Regulation of Potassium Balance
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
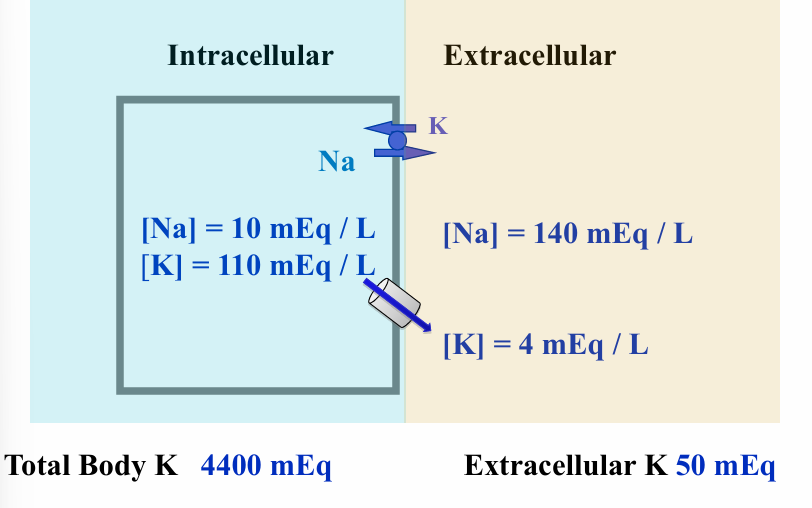
intracellular v extracellular K
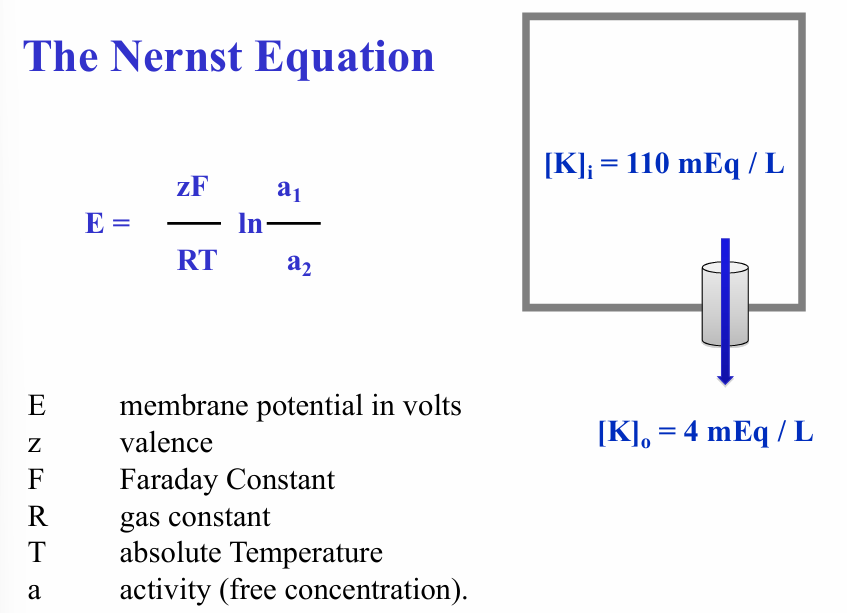
Nernst equation
potassium in diet
-abundant
-since all cells, plants and animal alike, have a high intracellular K
many observational studies show that a high K diet associated with
-lower bp, stroke, and decreased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
____ is an important determinant of serum K in the steady state
-dietary K
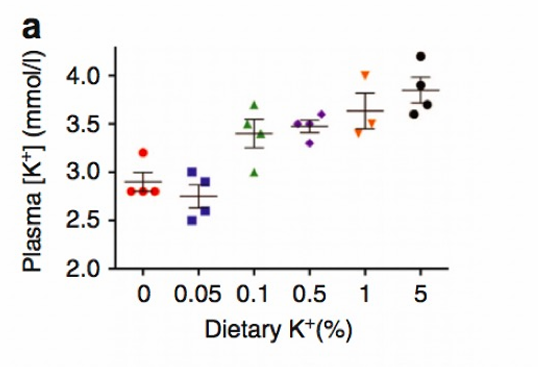
an increase in dietary K is
-excreted rapidly
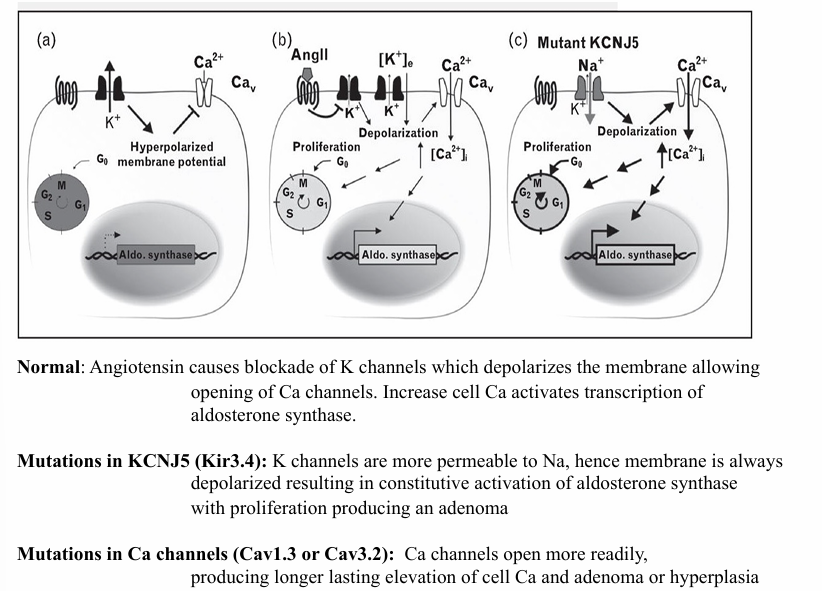
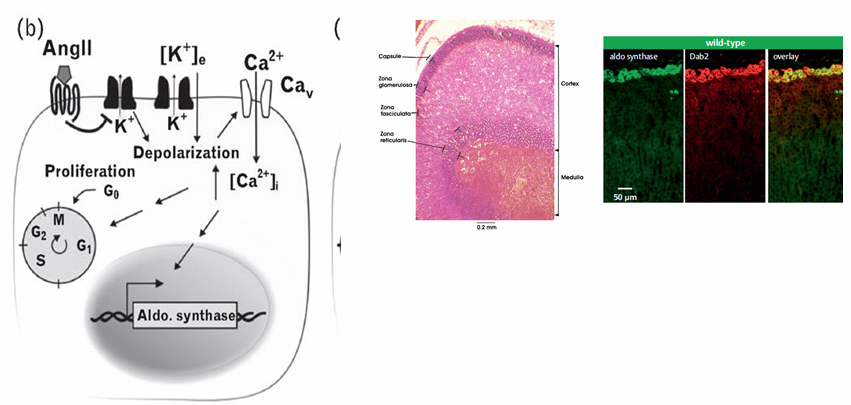
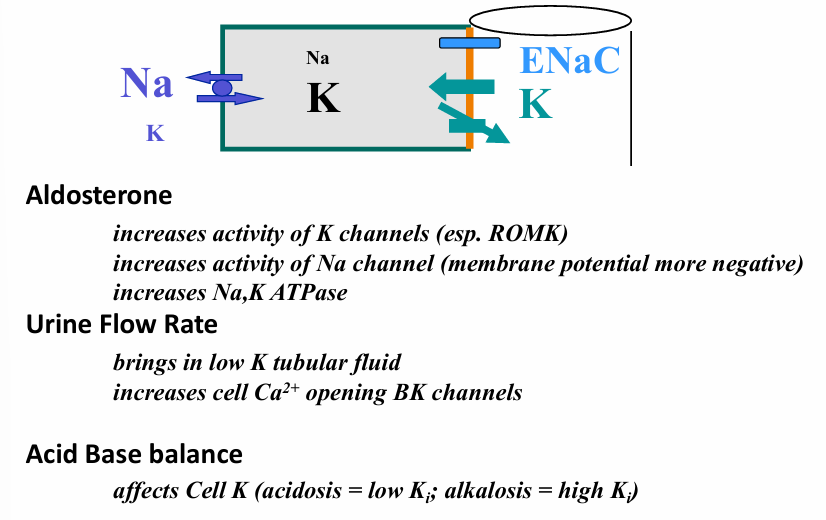
aldosterone production
-produced in the zona glomerulosa
-angiotensin II (and high plasma K) depolarize the membrane leading to open Ca channels high cell Ca induces aldosterone synthase
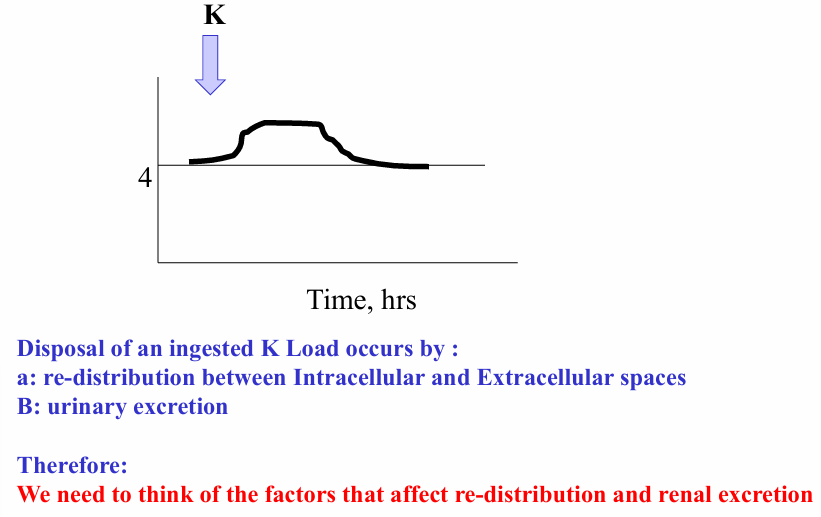
disposal of ingested K
-occurs by re-distribution into the intracellular space and by renal excretion
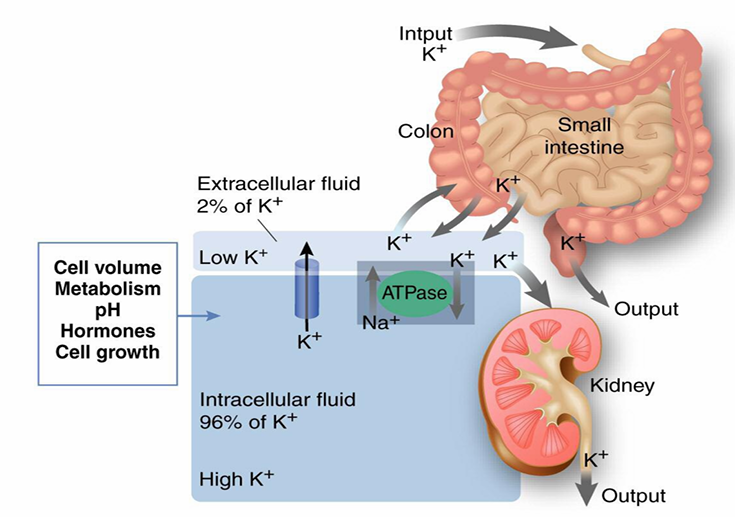
disposal of an ingested K load occurs by
-re-distribution and by urinary excretion
K filtering
-freely filtered
->95% of filtered K is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule and thick ascending limb
-what appears in the urine is secreted by the distal tubule and collecting duct
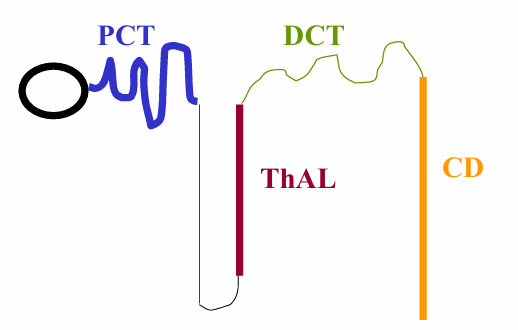
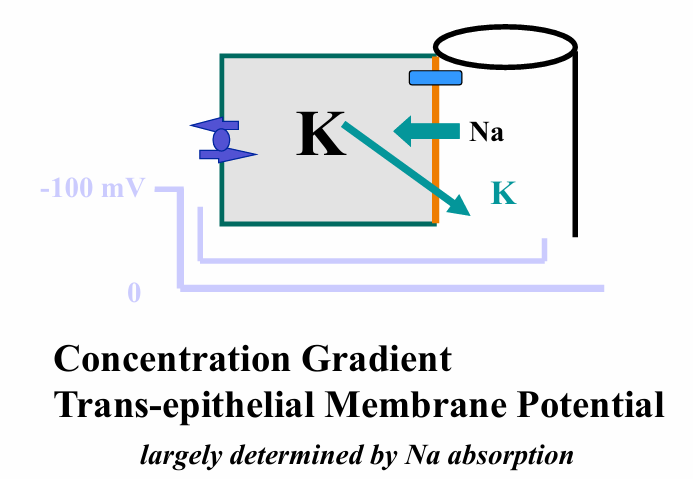
K secretion in collecting duct
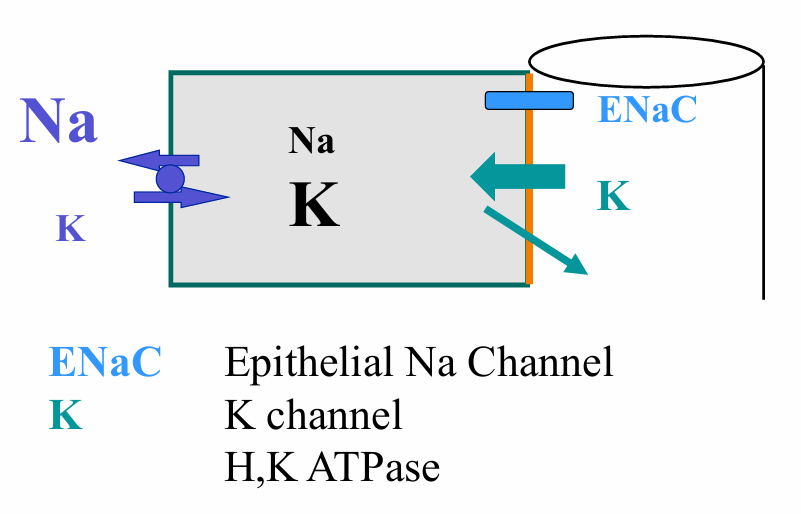
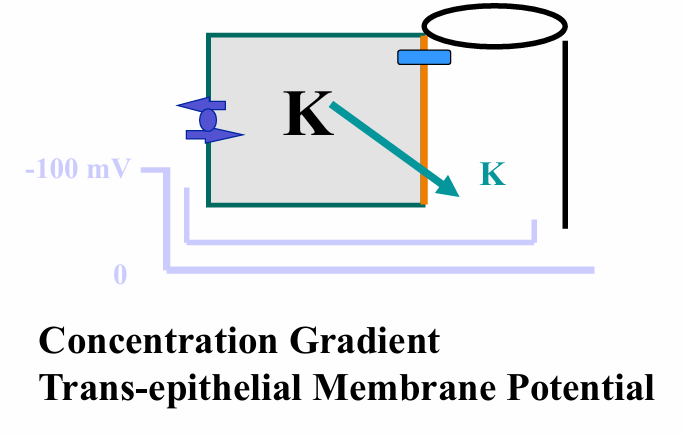
driving forces for K secretion in collecting duct
2 types of K channels mediate K secretion
1) ROMK: small conductance channel
2) BK: large conductance, calcium sensitive
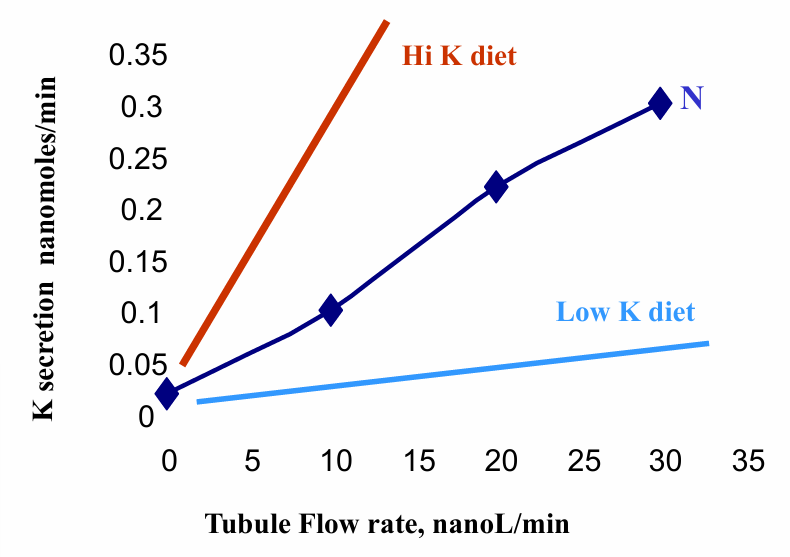
K secretion (and excretion) depends on
-urine flow rate
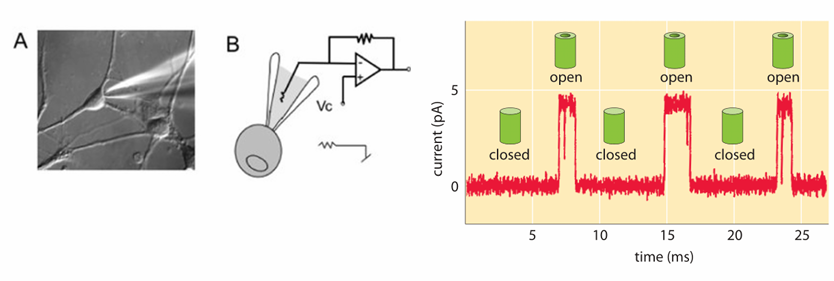
BK potassium channels
-expressed in many epithelial cells including principal cells and intercalated cells (they are responsible for flow dependent K secretion)
-characteristics: 2 subunits- alpha is the channel, beta a regulator and expressed in different cell types; activated by an increase in intracellular calcium; specifically blocked by iberiotoxin (red scorpion)
flow dependent K secretion
-knockout of BK channels in intercalated cells abolishes flow dependent K secretion
-BK potassium channels respond to flow
how does flow affect K secretion?
-BK channels composed of alpha subunit and 1 of 4 beta subunits
-beta subunits increase the calcium sensitivity
flow dependent K secretion
-high urine flow increases intracellular calcium in both principal and intercalated cells
-BK channels are calcium-activated K channels
how does high flow rate increase cell calcium?
flagella and cilia
-contains close to 400 proteins
-mutations of many of these genes lead to a variety of cystic kidney diseases
-also many other organ specific disease “ciliopathies”
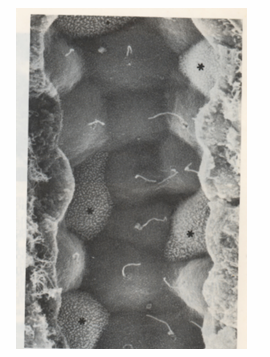
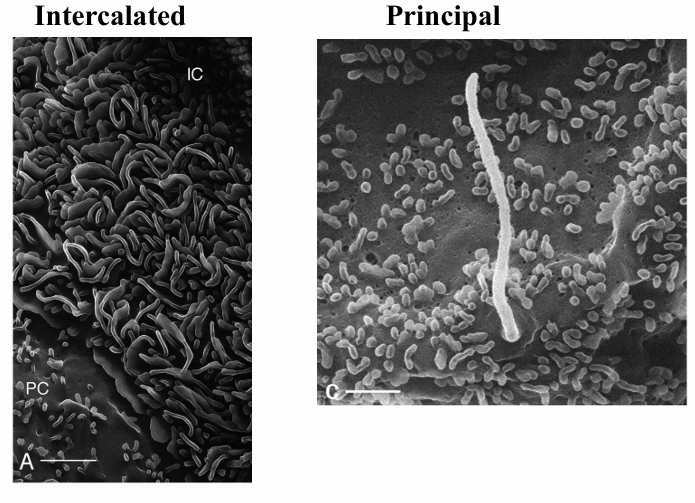
-cortical collecting tubule in the kidney
-showing principal (with flagella) and intercalated cells (*)
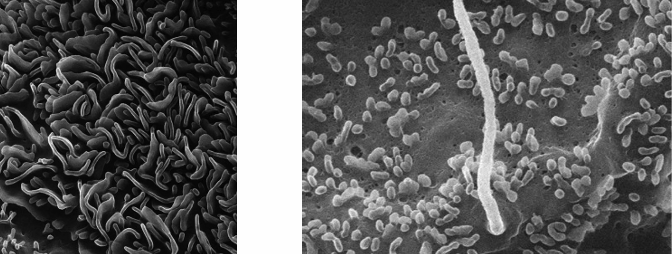
how does high flow rate increase cell calcium?
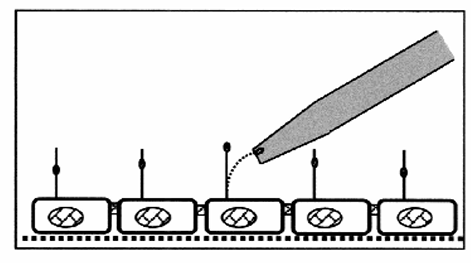
increased flow rate increases
-cell Ca2+ due to stimulation of the cilium in both principal cells and intercalated cells
secretion and reabsorption of K
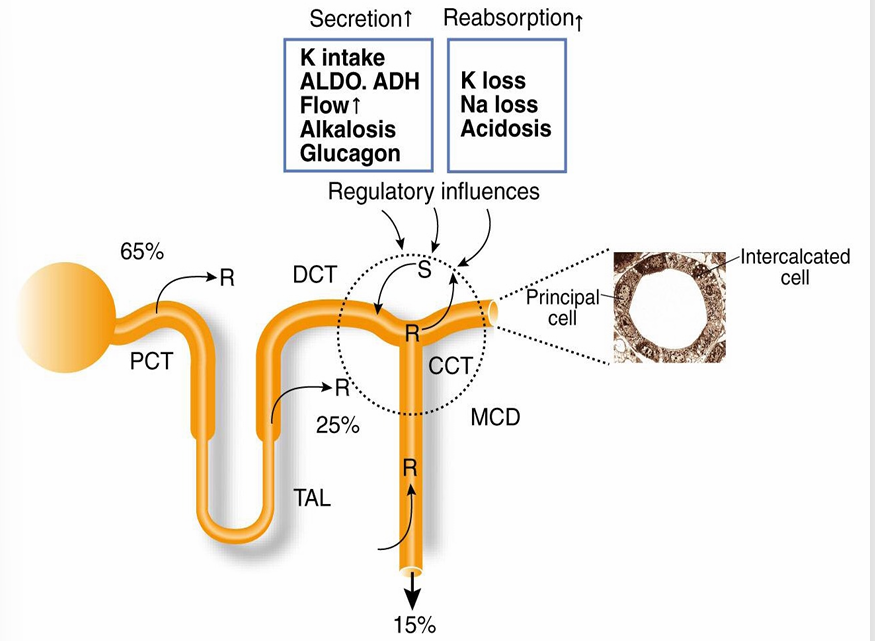
regulation of K secretion
approach to patient with K disorders
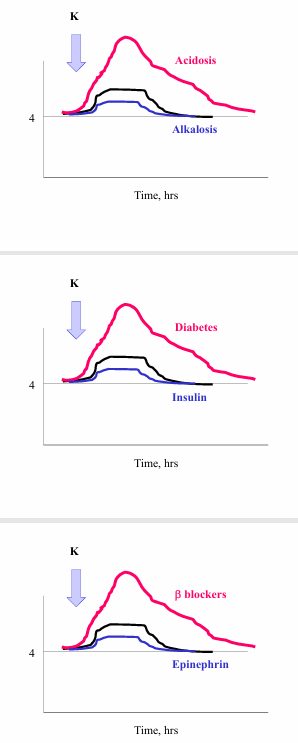
redistribution of K between ECF and ICF
-insulin
-acid base balance
-epinephrine
driving forces for K secretion in collecting duct
hypokalemia

hyperkalemia

clinical manifestations of hypokalemia
-muscle weakness: eventually paralysis; occasionally rhabdomyolysis
-cardiac arrhythmias
clinical manifestations of hyperkalemia
-cardiac arrhythmia
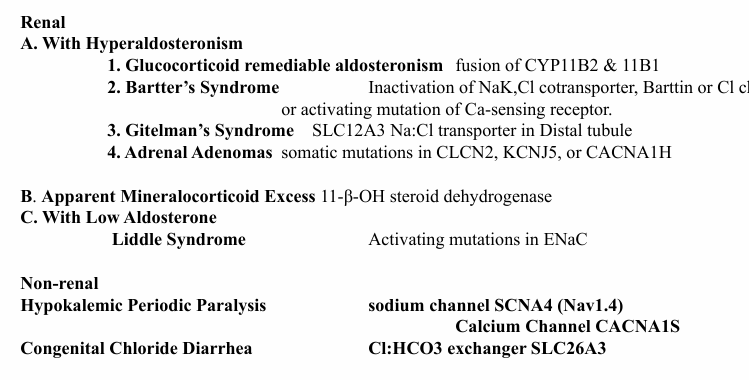
hypokalemia genetic syndromes
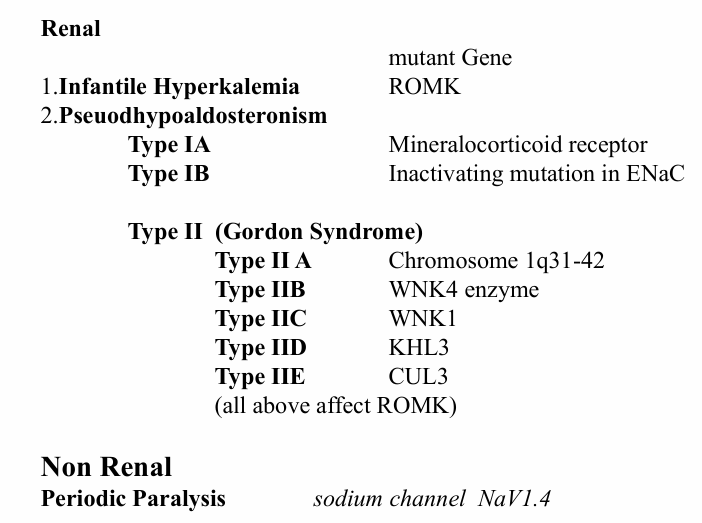
hyperkalemia genetic syndromes
thick ascending limb- Bartter’s syndrome
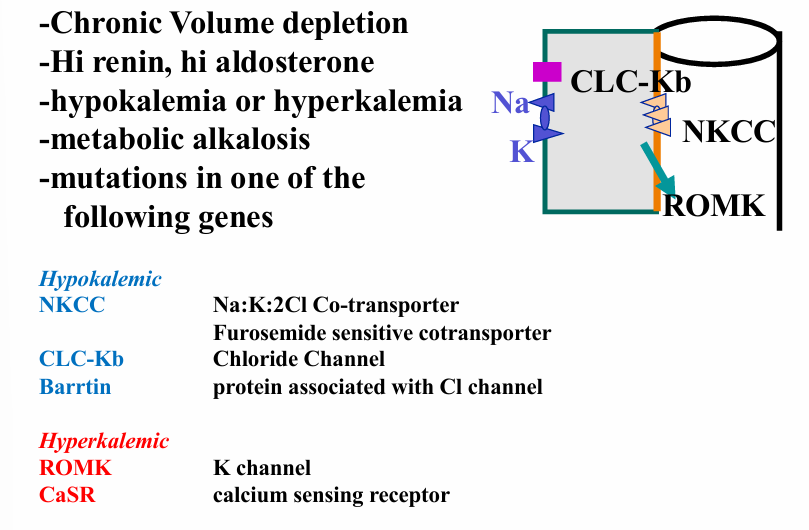
hyperaldosteronism
-secondary: high renin- high angiotensin II states volume depletion, CHD, cirrhosis
-primary: adrenal adenoma, adrenal hyperplasia
aldosterone and K- reciprocal regulation
-aldosterone synthesized only in the zona glomerulosa
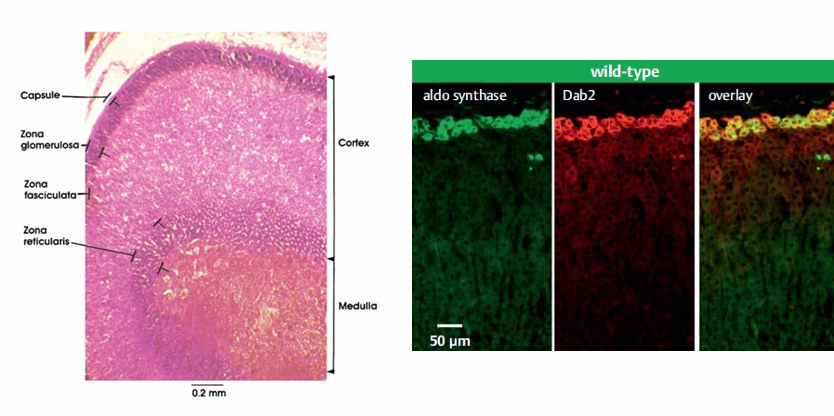
mutations in KCNJ5, Ca channels