain osteocytes
12
New cards
Function of osteocytes
bone maintenance and communication
-respond to need for more/less minerals
-alert BMU to damaged bone
-respond to need for more/less minerals
-alert BMU to damaged bone
13
New cards
Layers of bone
periosteum and endosteum
14
New cards
Periosteum
fibrous membrane covering a bone
15
New cards
Endosteum
lining of the medullary cavity
16
New cards
Lamellar bone
mature bone
17
New cards
lamellae
sheets of mature bone, 3-7 microns thick
18
New cards
Haversian canal
central, longitudinal canals of bone that carry blood vessels and nerves to deliver nutrients and signals through bone matrix
19
New cards
Osteon
basic unit of lamellar bone
-Includes osteocyte, haversian canal, and circular sheets of lamellae
-Includes osteocyte, haversian canal, and circular sheets of lamellae
20
New cards
Volkmann's Canals
transverse canals that connect Haversian canals, also carry blood vessels and nerves
21
New cards
endochondral ossification
process in which bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage
1. Bone collar formation
2. Calcification of cartilage, cavitation begins
3. spongy bone forms in center shaft
4. Medullary cavity forms, SOCs appear, ossification continues
5. Ossification of epiphyses, hyaline cartilage only remains in epiphyseal plate and articular cartilage
1. Bone collar formation
2. Calcification of cartilage, cavitation begins
3. spongy bone forms in center shaft
4. Medullary cavity forms, SOCs appear, ossification continues
5. Ossification of epiphyses, hyaline cartilage only remains in epiphyseal plate and articular cartilage
22
New cards
intramembranous ossification
bone develops from a fibrous membrane
1. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into osteoblasts and form ossification center
2. Osteoid secreted and calcifies which traps osteoblasts to become osteocytes
3. Osteoid laid in random pattern, forms woven bone. Mesenchyme condenses on outer layer of woven bone and becomes periosteum
4. Lamellar bone replaces woven bone forming compact bone sheets and red marrow appears
1. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into osteoblasts and form ossification center
2. Osteoid secreted and calcifies which traps osteoblasts to become osteocytes
3. Osteoid laid in random pattern, forms woven bone. Mesenchyme condenses on outer layer of woven bone and becomes periosteum
4. Lamellar bone replaces woven bone forming compact bone sheets and red marrow appears
23
New cards
Types of bones
compact (dense/cortical) and spongy (trabecular/cancellous)
24
New cards
functions of skeleton
Hematopoiesis, mineral/fat storage, support, protection, movement
25
New cards
stored in medullary cavity, mostly fat
yellow marrow
26
New cards
stored within cancellous tissue
red marrow
27
New cards
minerals in bone
mostly calcium and phosphate
28
New cards
Trabecular bone makes up
flat bones, articular ends of long bones
29
New cards
Compact bone makes up
external surfaces of bone, shaft of long bone
30
New cards
Bones longer than they are wide
long bone
31
New cards
generally cube shaped bones, or bones that form within tendons
short bones
32
New cards
thin, flattened and slightly curved bones
flat bones
33
New cards
bones with complicated shapes
irregular bones
34
New cards
Long bones make up the
appendicular skeleton
35
New cards
short bone examples
carpals, tarsals, and patella
36
New cards
flat bone examples
skull, ribs, sternum, and pelvis
37
New cards
irregular bone examples
vertebrae, mandible and parts of the splanchnocranium
38
New cards
Primary ossification of the humerus
diaphysis
39
New cards
Secondary ossification centers of the humerus
head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, medial epicondyle, trochlea, capitulum, lateral epicondyle
40
New cards
SOC's of humerus fusion age
14-16 years
41
New cards
Humerus muscle attachment site
deltoid tuberosity
42
New cards
Deltoid tuberosity
deltoid
43
New cards
radius muscle attachment sites
radial tuberosity, pronator teres
44
New cards
radial tuberosity
biceps brachaii
45
New cards
pronator teres
pronator teres
46
New cards
ulna muscle attachment sites
olecranon process, pronator quadratus ridge
47
New cards
olecranon process
triceps
48
New cards
pronator quadratus ridge
pronator quadratus
49
New cards
POCs of radius and ulna
diaphysis
50
New cards
SOCs of radius and ulna
proximal and distal epiphyses
51
New cards
Skull
entire head
52
New cards
Mandible
lower jaw alone
53
New cards
Cranium
skull without mandible
54
New cards
Calotte
skull cap (hat brim)
55
New cards
Splanchnocranium
facial skeleton
56
New cards
Neurocranium
braincase, everything the brain touches
57
New cards
frontonasal suture
small, horizontal suture that separates the nasal bones from the frontal
58
New cards
frontomaxillary suture
paired, small sutures that are found on the side of the frontal bone just lateral to the nasal bones and run diagonally to the maxilla
59
New cards
sinuses of the skull
frontal sinus, sphenoid sinus, maxillary sinus
60
New cards
sphenoid sinus
located in the body of the sphenoid
61
New cards
maxillary sinus
triangular in shape, located in the middle of the maxilla visible when cut in half
62
New cards
nasion
middle point where nasals connect with the frontal bone, 2
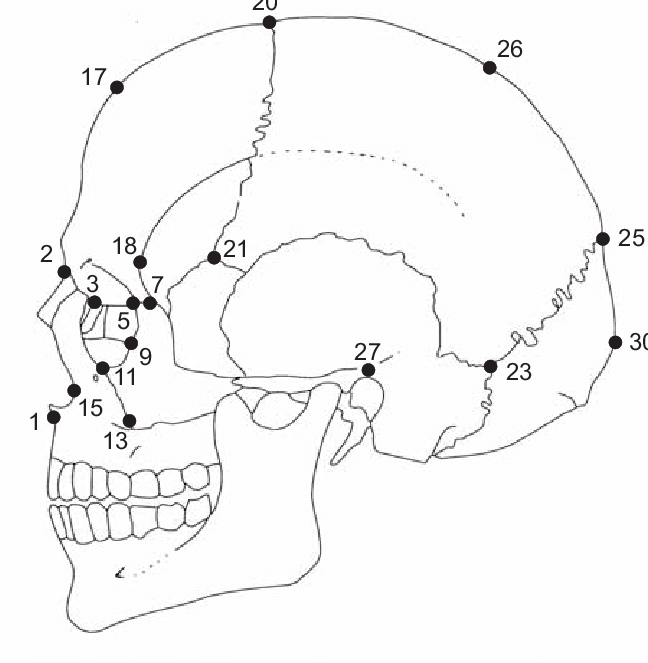
63
New cards
glabella
located just above the nasion on the metopic suture where the superciliary arch meets the rest of the frontal bone, below 17
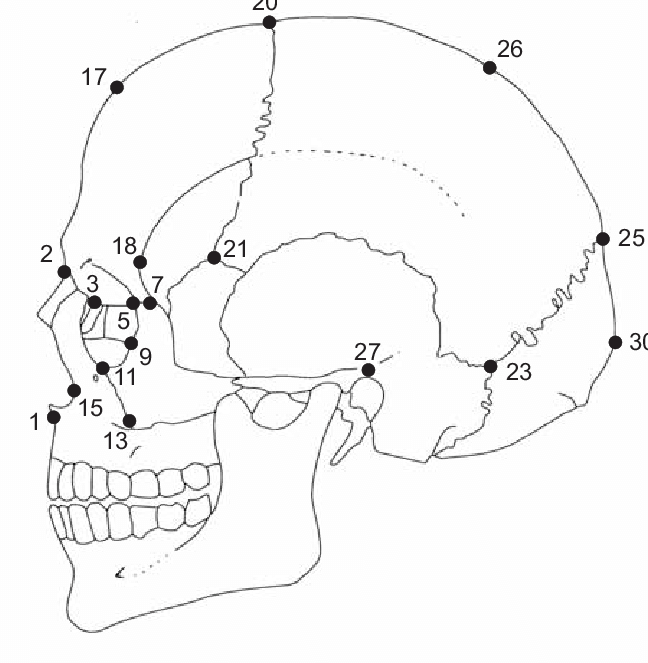
64
New cards
bregma
20, intersection of coronal and sagittal sutures
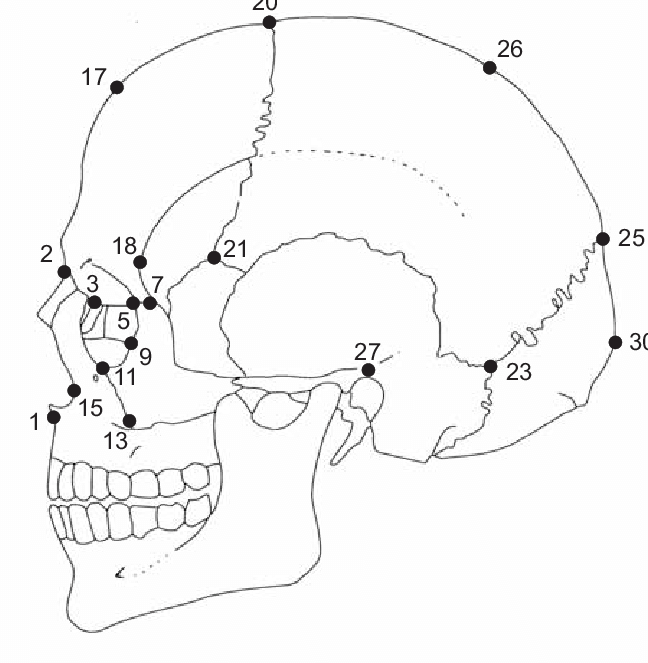
65
New cards
dacryon
located at the junction of the lacrimal and the frontal, 3
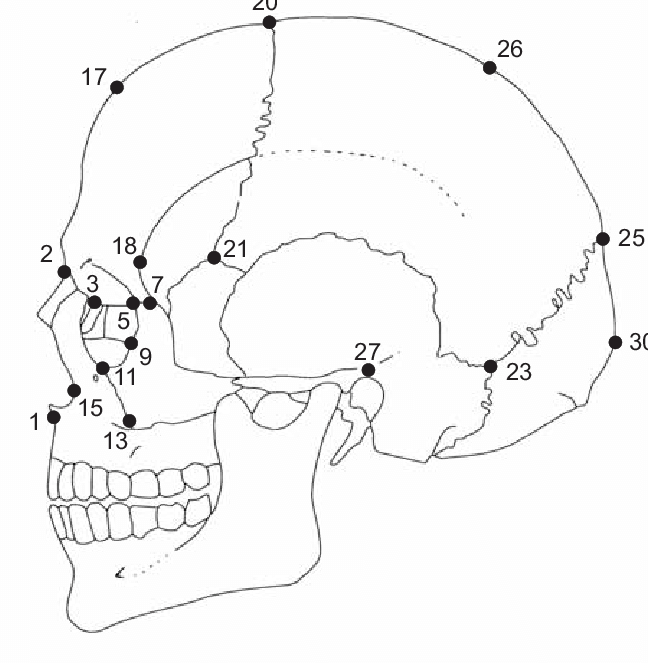
66
New cards
prosthion
On the midline of the alveolar process of the maxilla, below 1
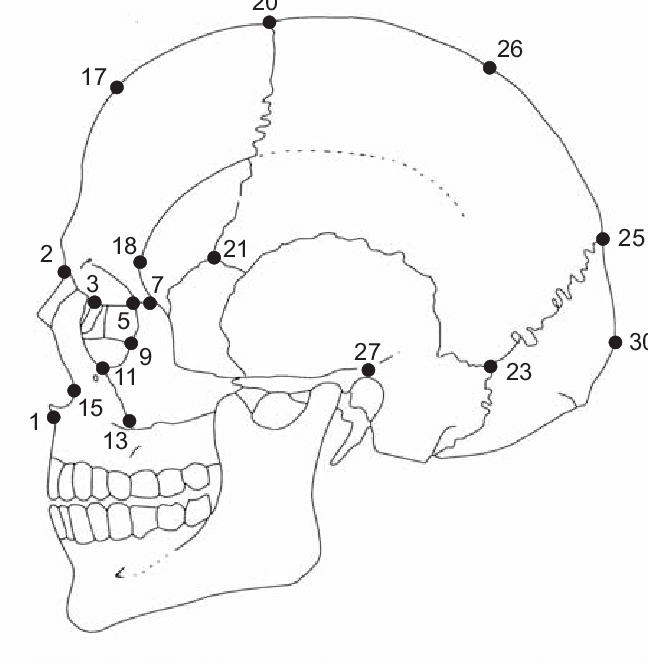
67
New cards
Alare
located on most lateral point of the nasal aperture, 15
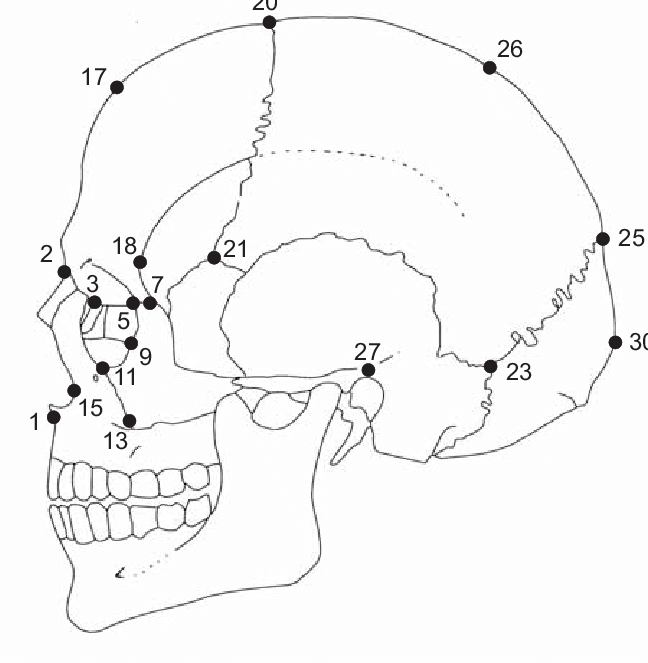
68
New cards
ectoconchion
most lateral point on the orbital margin, between 5 and 9
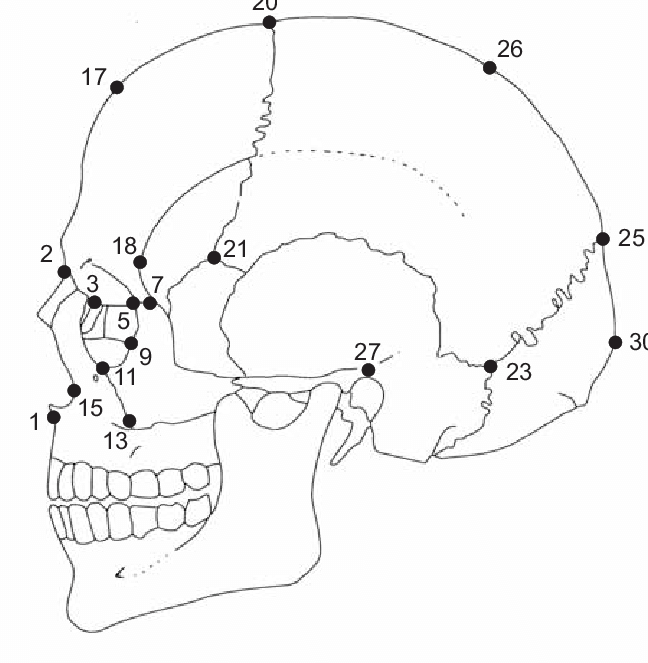
69
New cards
euryon
greatest cranial width, along temporal line between 26 and 27
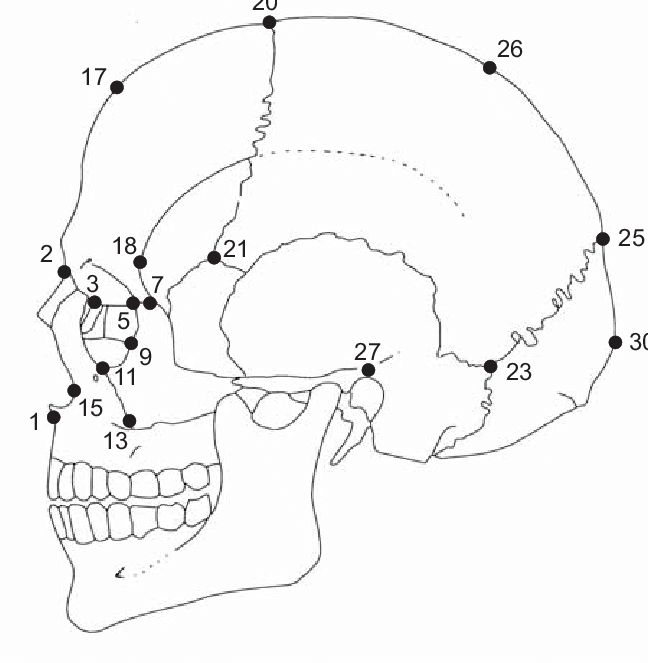
70
New cards
opisthocranium
point at the rear of the skull furthest from the glabella, 30
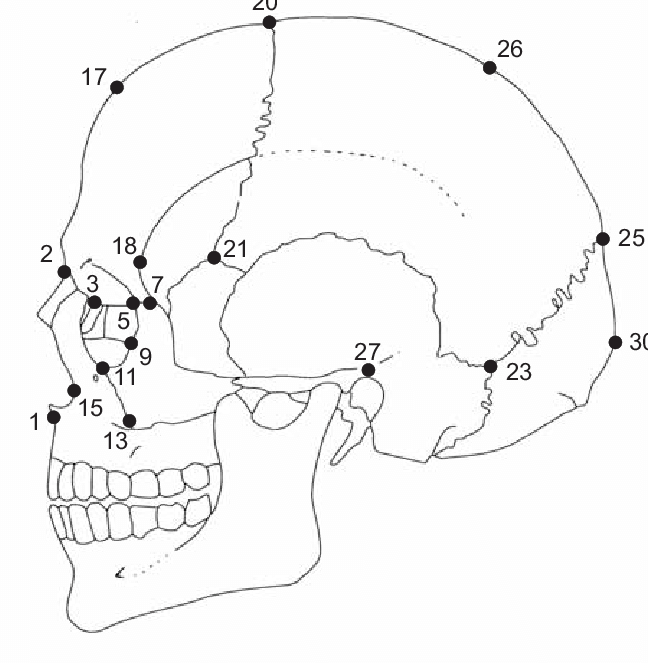
71
New cards
opisthion
midline posterior margin of foramen magnum
72
New cards
basion
midline anterior margin of foramen magnum
73
New cards
lambda
intersection of the sagittal and lambdoidal suture, 25
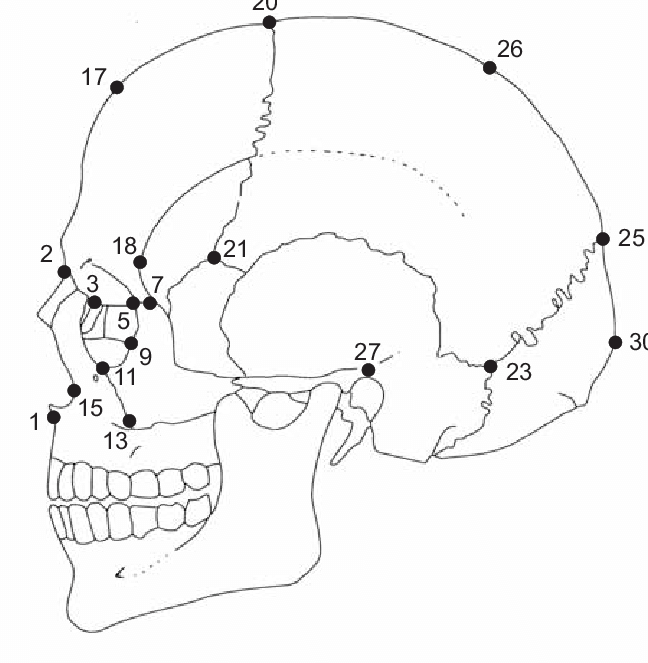
74
New cards
frontal ossification
intramembranous, frontal boss POC, develops in 2 halves
75
New cards
frontal articulations
parietals, zygomatics, nasals, maxilla, ethmoid, sphenoid, lacrimals
76
New cards
parietal ossification
intramembranous, parietal boss
77
New cards
parietal articulations
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid
78
New cards
occipital ossification
intramembranous: squama
endochondral: basilar and lateral portions
endochondral: basilar and lateral portions
79
New cards
occipital articulations
temporals, parietals, sphenoid
80
New cards
temporal ossification
intramembranous: squama
endochondral: petrous portion, zygomatic process, mastoid process
endochondral: petrous portion, zygomatic process, mastoid process
81
New cards
temporal articulations
parietals, occipital, sphenoid, zygomatic, mandible
82
New cards
nasal ossification
intramembranous, nasal halves
83
New cards
nasal articulations
frontal, maxilla, ethmoid, nasal
84
New cards
sphenoid ossification
endochondral: body, lesser wings, greater wings
85
New cards
sphenoid articulations
frontal, parietals, occipital, temporals, ethmoid, maxillae, palatines, zygomatics, vomer
86
New cards
zygomatic ossification
intramembranous, L & R
87
New cards
zygomatic articulations
frontal, temporal, maxillae, sphenoid
88
New cards
Maxilla ossification
intramembranous, L & R
89
New cards
Maxilla articulations
frontal, nasals, zygomatics, lacrimals, palatines, sphenoid, inferior nasal conchae, vomer
90
New cards
Mandible ossification
intramembranous, L & R
91
New cards
mandible articulations
temporals
92
New cards
palatine ossification
intramembranous, L & R
93
New cards
palatine articulations
maxilla, sphenoid, ethmoid, inferior nasal concha, vomer, palatine
94
New cards
Ethmoid ossification
endochondral: L&R labyrinth, perpendicular process
95
New cards
ethmoid articulations
frontal, sphenoid, nasals, maxilla, lacrimals, inferior nasal concha, vomer
96
New cards
lacrimal ossification
intramembranous, L & R
97
New cards
lacrimal articulations
maxilla, frontal, ethmoid, inferior nasal concha
98
New cards
Vomer ossification
intramembranous: L & R plates
endochondral: fusion of plates
endochondral: fusion of plates
99
New cards
vomer articulations
sphenoid, ethmoid, palatines, maxilla
100
New cards
Inferior nasal concha(e) ossification
endochondral: L & R