AP PSYCHOLOGY: Unit 4 Flashcards
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
learning
a relatively permanent change in an organism's behavior due to experience.

habituation
an organism's decreasing response to a stimulus
with repeated exposure to it
associative learning
learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning).

stimulus
any event or situation that evokes a response
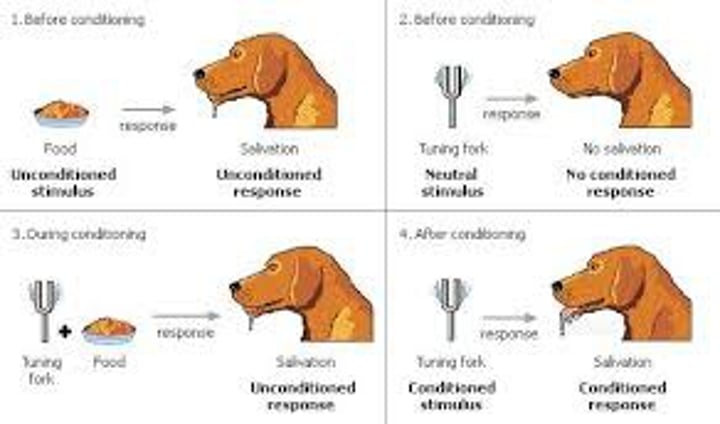
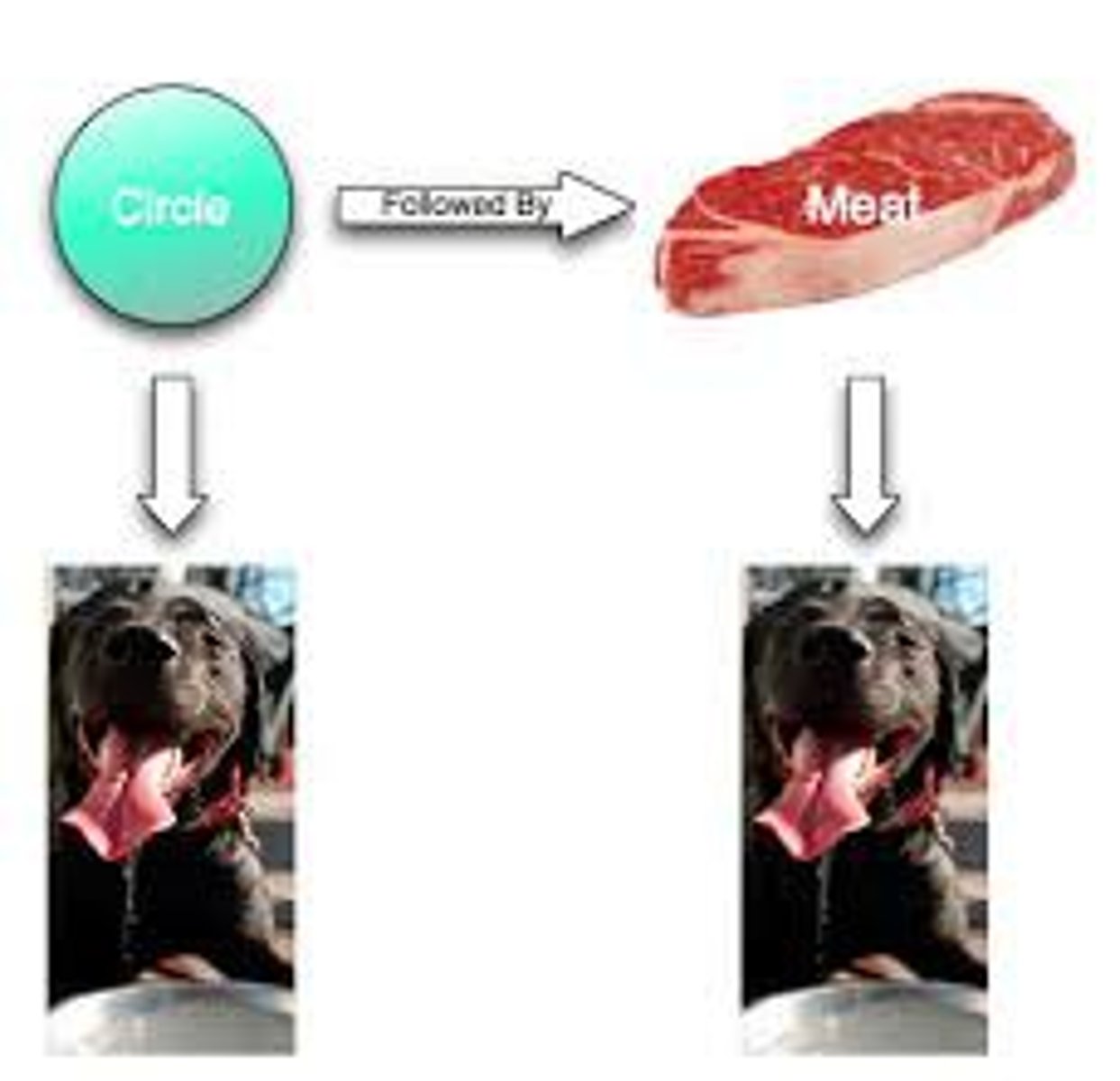
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which an organism comes to associate stimuli. A neutral stimulus that signals an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) begins to produce a response that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus.
behaviorism
the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes. Most research psychologists today agree with (1) but not with (2).

neutral stimulus
(prior to conditioning) is a stimulus that produces no response other than catching your attention.
unconditioned response (UCR)
in classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (UCS), such as salivation when food is in the mouth.

unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally—naturally and automatically—triggers a response.

conditioned response (CR)
in classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus (CS).

conditioned stimulus (CS)
in classical conditioning, an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response.

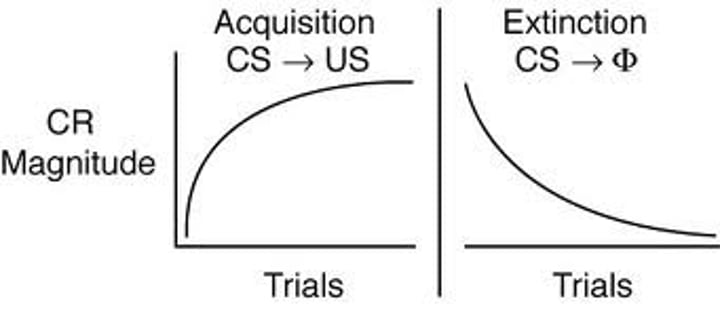
acquisition
in classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.
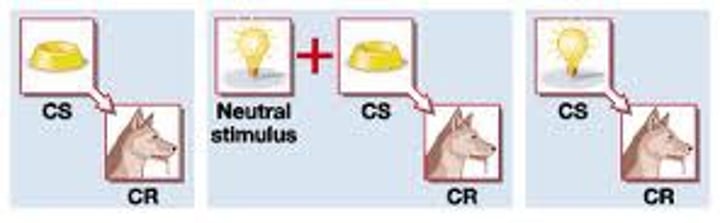
higher-order conditioning
a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also called second-order conditioning.)
extinction
A process by which a response that has been learned is weakened by the absence or removal of stimuli or reinforcement.
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished conditioned response.
generalization
responding similarly to a range of similar stimuli
discrimination
in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus.

John B. Watson
founder of behaviorism
learned helplessness
showed the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal (or human) learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events. Experiment initially done by Martin Seligman.
respondent behavior
behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus.

operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher.
operant behavior
the network of factors and events involved in the behavior of human and non-human animals

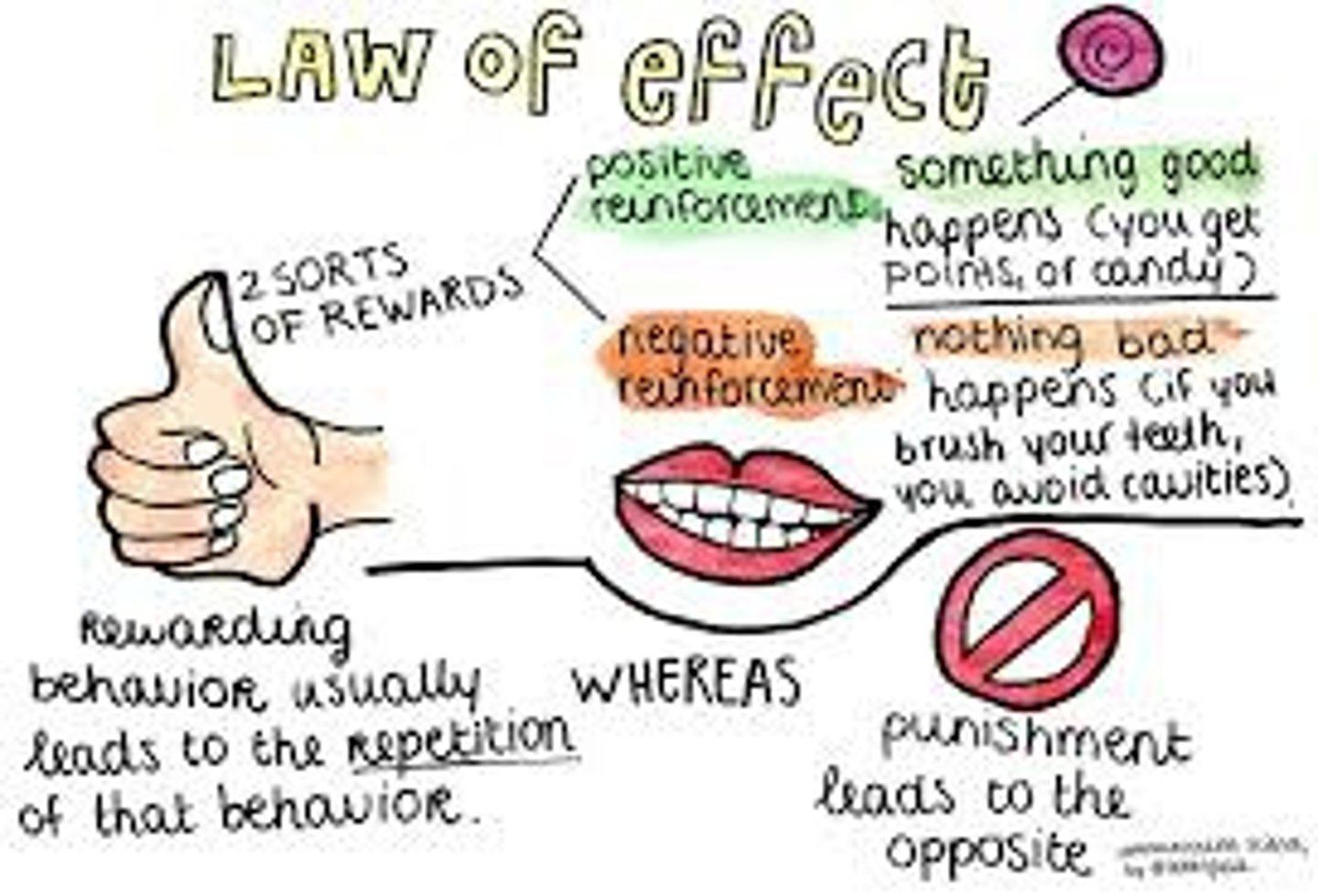
law of effect
The principle that behaviors are selected by their consequences..rewarded behavior is likely to occur again. (Edward Thorndike)
shaping
an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior.

reinforcer
in operant conditioning, any event that strengthens the behavior it follows.
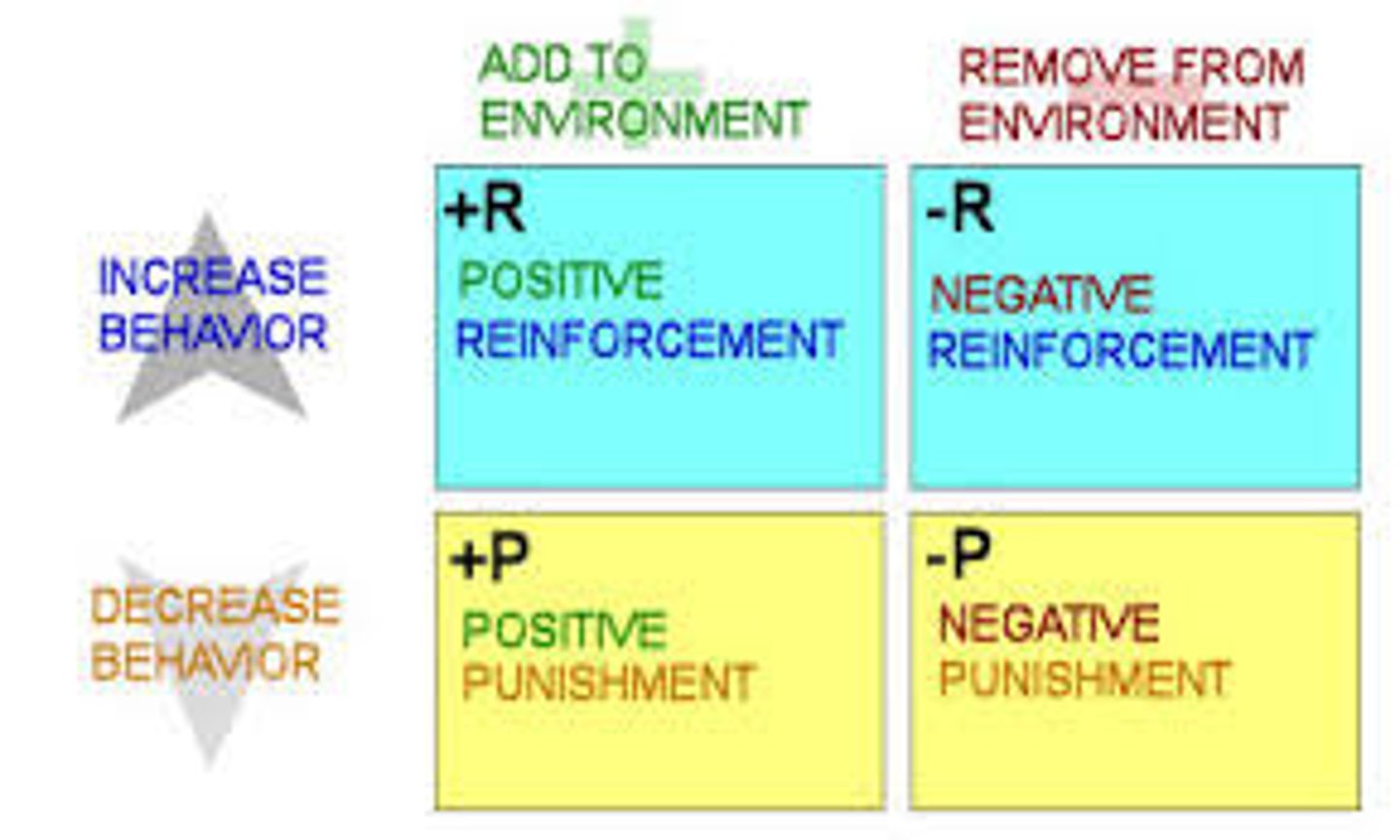
positive reinforcement
increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food. Any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response.

negative reinforcement
increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli, such as shock. Any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response.

discriminative stimulus
in operant conditioning, a stimulus that elicits a response after association with reinforcement (in contrast to related stimuli not associated with reinforcement)
primary reinforcer
an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need.

conditioned (secondary) reinforcer
a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer; (we need to learn this is important)

reinforcement schedules
a pattern that defines how often a desired response will be reinforced
continuous reinforcement schedule
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs. (Goes away easily or quickly once reinforcement is gone.)

partial (intermittent) reinforcement schedule
reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction than does continuous reinforcement.

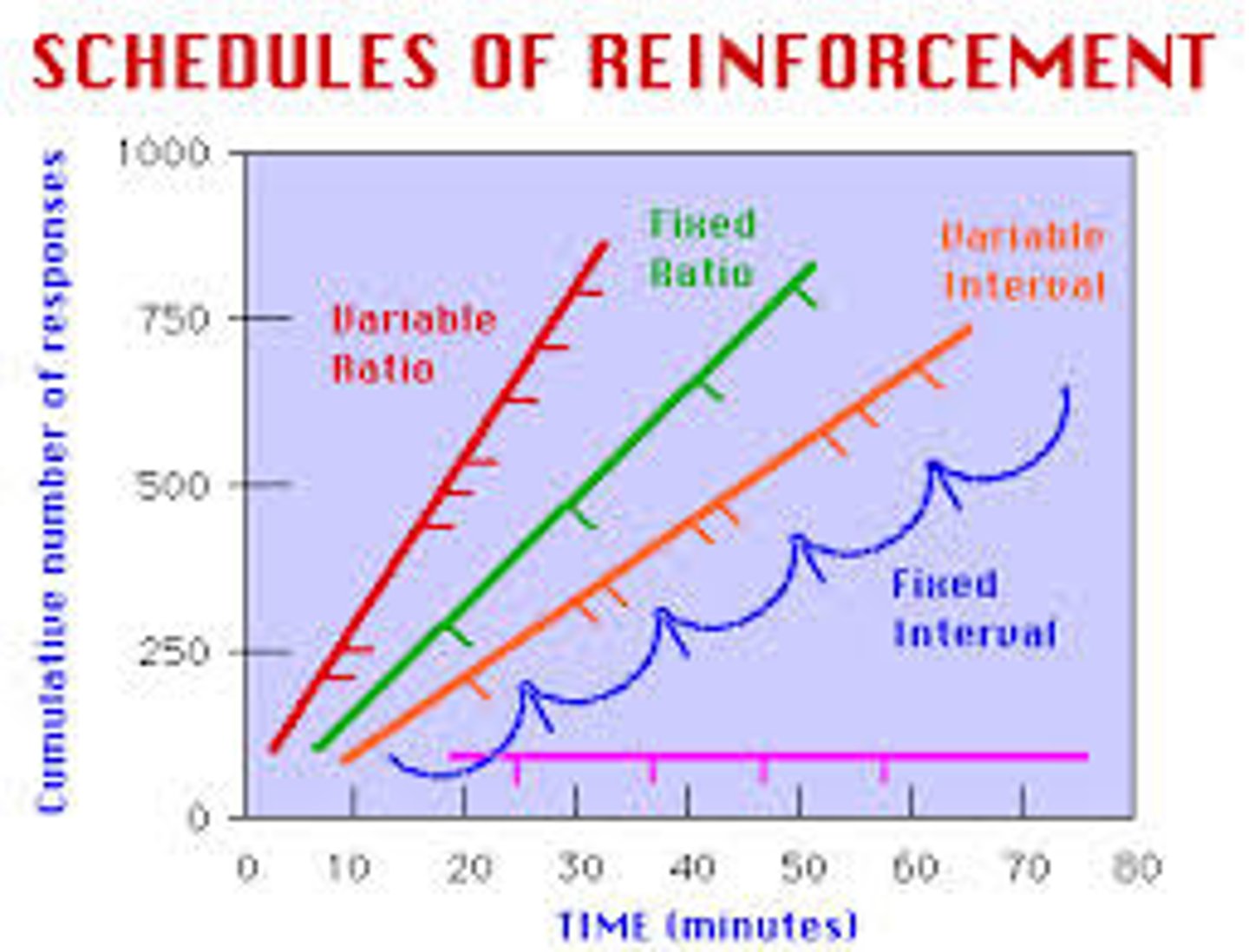
fixed-ratio schedule
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses. (Causes very fast responding as subject knows what to do to get rewarded.)
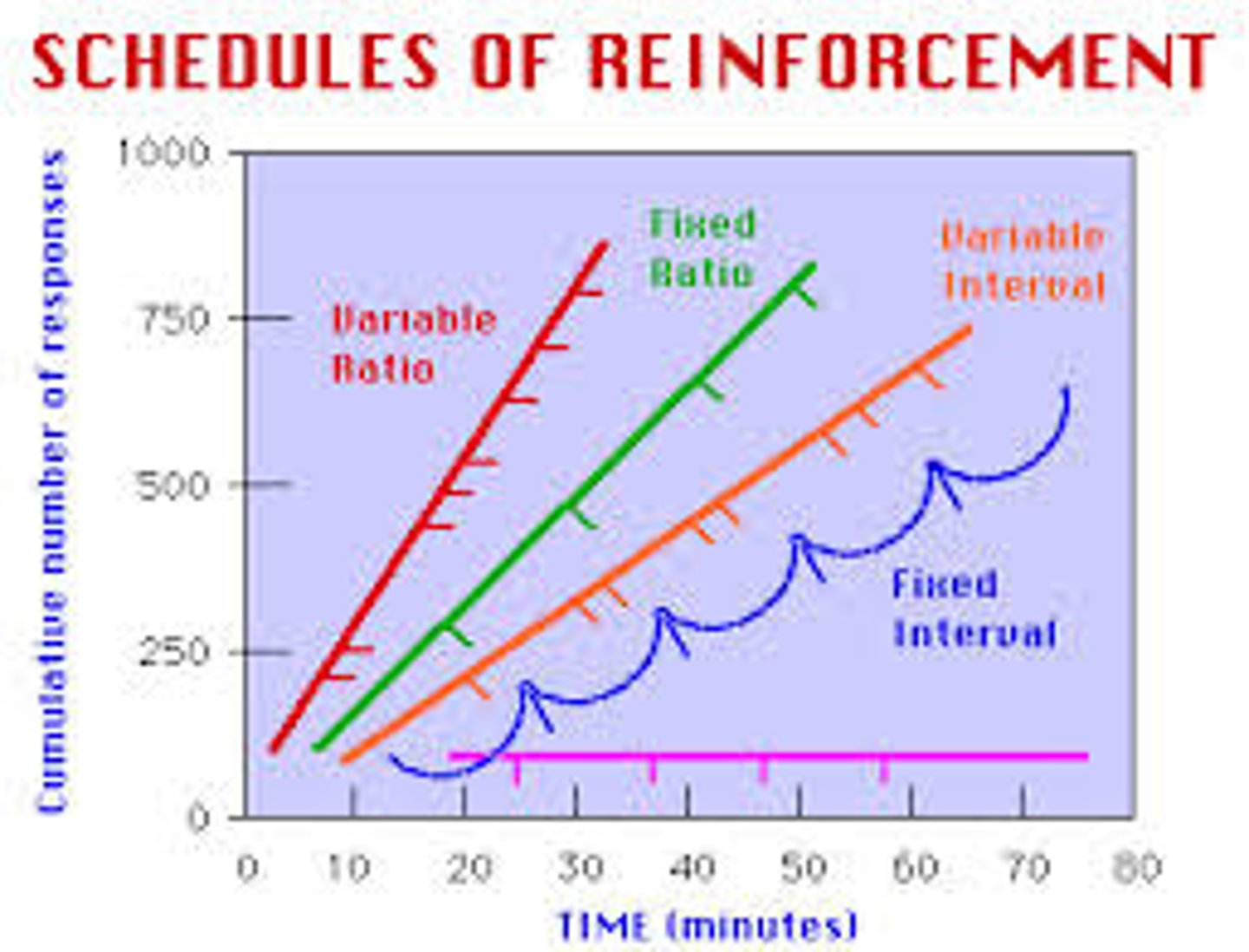
variable-ratio schedule
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses. (Causes very fast responding as subject doesn't know how much they have to do to get reward; very resistant to extinction)
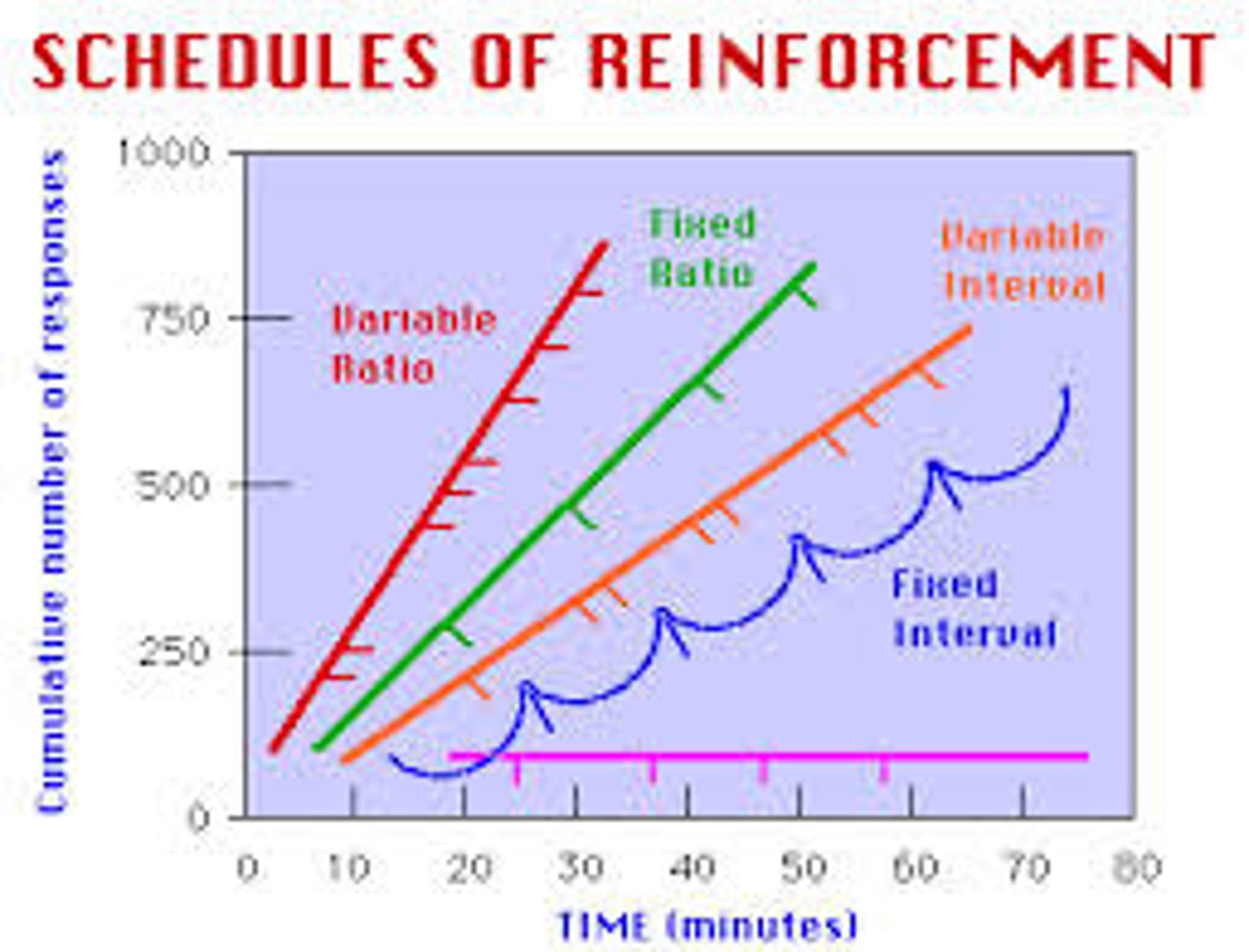
fixed- interval schedule
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed.
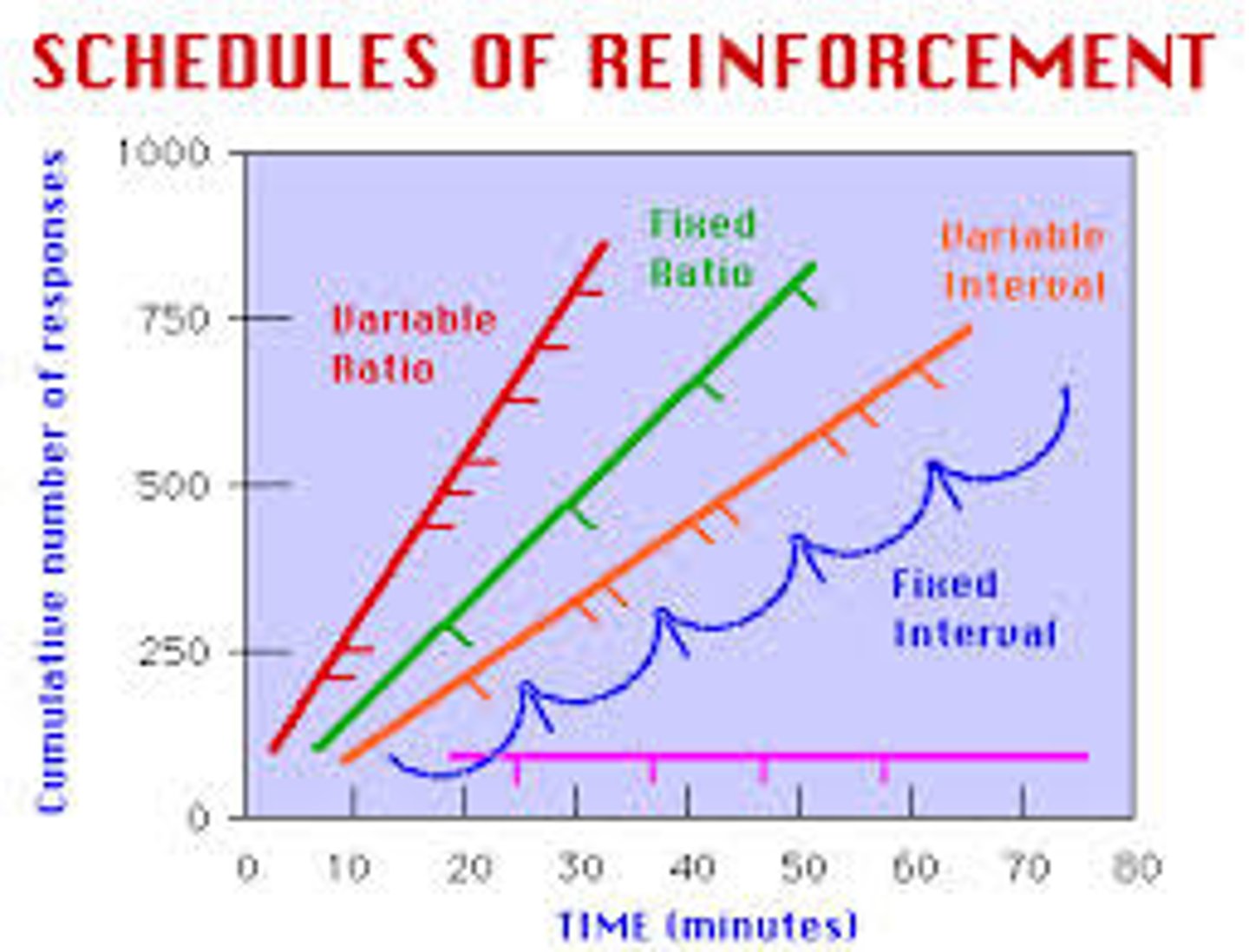
variable-interval schedule
in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals.
punishment
an event that decreases the behavior that it follows. (can be positive or negative)

positive punishment
Administer an aversive (unfavorable) stimulus to decrease behavior. (i.e., spanking, receiving a parking ticket)
negative punishment
Withdraw a desirable stimulus to decrease behavior. (i.e., child on a time out, having driver's license taken away)
preparedness
a biological predisposition to learn associations, such as between taste and nausea, that have survival value
instinctive drift
the tendency of learned behavior to gradually revert to biologically predisposed patterns
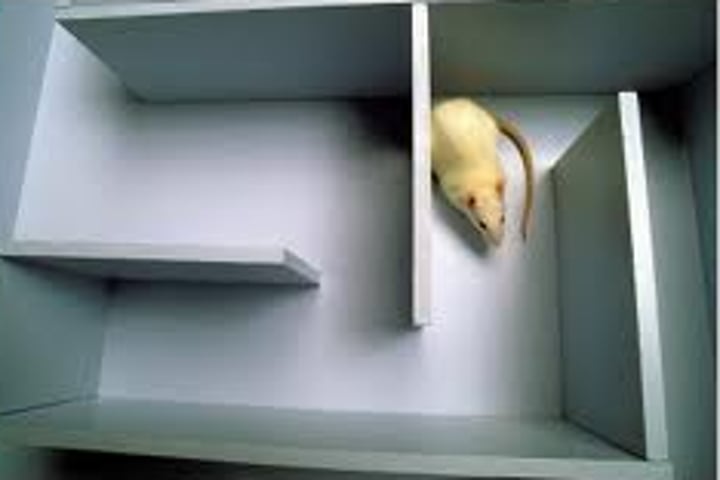
cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment.
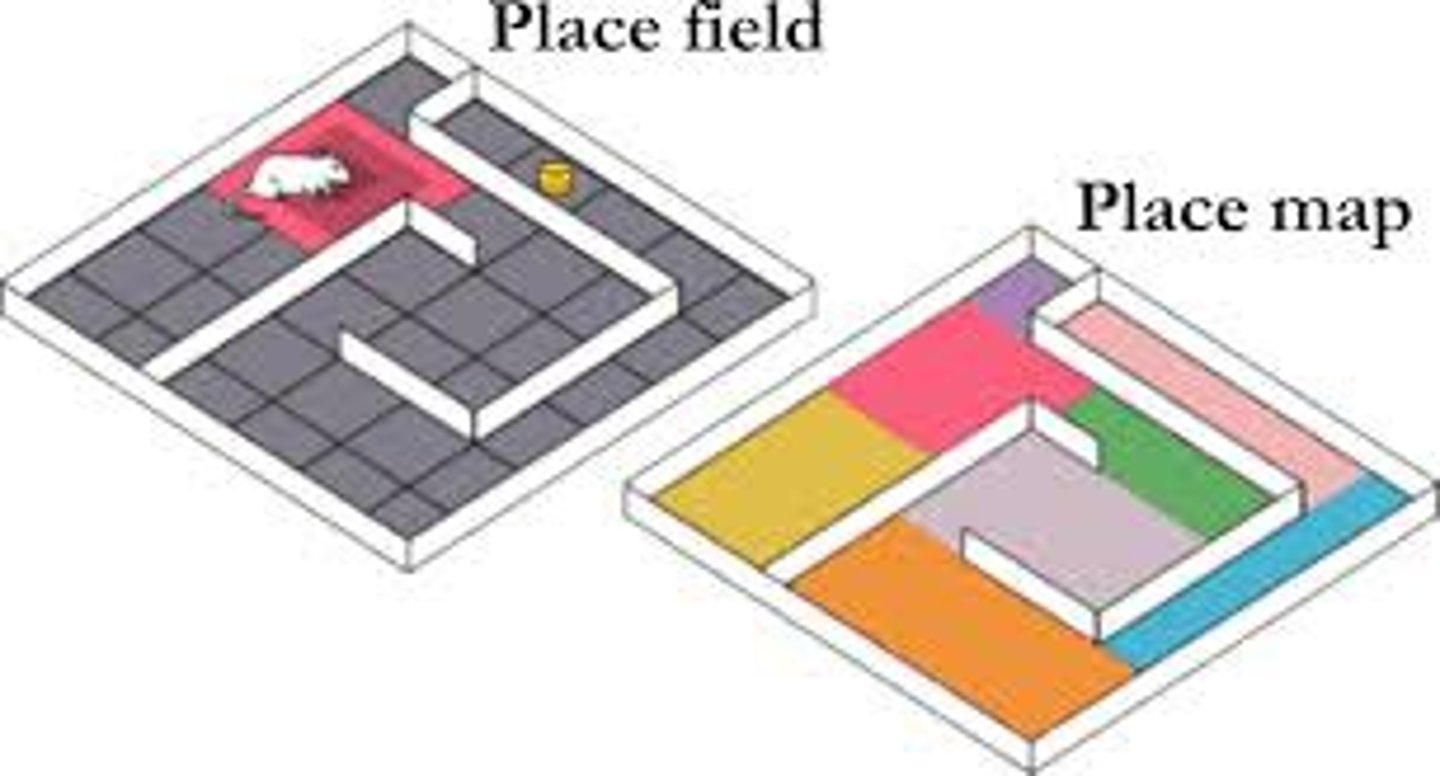
latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it.

insight
a sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem; it contrasts with strategy-based solutions.

intrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake.
extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment.
biofeedback
a system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension.

observational learning-aka social learning
learning by observing others (also called social learning); primary experiment done by Albert Bandura with Bobo Doll

modeling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior

mirror neurons
frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. The brain's mirroring of another's action may enable imitation and empathy.

prosocial behavior
positive, constructive, helpful behavior. The opposite of antisocial behavior.

antisocial behavior
disruptive acts characterized by covert and overt hostility and intentional aggression toward others.

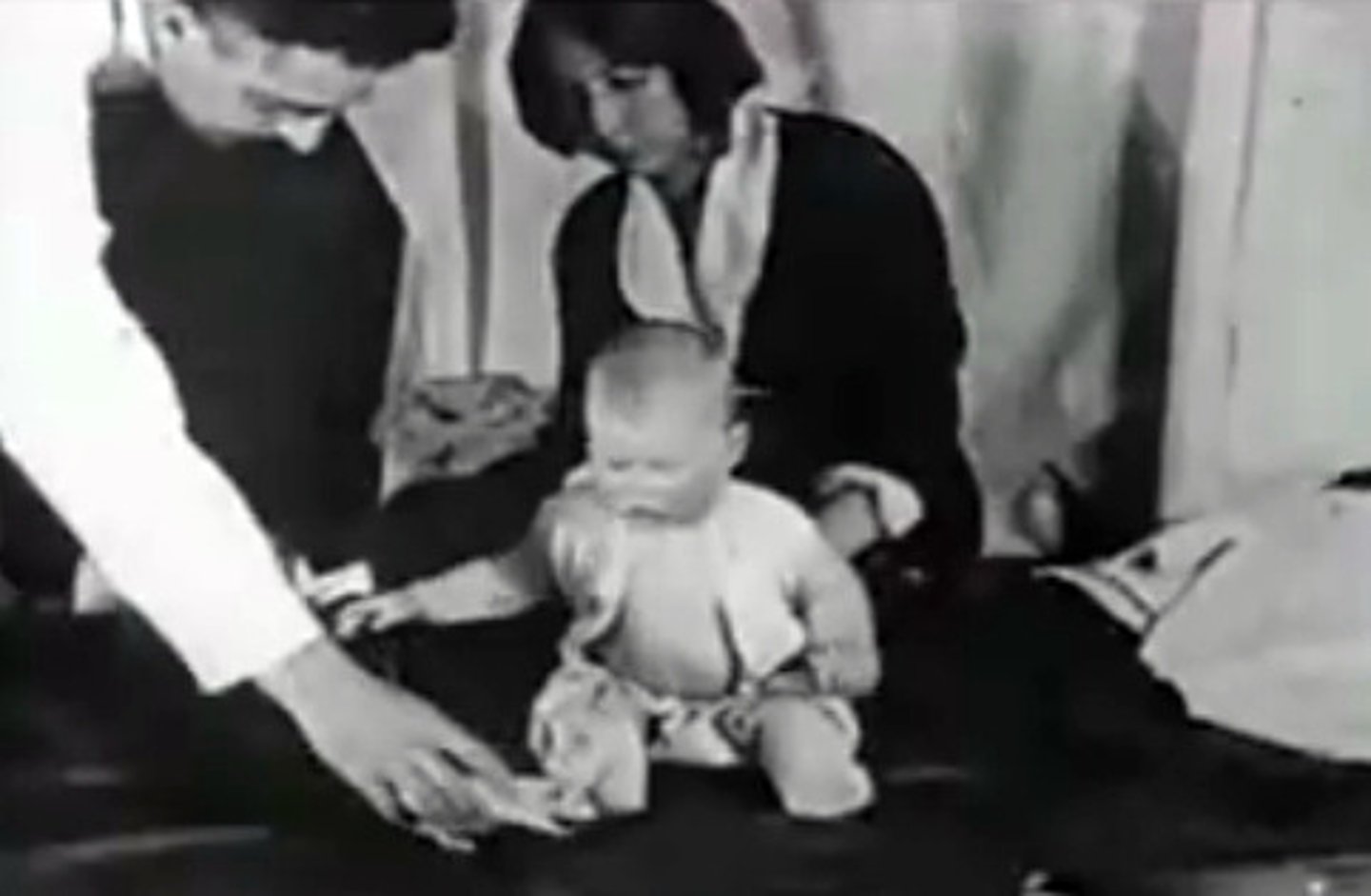
Little Albert
Experiment done by Behaviorist, John B. Watson, classically conditioned Little Albert to fear a white rat (as well as all furry animal)
Instinctive Drift
Tendency for animals to move towards their biologically predisposed instinctive behaviors.

Aversive Conditioning
a technique used to reduce the appeal of behaviors one wants to eliminate by associating them with physical or psychological discomfort (Associating something negative with a behavior one wants to stop.)

Taste Aversion
is a learned response to eating spoiled or toxic food. When this takes place, you avoid eating the foods that make you ill. It can be so powerful that sometimes you also avoid the foods that you associate with an illness, even if the food did not cause the illness.

John Garcia
He along with Robert Koelling studied taste aversion in 1966 while researching the effects of radiation on laboratory rats. Noticed the laboratory rats started to avoid drinking the water from plastic bottles in the radiation chambers. Realizing the rats might be associating the plastic-tasting water with the sickness experienced from radiation, the researchers designed an experiment to test their hypothesis. Primary researcher with Taste Aversion.

Biological Predispositions
biological constraints predispose organisms to learn associations that are naturally adaptive.
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorism's most influential and controversial therapist. Proved that reinforcements can make animals do almost any task.

Edward Thorndike
Developed term "law of effect" proving that reward behavior is likely to occur again by using cats and having them escape his puzzle boxes.
Immediate Reinforcer
A type of reinforcer that occurs instantly after a behavior.
(A rat gets a food pellet for a bar press.)
Delayed Reinforcer
A type of reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. (A paycheck that comes at the end of a week.)
Token Economy
Every time a desired behavior is performed a reward/token is given. One can trade tokens for a variety of prizes (reinforcers); Used in homes, prisons, mental institutions, therapy and prisons

Overjustification Effect
when an expected external incentive such as money/prizes decreases a person's intrinsic motivation to perform a task.

Teaching Machines
Skinner introduced this concept for schools to shape students learning in small steps and provide reinforcements for correct rewards.

Albert Bandura
pioneer in observational learning (AKA social learning), stated that people profit from the mistakes/successes of others; Studies: Bobo Dolls-adults demonstrated 'appropriate' play with dolls, children mimicked play
cognitive learning
the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language
Edward Tolman
cognitive psychologist; latent learning and cognitive map
emotion-focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction
personal control
our sense of controlling our environment rather than feeling helpless
external locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate. (Rotter)
internal locus of control
the perception that you control your own fate (Rotter)
Ivan Pavlov
discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell
John Watson
Early behaviorist; famous for the "Little Albert" experiments on fear conditioning
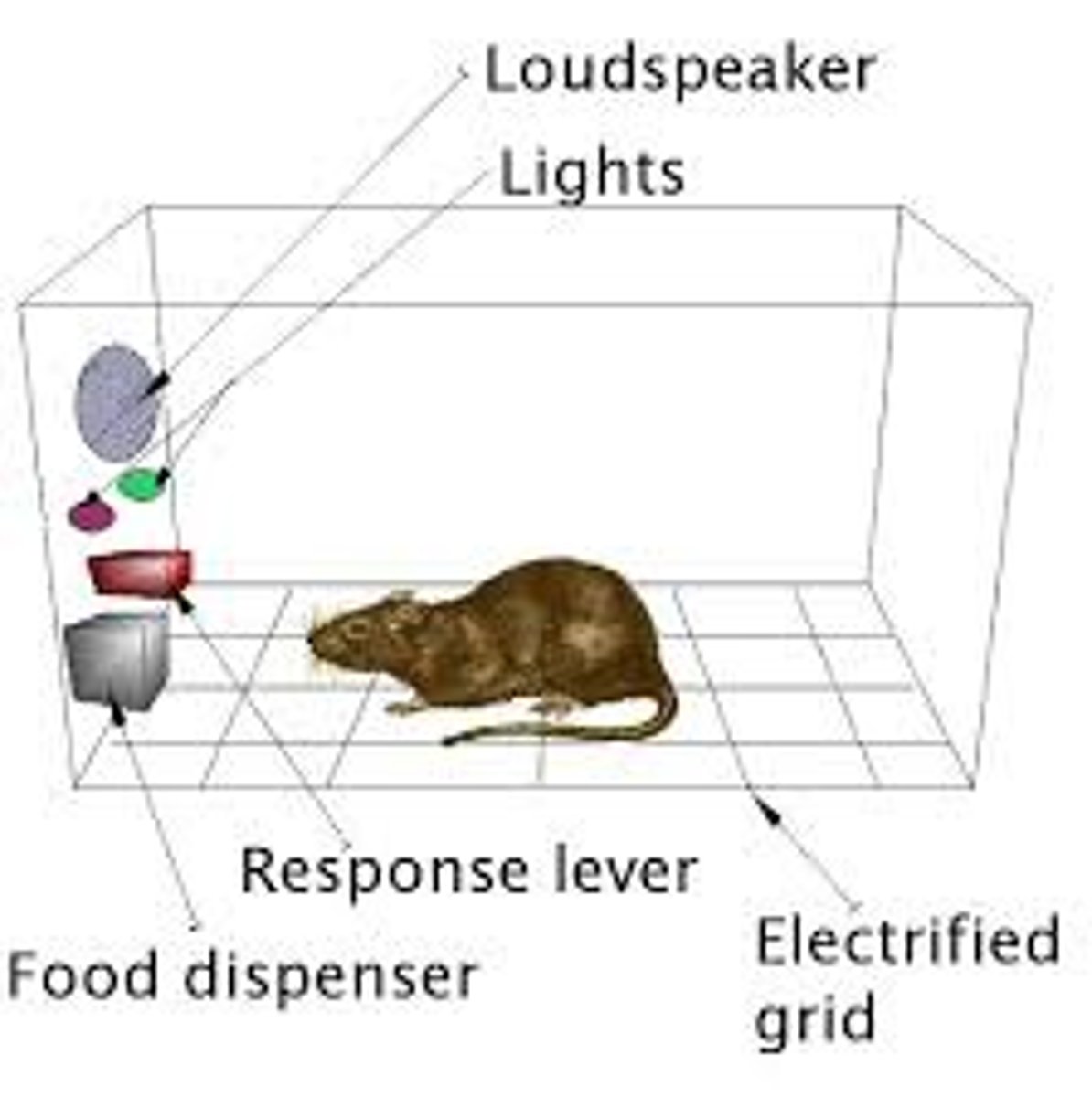
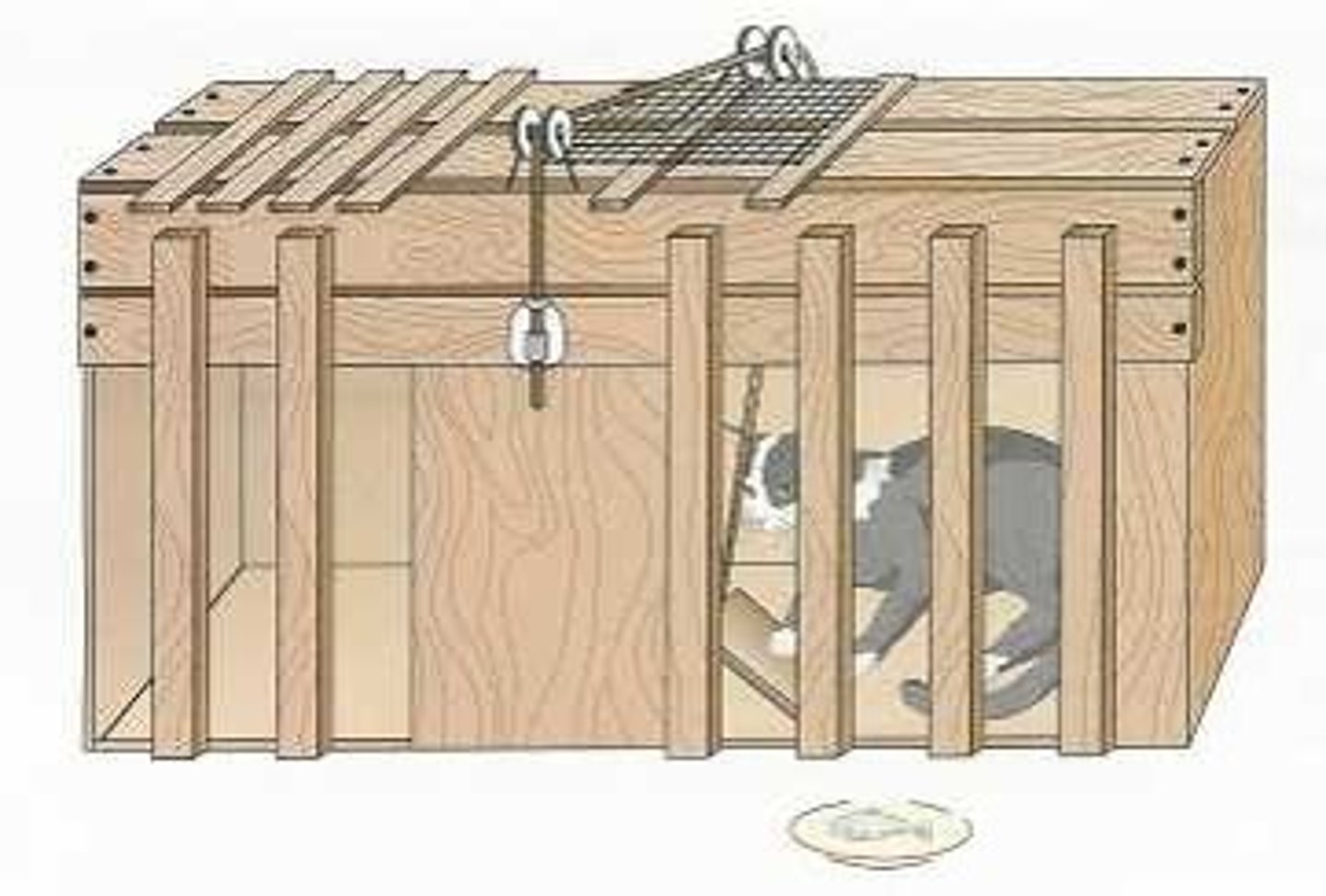
Operant Chamber (Skinner Box)
a chamber containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer, with attached devices to record the animal's rate of bar pressing or key pecking. Used in operant conditioning research
Robert Rescorla
American psychologist who experimentally demonstrated the involvement of cognitive processes in classical conditioning
reinforcement
in operant conditioning, any event that strengthens the behavior it follows
reinforcement schedule
a pattern that defines how often a desired response will be reinforced
Pairing
often seen in a classical conditioning, the connection between a UCS & CS