gcse geography: physical landscapes in the uk
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dosnt include cow resovoir
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
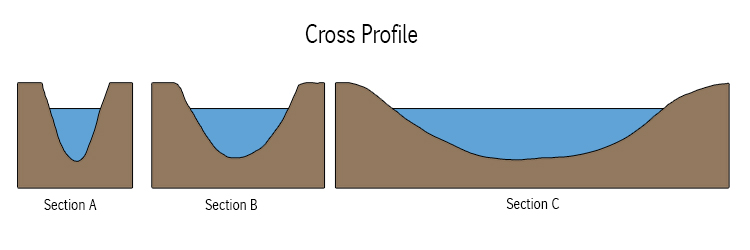
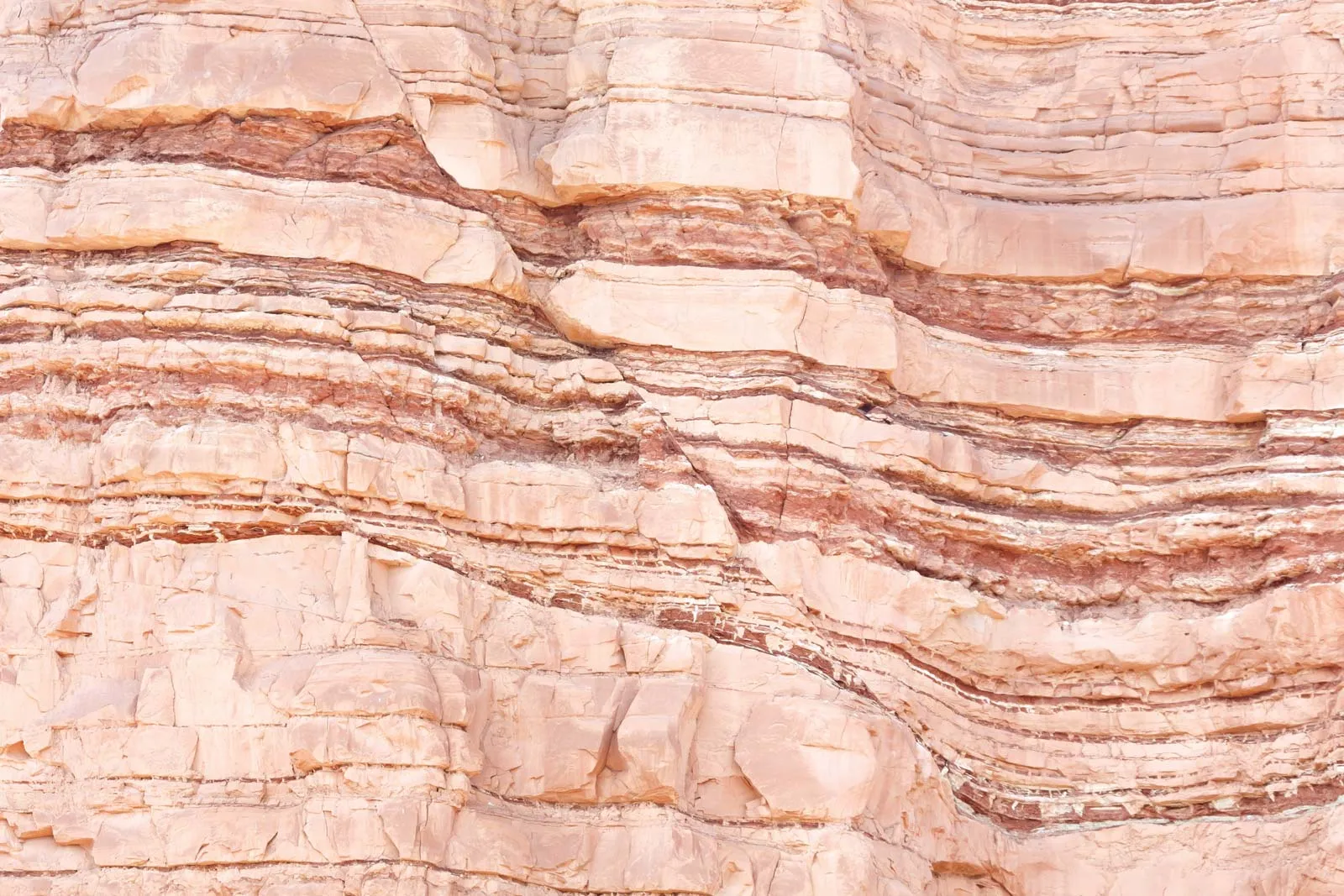
* **v shaped** valley with **steep** sides
* **narrow** and **shallow** channel
* **gently sloping** valley sides
* **wider ,deeper** channel
* very **wide** almost **flat** valley
* very **wide , deep** channel
* happens mostly in the upper and middle course
* makes channel deeper
* mostly in lower and middle courses
* makes river channel wider
* abrasion
* attrition
* solution
* most erosion happens by abrasion
* suspension
* saltation
* solution
* occurs when loses velocity and energy
* dominant in the lower course
1. the volume of water falls
2. the amount of eroded material increases
3. the water is shallower
4. the river reaches its mouth
* the next heaviest is then deposited
* only lightest and smallest particles remain and these can travel further distance downstream
1. waterfalls form where a river flows over an area of **hard rock followed** by an area of **softer rock**
2. the softer rock is **eroded** (by hydraulic action and abraion) more than hard rock creating a **step** in the river
3. as water flows over the step it erodes more and more of the sifter rock
4. a **steep drop** is eventually created which is called a waterfall
5. the hard rock is eventually **undercut** by erosion and becomes unsupported and **collapses**
6. collapsed rocks are **swirled** around at foot of waterfall where they erode the sifter cock by abrasion which created a deep **plunge pool**
7. over time more undercutting causes more collapses
8. the waterfall **retreats** creating a steep sided **gorge**
1. the current is **faster** on the **outside** of the bend because the river channel is **deeper**
2. the faster water has more energy so begins to **erode** the outside of the bend
3. the current is **slower** on the **inside** of the bend because the river channel is **shallower**
4. eroded material is **deposited** on the inside of the bend forming **slip off slopes**
1. **erosion** causes the **outside bends** to get closer until theres only a small but of land left between the bends (called the **neck**)
2. the river **breaks through** this land usually during a flood and the river flows along the **shortest course**
3. **deposition** eventually **cuts of** the meander forming an **oxbow lake**
1. In the upper course there is more **vertical erosion**.
2. The river cuts down into the valley.
3. If there are areas of hard rock which are harder to erode, the river will bend around it.
4. This creates **interlocking spurs** of land which link together like the teeth of a zip.
* when rivers flood, the water slows down and deposits the material it’s transporting
* during flood, eroded material is deposited over whole flood plain
* **heaviest** material **deposited closest** to river **channel** as gets dropped first when river loses its energy
* over time , deposited materials **builds up** creating **levees** along the edges of the channel
* The river here is tidal and when the sea retreats the volume of the water in the estuary is reduced.
* When there is less water, the river deposits silt to form **mudflats** which are an important habitat for wildlife.
\
1. precipitation
2. geology
3. relief
* means water cant infiltrate the ground
* water travels as surface run off which reaches river quickly
* leads to more surface run off
* thie leads to more surface run off
1. deforestation
2. urbanisation
* cutting them down means less interception so more water reaches the ground
* leads to more surface run off
* efficient drainage networks mean water reaches river channel quickly
* river levels rise leading to flooding
* Vegetation
* Valley side steepness
* Soil type
1. dams and reservoirs - dams are barriers in upper course of river and reservoirs (artificial lakes )are built behind the dam
2. channel straightening - meanders are removed by building straighter, artificial channels
* reservoirs **store water**, control water flow and also prevent floods downstream
* can be used to generate **hydroelectric power**
\
==disadvantages:==
* dams are **expensive** to build
* creating reservoir can **flood** existing settlements
* **water leaves** the area **quickly** rather than building up reducing flood risk
\
==disadvantages:==
* **flooding** may happen **downstream** instead
* faster moving water may cause more **erosion** downstream
* planting trees - planting trees in river valley increases amount of interception (and lag time )
* flood **risk** reduced as fewer **impermeable surface** are created (e.g) roads
* **impacts** of flooding are reduced - there are no building to damage
\
==disadvantages:==
* **expansion** of an urban area is **limited** if there arent any other suitable building sites
* **cant help** with areas with **existing buildings**
* discharge and flood risk decrease
* vegetation **reduces soil erosion** in the valley and provided **habitats** for wildlife
\
==disadvantages:==
* **less** land available for **farming**
whats freeze thaw weathering
water enters rock that has cracks
when the water freezes it expands which puts pressure on the rock
when the water thaws it contracts, which releases the pressure on the rock
repeated freezing and thawing widens the cracks causing the rock to break up
whats salt weathering
saltwater contains salt which can weather rocks as waves crash onto cliffs
the seawater evaporates from the cliffs leaving behind salt crystals
if the crystals get into cracks/holes they expand
this puts pressure on the rocks and flakes may eventually break off
whats carbonation
rainwater reacts with carbon dioxide in the air in it making a weak carbonic acid
carbonic acid reacts with alkaline rock
the rocks are dissolved by the rainwater over time
slides
slumps
rockfalls
mud slides
rock slides
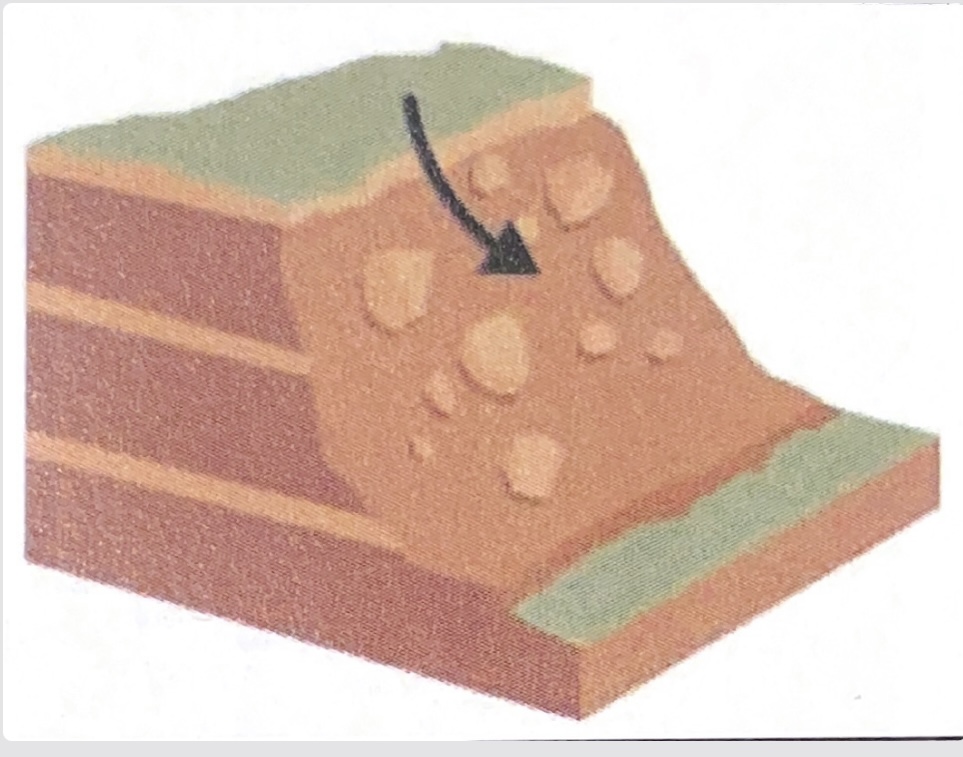
what mass movement does this show?
slide
when does slumping happen
it happens where the rock in the cliff is very soft, this easily fills with water and slowly slips down into the sea
is very common in cliffs with slippery clay at the bottom
follows a concave slip line because it rotates as it slips
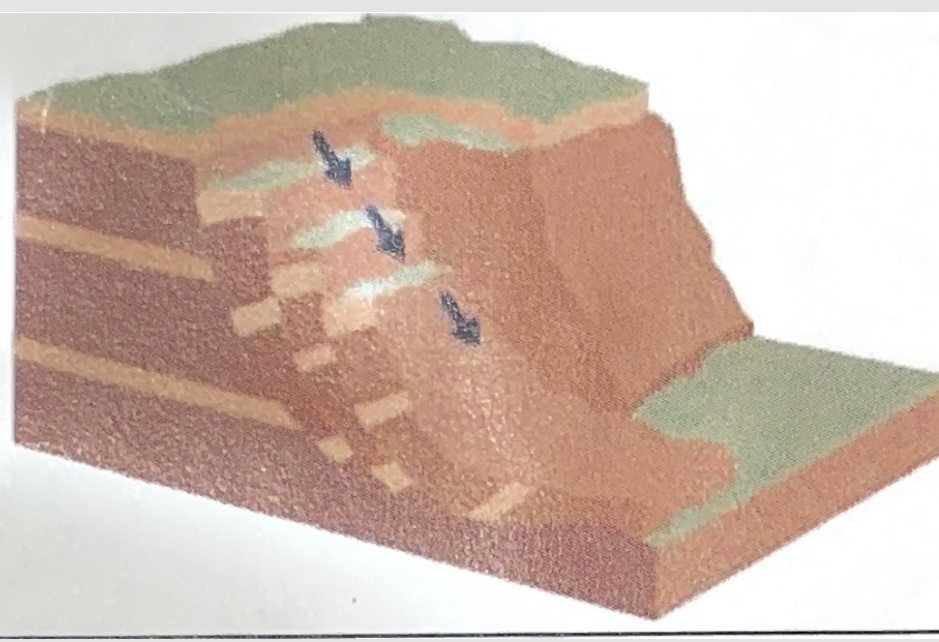
what type of mass movement does this show
slumping
fragments of rock break away from the cliff face, usually from freeze thaw weathering
as they fall they loose contact with the cliff face as cliffs are normally steep
due to falling, the rocks fan out at the base of the slope to form a scree slope
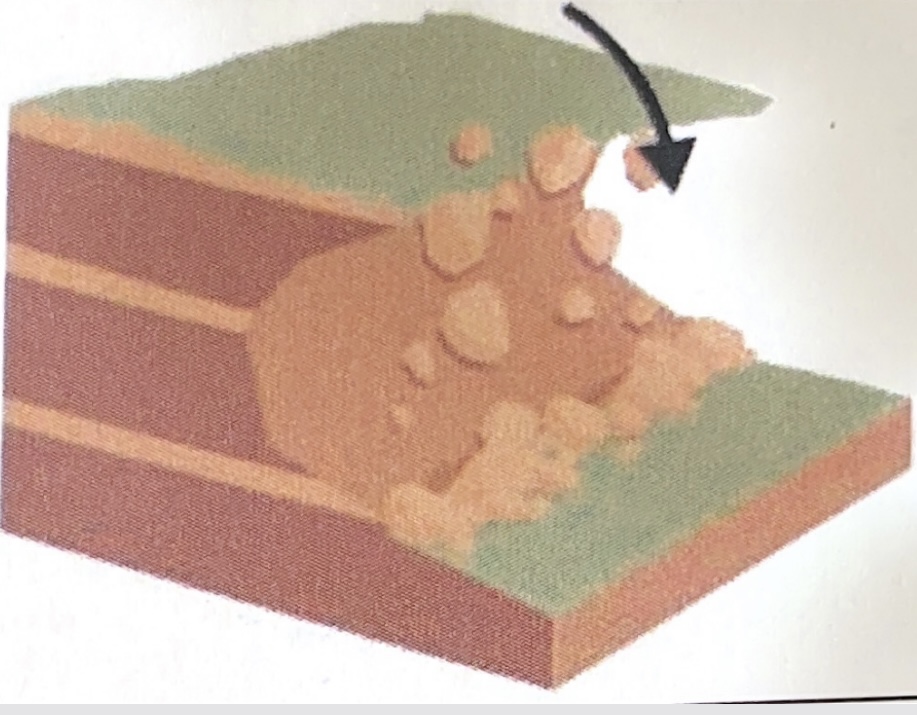
what type of mass movement does this show
rock falls
what is erosion
the wearing away if rocks by the action of water or weather
whar are destructive waves
waves that erode the coast
what are the characteristics of destructive waves
high wave frequency
weak swash ( brings onshore little material)
string backwash (removes beach material)
high and steep waves with high energy
what are constructive waves
waves that deposit materials
what are the characteristics of constructive waves
lower wave frequency
more powerful swash than backwash so more material is deposited
low and long waves with low energy
what type of beach do deconstructive waves create
steep, narrow beach
what type of beach do constructive waves create
a wide gently sloping beach
what is longshore drift
the movement of sediments along a coast by waves that approach at an angle to the shore but then the swash recedes directly away from it
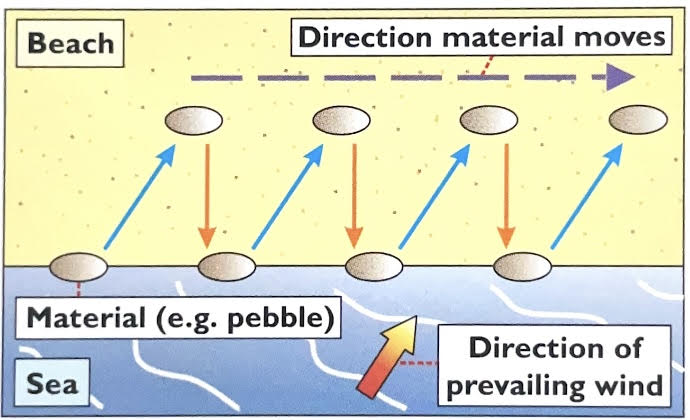
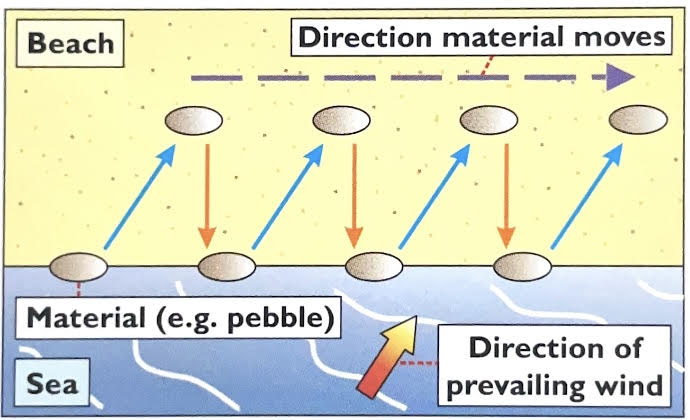
whats the process of longshore drift
waves follow the direction of the prevailing wind
they usually hit the coast in an angle thats not a right angle
the swash carries material up the beach in the same direction as the waves
the backwash then carries material down the beach at right angles back towards the sea
over time material zig zags along the coast
what is deposition on the coastline
where waves drop and leave behind the material they were transporting
results in more sediment staying on the beach than being taken away by backwash
why does deposition happen on the coastline
takes place where the flow of water slows down
waves lose energy and are no longer able to transport material
where does deposition happen on the coastline
waves lose energy in sheltered bays where water is protected by coastal land forms ( headland, spits or bars)
sediment can no longer be carried or moved
what are the 2 reasons the amount of material deposited on a beach increases
lots of erosion elsewhere on coast (more material available)
lots of material transported into area
what is a landform
a feature of the landscape that has been formed by processes of erosion, transportation and/or deposition
how does geology and rock type influence coastal landforms
hard rocks e.g. granite will take a longer time to erode
soft rocks e.g. sandstone erode more quickly
rocks with joints and weaknesses in the rock erode faster
whats differential erosion
when some rocks erode at a faster rate than others
whats a disconcordant coastline
are made up of alternate bands of hard and soft rock at right angles to the coast
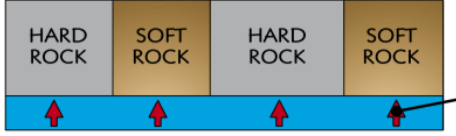
whats a concordant coastline
alternating bands of hard and soft rock parallel to the coast
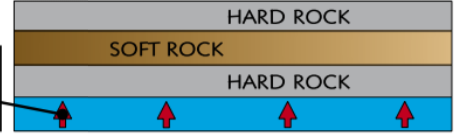
what is folding in rock
many sedimentary rock formed on the sea bed and were raised to the surface by mountain building tectonic processes
were so powerful that they folded the rocks so their layers were no longer horizontal
creates lines of weakness which are more easily eroded
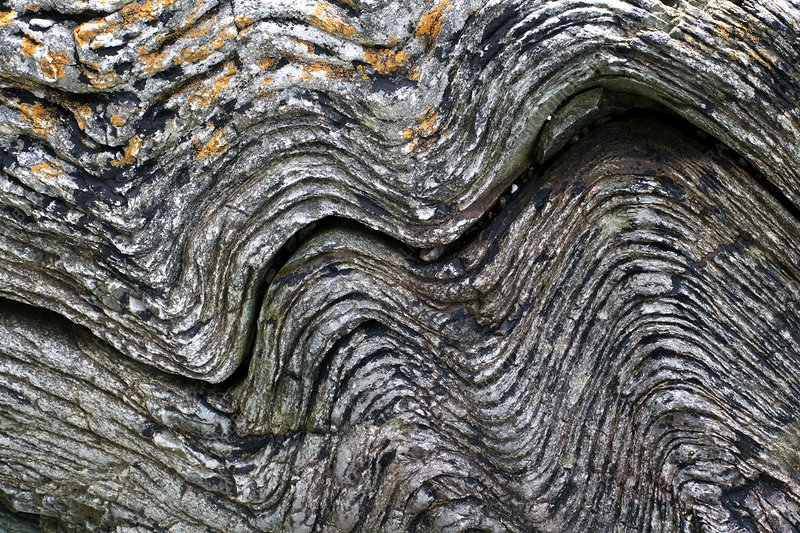

whats fault line in rock
when tectonic forces caused rocks to fold they sometimes snapped the layers rather than bending them
movement can then occur as the rock layers are no longer joined and a fault is formed
creates lines of weakness that are more easily eroded
