Animal Anatomy Lab Exam 1
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
epithelial tissue major functions
protection, secretion/excretion, absorption
epithelial cell classification
number of layers, shape of cells
epithelial tissue composition
line and cover surfaces both internally and externally (digestive tract, lungs, bladder, skin, etc)
simple
one layer of cells
stratisfied
more than one layer of cells
squamous
very thin, look like fried eggs
cuboidal
cube-shaped, nuclei arranged in single row
columnar
elongated, nuclei arranged in a row at base of cell
simple epithelium
single layer of cells that is fragile and lines internal compartment and passageways such as blood vessels
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells, perform filtering or exchange function
mesothelium
simple squamous epithelium that lines the chest, heart, and abdominal cavities
endothelium
simple squamous epithelium that lines the blood vessels and lymphatic vessels
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube shaped cells, found in ducts or glands (kidney, thyroid, salivary, pancreas, ovary)
simple columnar epithelium
elongated cells between apical and basal surfaces, typically found in the digestive tract
goblet cells
specialized columnar cell, has a secretory function that produces mucus that lubricates intestinal wall
stratified epithelia
located in areas that are subject to mechanical or chemical stress (surface of skin or mouth)
stratisfied squamous epithelium
protection (skin, oral cavity, esophagus, vagina, cornea)
stratisfied columnar epithelium
protection and secretion (some glands, conjunctiva, pharynx, urethra, anus)
pseudostratified epithelia
only one layer thick but has staggered nuclei and two different cell orientations, possess goblet cells and have a ciliated surface
transitional epithelia
surface layer consists of large, round cells. deeper consists of cuboidal or columnar cells
basement membrane
glue-like material secreted by the base layer of epithelial cells, network of fibers that cement epithelial cells to underlying connective tissue
microvilli
finger-like projections of epithelial cells that increase surface area to increase absorption
brush border
apical surface covered in microvilli
cilia
hair-like structures that beat in a rhythmic fashion to move materials across epithelial cell surfaces
keratin
protective waterproof material produced by epithelial cells in skin
connective tissue
supports and binds cells and tissues together and is composed of extracellular fibers, ground substance, and cells
three broad categories of connective tissue
connective tissue proper (loose and dense), fluid connective tissue (blood and lymph), and supporting connective tissue (cartilage and bone)
adipose
"chicken wire" loose connective tissue proper filled with adipocytes or fat cells found beneath skin, between muscles, behind eyeballs, etc.
blood
fluid connective tissue, red blood cells
bone
supporting connective tissue, hardest and most rigid, compact and spongy
muscle tissue
highly specialized cells that have the baility to contract to help move our bones, blood, and soft tissues (smooth, cardiac, skeletal)
smooth muscle description
lack striation or bands with central nucleus
smooth muscle location
walls of hollow organs, skin attached to hair, eye iris
smooth muscle function
moves food through digestive tract, causes hair to stand erect, moves fluid through vessels
cardiac muscle description
striated, involuntary, cylindrical and branched with single central nucleus
cardiac muscle location
only found in the heart
cardiac muscle function
pumps blood through vascular system
skeletal muscle description
striated, voluntary, striped, long, and cylindrical with multiple non-central nuclei
skeletal muscle location
attached to bone, skin, eyeballs, and esophagus
skeletal muscle function
voluntary movement
nervous tissue
found in brain, spinal chord, and nerves, made up of cells that are packed very closely together (highly branched), can appear quite different depending on location and histological technique
neurons
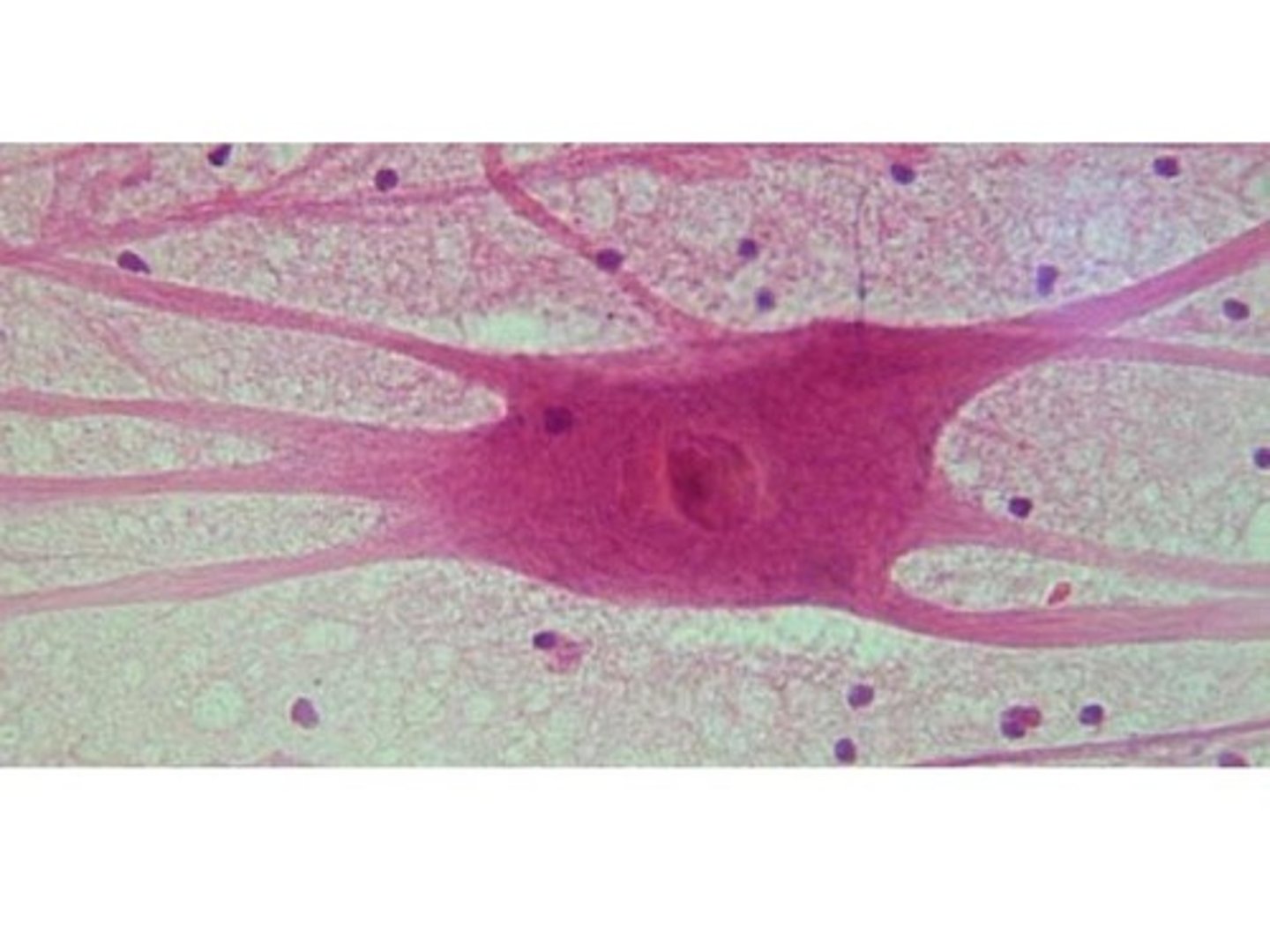
respond to stimuli, conduct electrical impulses, made up of cell body, dendrites, and axons
cell body (neuron)
nucleus and organells
dendrites (neuron)
receive stimuli
axons (neuron)
generate and transmit nerve impulses
neurological cells
support, protect, and bind neurons together
motor nerve cell
gray matter
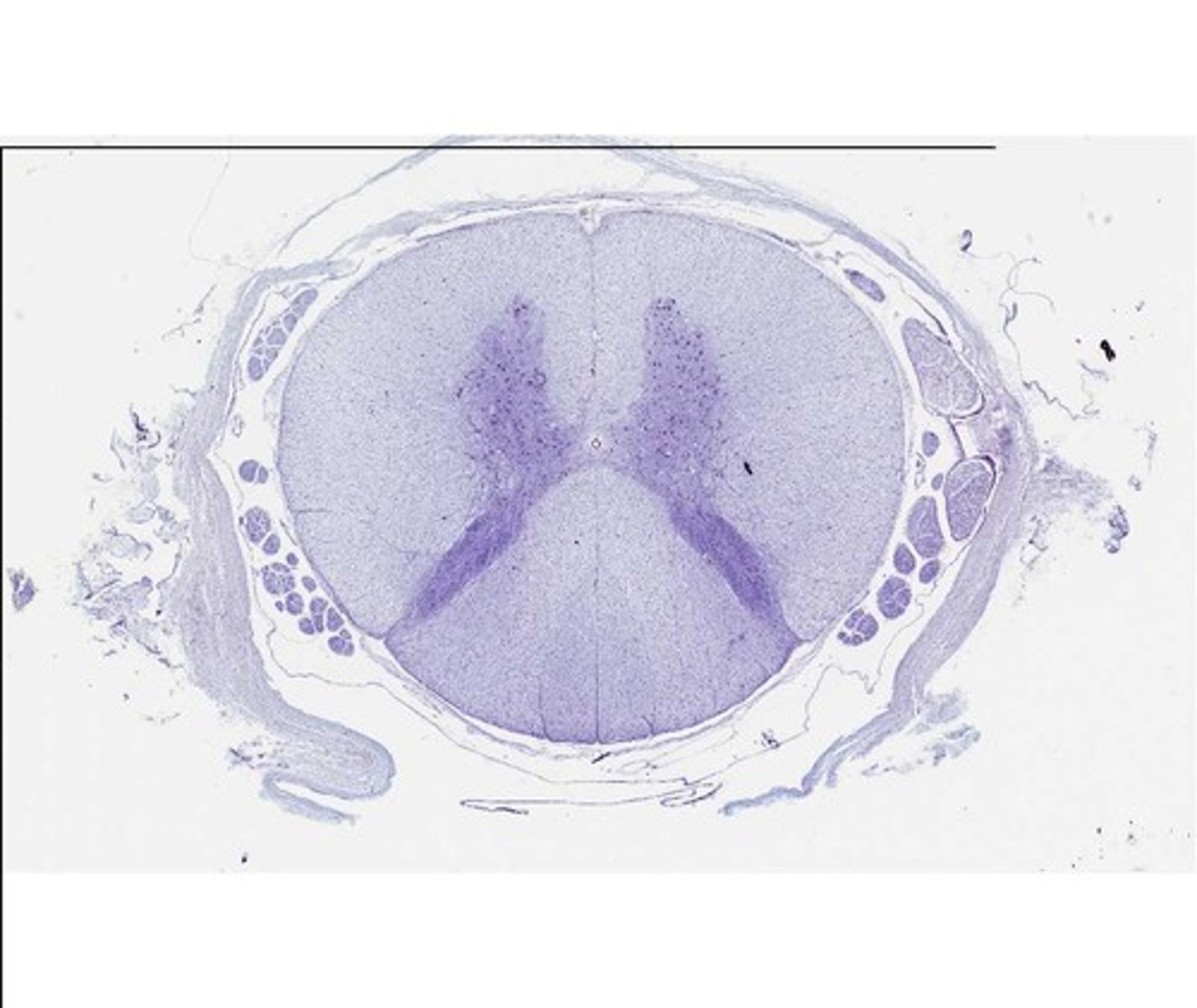
made up of the cell bodies of nerve cells
white matter
made up of the axons of nerve cells
mammalian spinal cord
dorsal plane
divides the body into dorsal and ventral parts
transverse plane
divides the body into cranial and caudal parts
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right parts
median (midsagittal) plane
divides body into equal left and right parts
cranial
toward the head
caudal
toward the tail
rostral
toward the nose
dorsal
toward the back
ventral
toward the belly
medial
toward the midline of the body
lateral
away from the midline of the body
deep
toward the center of the body
superficial
toward the surface of the body
proximal
closer to the point of attachment
distal
away from the point of attachment
cranial surface
front surface of the leg
caudal surface
back surface of the leg
dorsal surface
top of foot/body
palmar surface
palm of hand (front leg)
plantar surface
bottom of foot (back leg)
dorsal recumbency
lying on the back (belly up)
sternal/ventral recumbency
lying on the belly/sternum (back up)
lateral recumbency
lying on the side, left or right
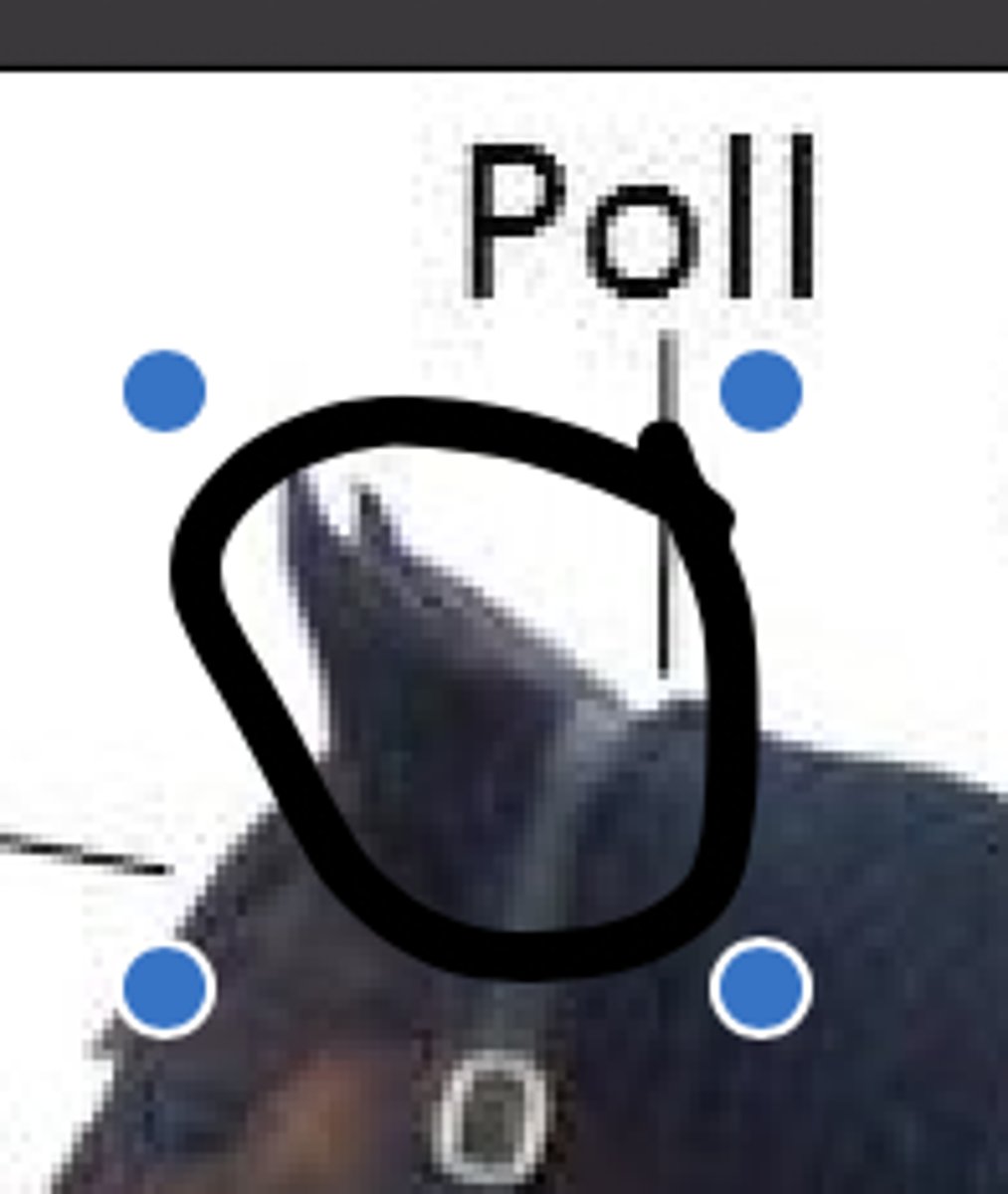
poll
top of the head between the ears

muzzle
rostral part of the face
withers
the highest part of the back at the base of an animal's neck

barrel
chest, side area above/caudal of the fore arm
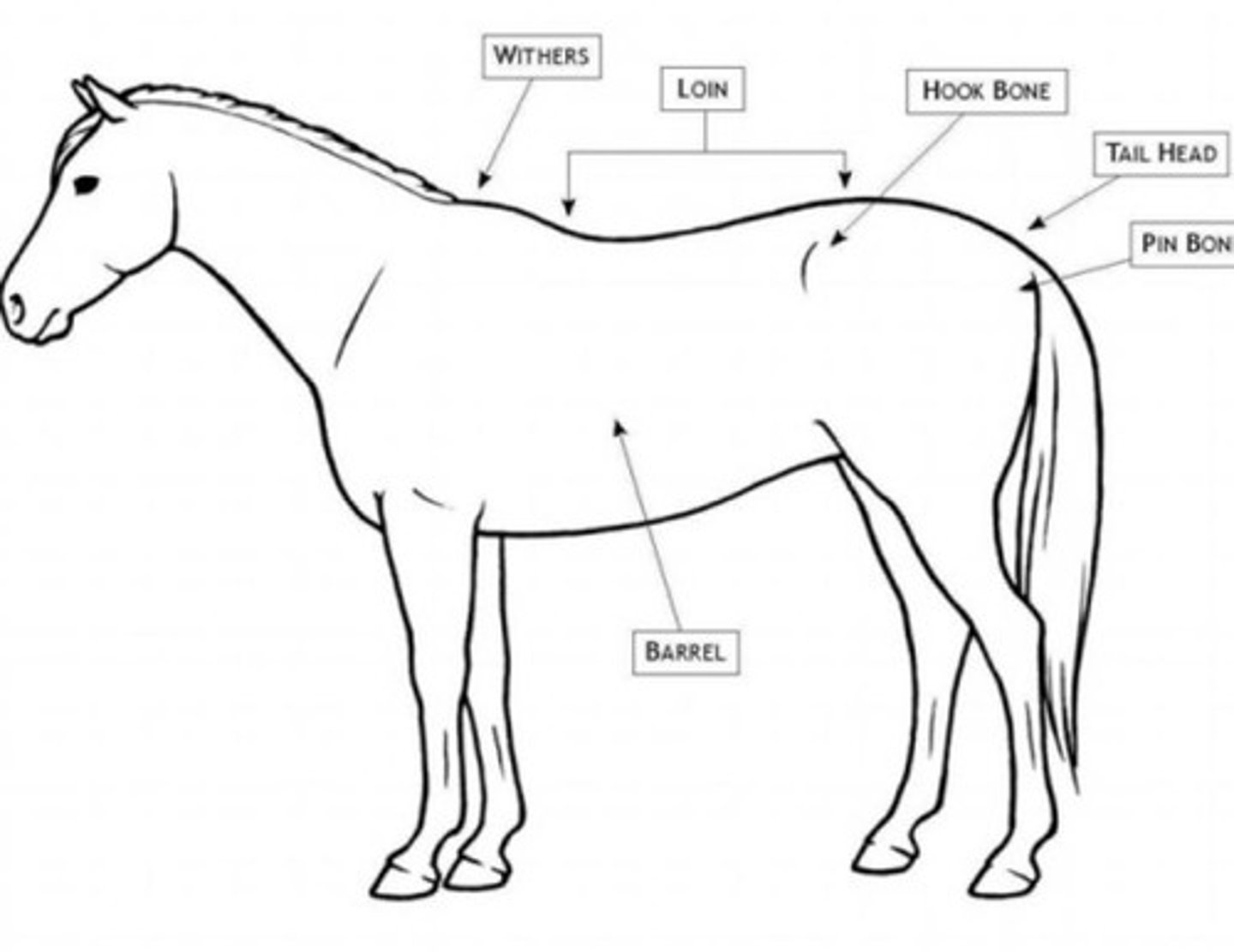
brisket
muscled portion between the front legs of the animal, chest
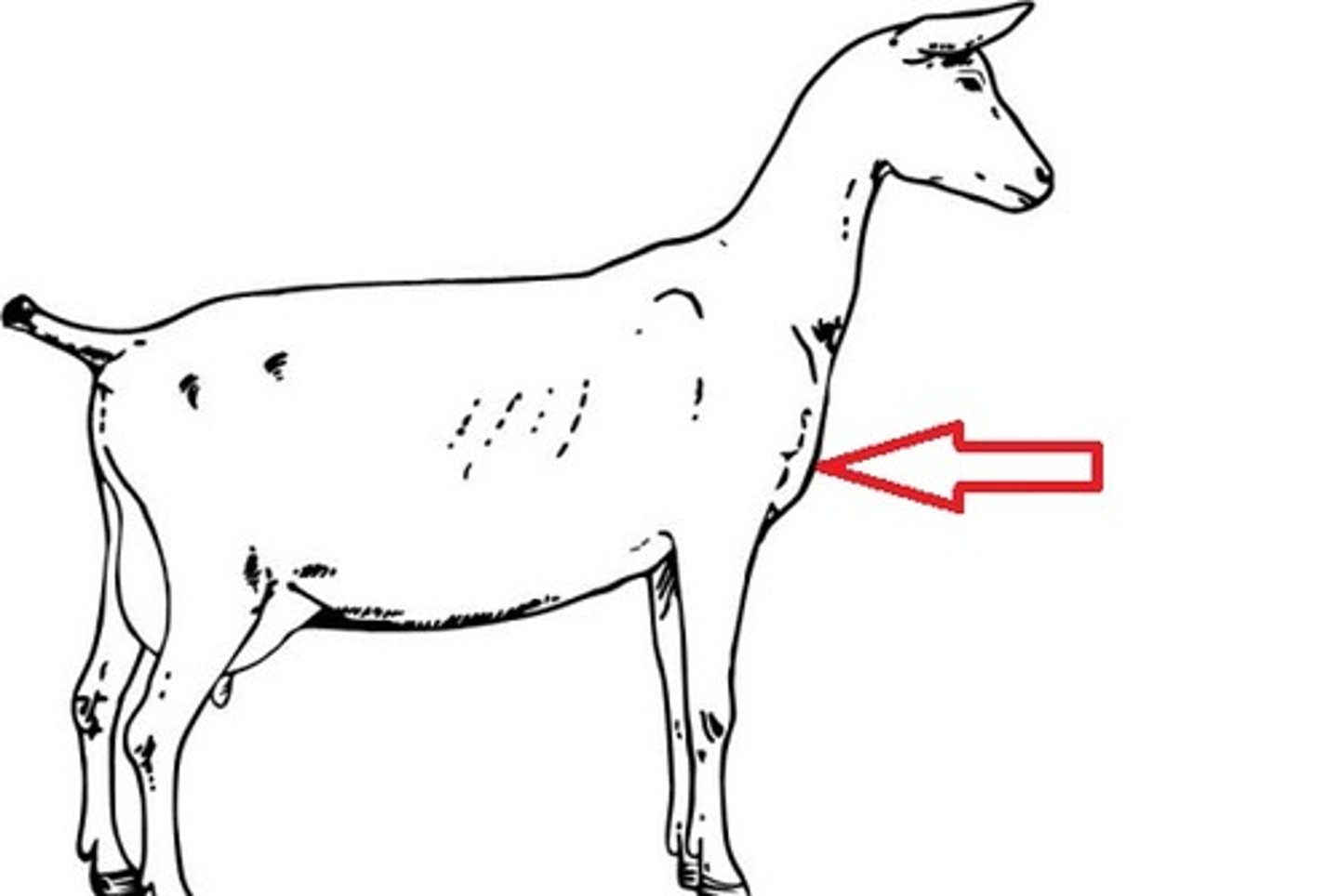
pastern
area of the limb between the fetlock and hoof
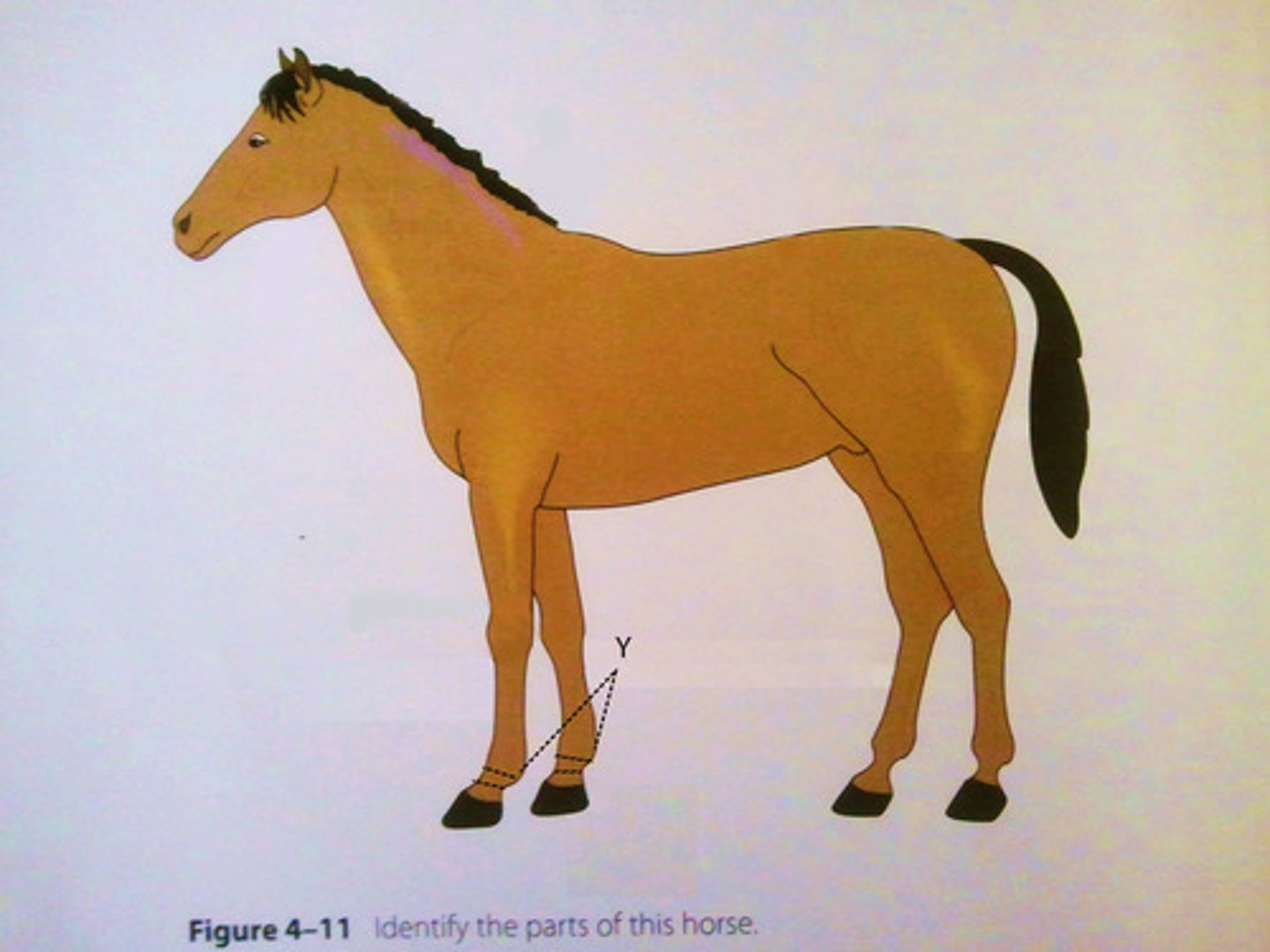
fetlock
area of the limb between the pastern and the cannon

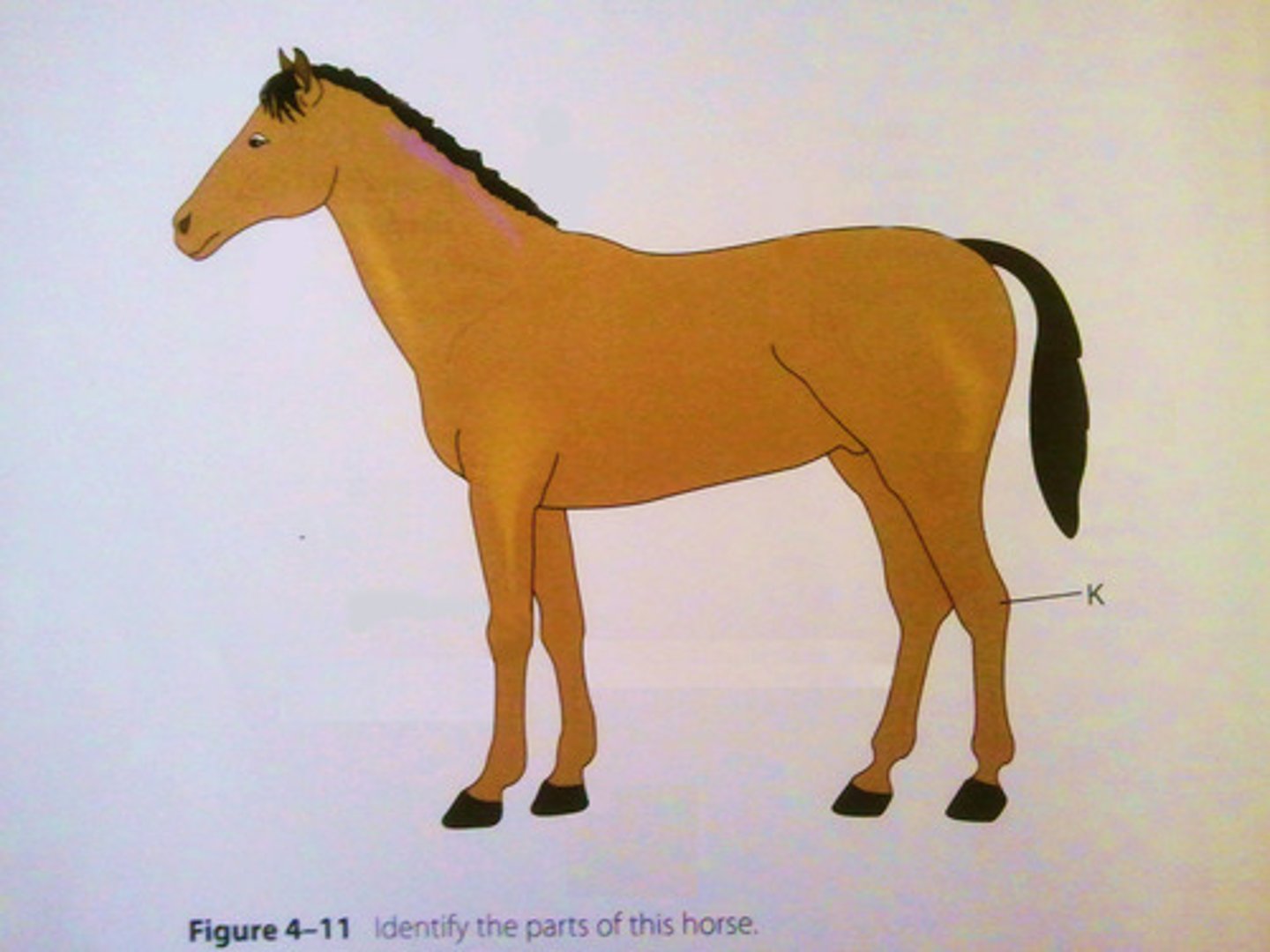
cannon
Large metacarpal or metatarsal bone of hoofed animals
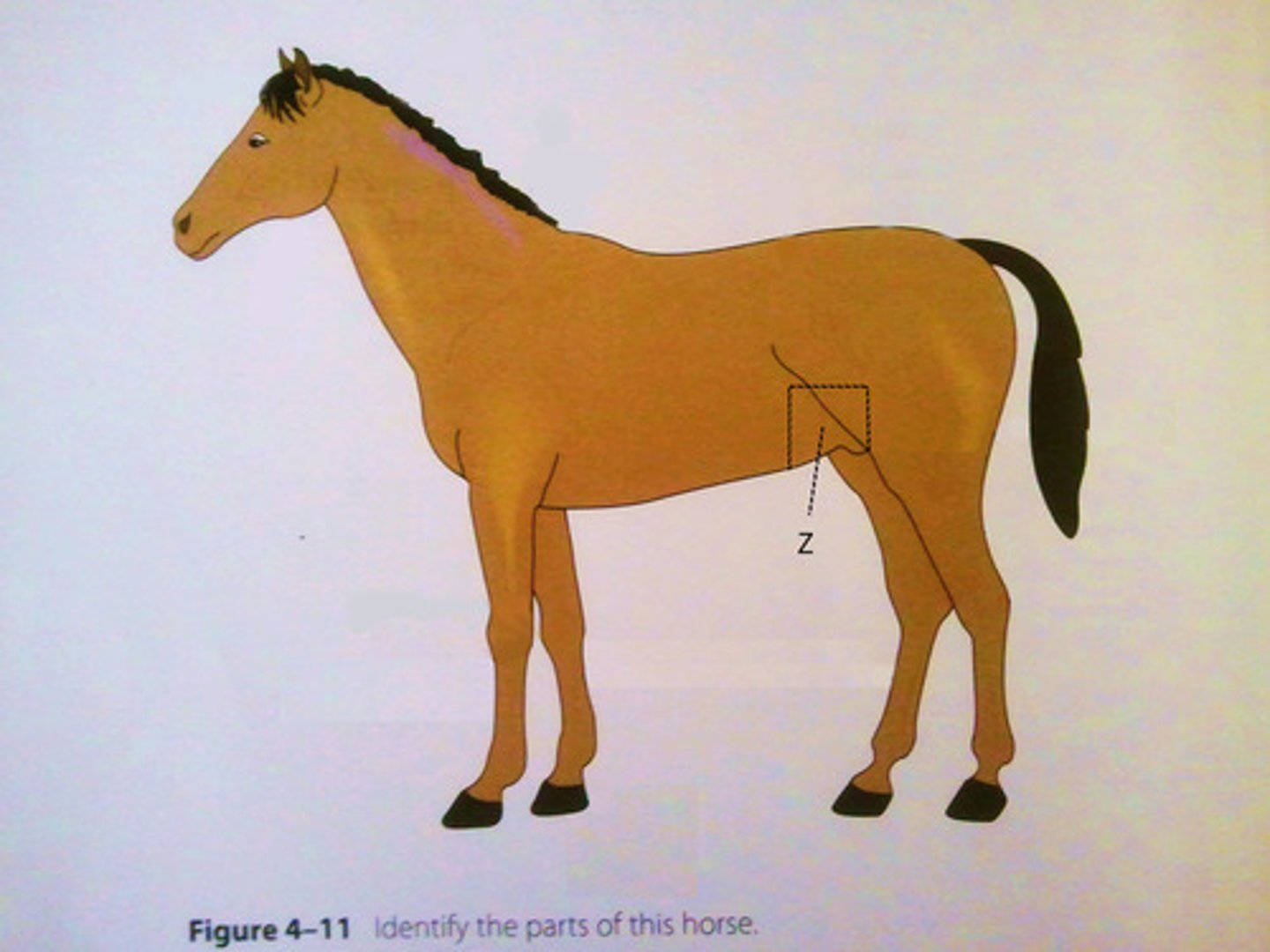
flank
side of the body between the ribs and ilium
hock
tarsal joint also called the tarsus

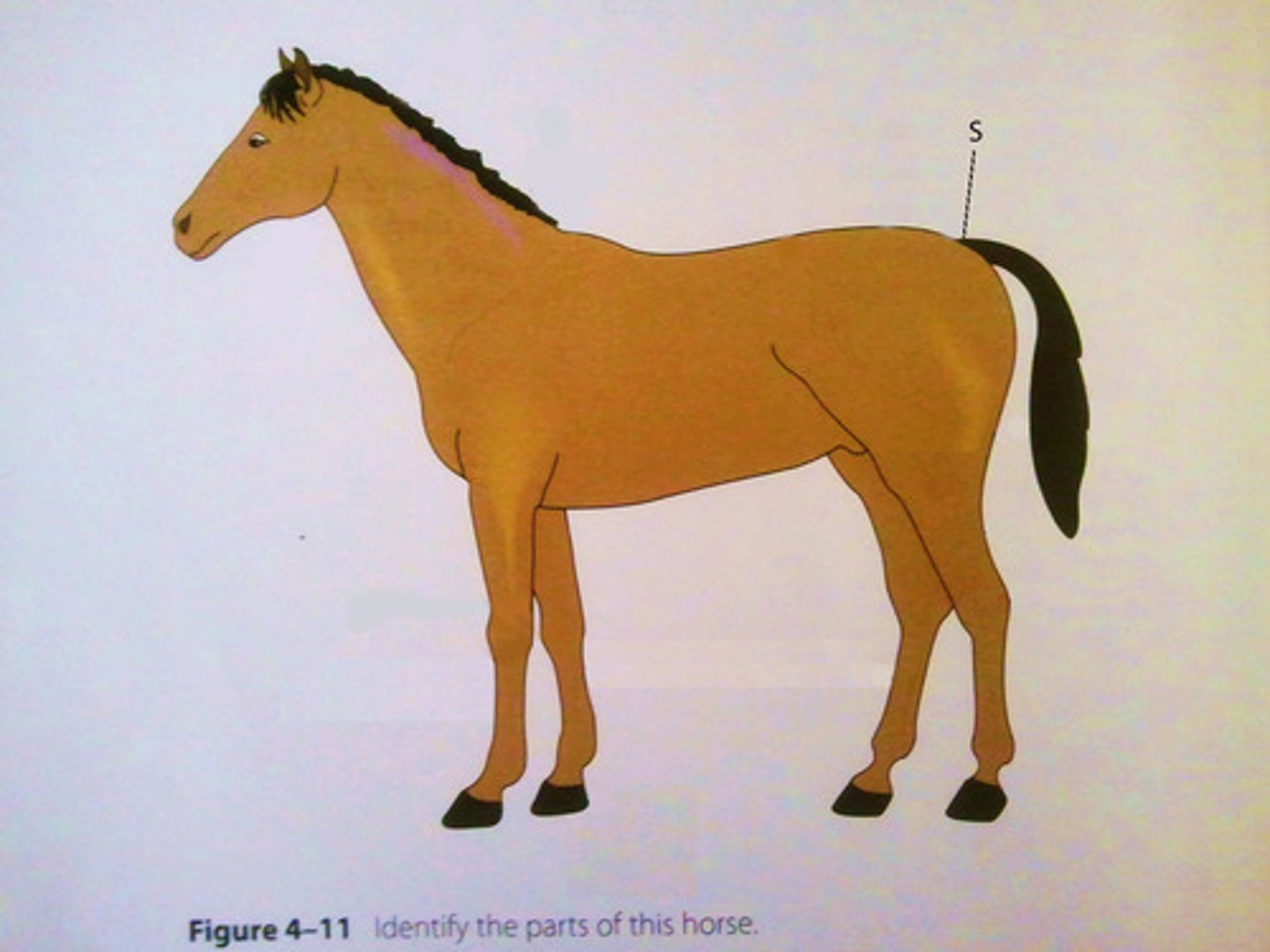
stifle
upper thigh joint
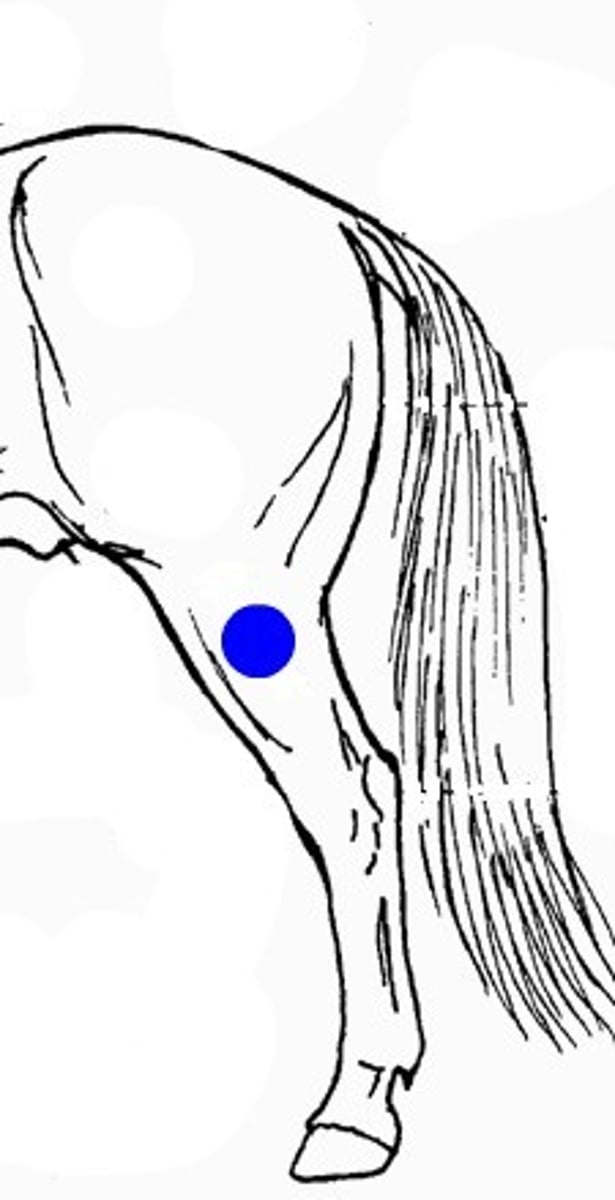
tailhead
base of the tail where it connects to the body

osmosis
the movement of a solvent (water) from high to low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane
isotonic
water movement into the cell is equal to water movement out of the cell
hypertonic
water moves out of the cell
hypotonic
water moves into the cell
hemolysis
destruction of red blood cells
integumentary system
composed of all 4 tissues (skin, hair, hooves, horns, claws)
keratinization
when cells expire by giving up vital organelles and nuclei to make room for keratin
keratin
hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails
basement membrane
separates epidermis and dermis
epidermis
outer layer of skin, composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that forms a waterproof sheild
dermis
highly fibrous middle layer of skin responsible for most structural strength of the skin (dense irregular connective tissue, collagen, fibers, hair follicles, nerve endings, glands, smooth muscle, blood vessels, and lymphatics)
2 layers of the dermis
papillary and reticular
papillary layer
thin and superficial outer layer of the dermis, directly beneath the epidermis
recticular layer
think and dense deeper layer of the dermis
dermal papillae
nipplelike projections that rise into the epidermis helping to cement the dermis and epidermis together