Vertebral Column
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vertebral formula, vertebral column, vertebrae, anticlinal vertebrae, ligaments, articulations, spinal cord, cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, muscles, ribs, sternum
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Vertebral formula: dog/cat
C7, T13, L7, S3, Cd (varible)
Vertebral formula: horses
C7, T18, L6(5), S5, Cd 15-21
Vertebral formula: ox
C7, T13, L6, S5, Cd 18-20
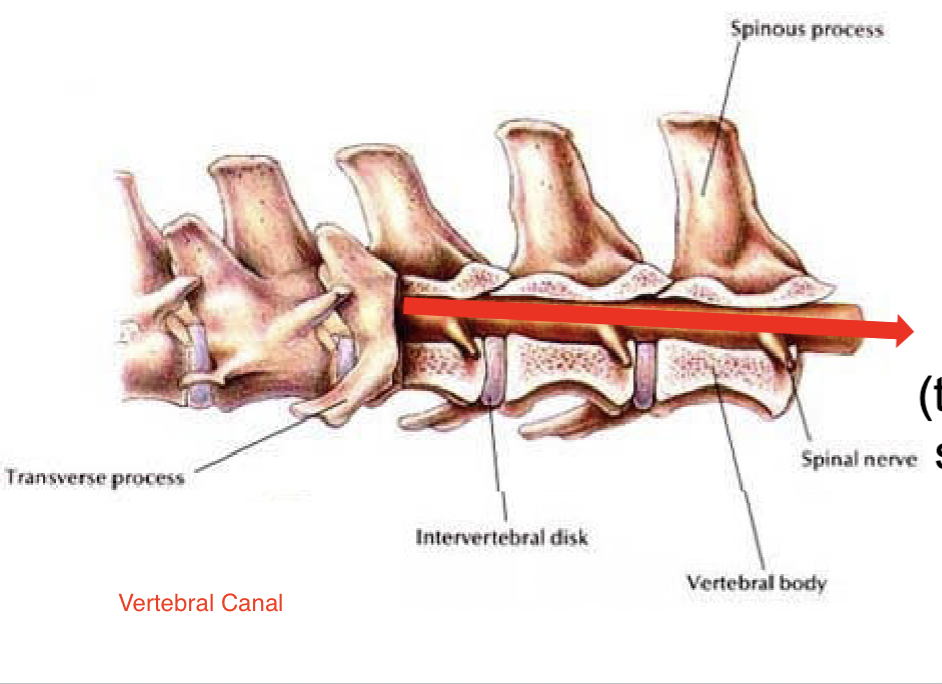
Vertebral canal
The passageway for the spinal cord collectively formed by all of the vertebral foramina
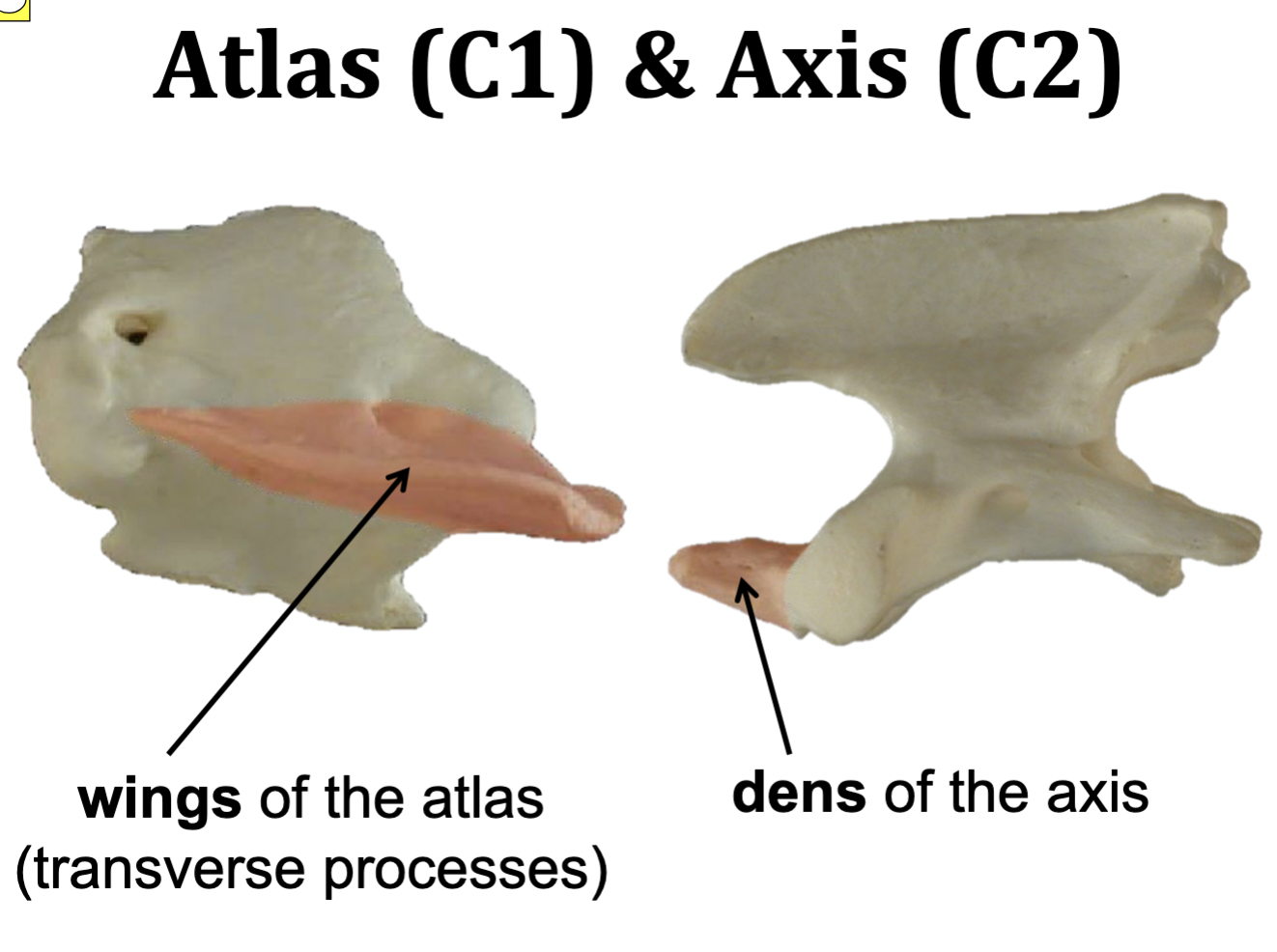
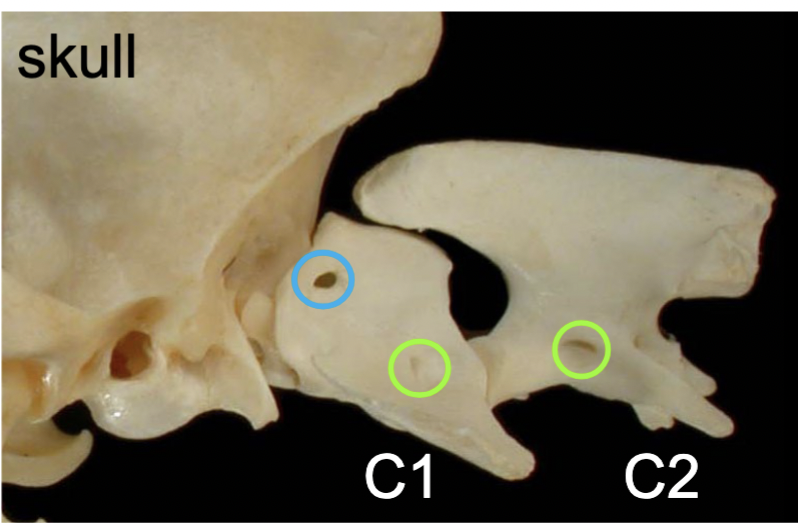
Atlas & Axis
Atlas = C1
Axis = C2
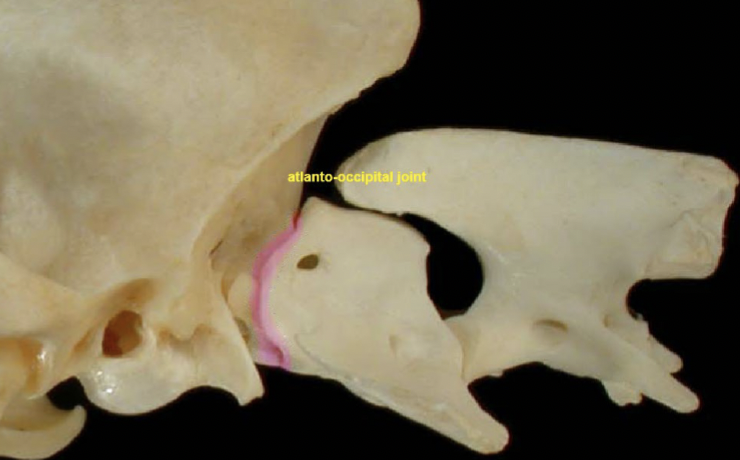
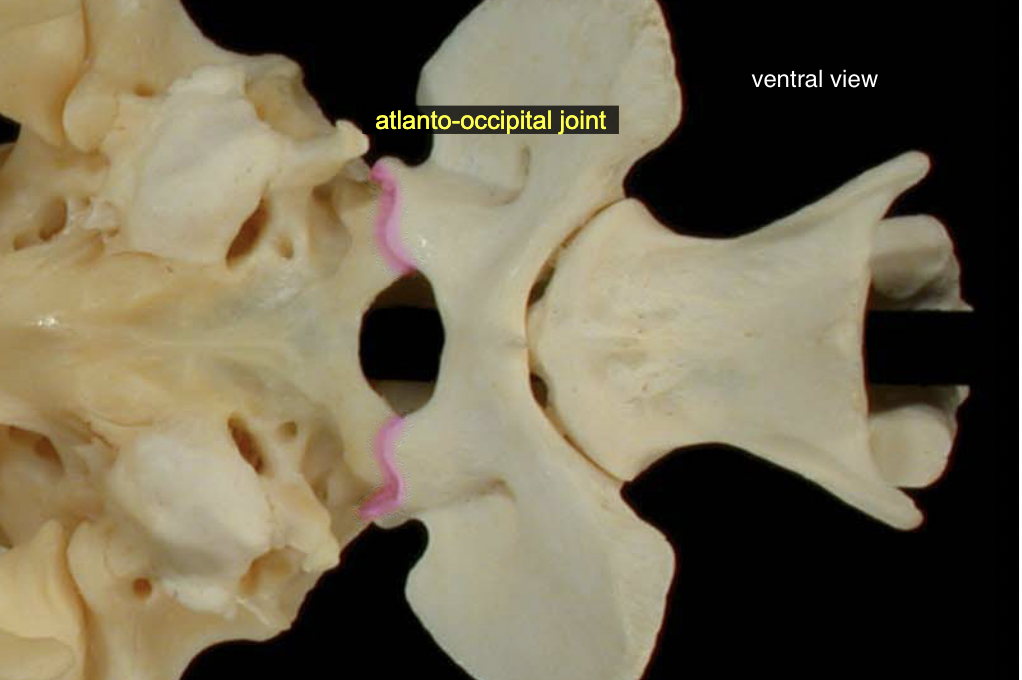
Atlanto-occipital jt
skull → C1
A: ventral flexion & extension (yes (knod) movement)
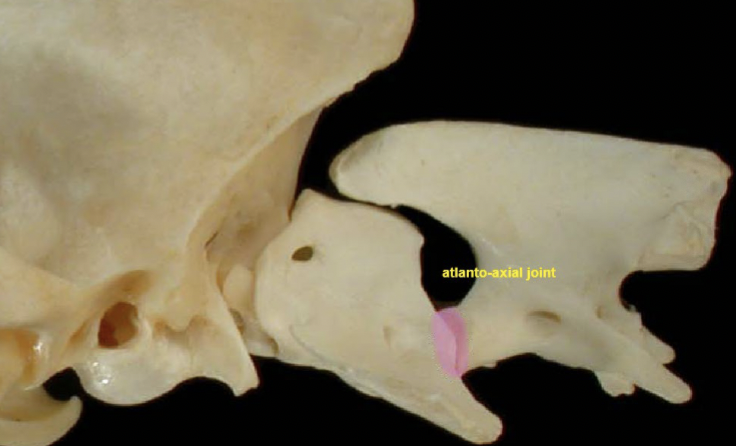
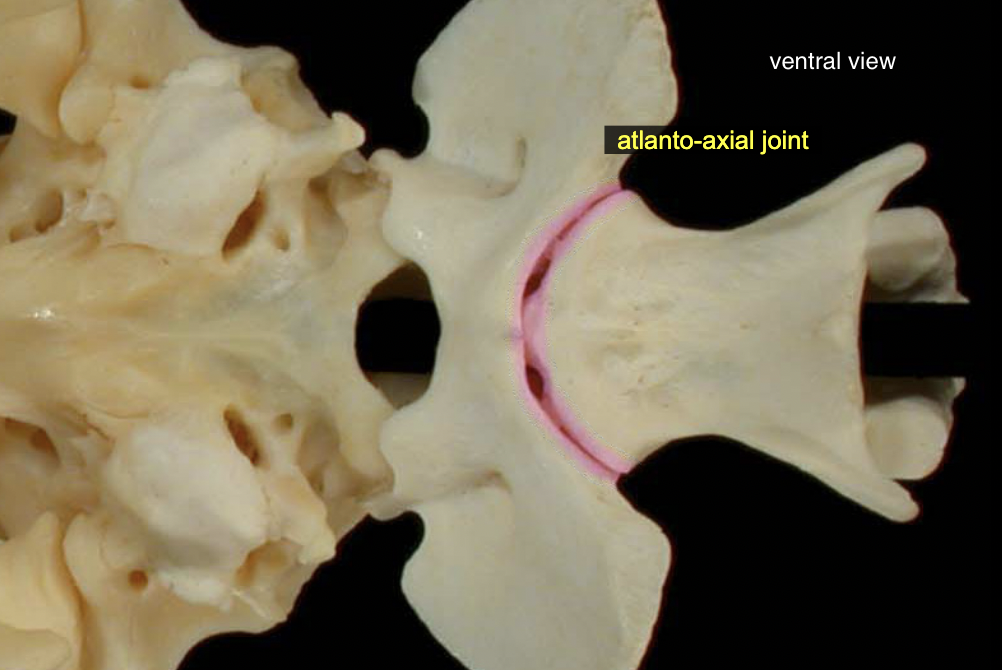
Atlanto-axial jt
C1 → C2
A: rotaion (no (turn) movement)
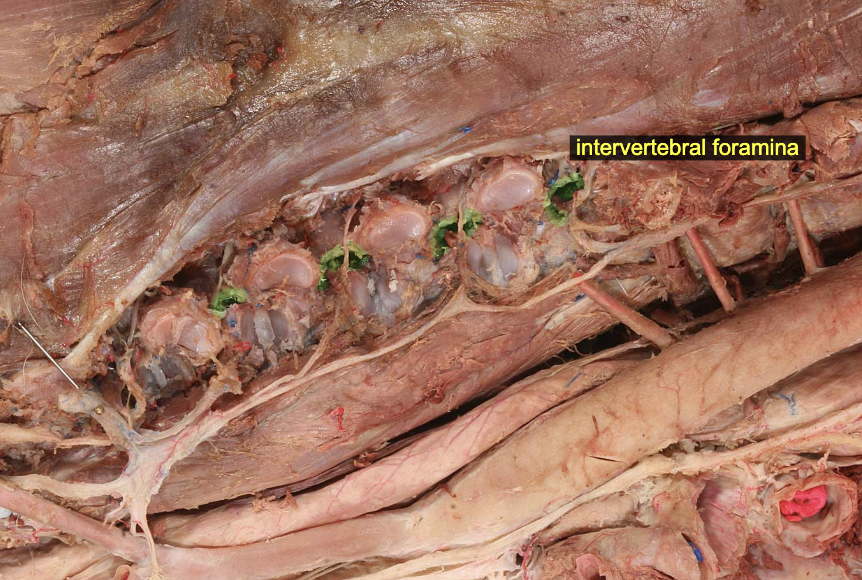
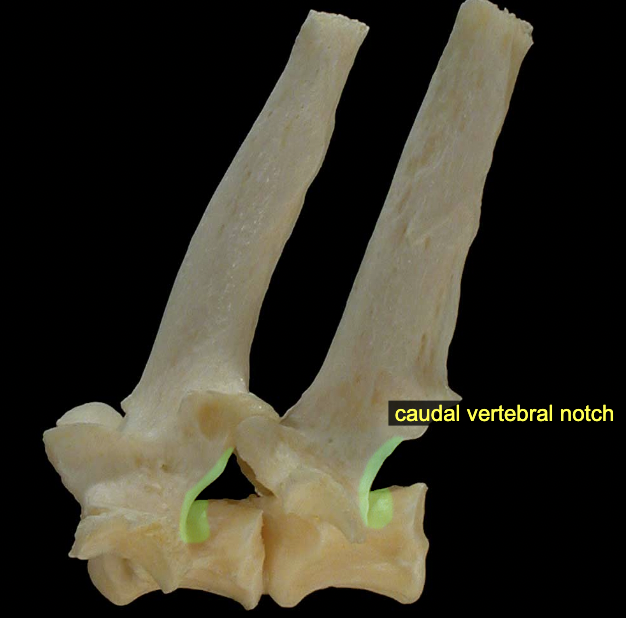
Intervertebral foramina
formed by cranial & caudal vertebral notches of neighboring vertebrae
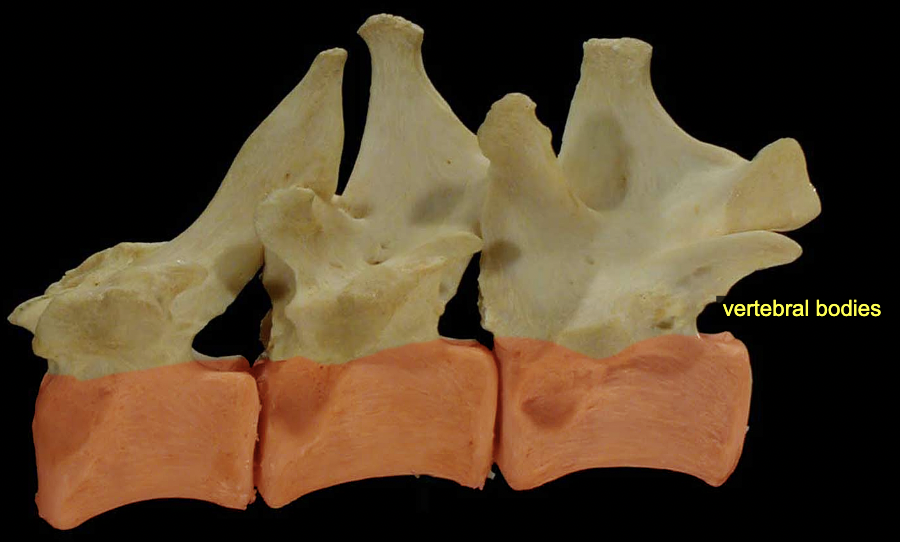
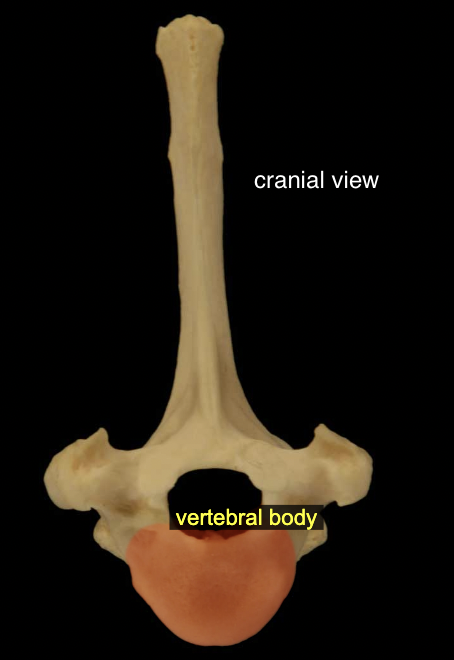
Vertebral body
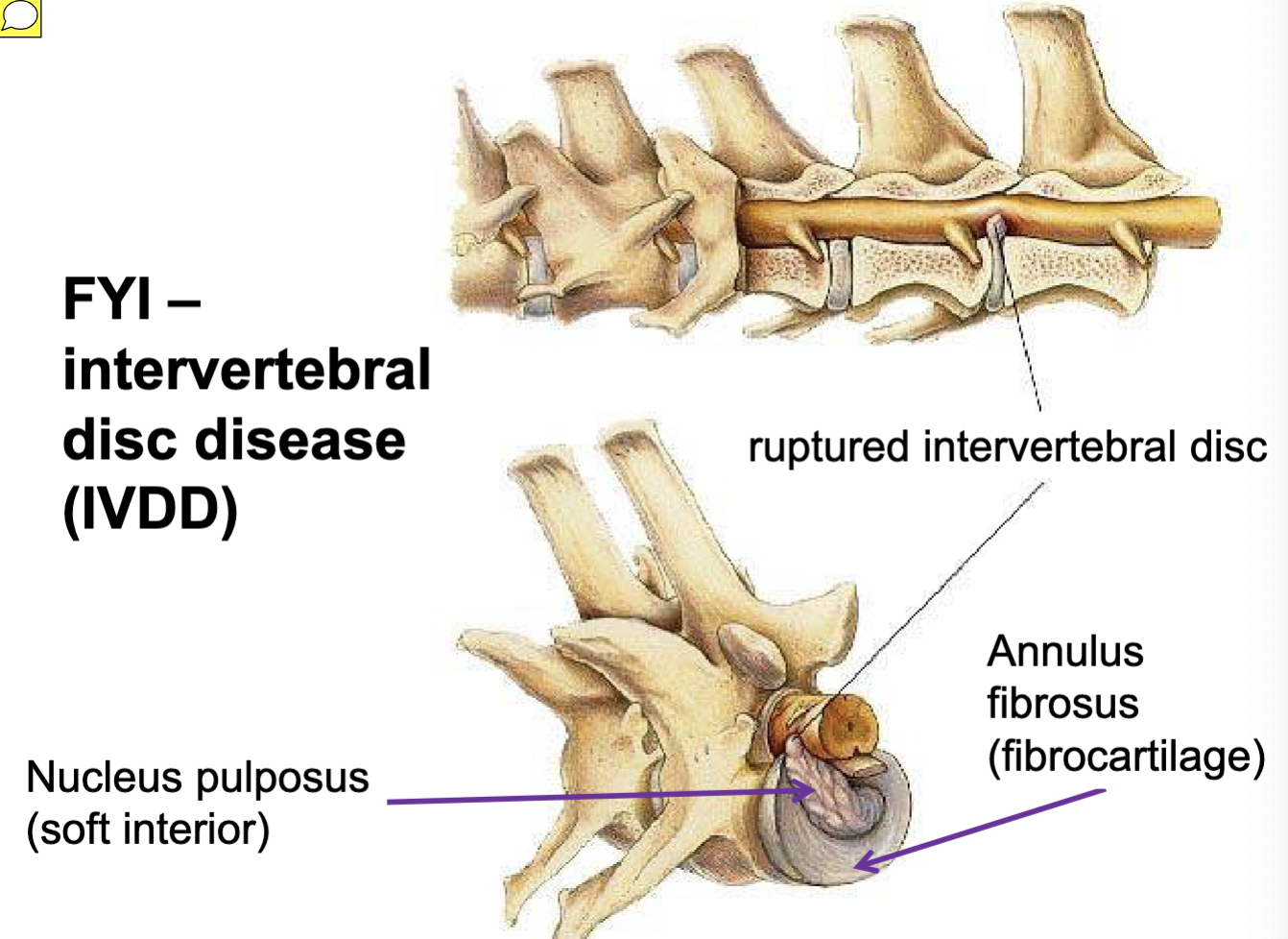
All vertebrae except the atlas (C1) possess a more-or-less cylindrical vertebral body. The bodies articulate with one another at specialized fibrocartilaginous joints called intervertebral disks.
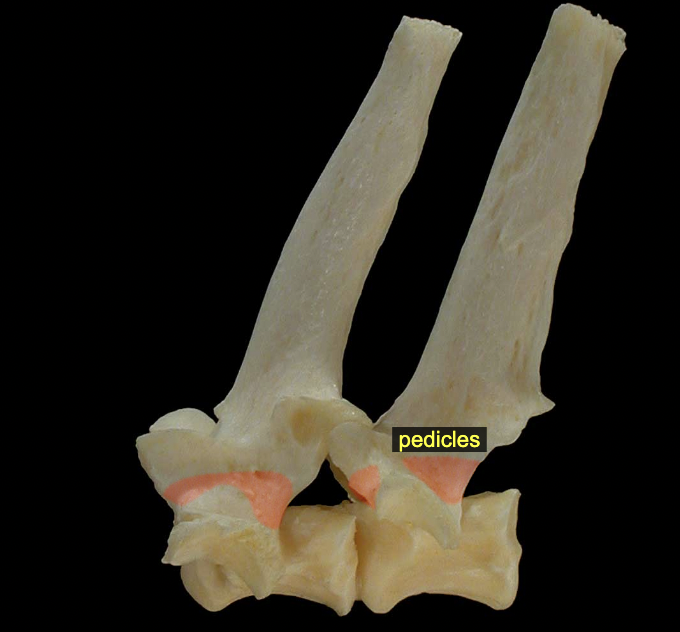
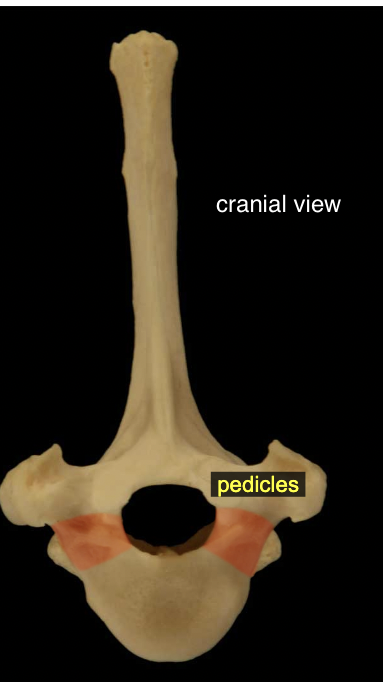
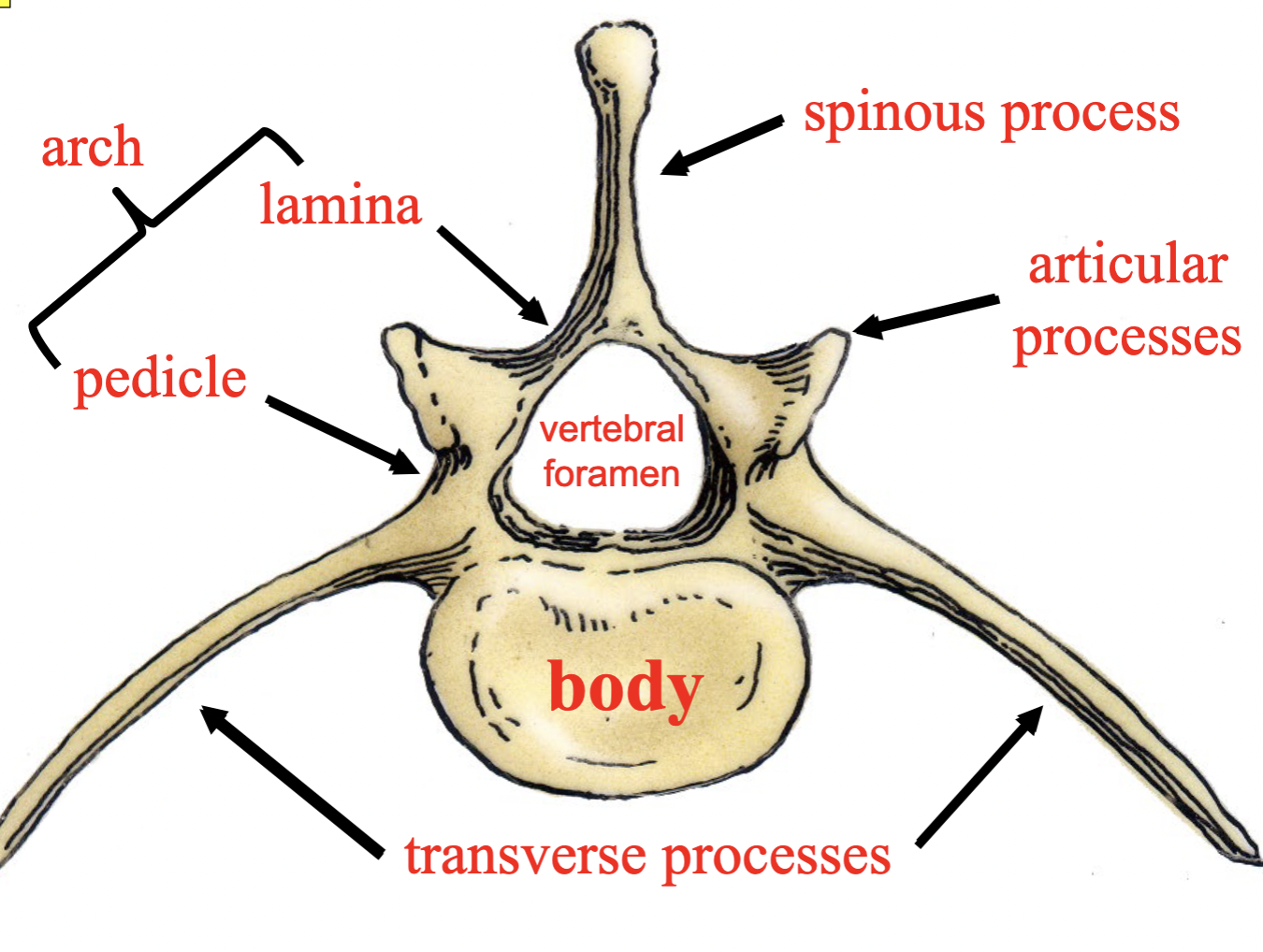
Vertebral arch: Pedicles
The flattened, dorsal part of the arch consists of right and left laminae; these are attached via pedicles to the body.
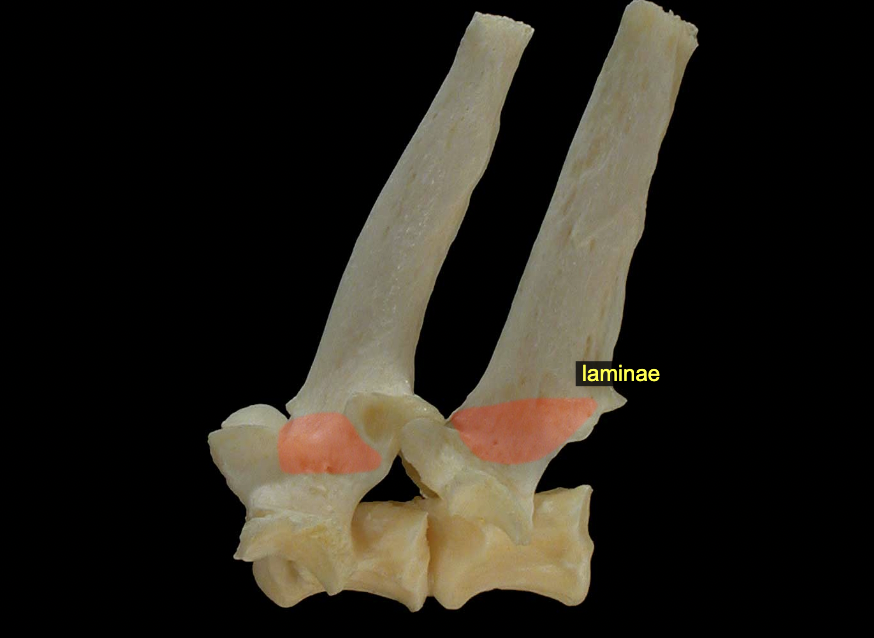
Vertebral arch: Laminae
The flattened, dorsal part of the arch consists of right and left laminae; these are attached via pedicles to the body

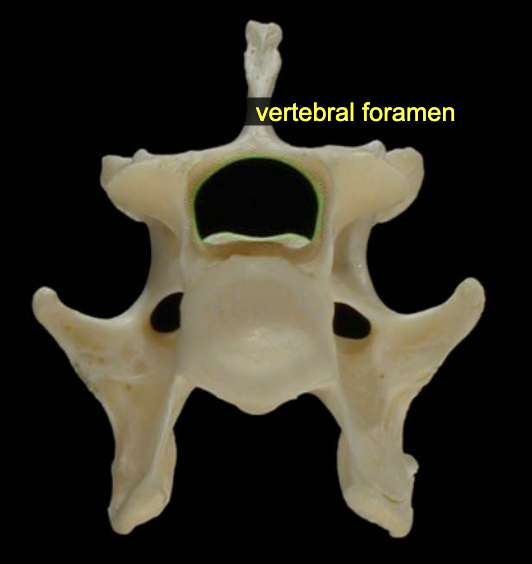
Vertebral foramen
Large passageway for the spinal cord seen in each vertebra
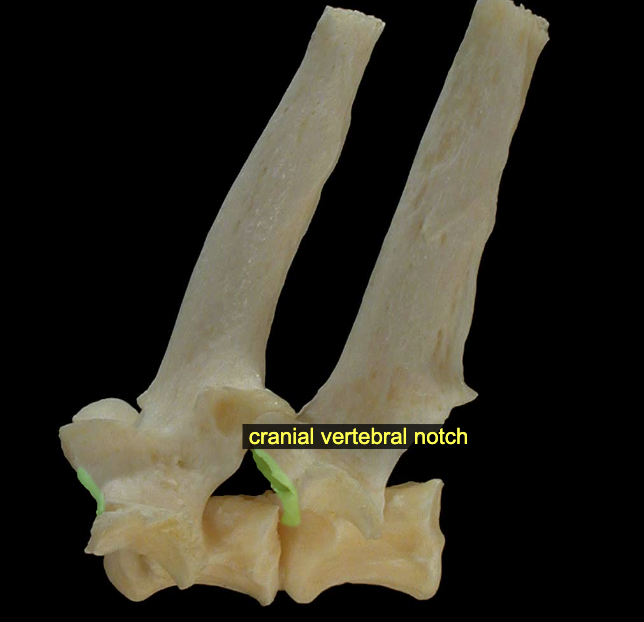
Vertebral notches (cranial & caudal)
The caudal vertebral notch of one vertebra aligns with the cranial vertebral notch of the next (caudal) vertebra, together creating an intervertebral foramen through which a spinal nerve will pass.
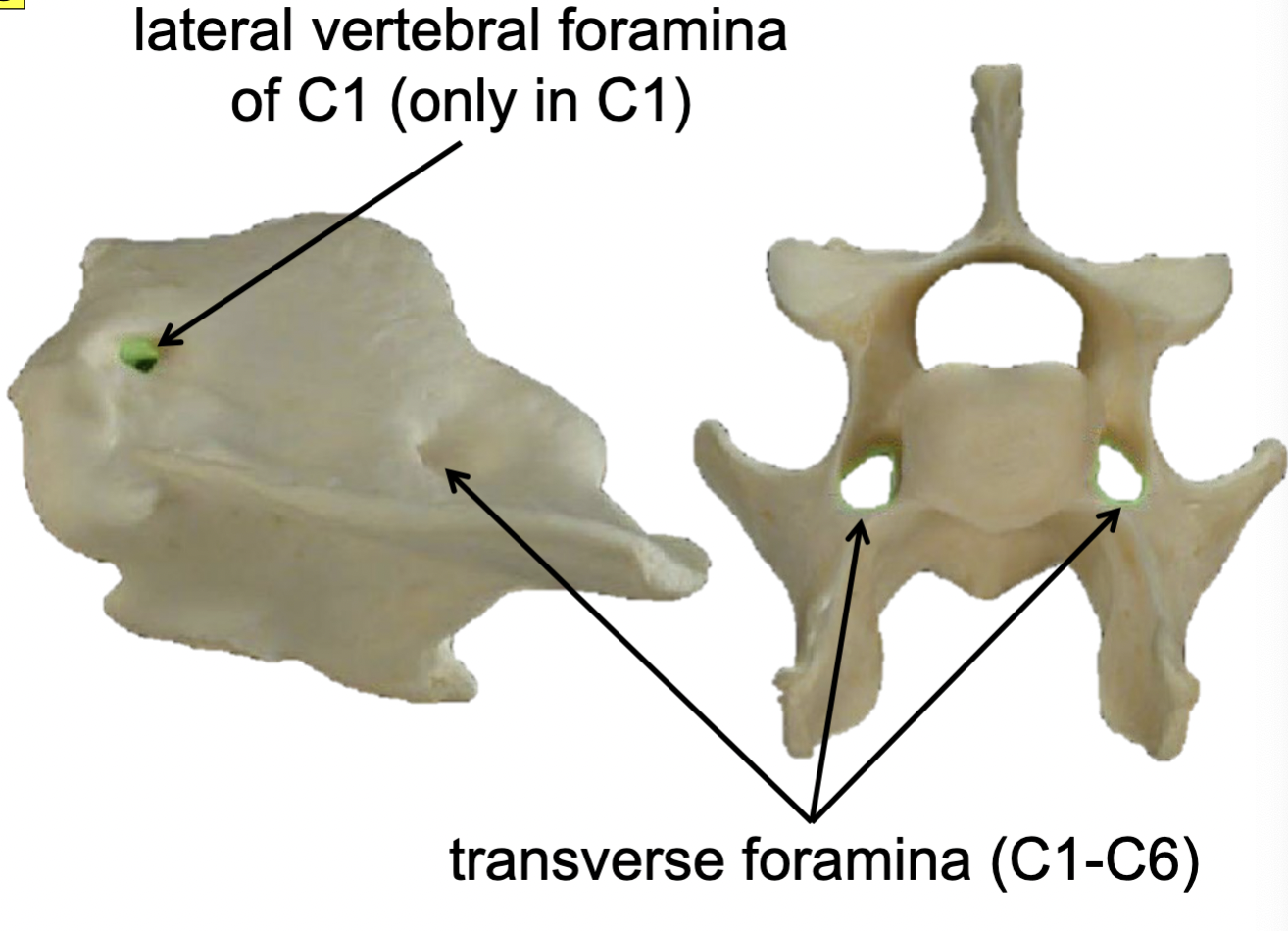
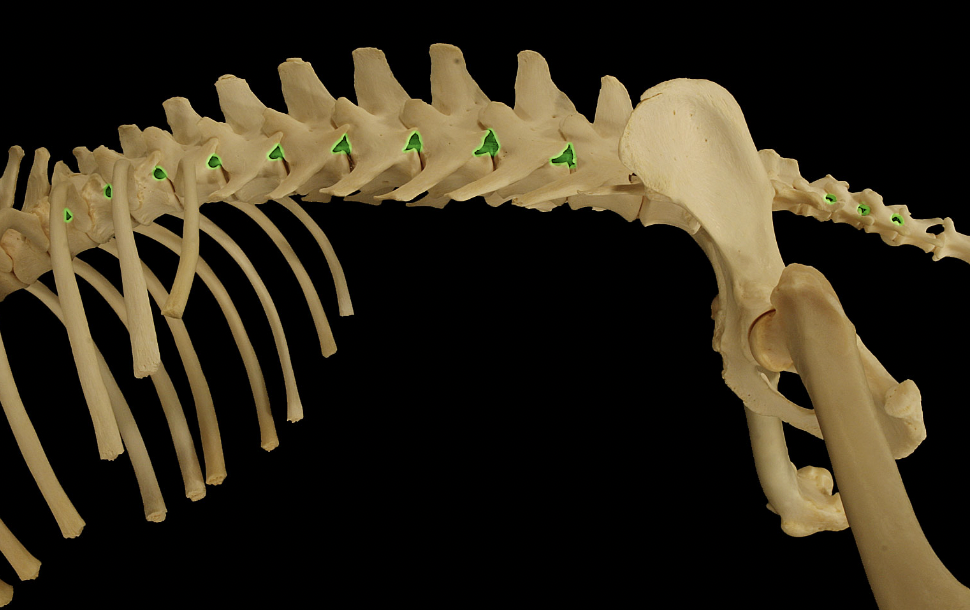
Transverse foramina (C1-C6)
cranial→caudal direction (green)
passageways for vertebral aa. & vertebral nn.
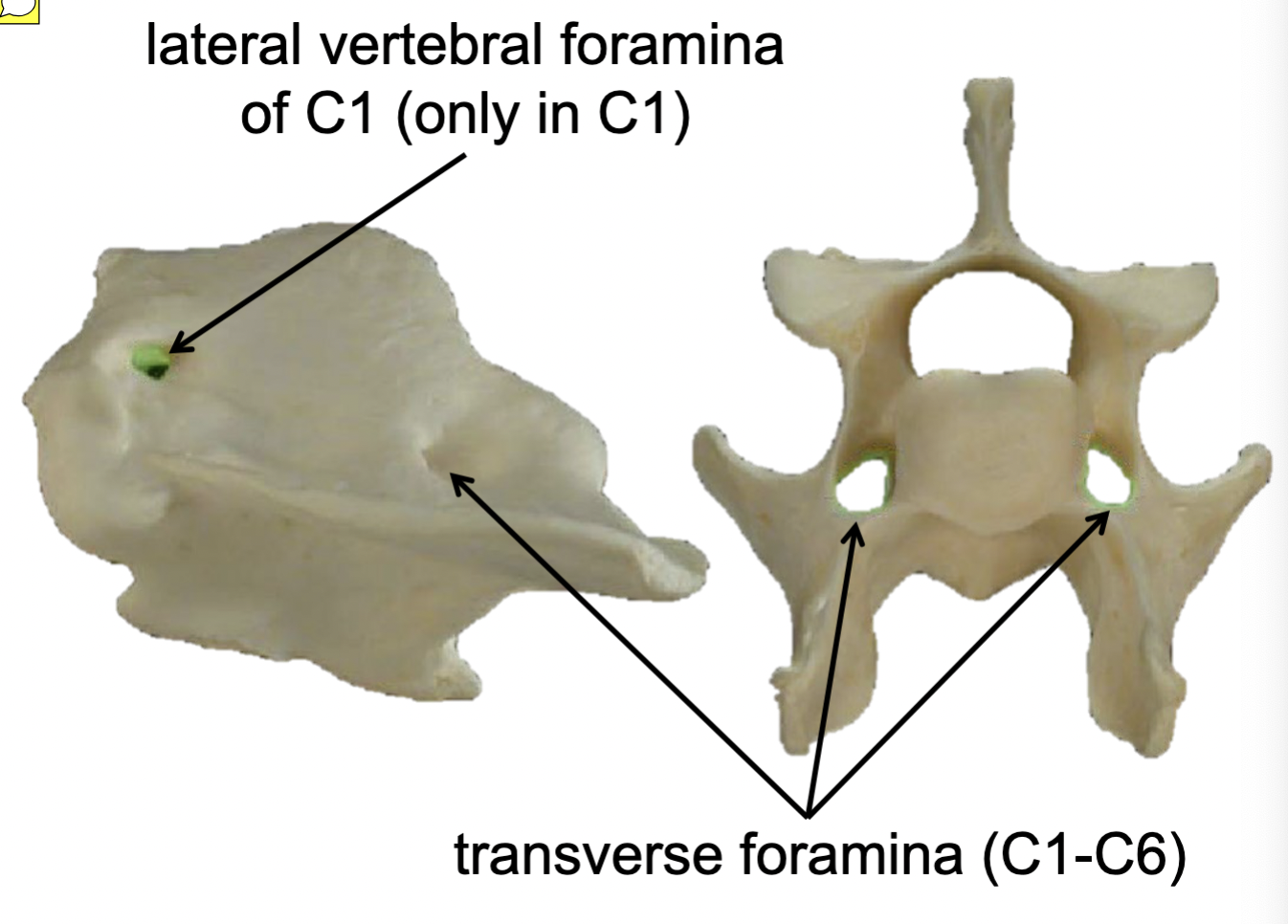
Lateral vertebral foramina of C1 (only in C1)
medial → lateral direction (blue)
passageways for 1st cervical spinal nn.
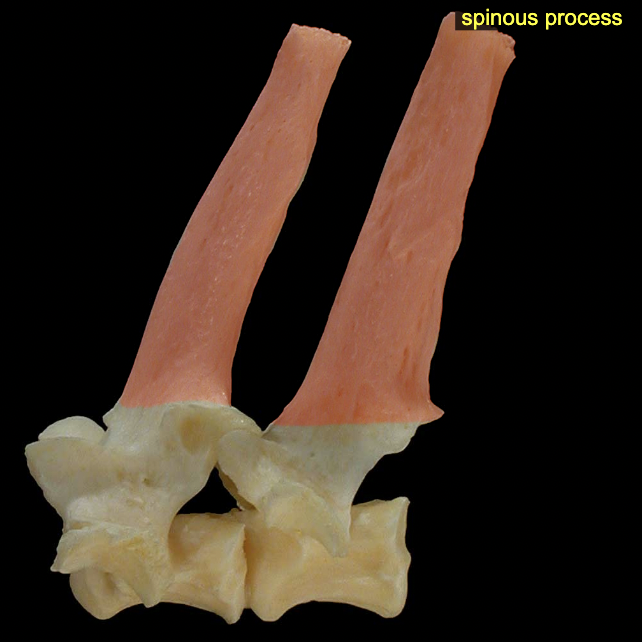
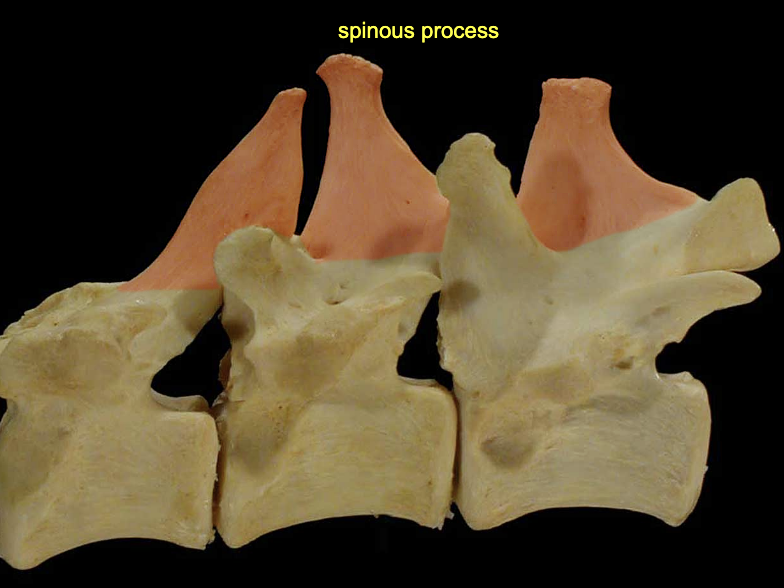
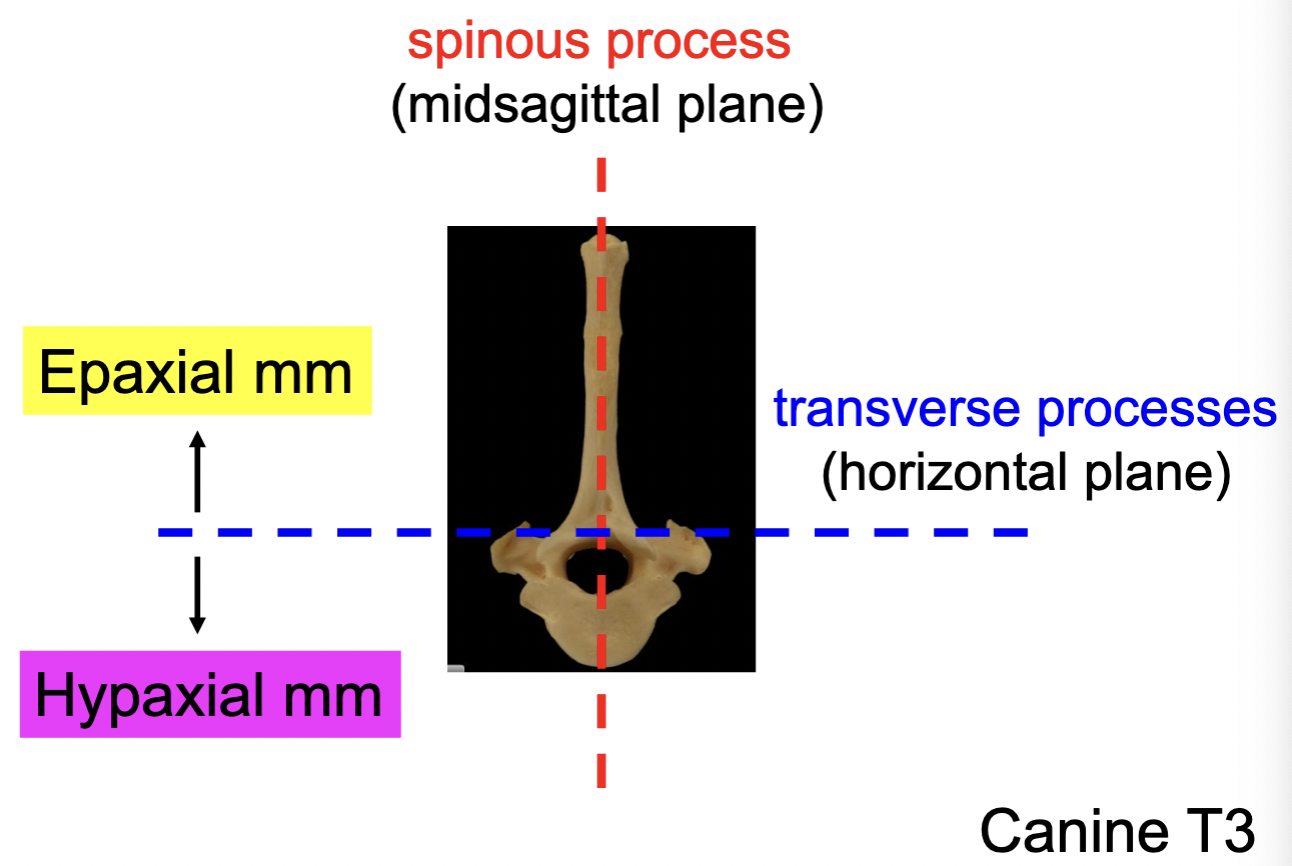
Spinous process
Projects dorsally from arch
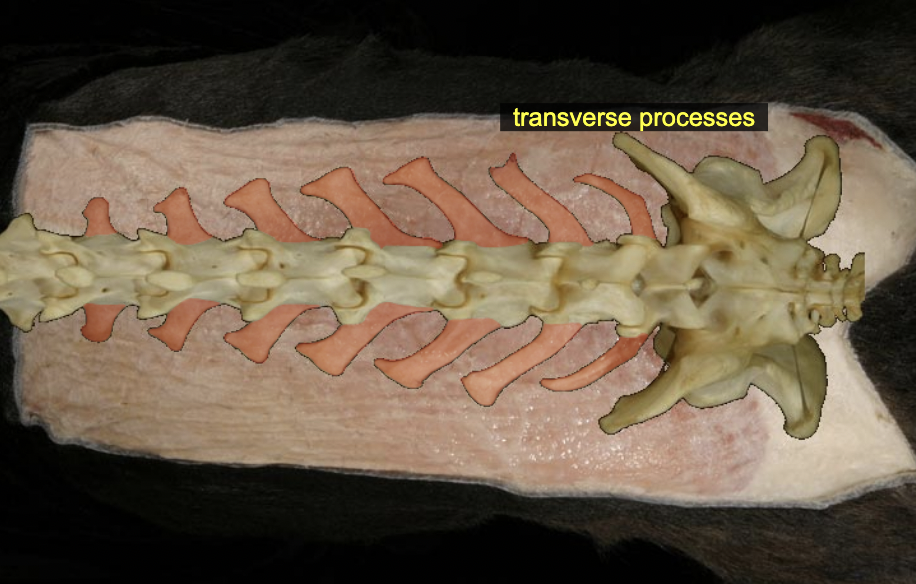
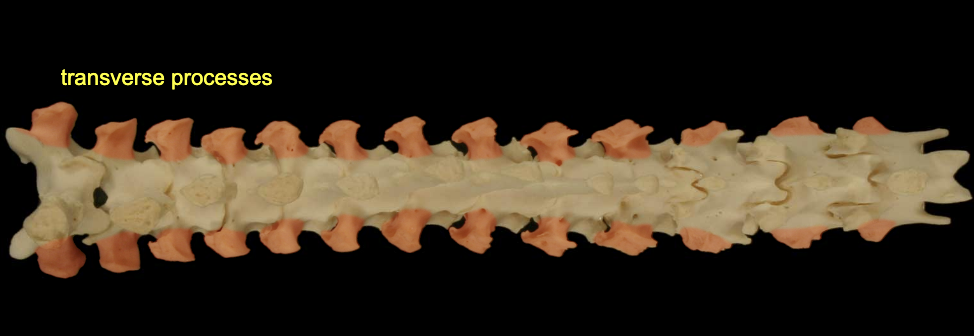
Transverse process
project laterally from arch
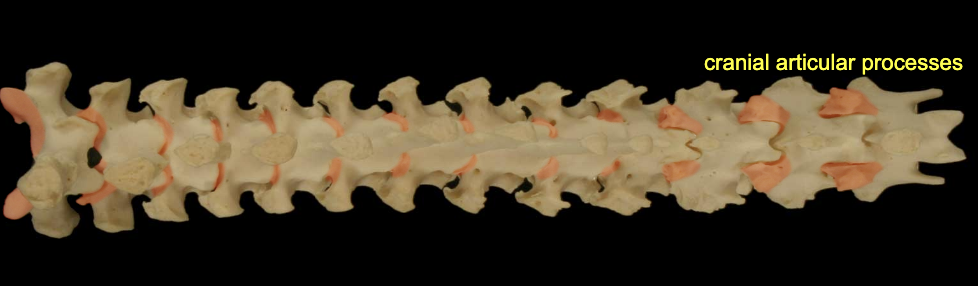
Articular process (cranial & caudal)
form synovial ht in b/w cranial & caudal
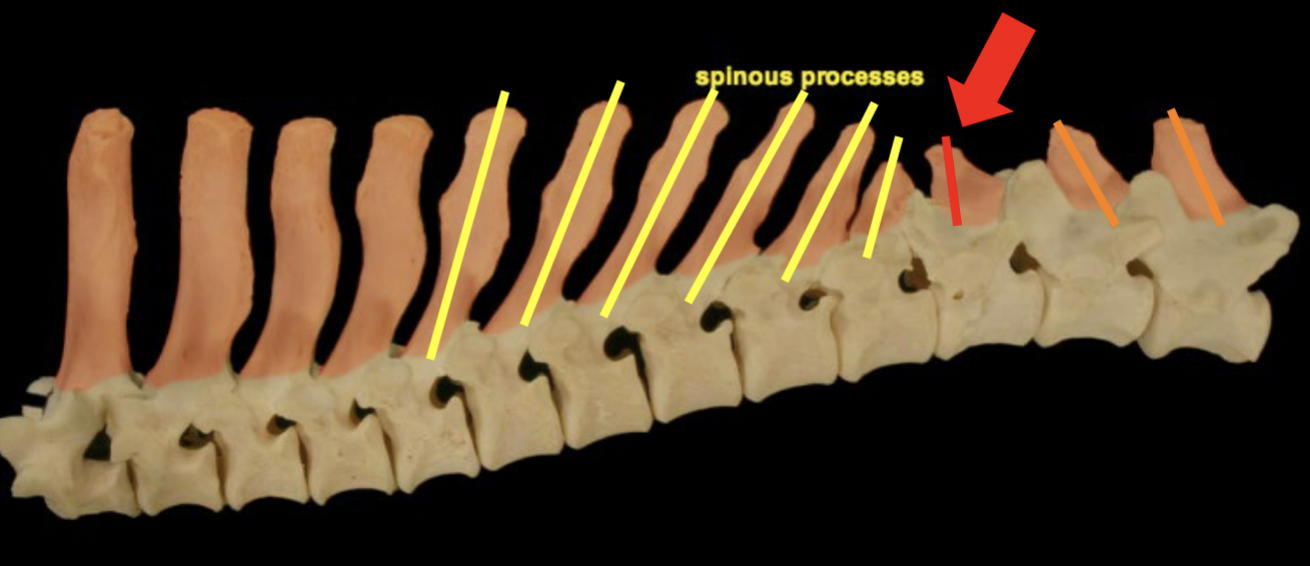
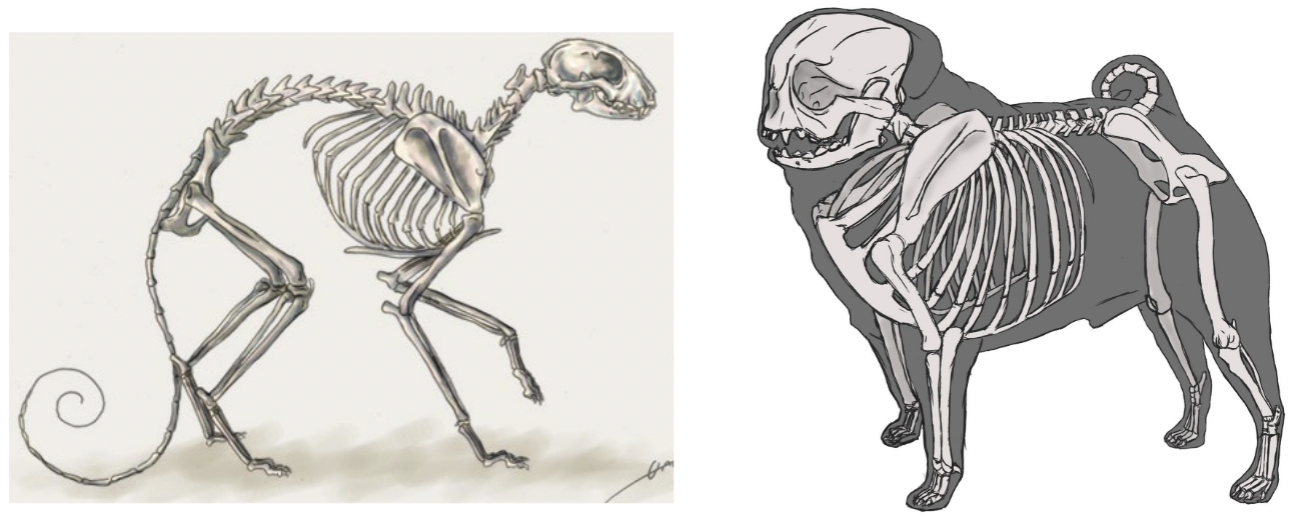
Anticlinal vertebrae: dog/cat
T:11
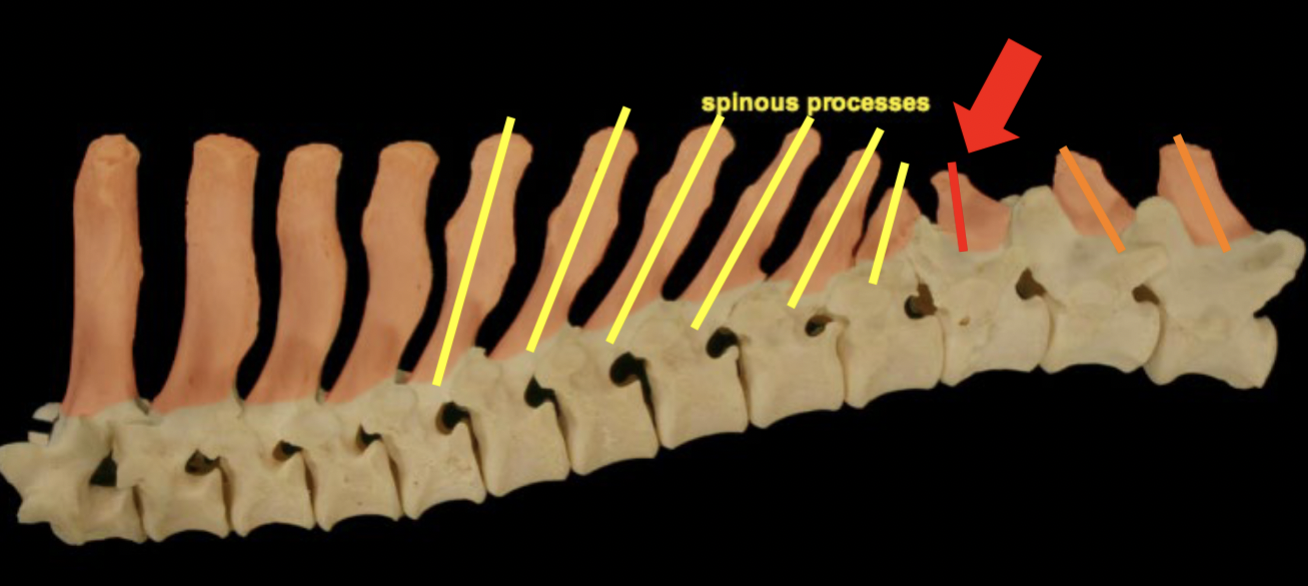
Anticlinal vertebrae: horse
T16
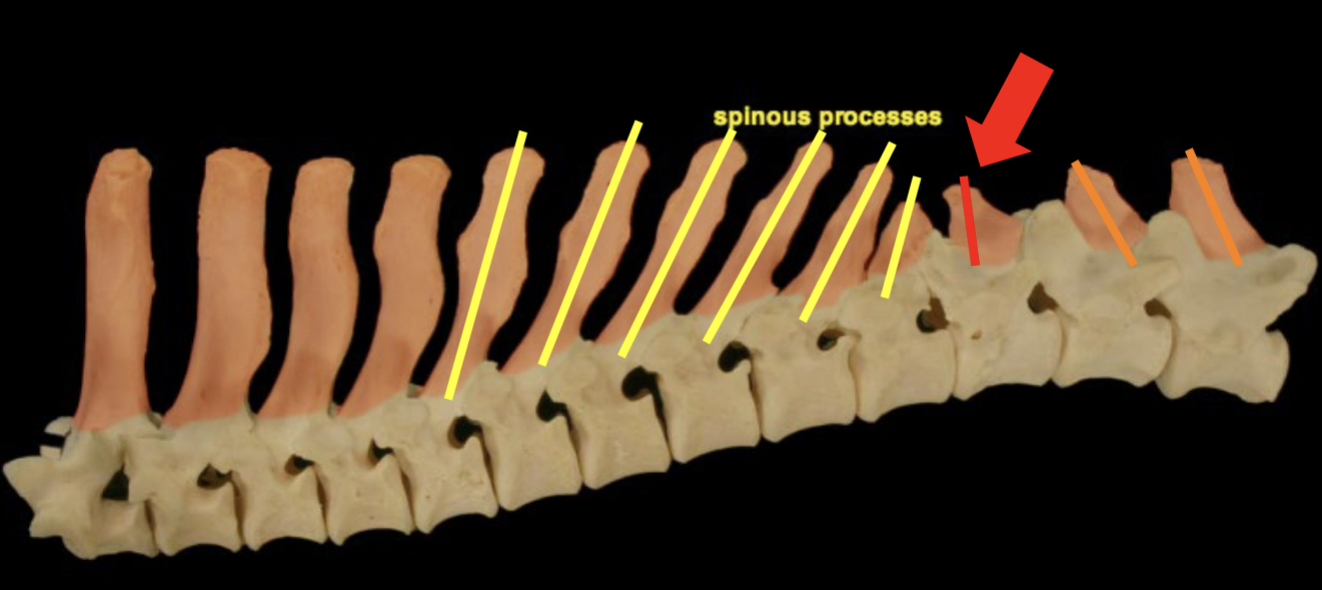
Anticlinal vertebrae: ox
T13
Sacral vertebrae
fused into 1 bone = sacrum
pelvic & dorsal sacral foramina transmit sacral spinal nn. rather than intervertebral foramina
Caudal (coccygeal, Cd) vertebrae
vertebrae of the tail, variable in number
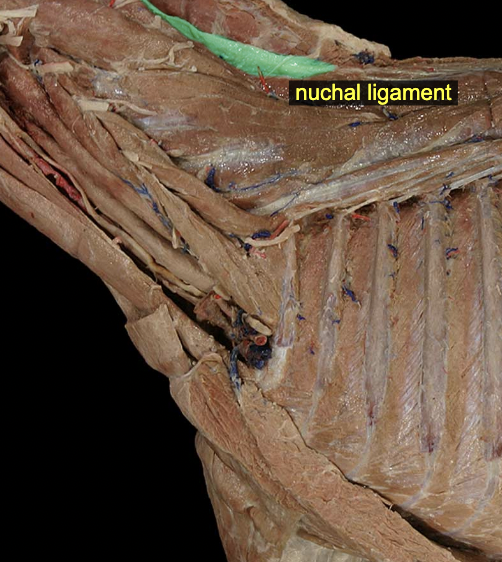
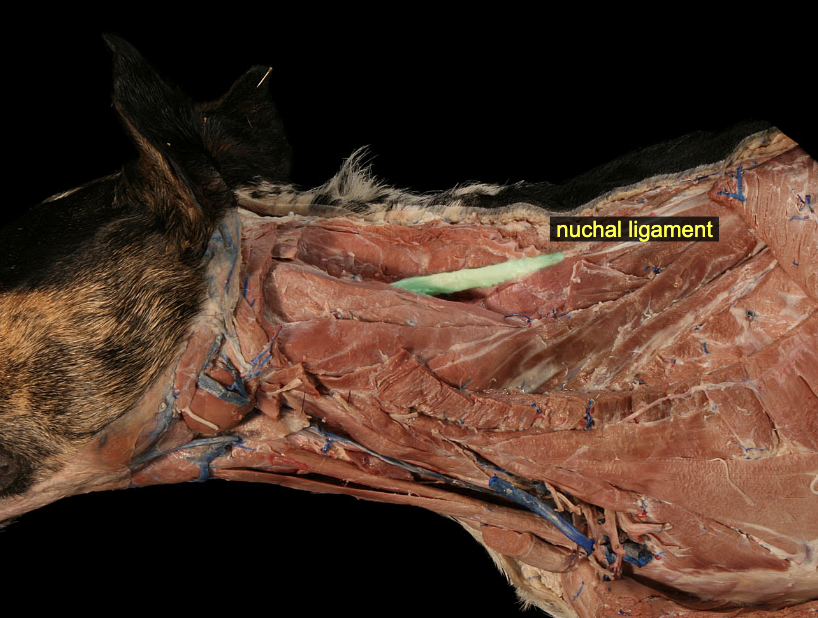
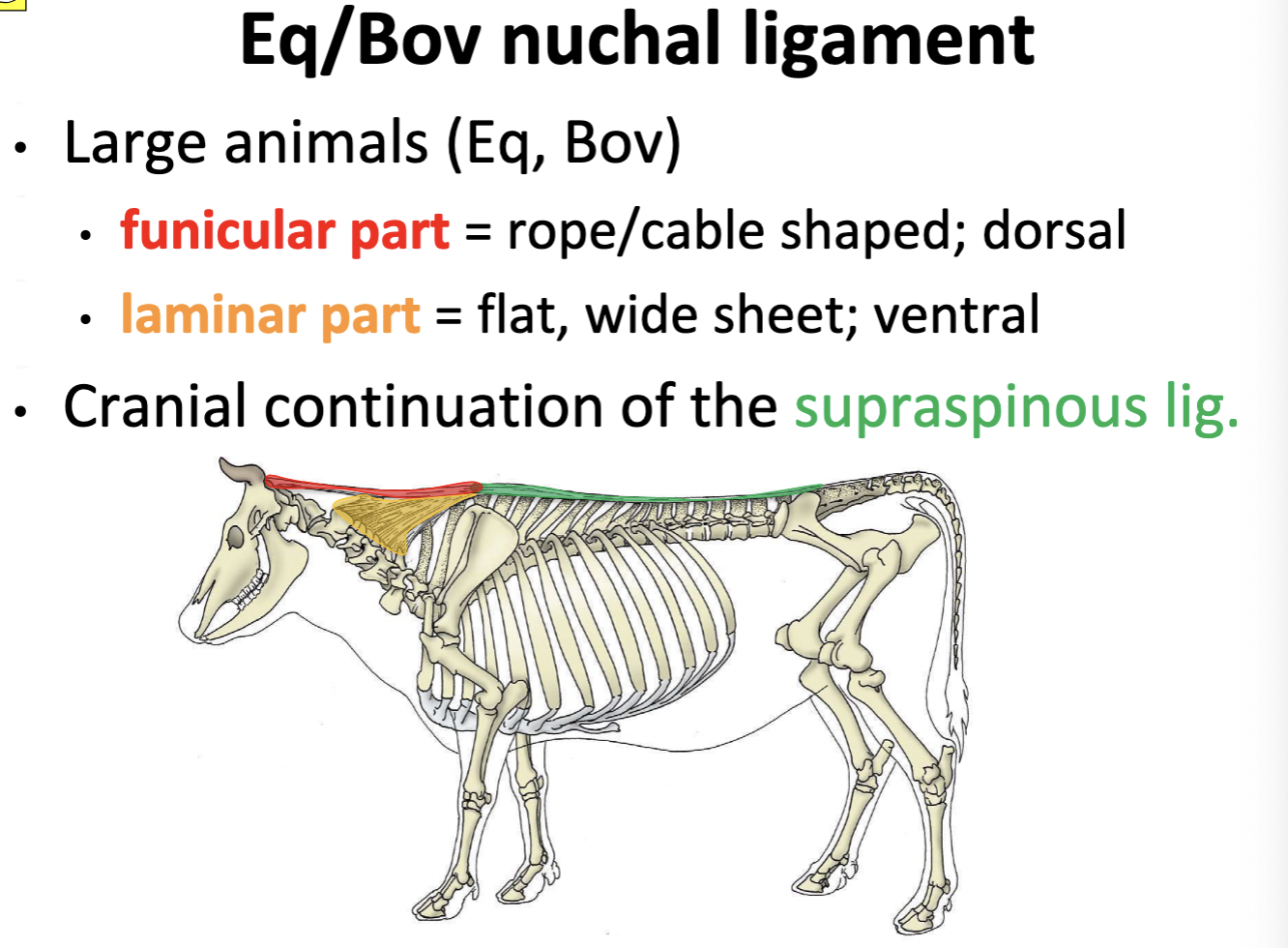
Nuchal ligament (ungulates: laminar & funicular parts)
elastic ligament on dorsal midline of the neck
A: provides passive support for the head against gravity
canine: spinous process of T1-C2 or skull in large animal
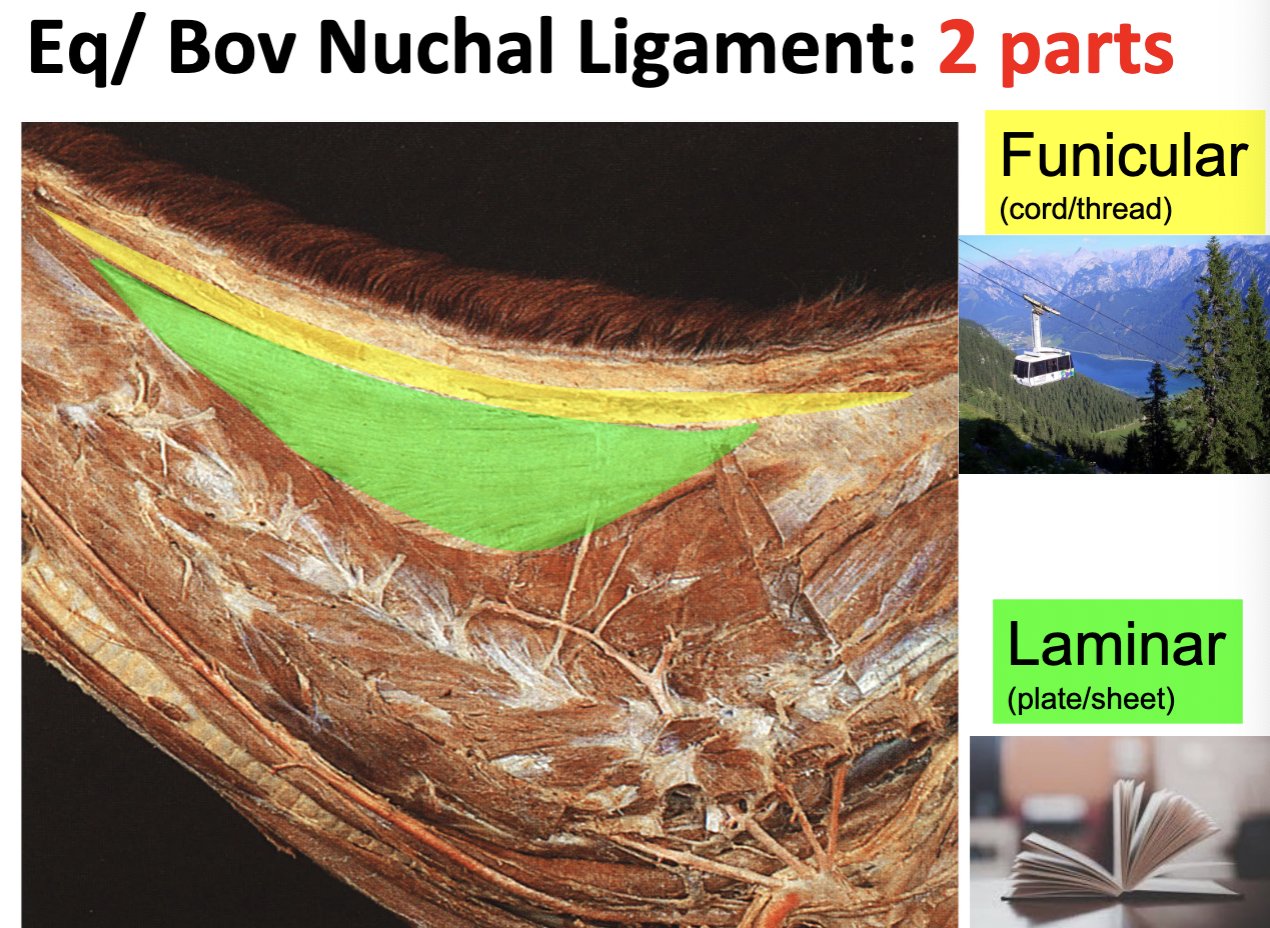
Nuchal ligament: Eq/Bov
funicular part = rope/cable shaped; dorsal
laminar part = flat, wide sheet; ventral
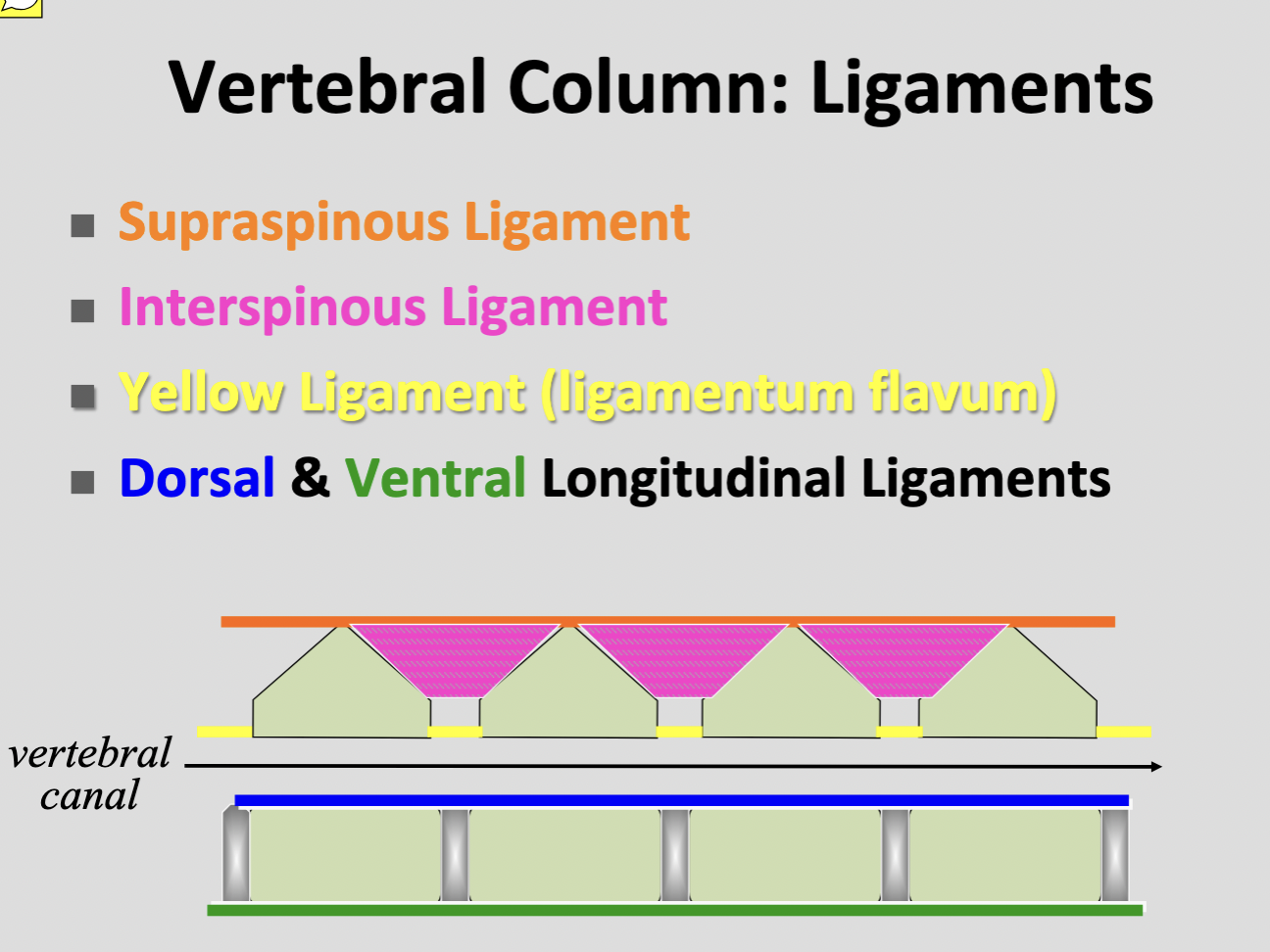
Supraspinous ligament
T1 → 3rd caudal vertebra
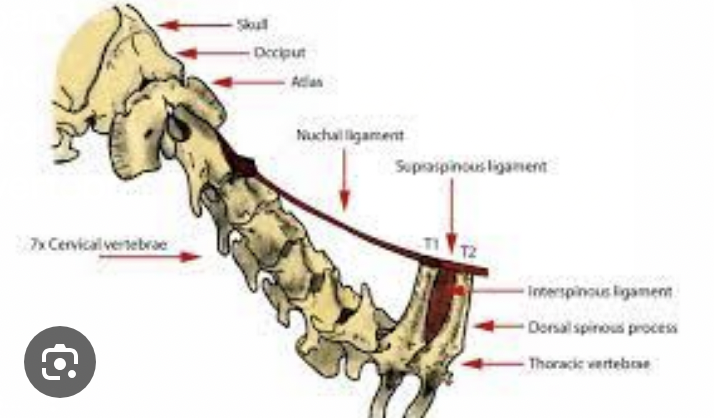
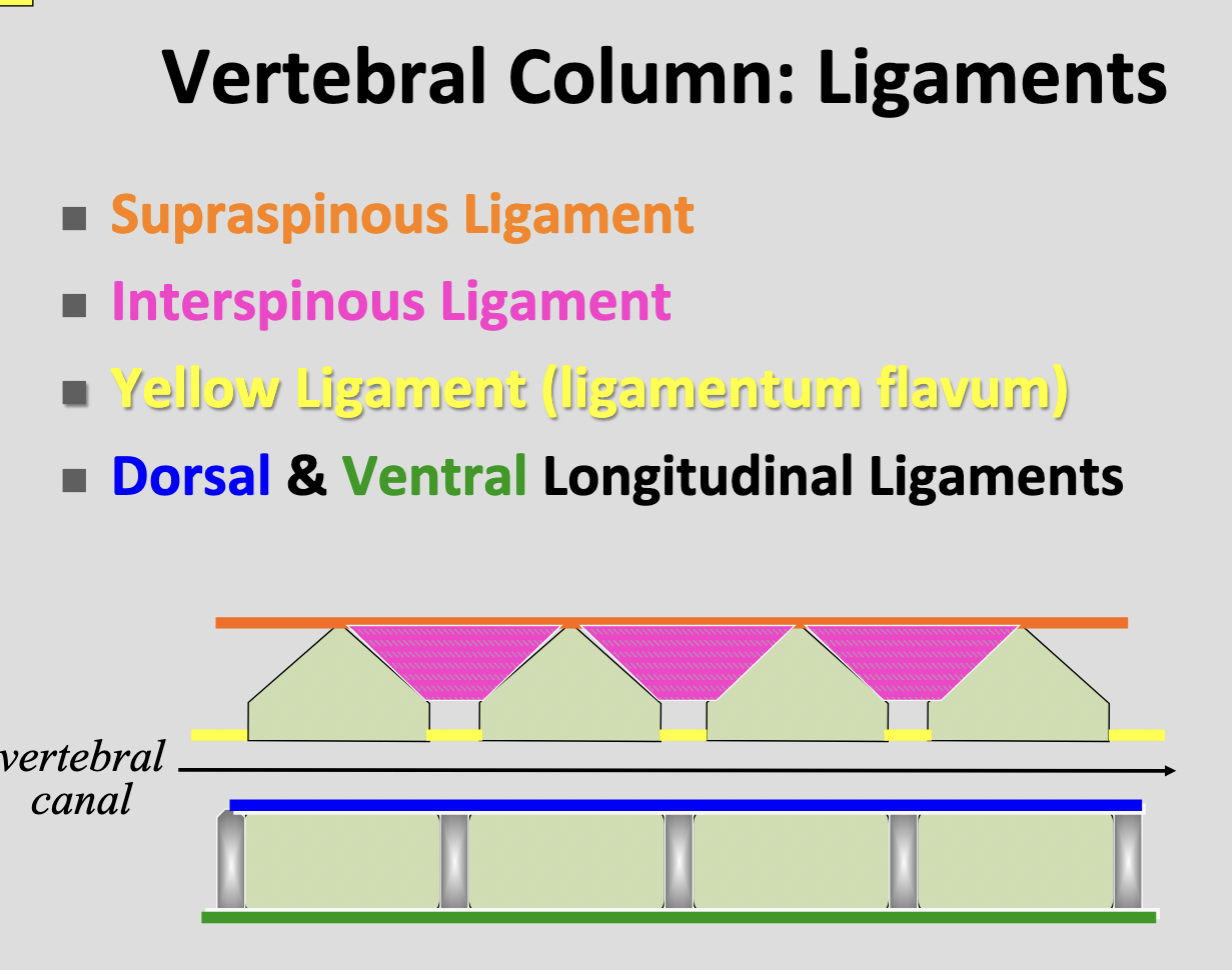
Interspinous ligament
tissue intersped with bundles of the interspinalis muscle
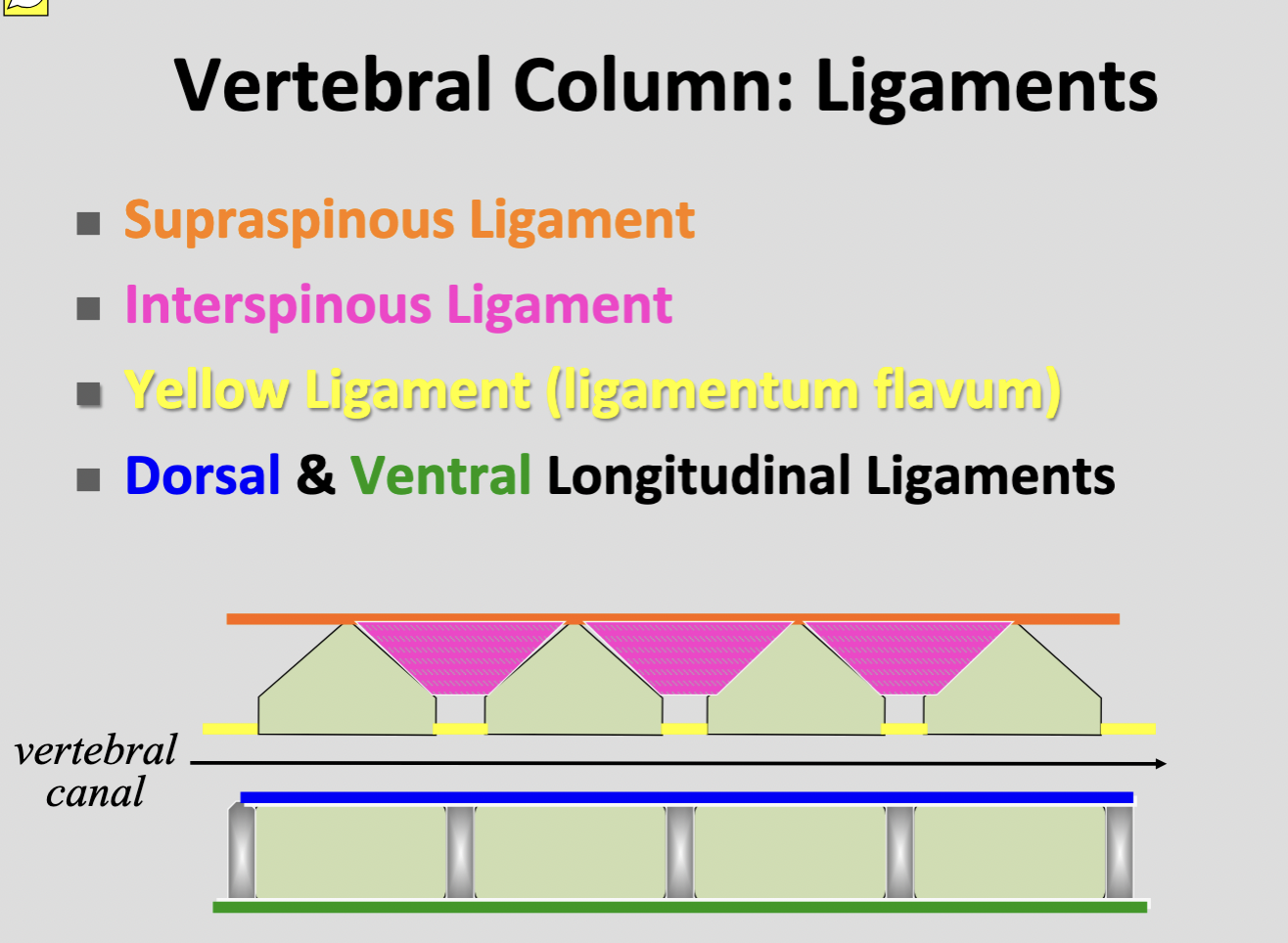
Dorsal longitudinal ligament
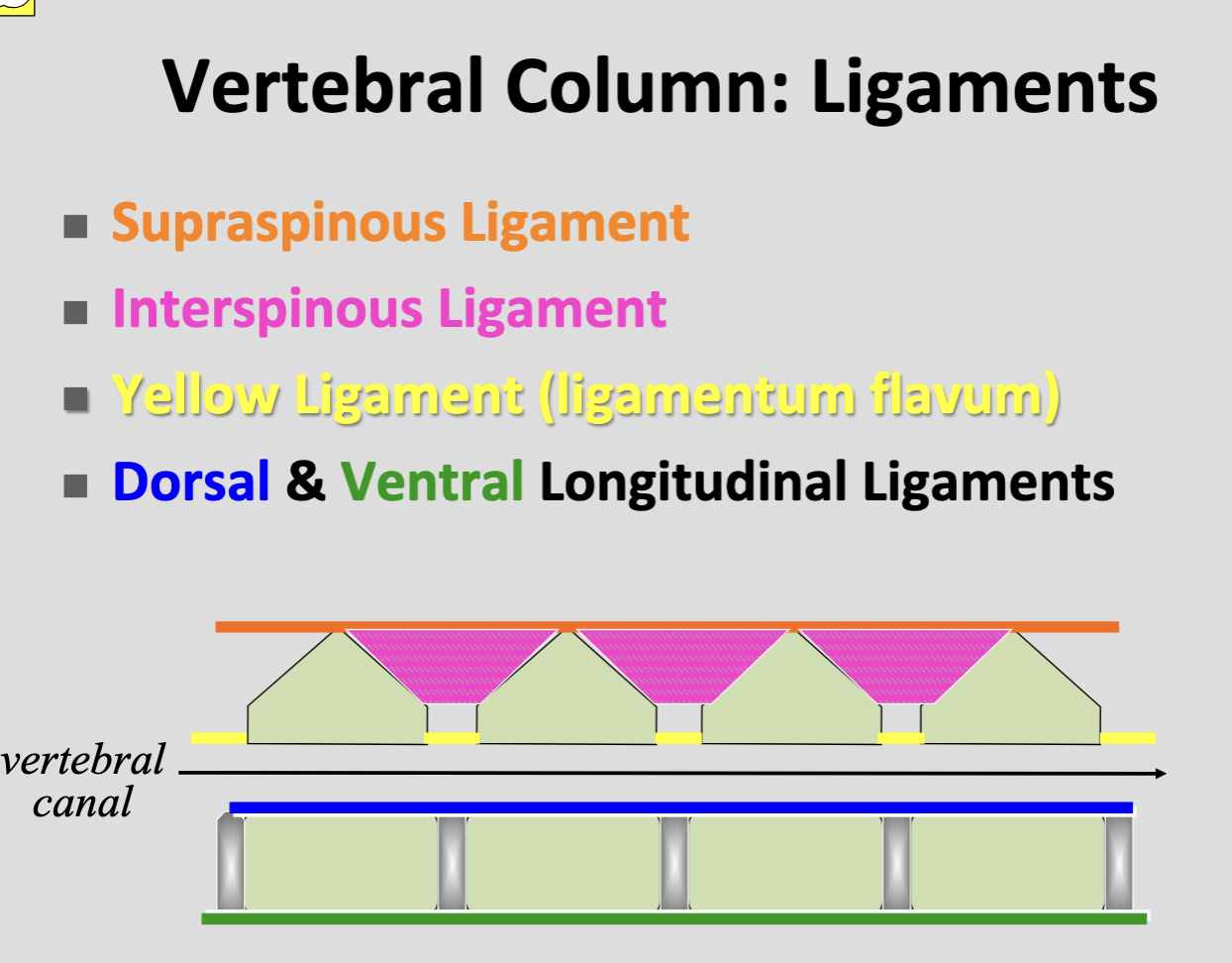
Ventral longitudinal ligament
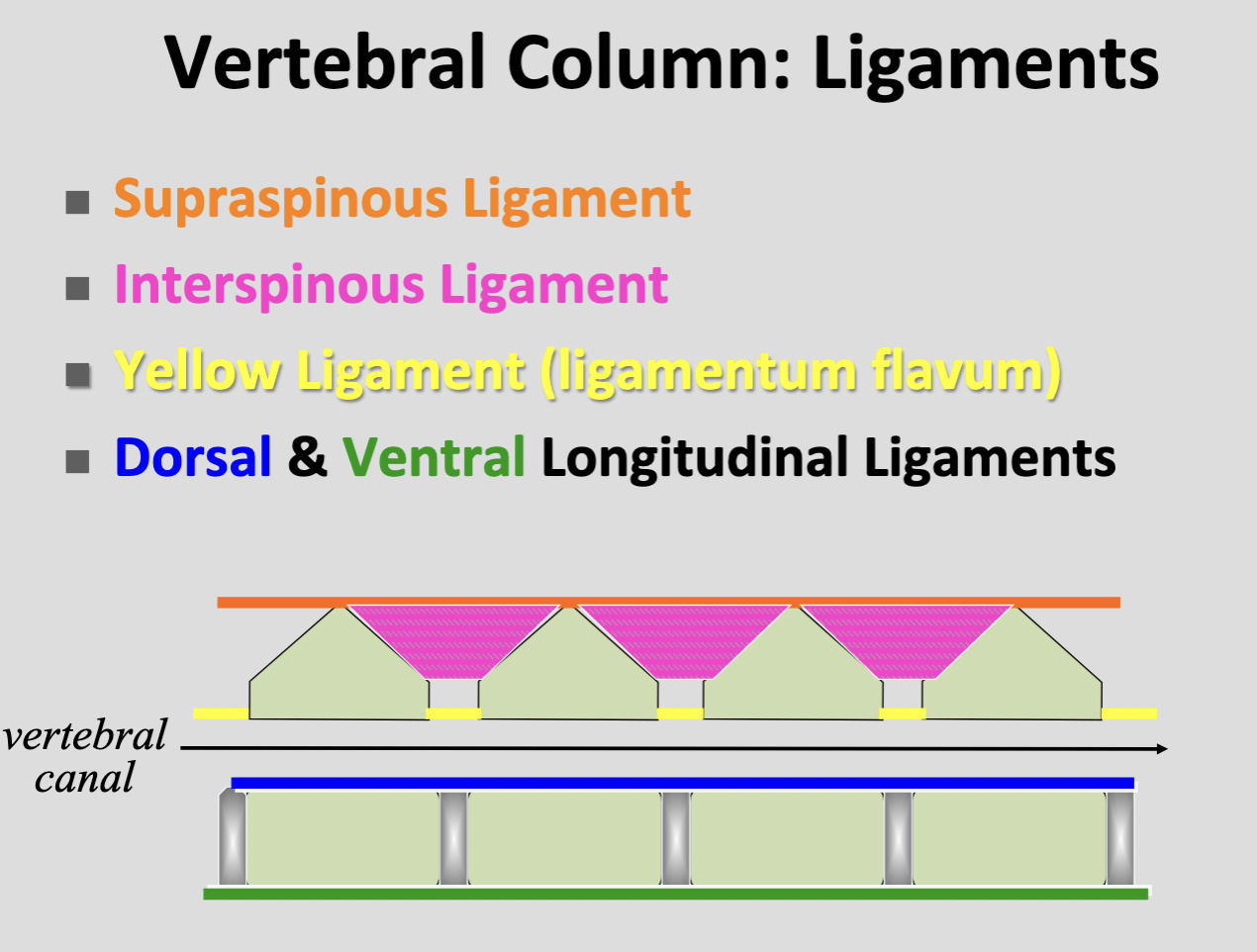
Ligamenta flava (yellow ligament)
elastic sheets filling the interacuate spaces b/w arches of adjacent vertebrae
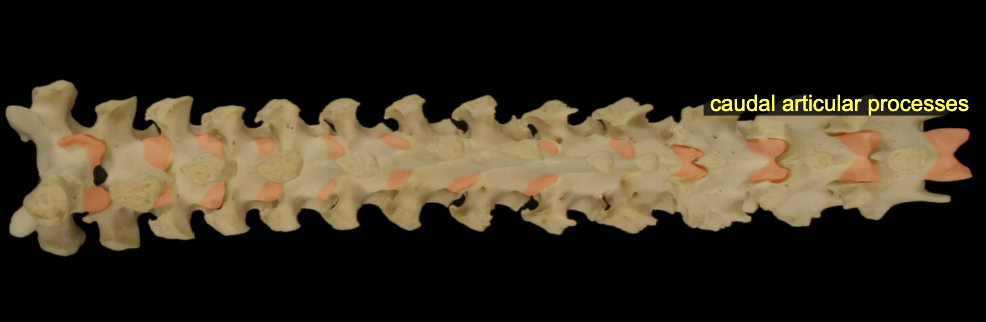
Articulations: caudal & cranial articular processes
Synovial jt
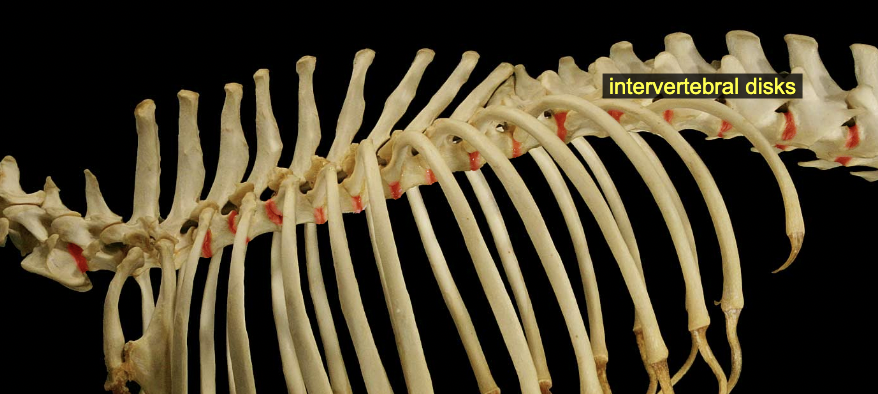
Articulations: intervertebral discs
Annulus fibrosus & nucleus pulposus = fibrocartilaginous jt
Articulations: sacroilliac jt
Synovial jt
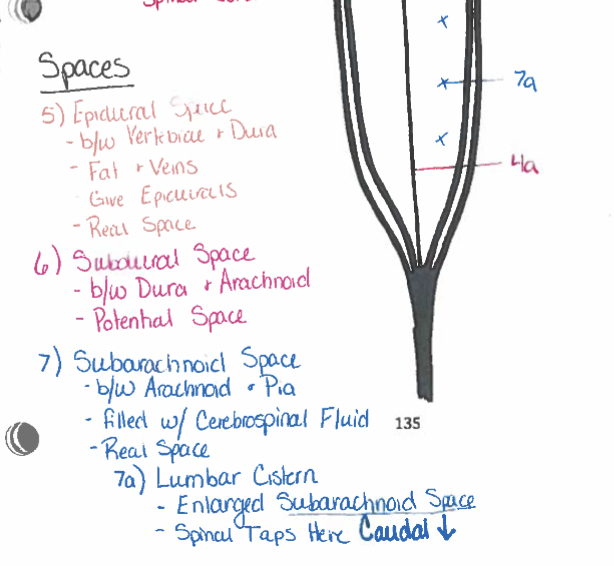
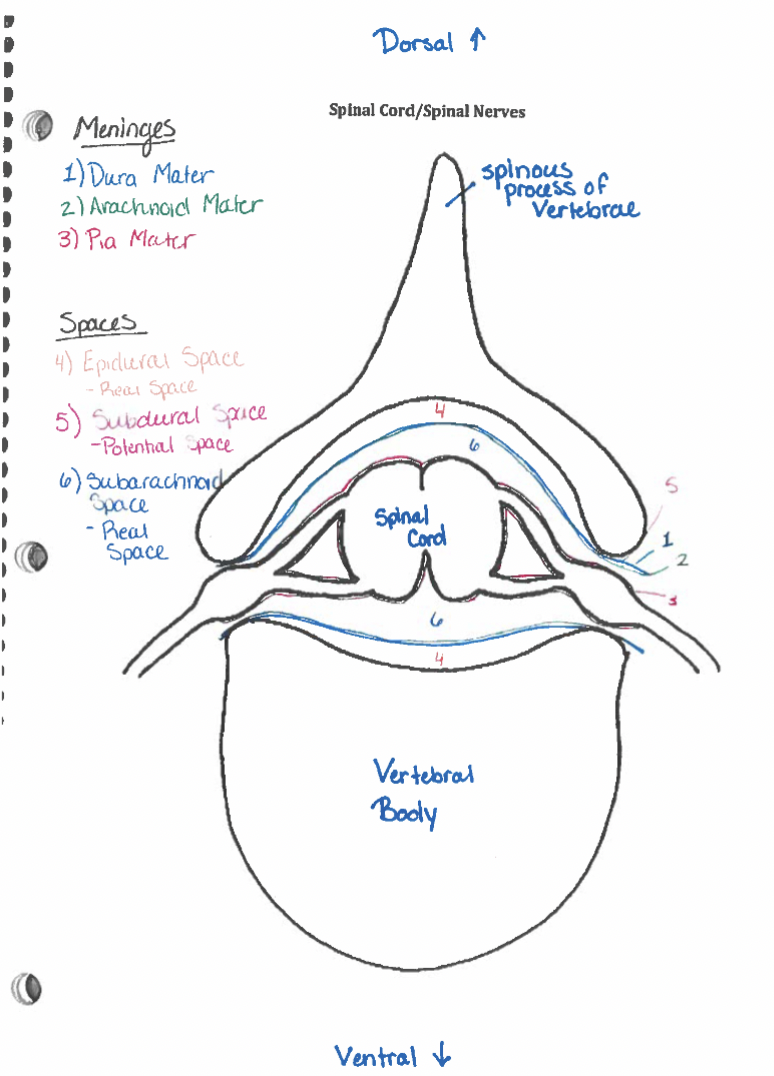
Epidural space
b/w dura & vertebrae (Real space, fat & veins, epidurals are given here)
Spinal nerves
Dorsal root ganglion
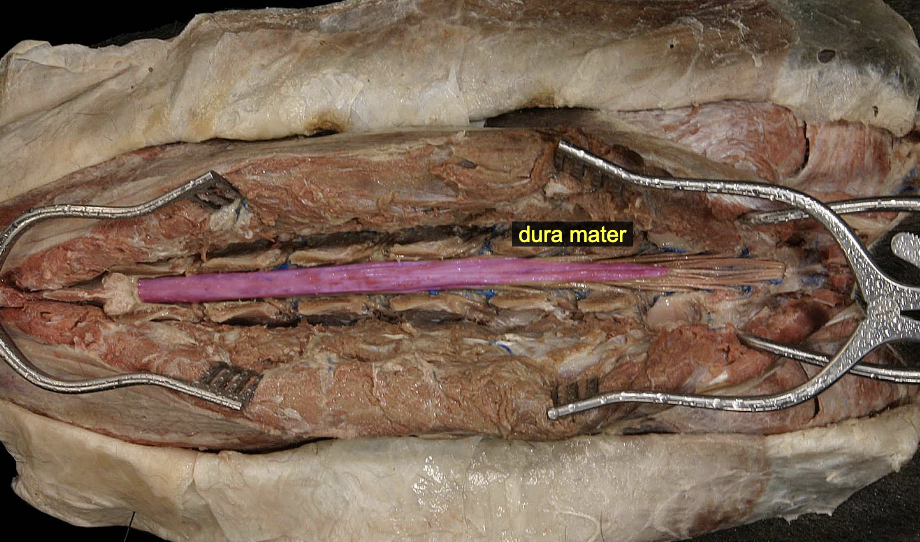
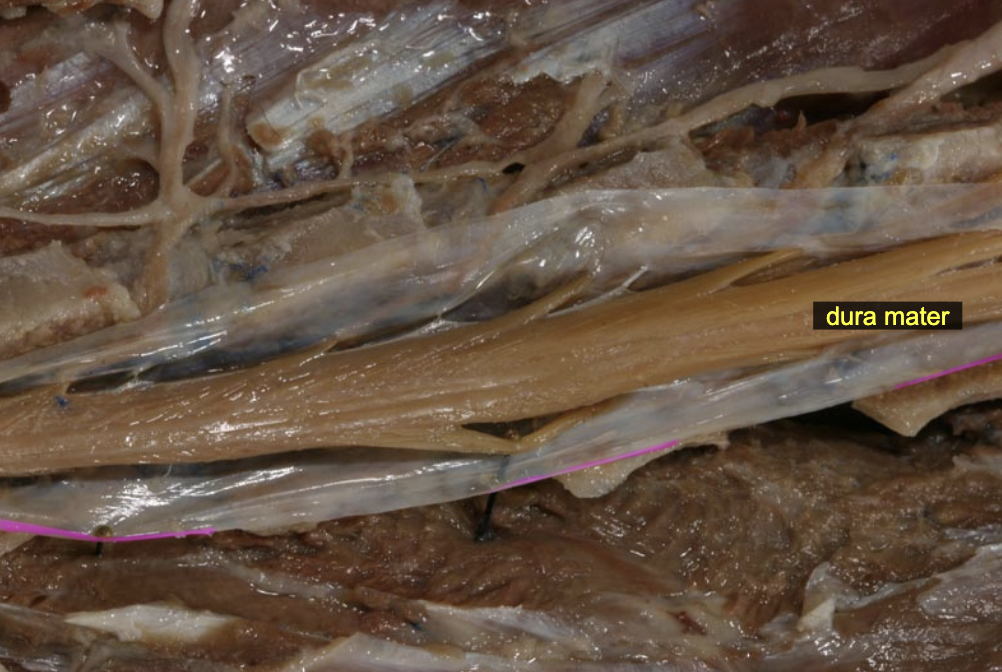
Dura mater
Subdural space
b/w dura & arachnoid (potential space)
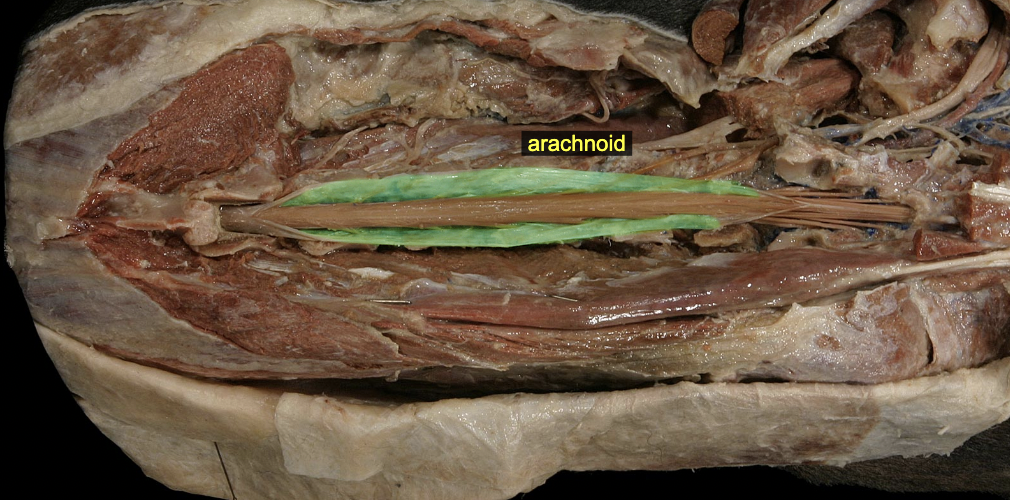

Arachnoid mater
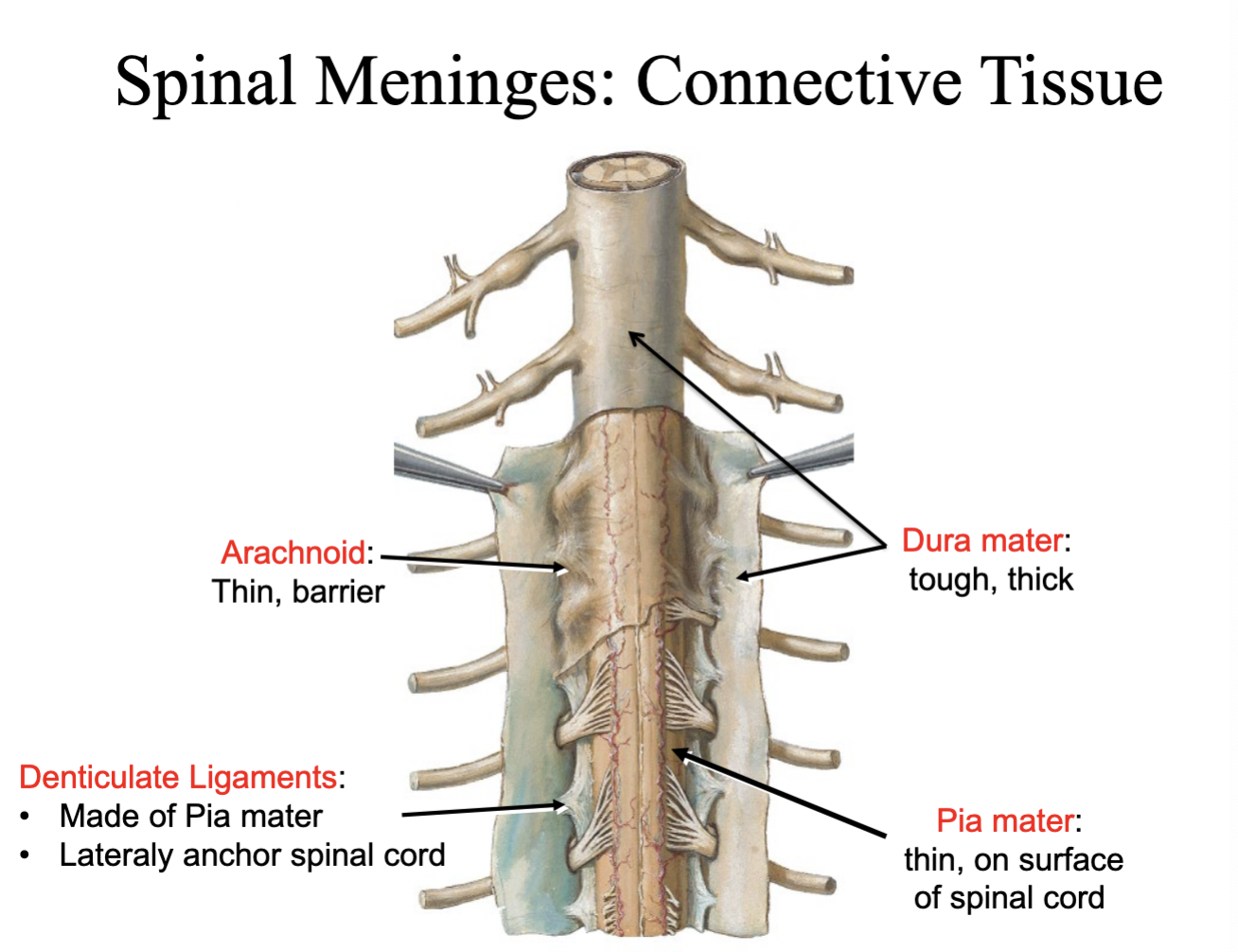
Subarachnoid space
arachnoid & pia (real space, cerebrospinal fluid here) (lumbar cistern)
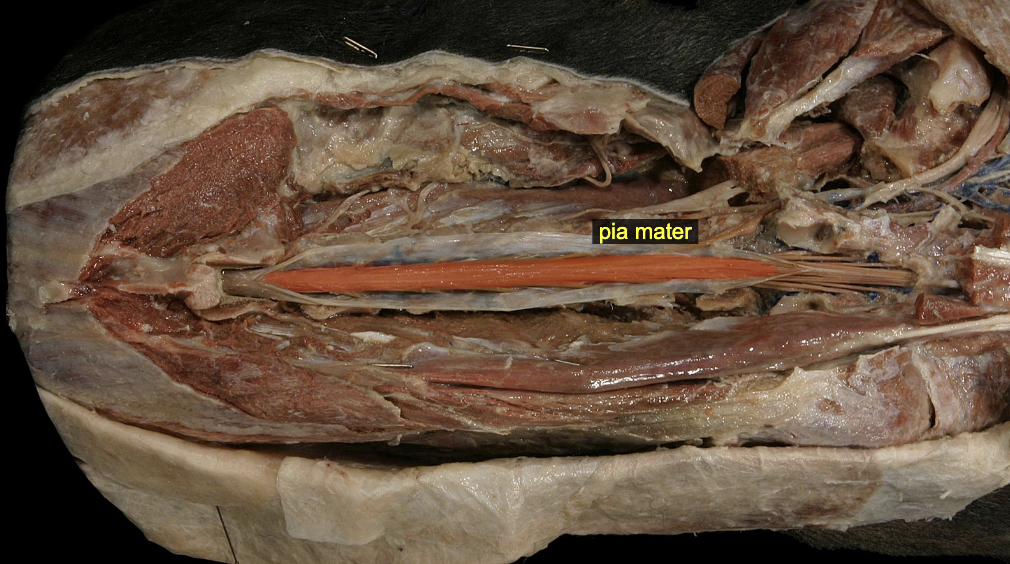
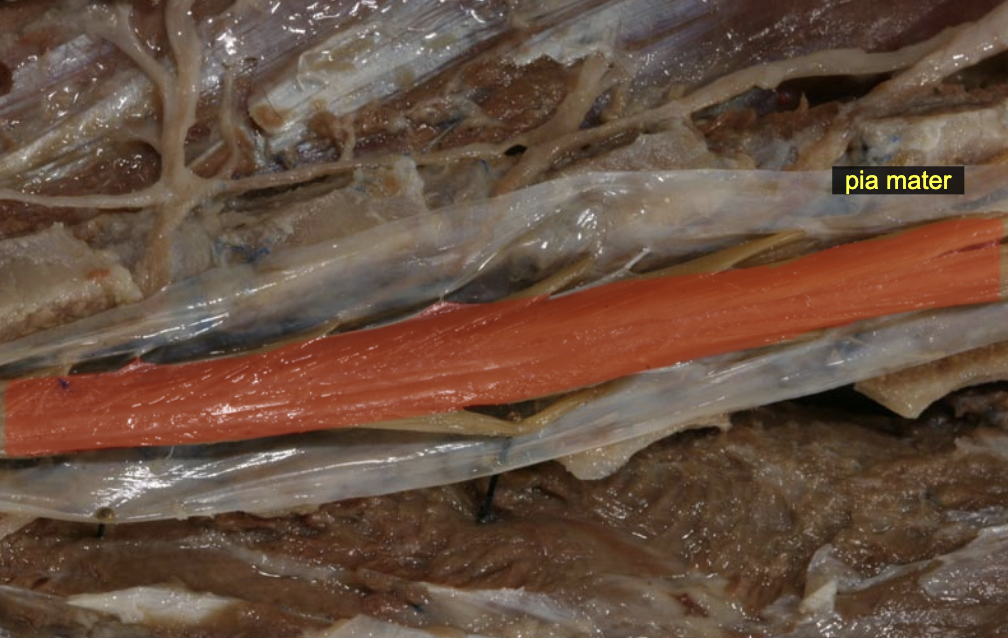
Pia mater: denticulate ligament
lateraly anchor spinal cord
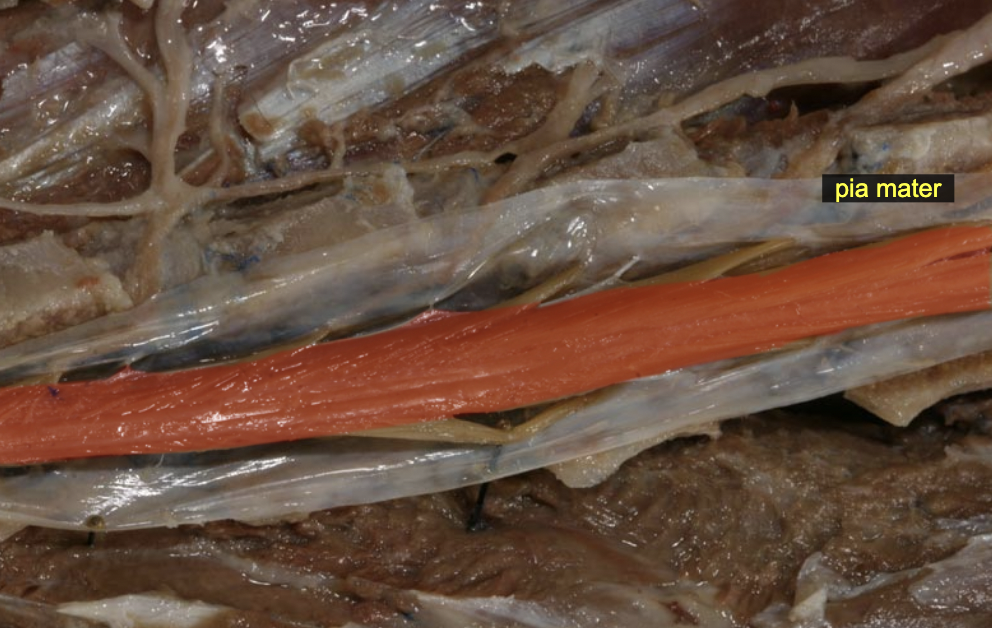
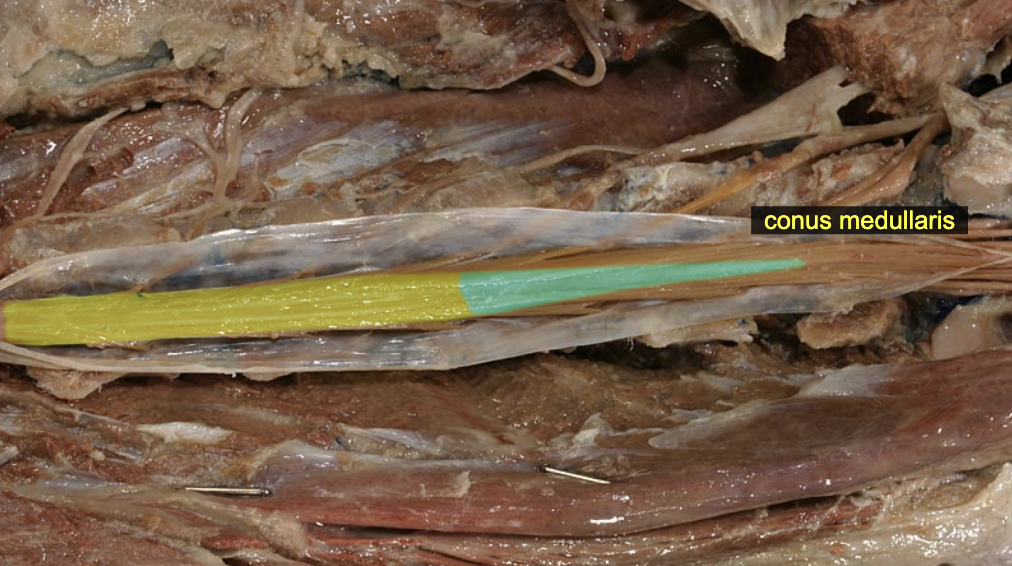
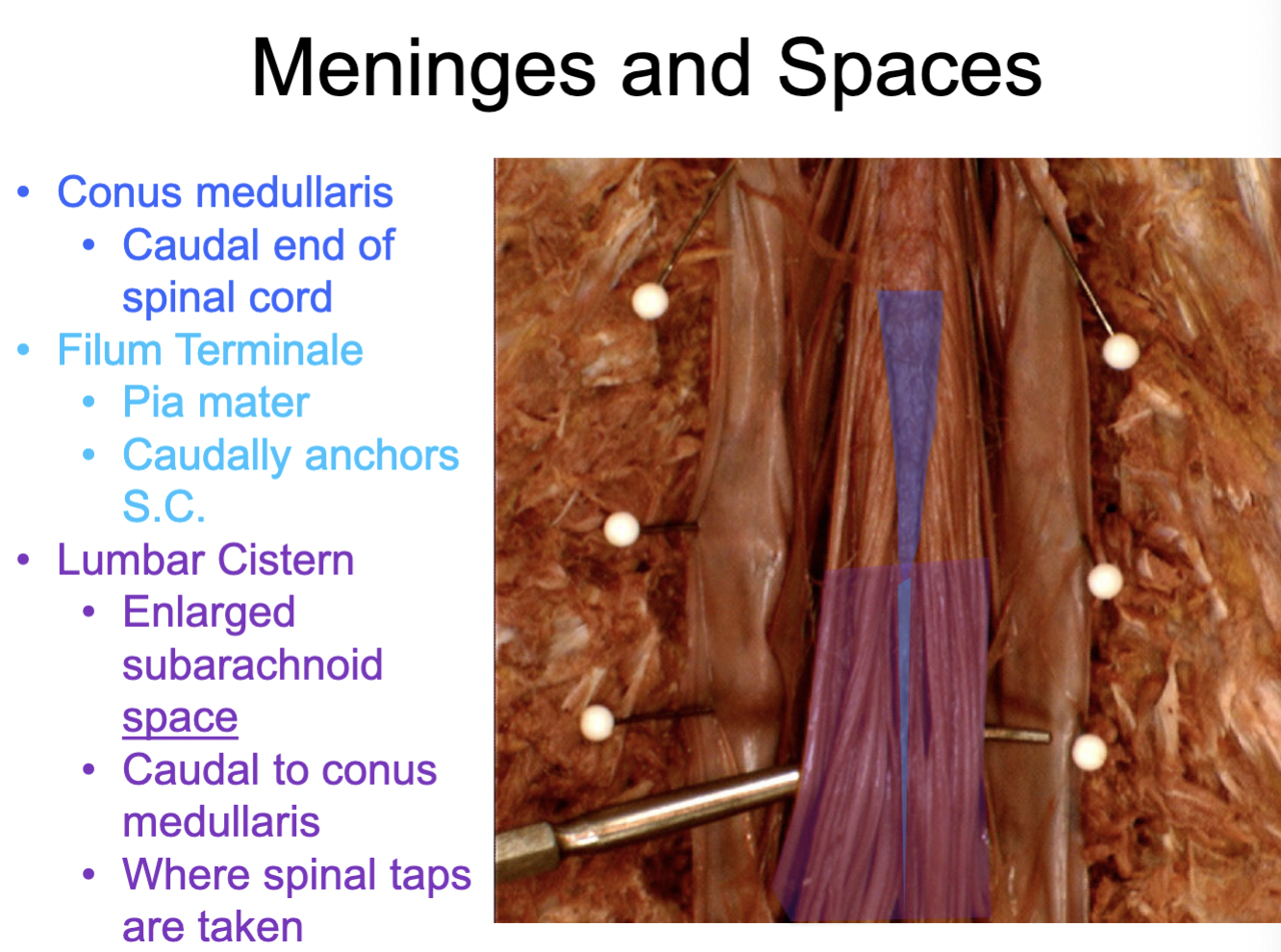
Pia mater: filum terminale
caudally anchors S. C.
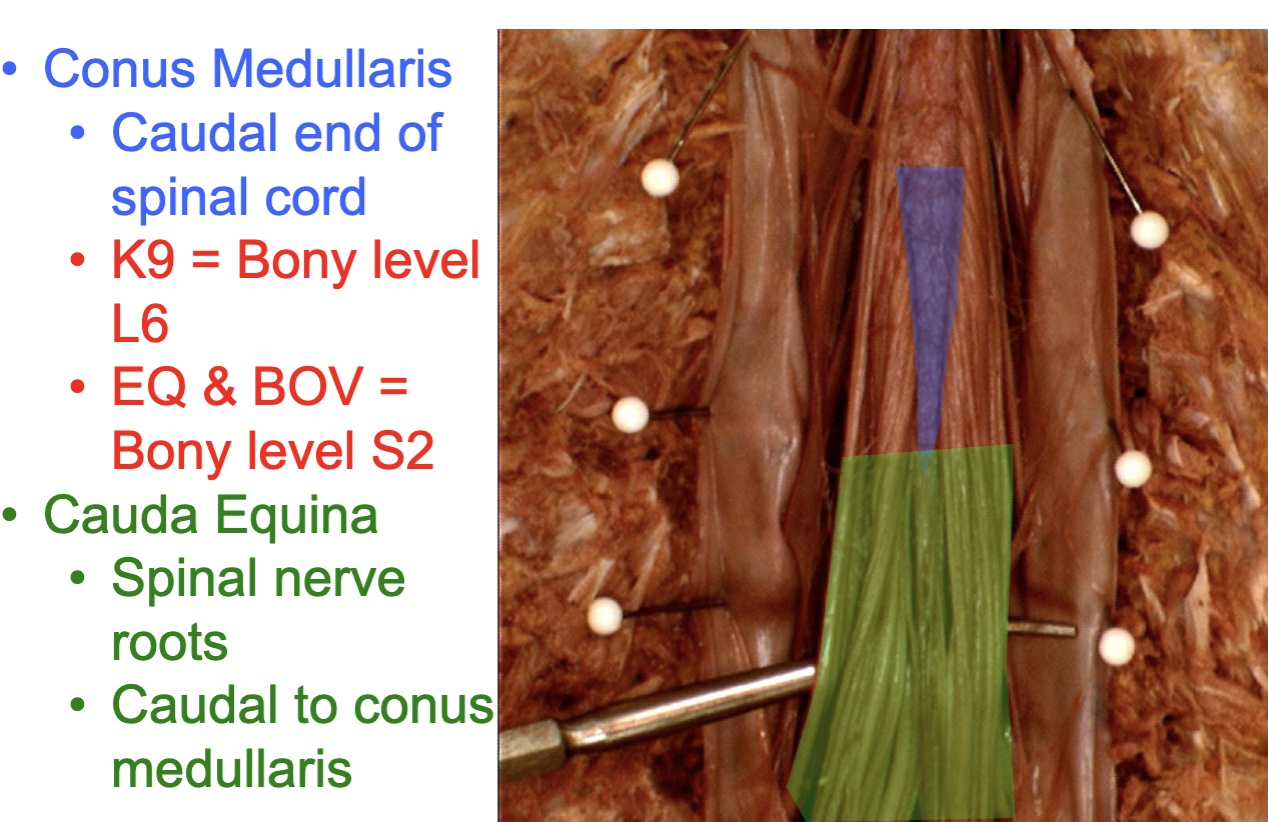
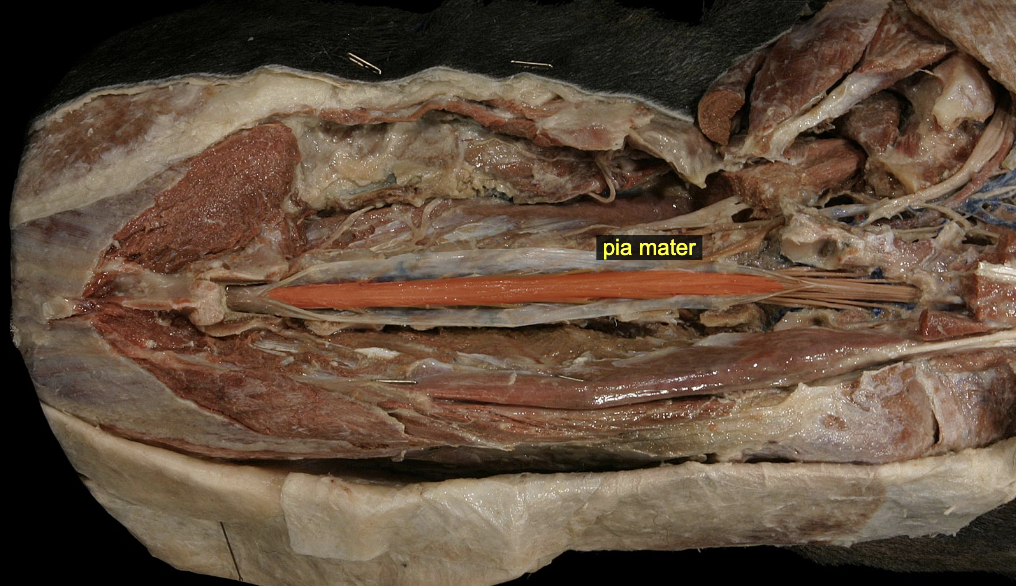
Conus medullaris
caudal end of spinal cord
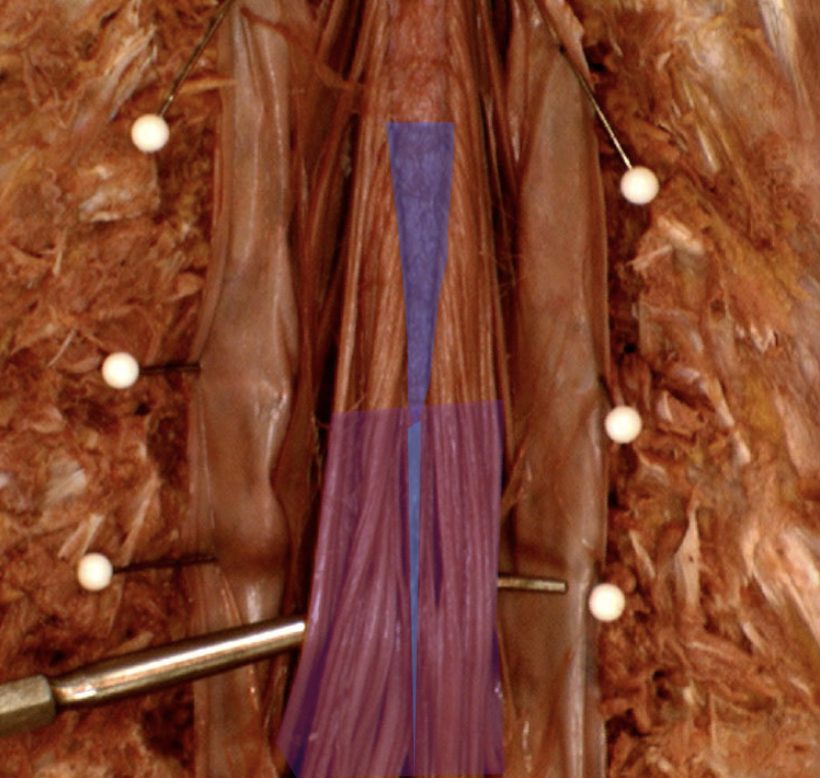
Lumbar Cistern (purple)
Lumbar cistern space: holds cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), where spinal taps occur
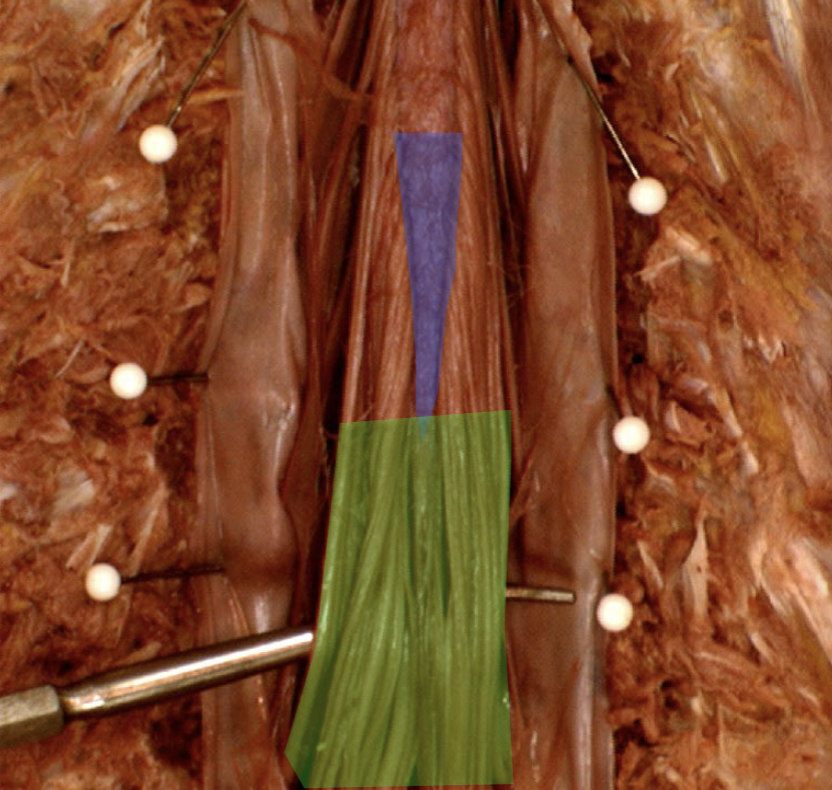
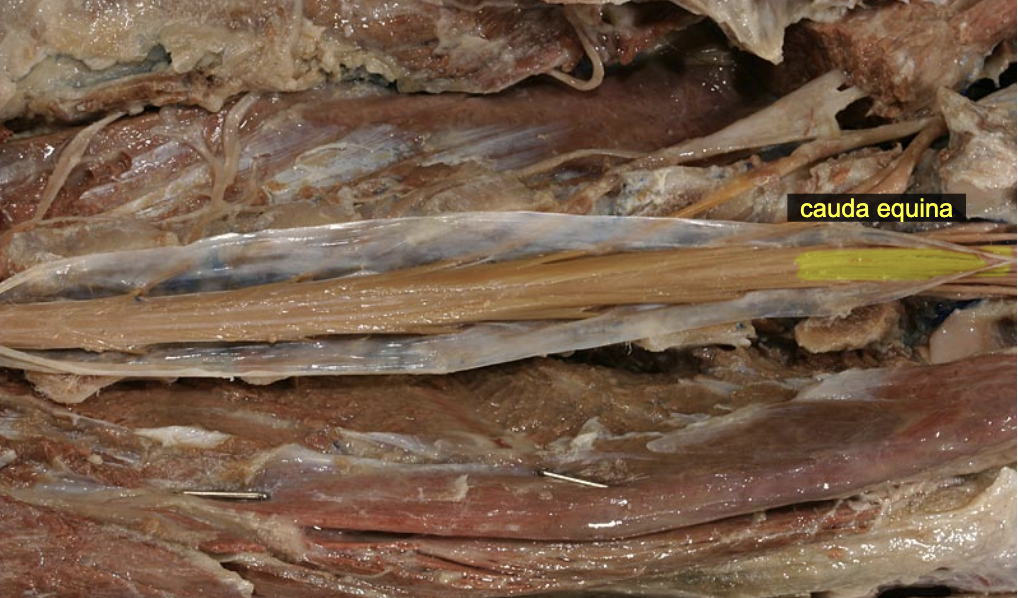
Cauda equina (green)
Spinal nerve root & CUDal to conus mendullaris
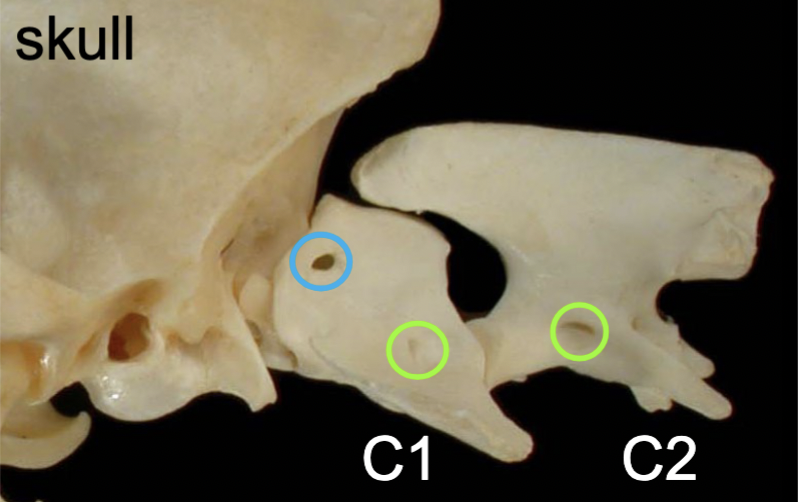
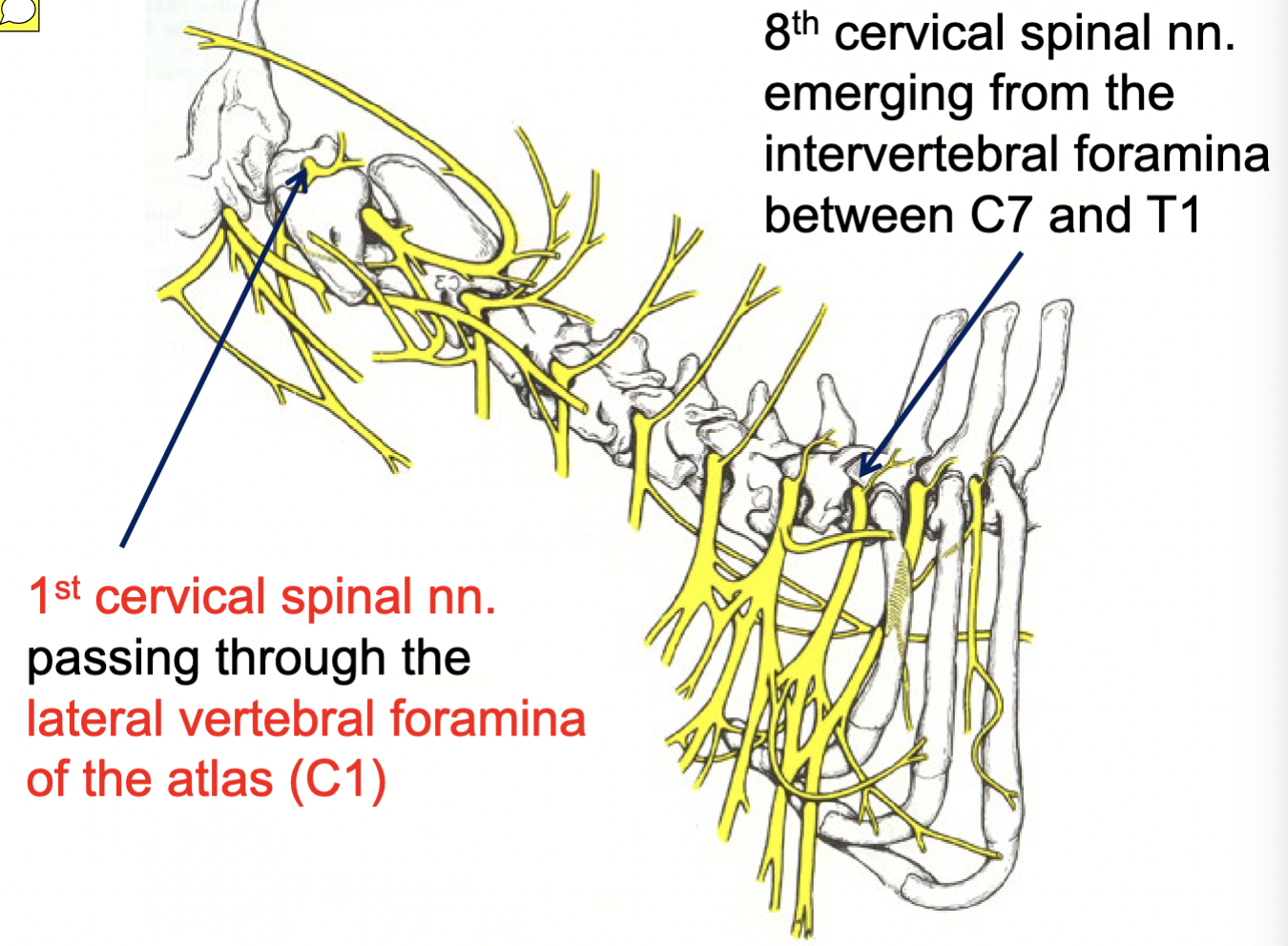
8th cervical spinal nn.
emerging from the intervertebral foramina b/w C7 & T1
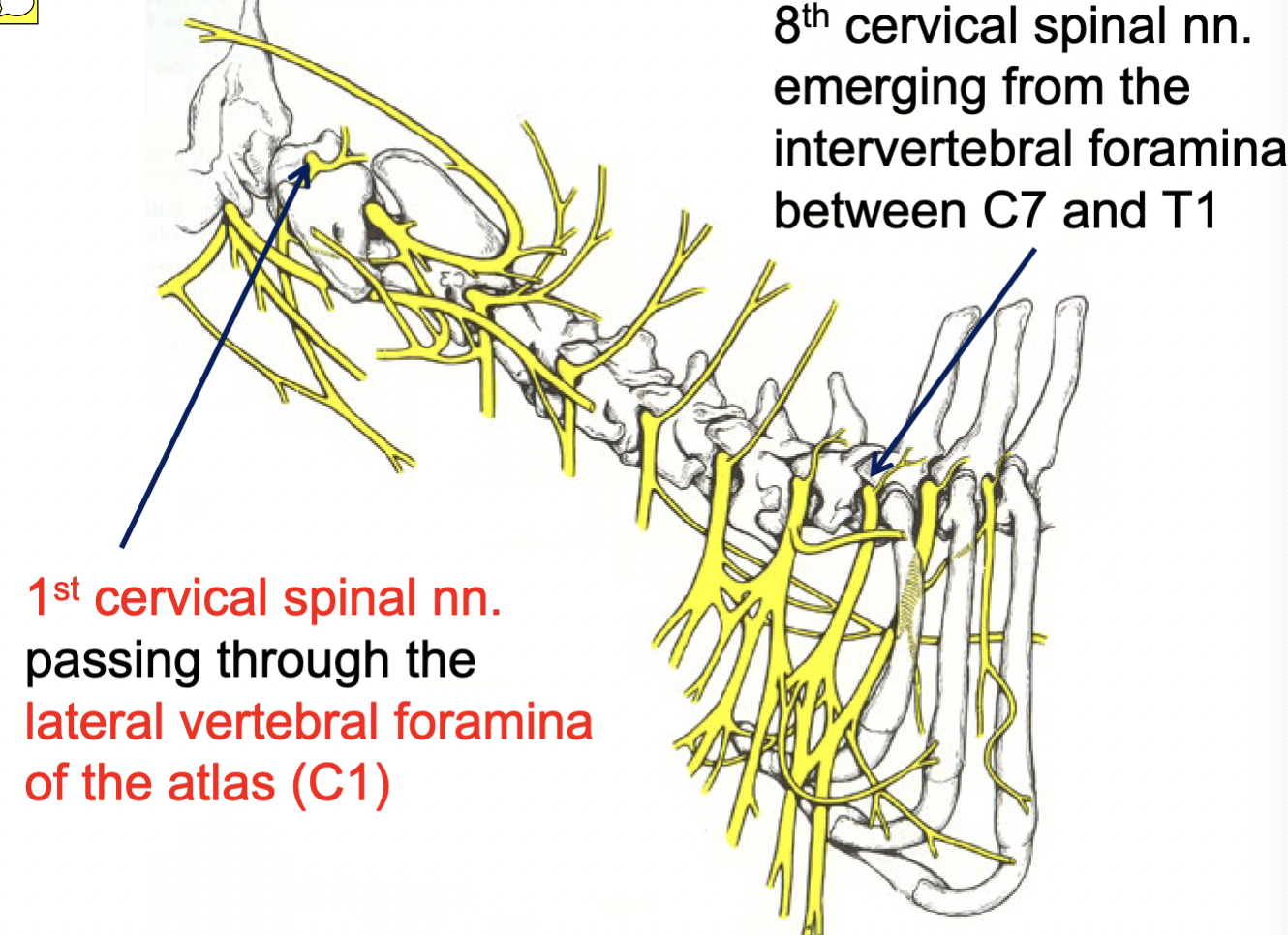
1st cervical spinal nn.
passing through the lateral vertebral foramina of the atlas (C1)
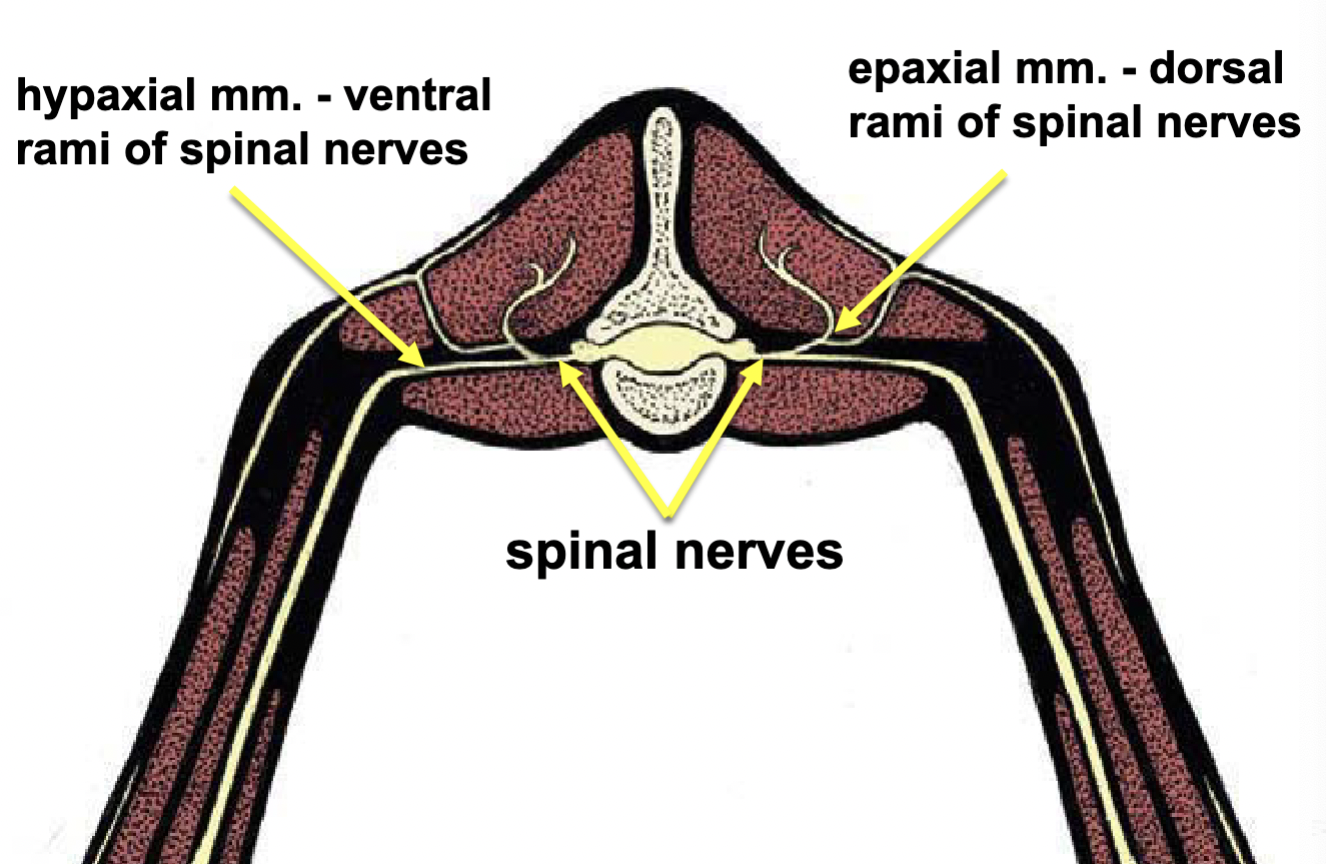
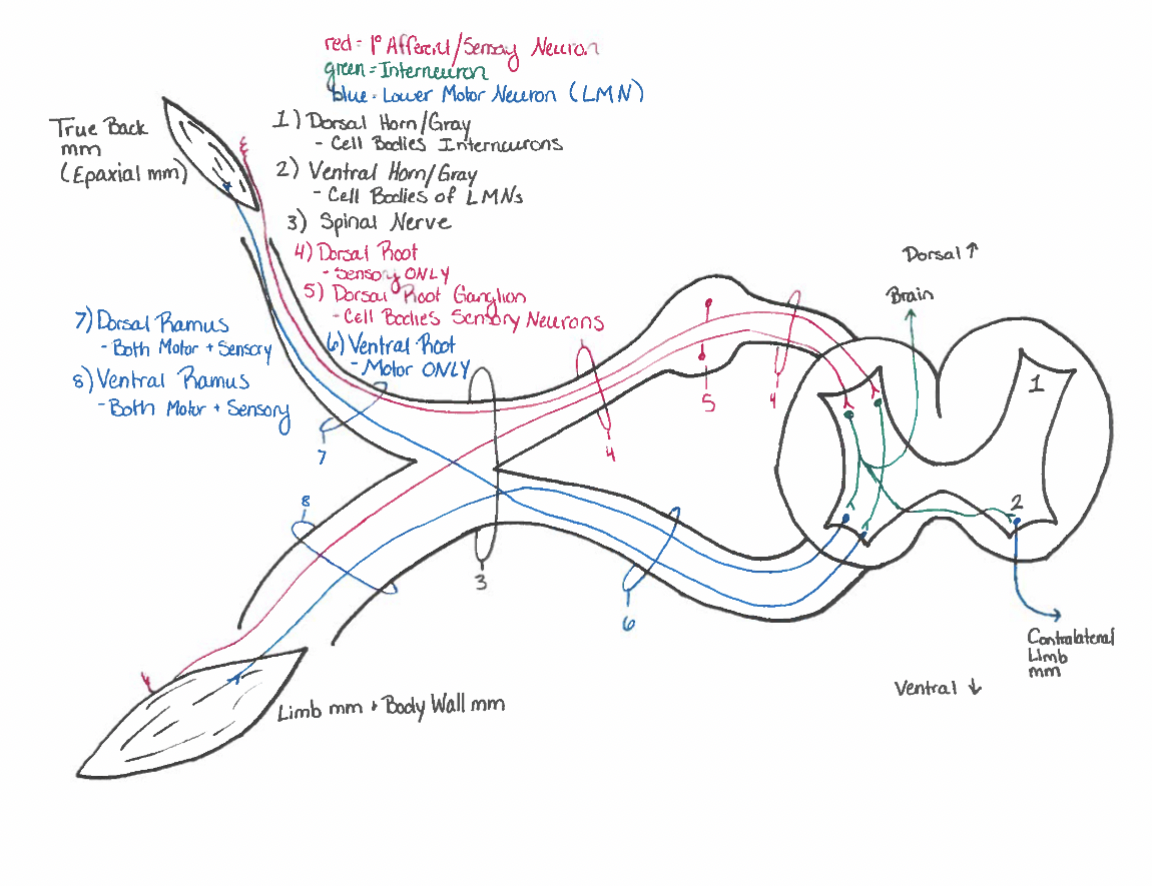
Epaxial vs. Hypaxial mm.
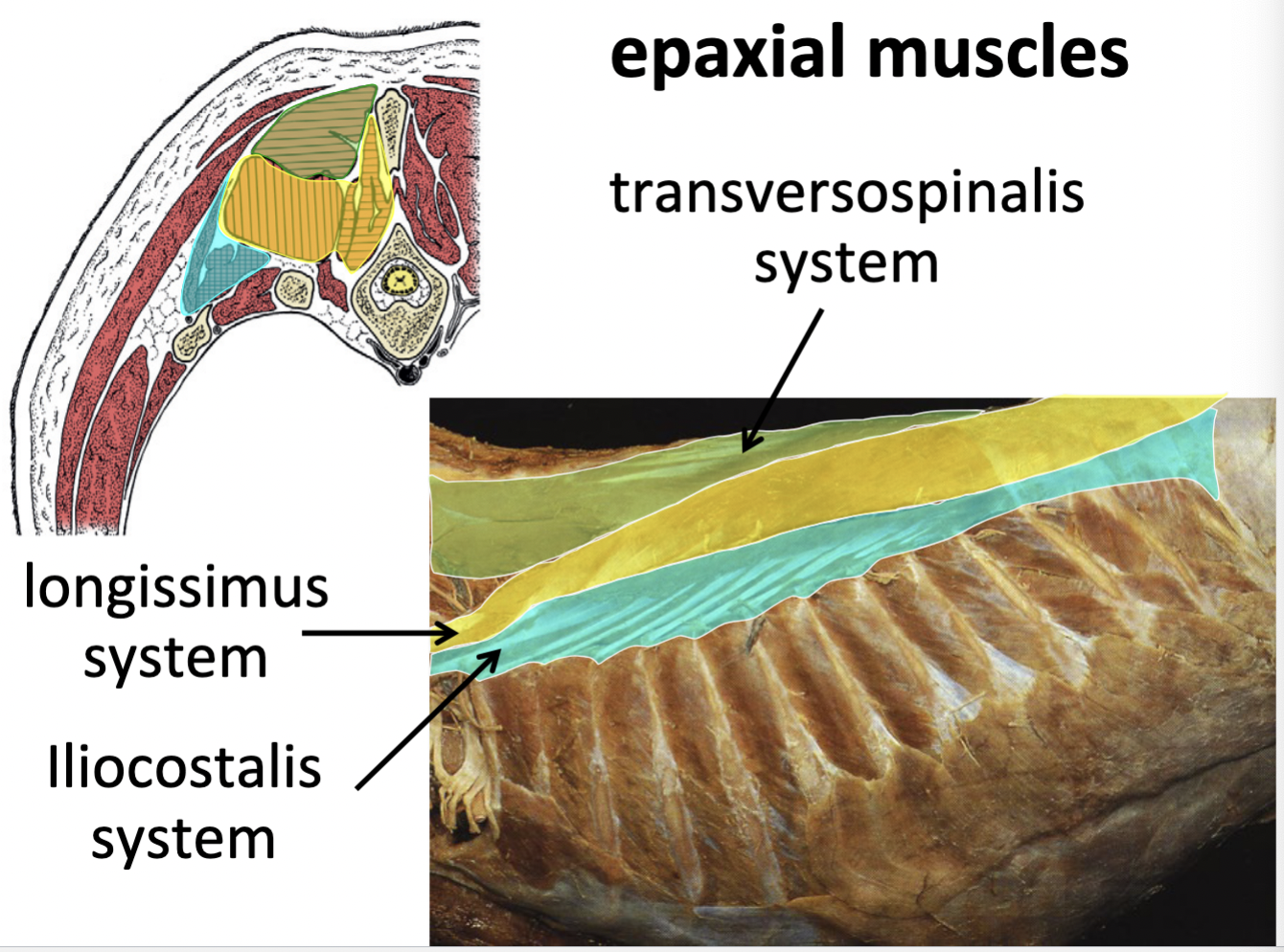
Epaxial muscle systems
I Love Taco’S
Transversopinalis mm.
Longissimus mm.
iliocostalis mm.
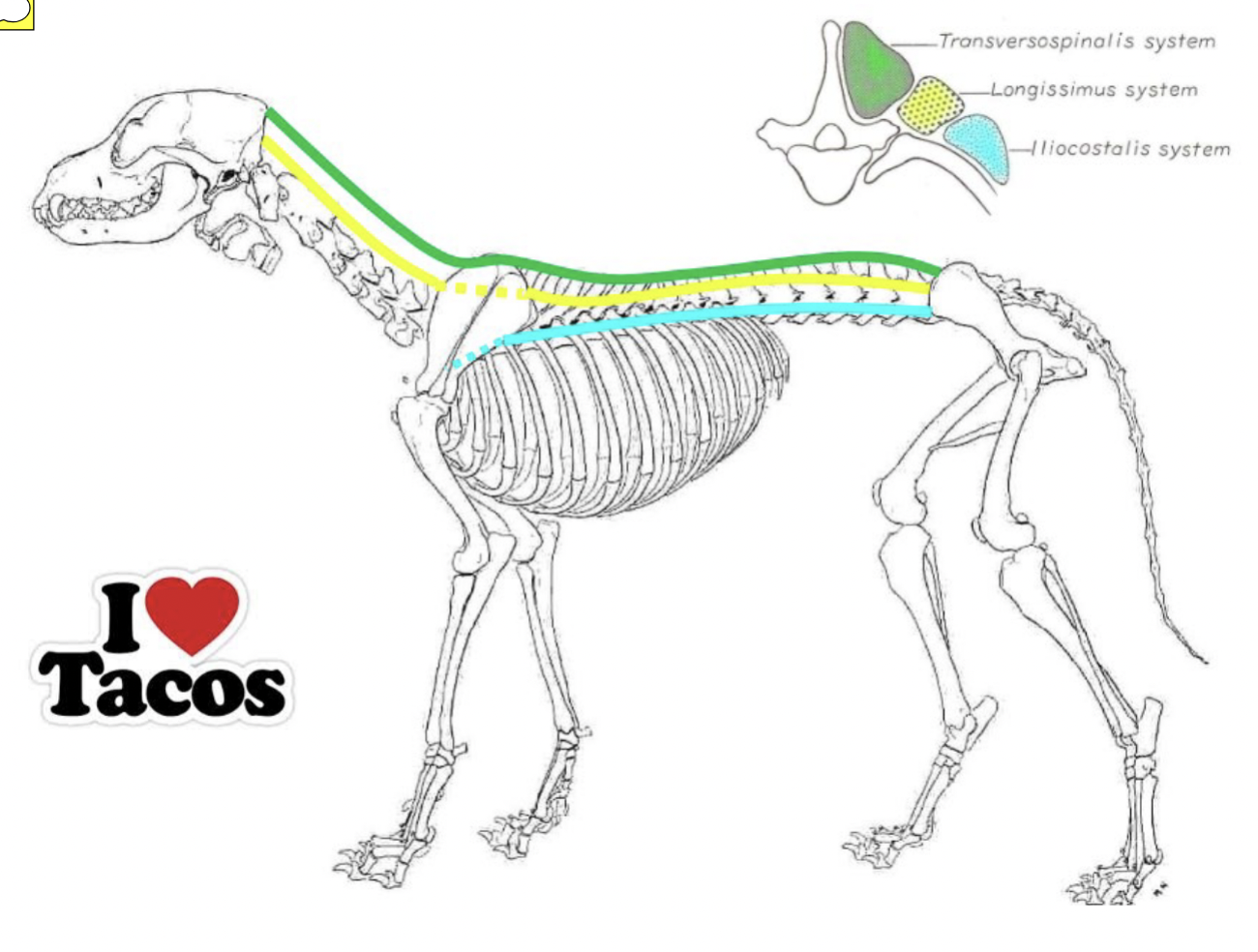
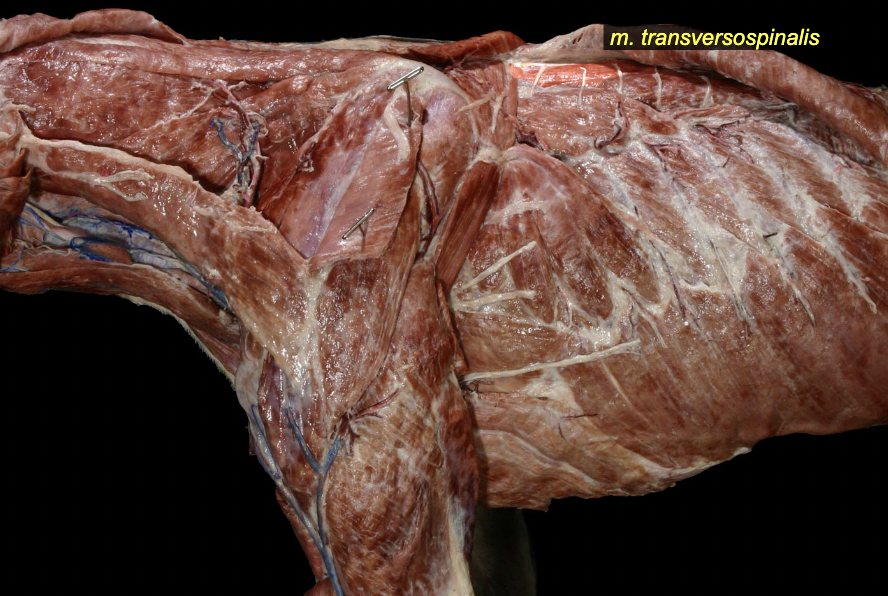
Transversopinalis mm.
most dorsal group
short muscles spanning b/w neighboring vertebrae
included splenius m.
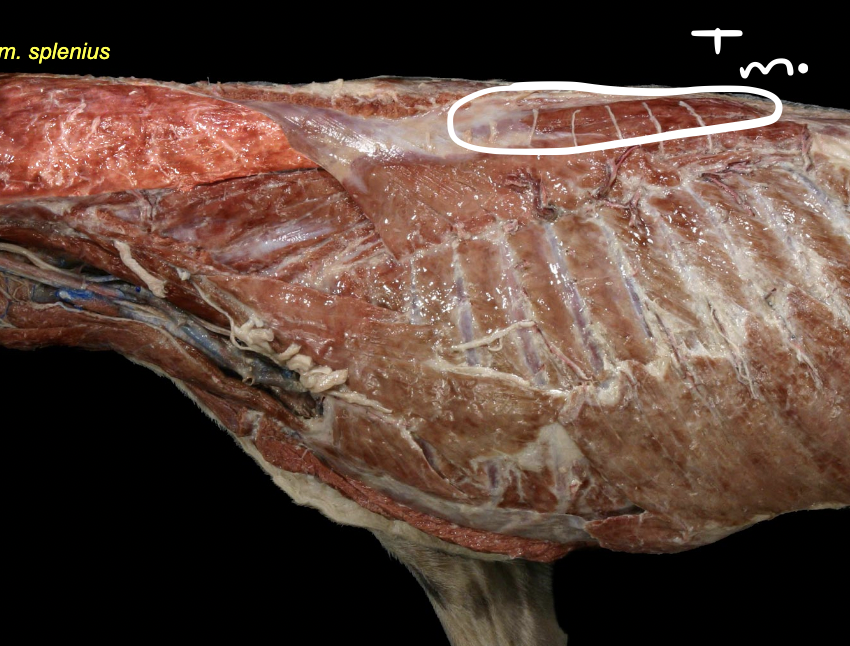
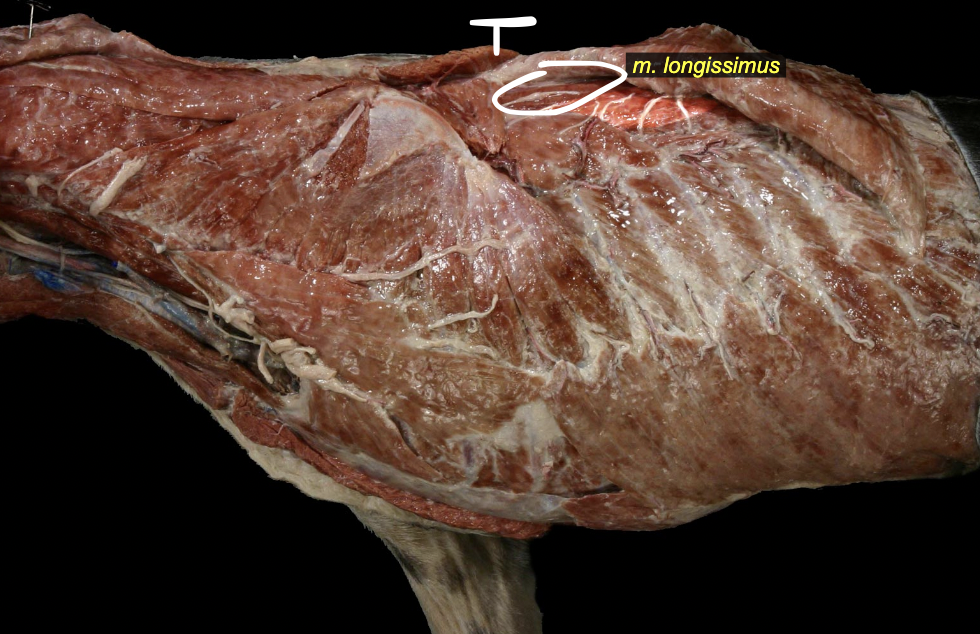
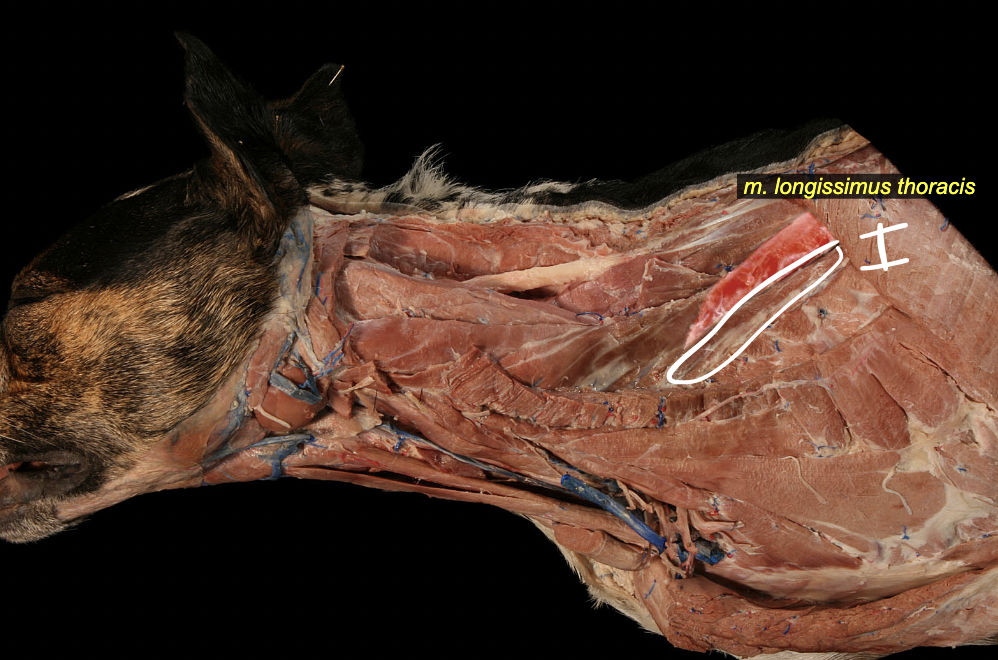
Longissimus mm.
middle group
wing of ilium → skull
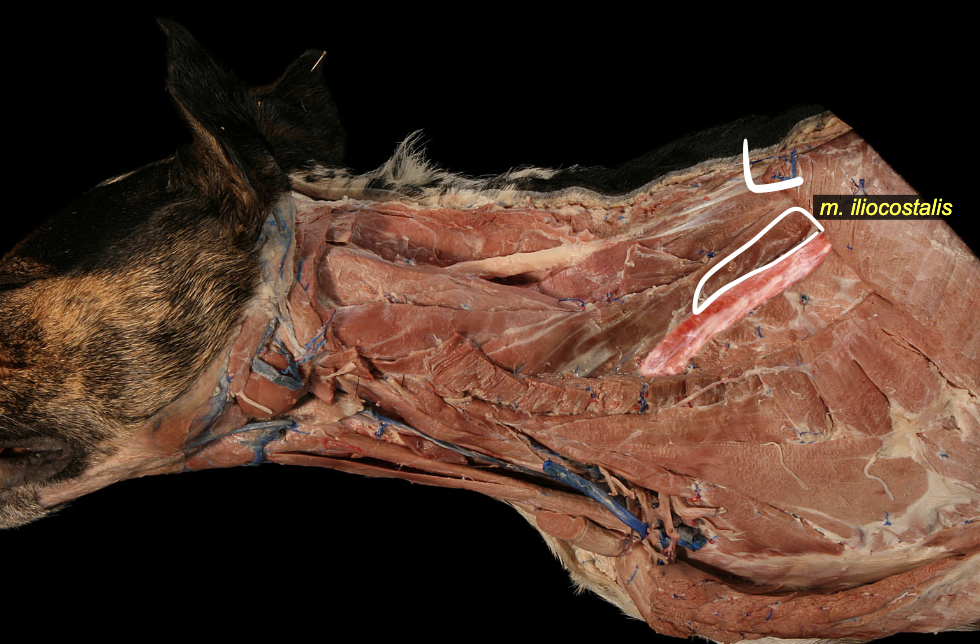
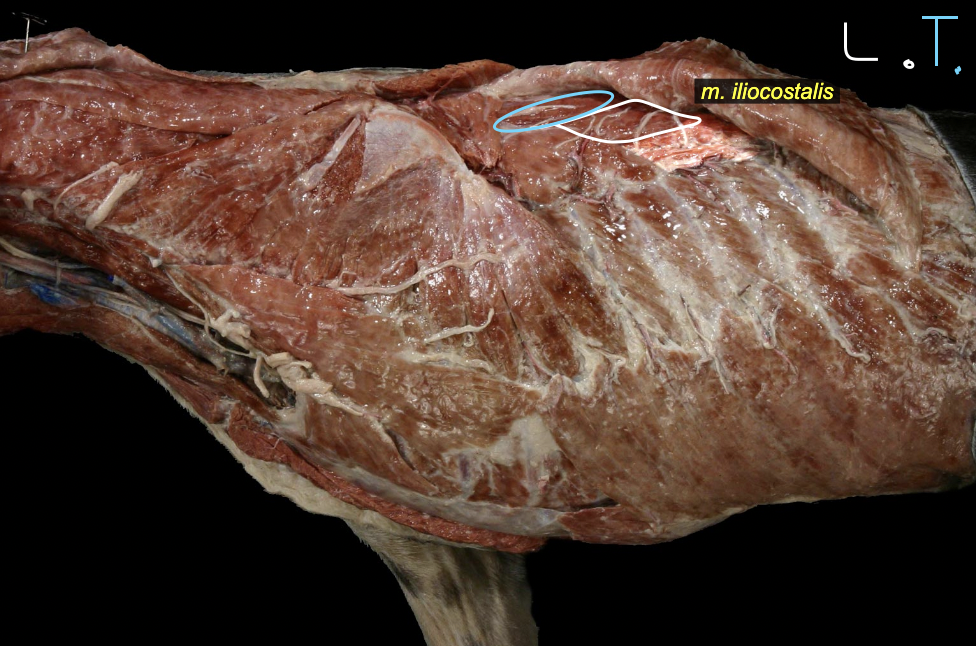
iliocostalis mm.
most ventral group
wing of illum → ribs

Epaxial muscle actions
extension of vertebral column (Bilateral contraction & lateral flexion (unilateral contraction)

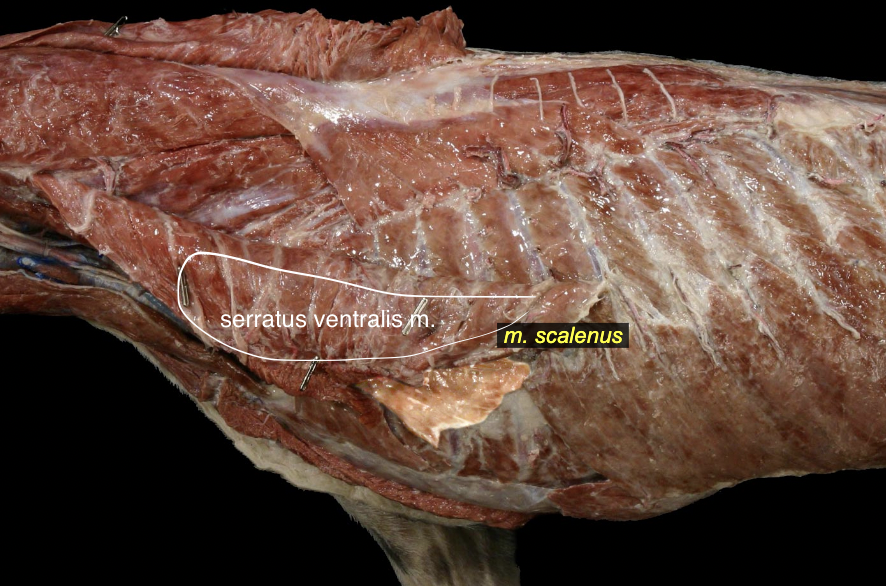
Serratus ventralis m.
possible Epaxial or Hypaxial mm. because location-wise epaxial but unknown. Just in the muscle section of the long list with the Epaxial & Hypaxial mm.
Epaxial vs. Hypacial muscle innervations
Epaxial mm. - dorsal rami of spinal nerves
hypaxial mm. - ventral rami of spinal nerves
Hypacial mm.
Scalenus m.
Sternothyroideus m.
Sternohyoideus m.
Scalenus m.
Sternothyroideus m.
Sternohyoideus m.
Spinal cord functions
sensory input & Processor to brain & different spinal cord regions
motor outflow & processor
relexes
Spinal cord functions: sensory input & Processor to brain & different spinal cord regions
Brain: brainstem, cerebellum, cerebrum
Different spinal cord regions: ipsilateral vs. contralateral & Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, caudal
Spinal cord functions: motor outflow & processor
lower motor neurons (LMNs): “final common pathway” & receive input from - UMNs (brain) & interneurons
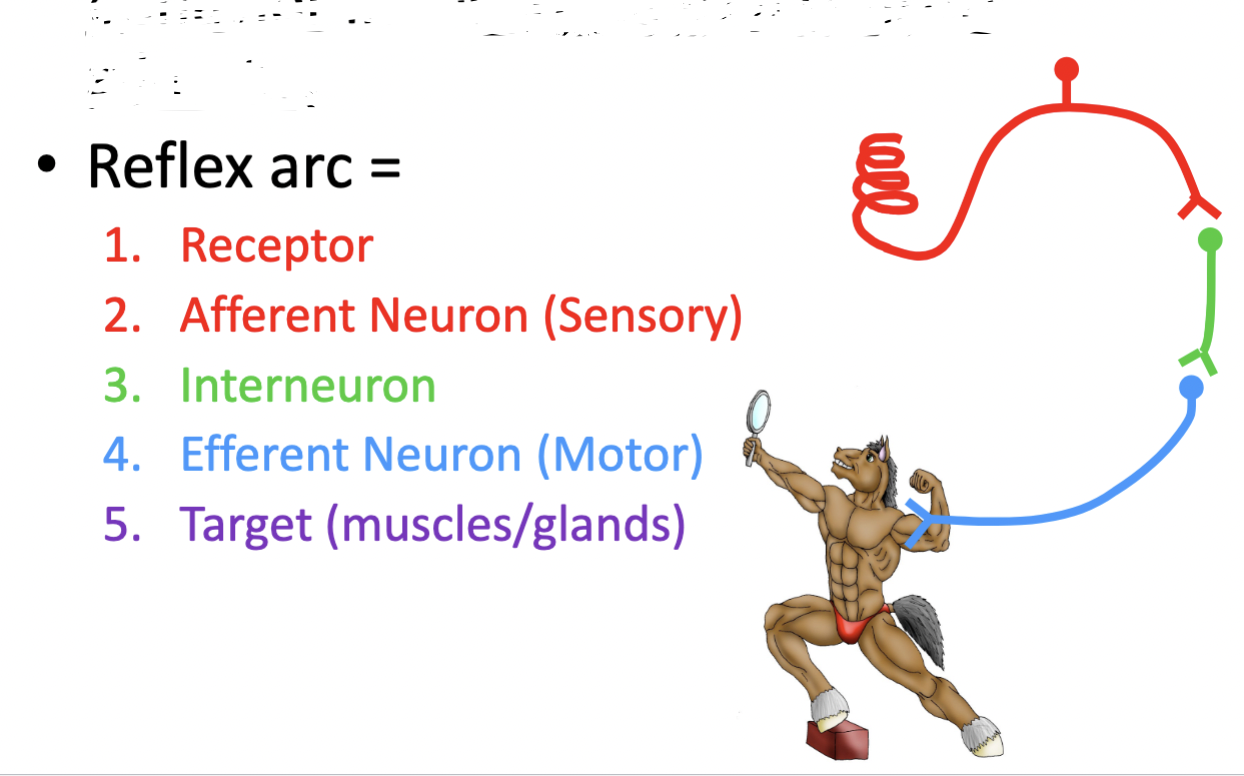
Spinal cord functions: reflexes
A stereotyped motor event driven by a sensory stimulus & local circuit - can operate without consciousness (without UMN from brain)
reflex arc = 1. receptor 2. afferent neuron (sensory) 3. interneuron 4. efferent neuron (motor) 5. target (muscles/glands)
Spinal cord: root vs. rami (branches)
spinal cord: external anatomy
2 spinal cord enlargements: 1. cervical enlargement - throacic limbs 2. Lumbosacral enlargement - pelvic limbs & some Autonomatic for Urogenital fxn
Why? more muscles & skin in those regions & they need more neurons to innervate them
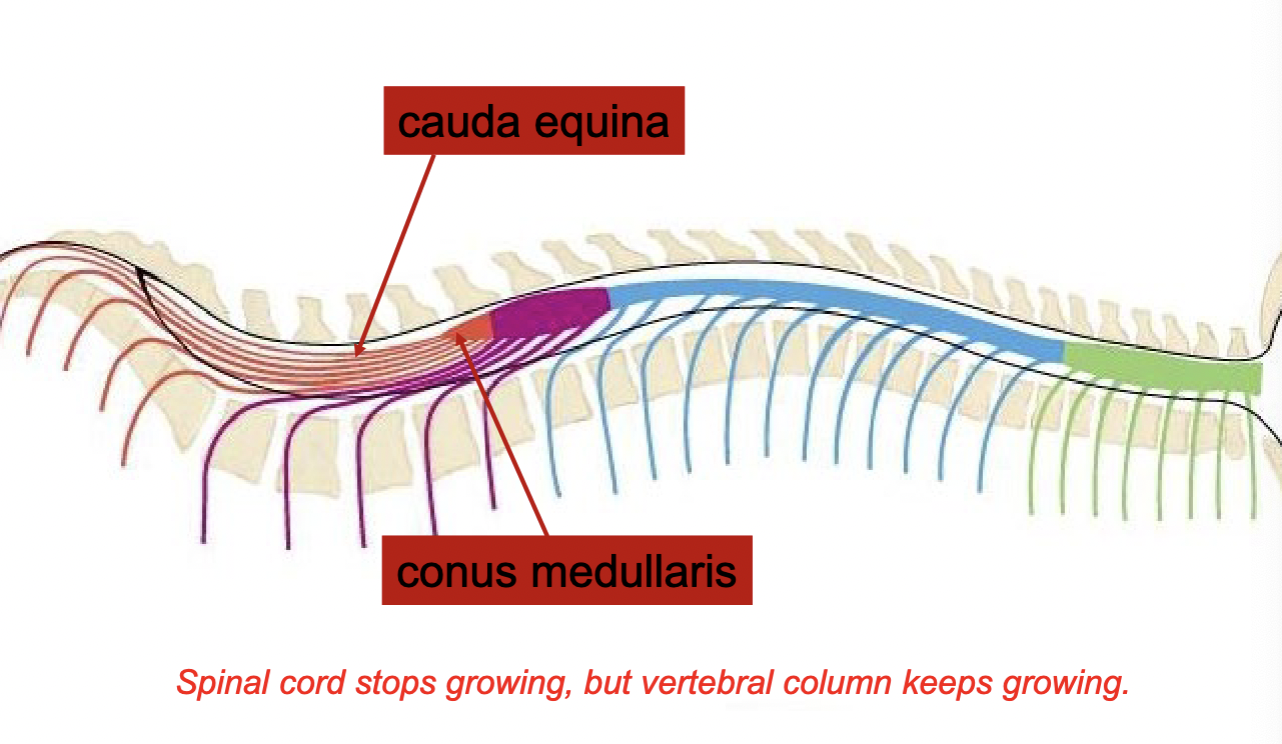
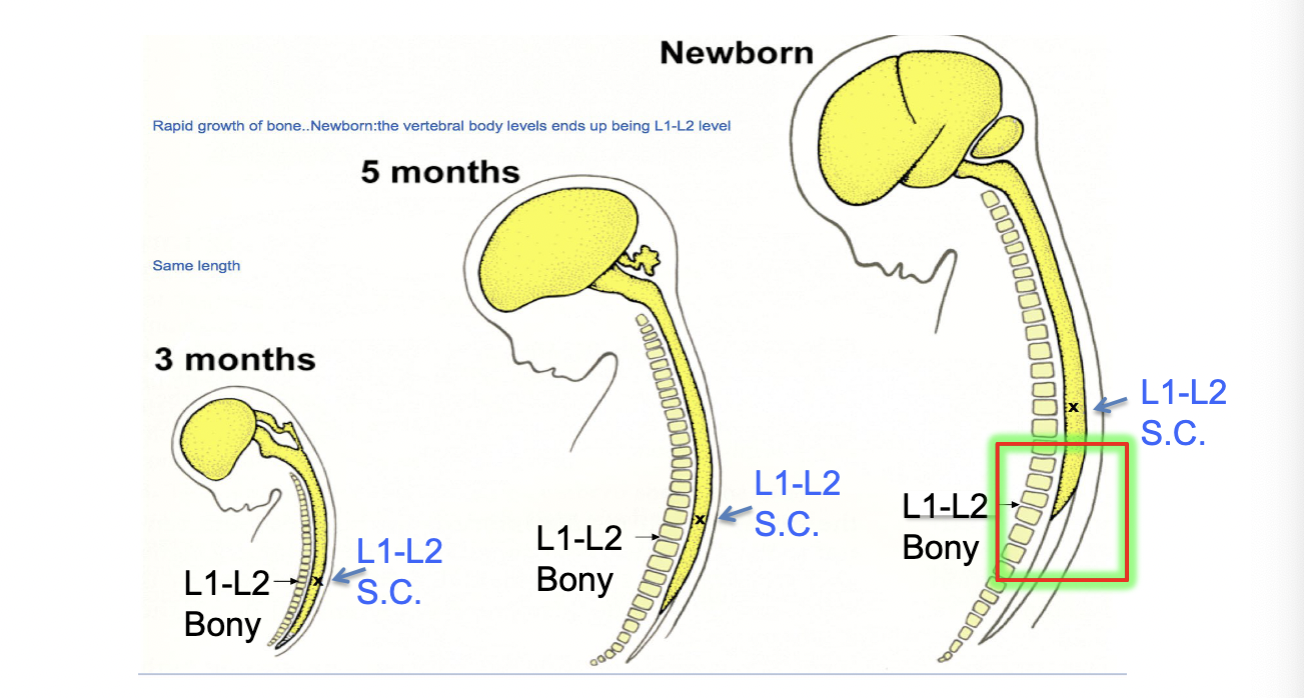
Spinal cord vs. Vertebrae
differential growth rates: spinal cord stops growing but vertebral column keeps growing
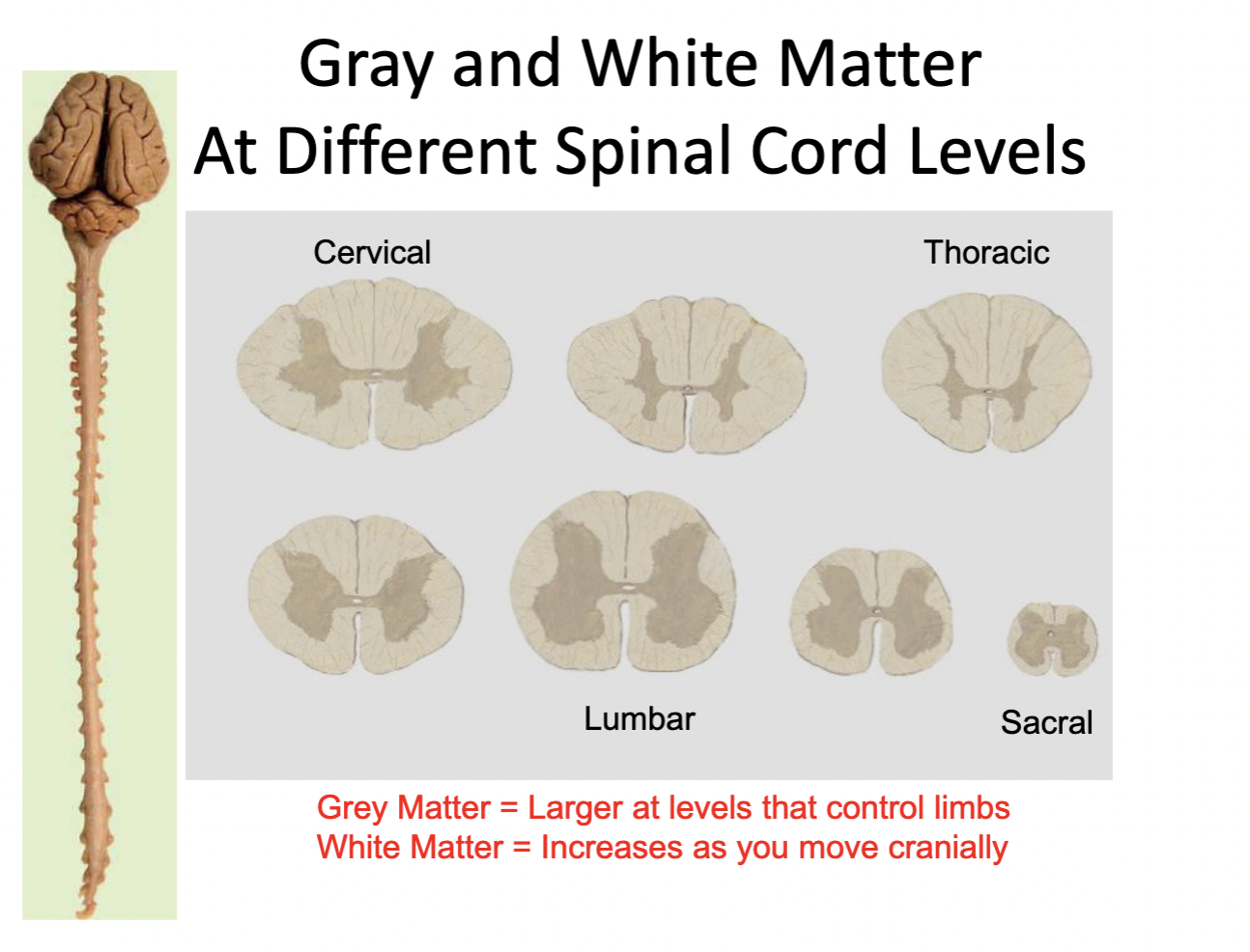
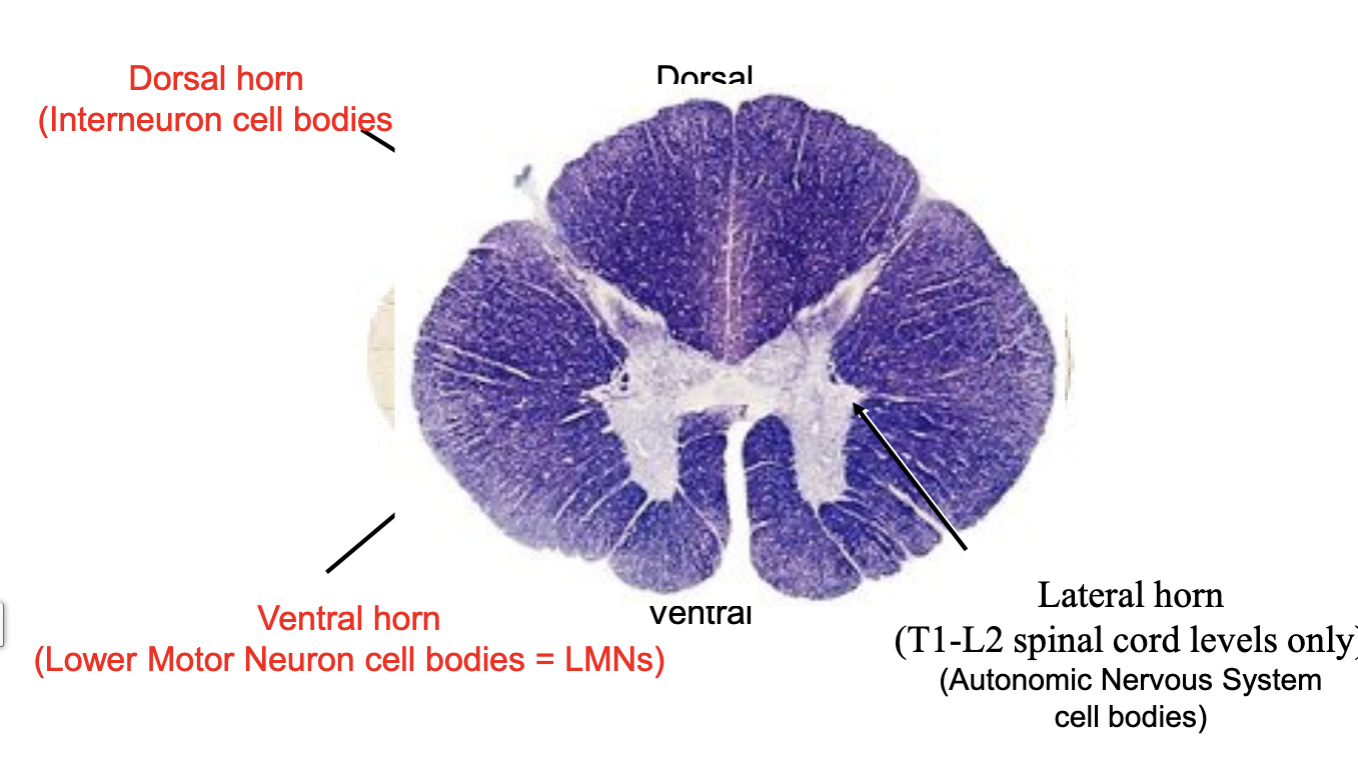
Spinal cord: internal anatomy
white matter & gray matter
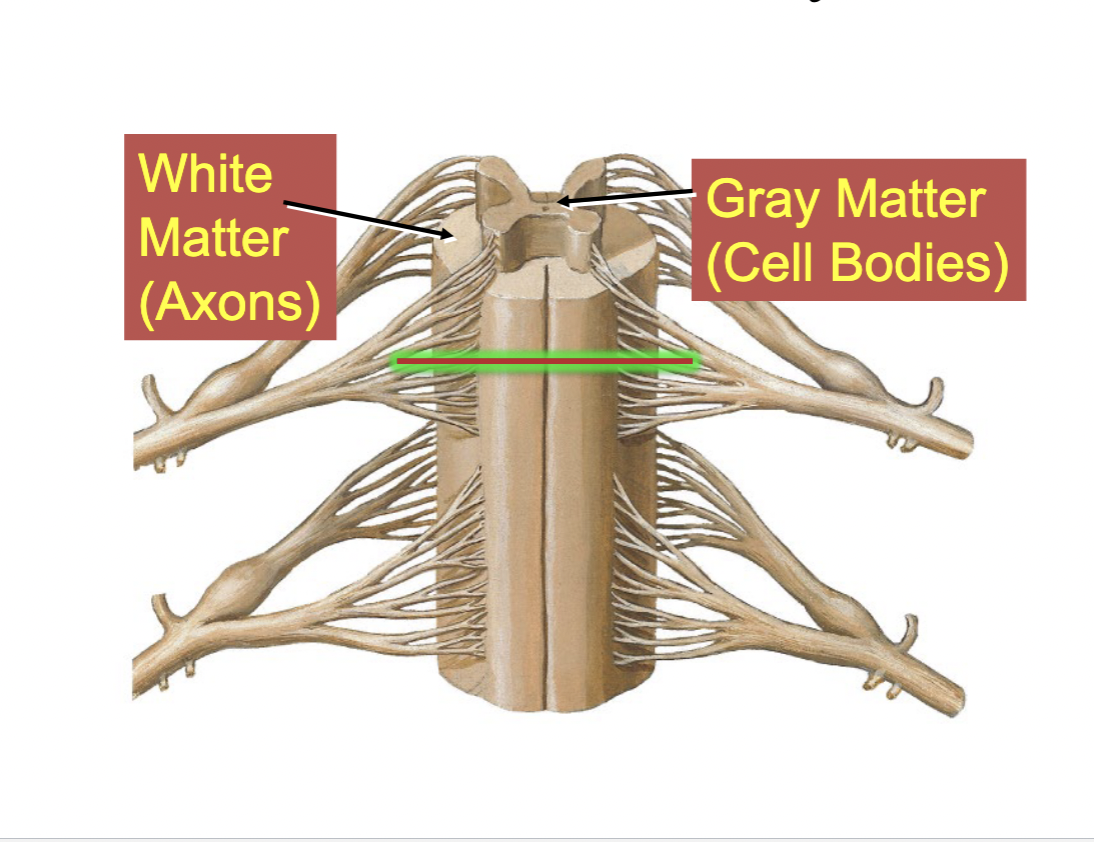
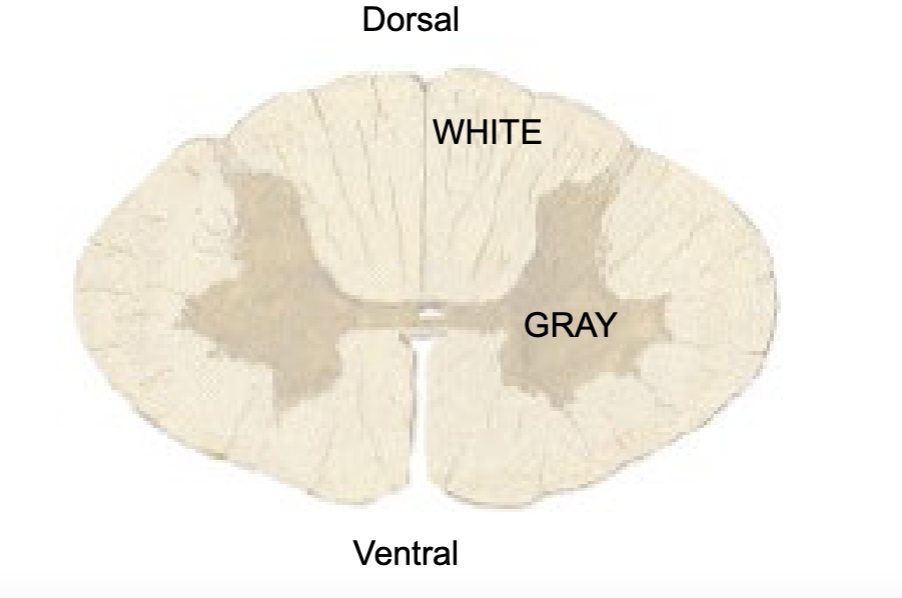
White matter
Neuron axons (myelinated)
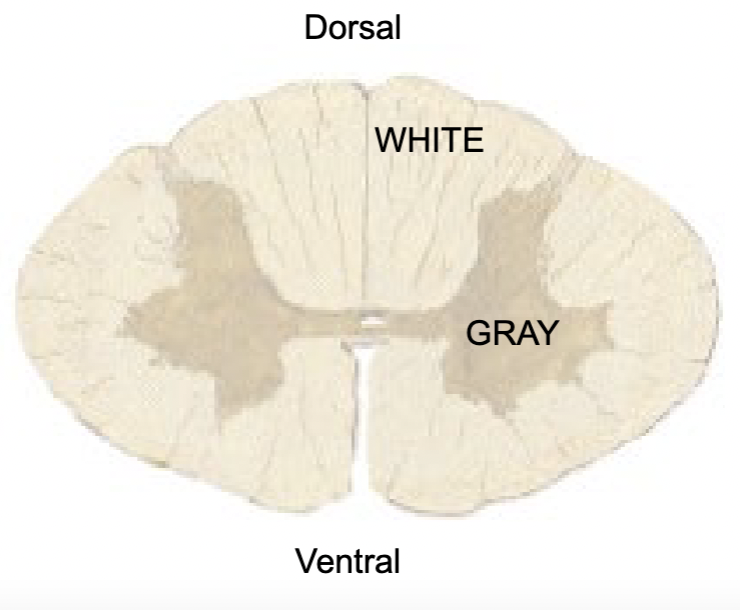
Gray matter
neuron cell bodies
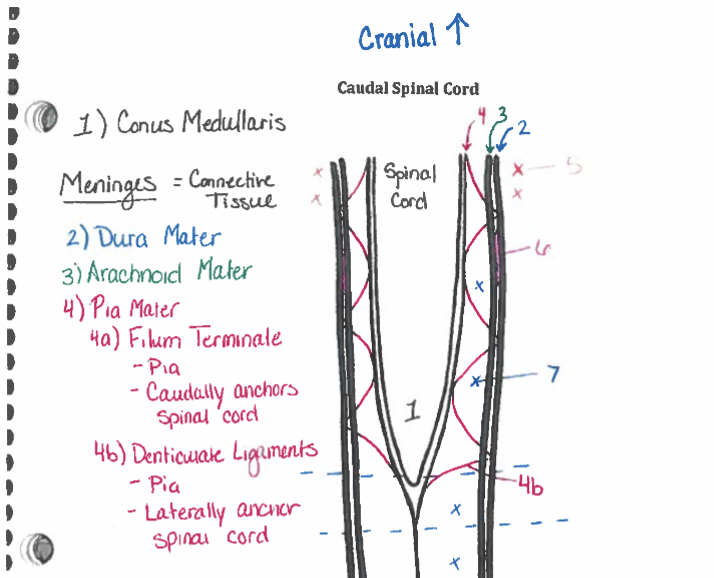
Meninges
Connective tissue members surrounding spinal cord (NOT nervous tissue)
Support & Protect CNS
Suspend CNS
3 layers: 1. dura mater (outermost layer) 1. Arachnoid (middle later) 3. pia mater (innermost layer)
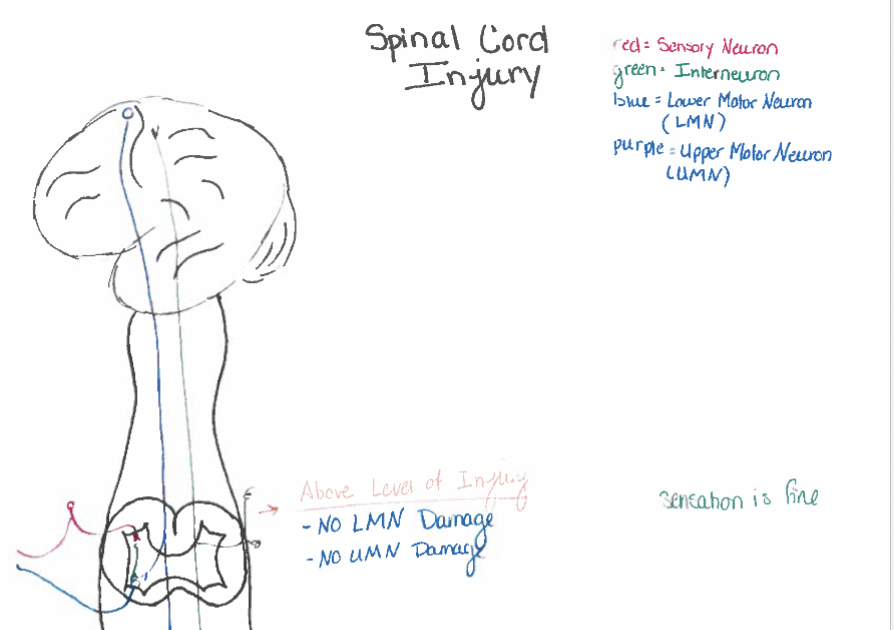
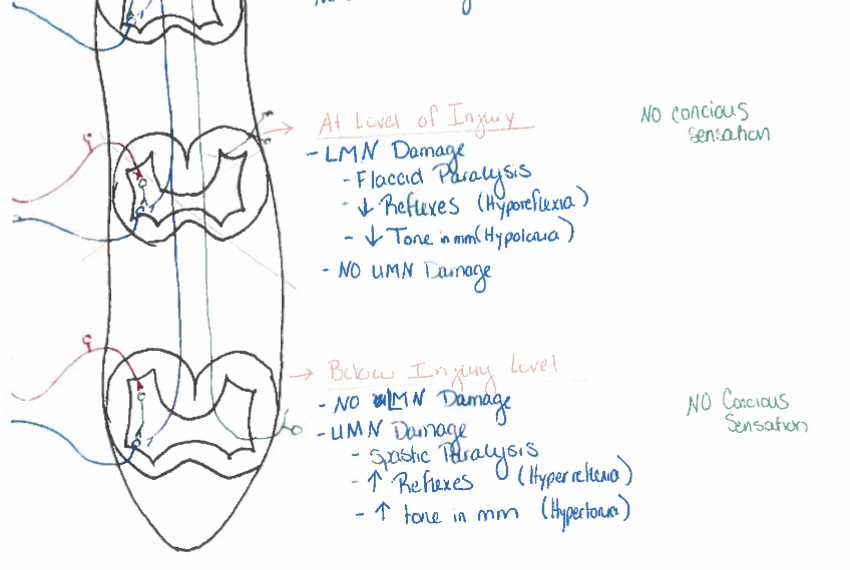
Spinal cord injuries
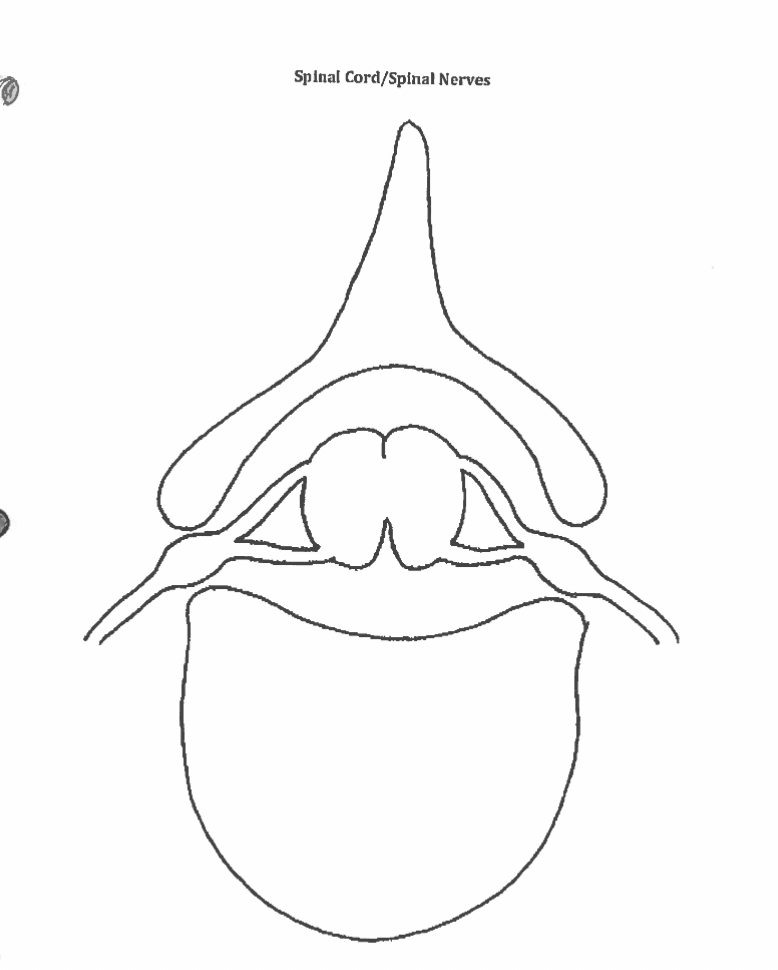
spinal cord/nerves
Spinal cord injuries
flaccid paralysis: at region supplied by damaged LMN
loss of sensations from body caudal to injury
no effect above injury