Chapter 12 - changes in species over time (evo)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is evolution?
Change in heritable traits of populations over generations.
Darwin & Wallace’s theory of natural selection (4 points)?
Overproduction (more offspring produced than can possibly survive)
variation (traits vary among individuals)
differential fitness (different traits = diff rates of survival/repro)
heritability (traits can be passed from generation to geenration)
geological time scale
chronological dating that relates geological strata (distinct layers of sedimentary rock/soil)
evidence for evolution
Paleontology - the study of the fossil record
Structural morphology - the study of structural features of related organisms
Molecular homology - the study of DNA similarities
the fossil record
over time, changes have occurred in the types of organisms living on the planet (e.g.tribolites, dinosaurs, etc)
What is the law of fossil succession?
Fossils appear in a predictable order in rock layers.
transitional fossil?
fossils that show features of both older and newer species.
e.g. Archaeopteryx (between reptiles and birds).
Four main fossil types?
Impression, mineralised, trace, mummified.
impression fossil
A mark or imprint of an organism left in rock (like a leaf print).
mineralised fossil
Organic material replaced by minerals, turning it into rock (like dinosaur bones).
trace fossil
Evidence of an organism’s activity, like footprints or burrows.
mummified fossil
Preserved soft parts of an organism, often in dry or cold conditions.
how do fossils form?
Organism dies → buried into sediments (e.g. ash from volcanic eruption, sediments on seafloor,etc → minerals replace it → fossil forms.
biosignatures/biomarkers
Physical or chemical signs in rocks or minerals from past life, e.g.,
Corrosion pits by microbes
Life-like isotopic ratios (C, S)
Stable molecules like steranes from cell membranes
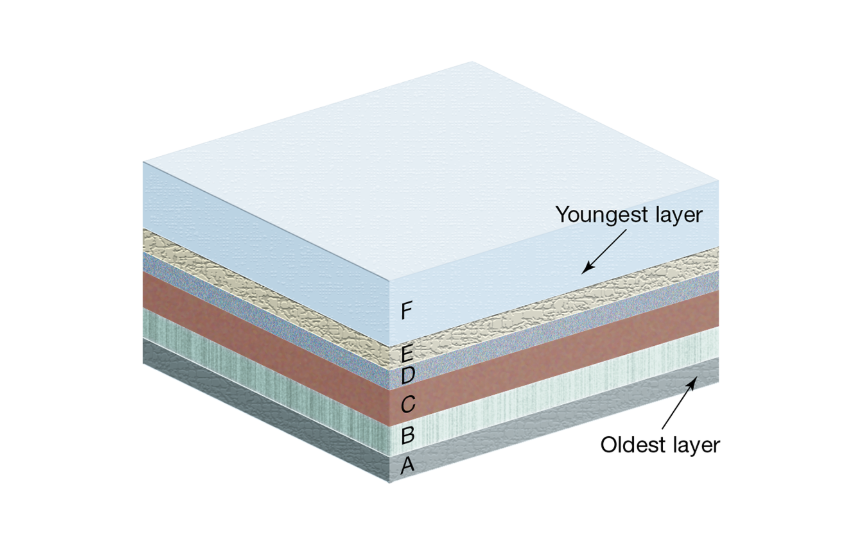
Relative dating
Tells which rock/fossil is older or younger, but not exact age.
absolute dating
Gives the exact age in years using methods like carbon dating.
what is relative age of rocks calculated by?
stratigraphy
younger strata of rock laid down over older strata of rocks
What is C-14 dating used for?
Organic remains up to ~60,000 years.
Definition of a species (biological concept)?
Can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
What is allopatric speciation?
New species form due to geographic isolation.
Darwin’s finches are an example of what?
Adaptive radiation.
What is convergent evolution?
Unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar environments.
What is sympatric speciation?
New species arise in the same area (often plants, polyploidy)
Prezygotic vs postzygotic barriers?
Prezygotic = prevent fertilisation; Postzygotic = after fertilisation (e.g., sterile hybrids).
Example of postzygotic isolation?
Mule (horse × donkey) is sterile.
fertile vs viable
fertile - ability to reproduce
viable - ability to survive