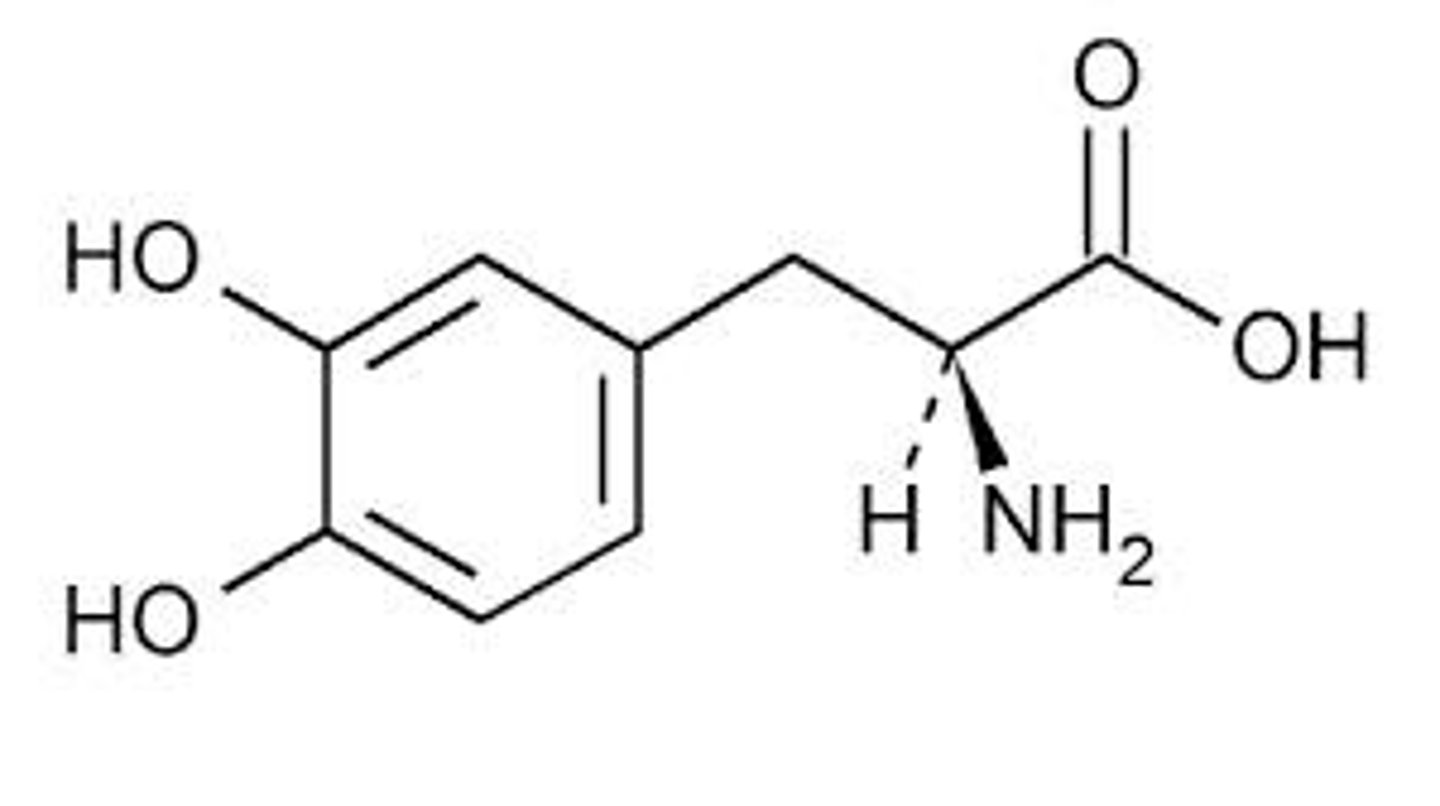
7.3 Biological Basis of Nervous System Disorders
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Dopamine Hypothesis
Schizophrenia is associated with an excess of dopamine in the brain.
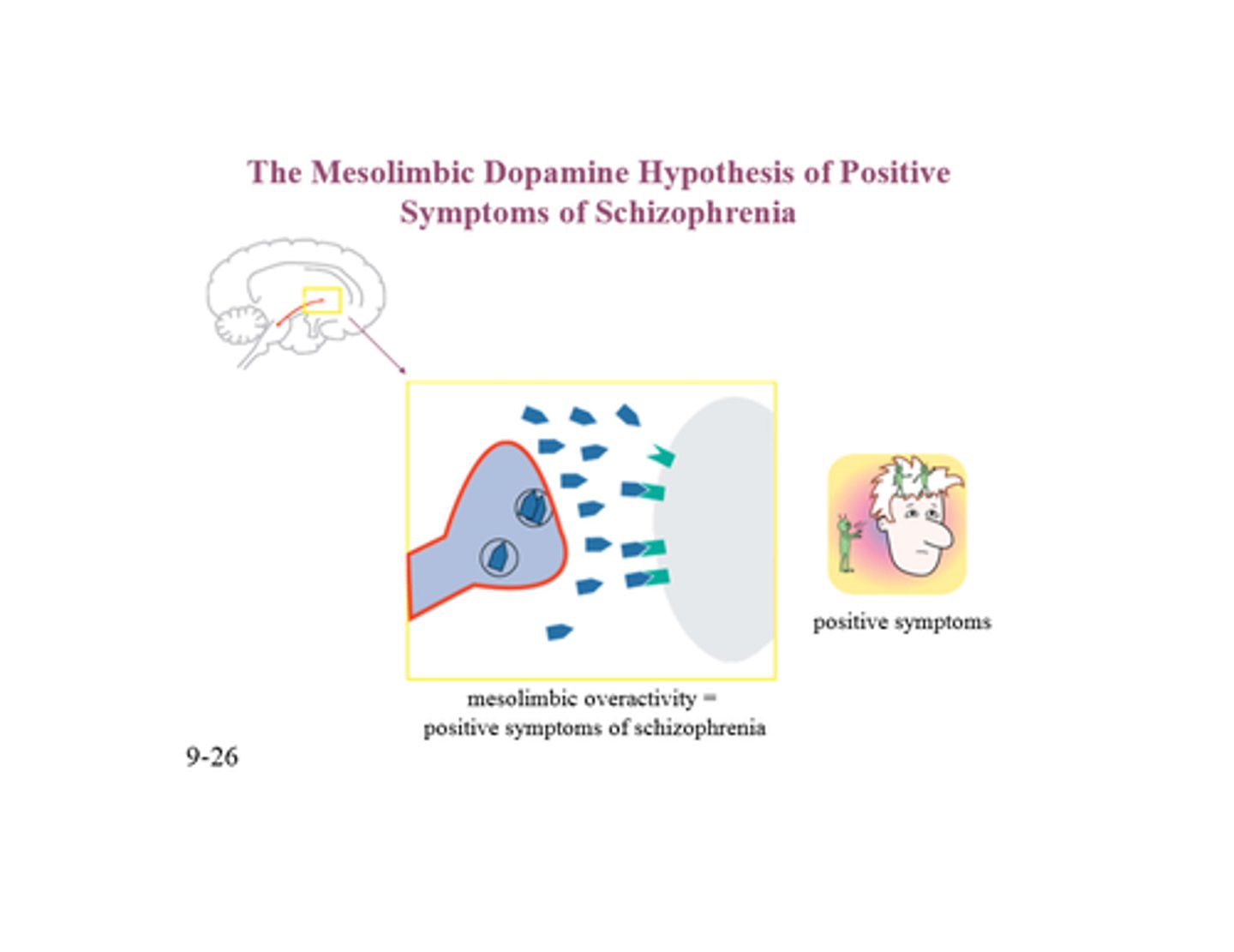
Neuroleptics
Used to treat schizophrenia becuase they block dopamine receptors.
Biomarkers of Depression
-High glucose metabolism in the amygdala.
-Hippocampal atrophy after a long duration of illness.
-Abnormally high levels of glucocorticoids.
-Decreased norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
Biomarkers of Bipolar Disorders
-Increased norepinephrine and serotonin.
-Higher risk if a parent has it.
-Higher risk for a person with multiple sclerosis.
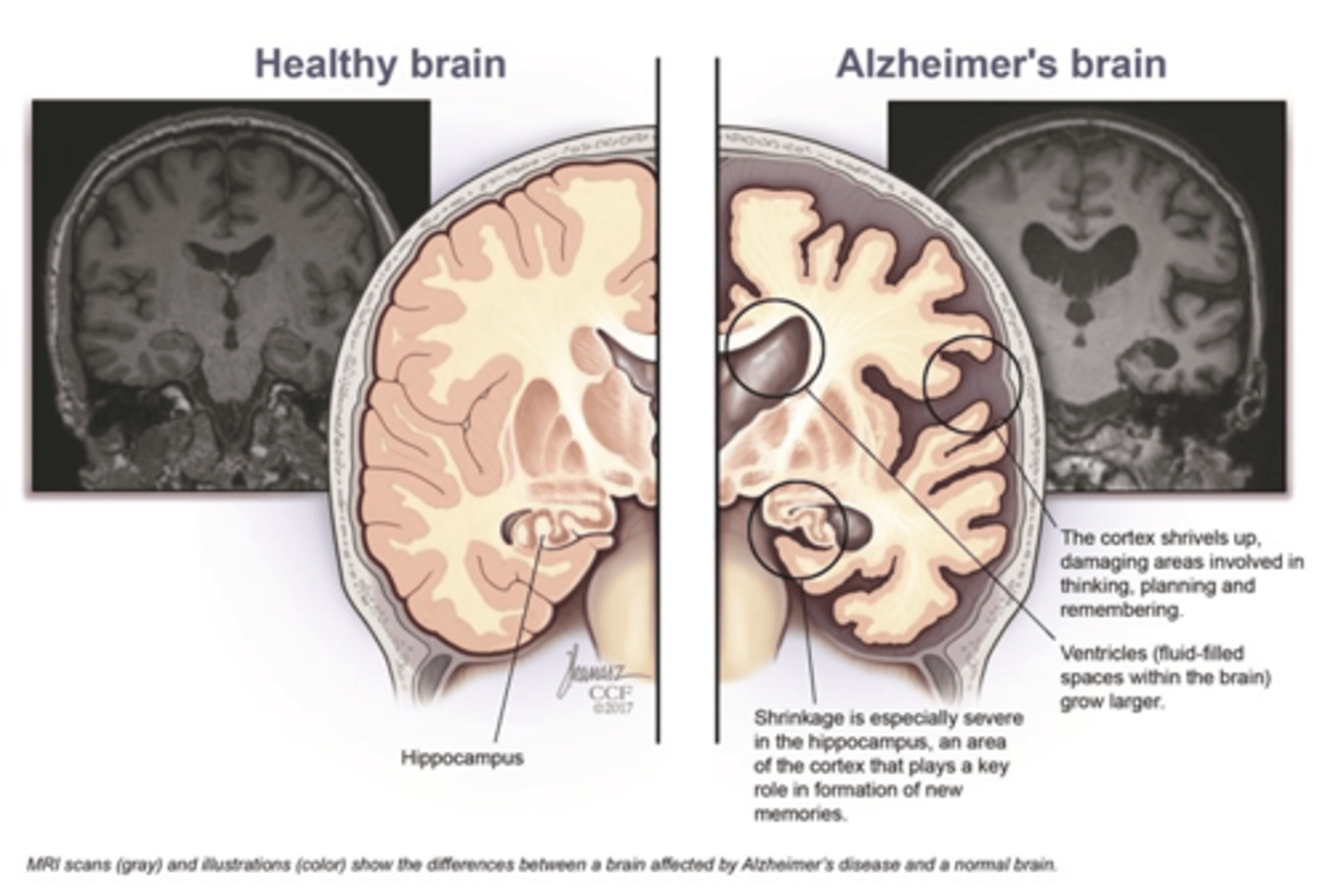
Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease
-Diffuse atrophy on CT.
-Flattened sulci on the cerebral cortex.
-Enlarged cerebral ventricles.
-Deficient parietal lobe blood flow.
-Acetylcholine reduction.
-Choline acetyltransferase reduction.
-Reduced metabolism in the temporal and parietal lobes.
-Beta-amyloid plaques.
-Neurofibrillary tangles of hyperphosphorylated tau protein.
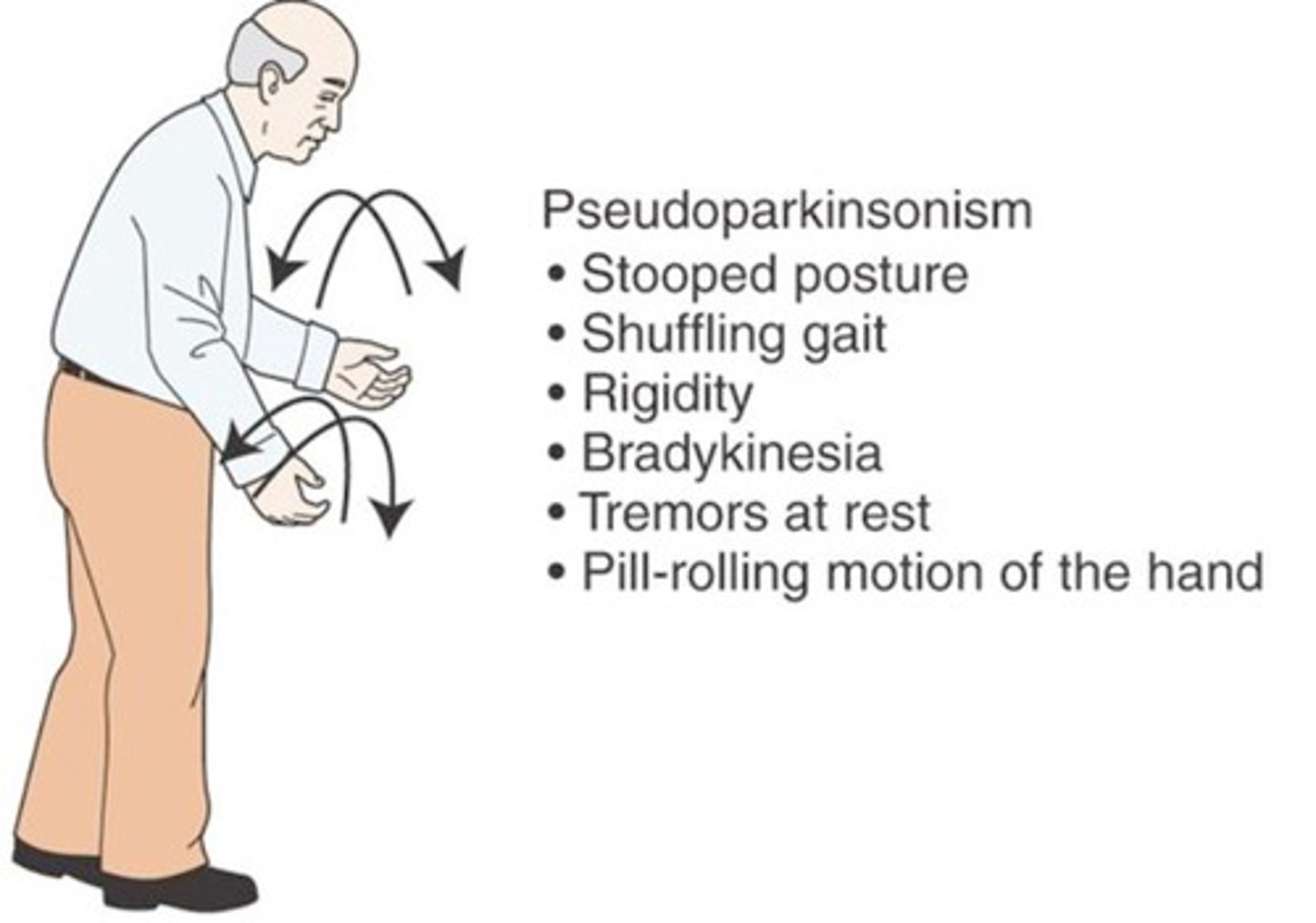
Parkinson's Disease
Bradykinesia, resting tremor, pill-rolling tremor, masklike facies, cogwheel rigidity, shuffling gait.
Resting Tremor
A tremor that appears when the muscles aren't being used.
Pill-Rolling Tremor
Flexing and extending the fingers while moving the thumb back and forth. Characteristic of Parkinson's.
Masklike Faces
A facial expression consisting of static and expressionless facial features.
Cogwheel Rigidity
Muscle tension that intermittently halts movement as an examiner attempts to manipulate a limb.
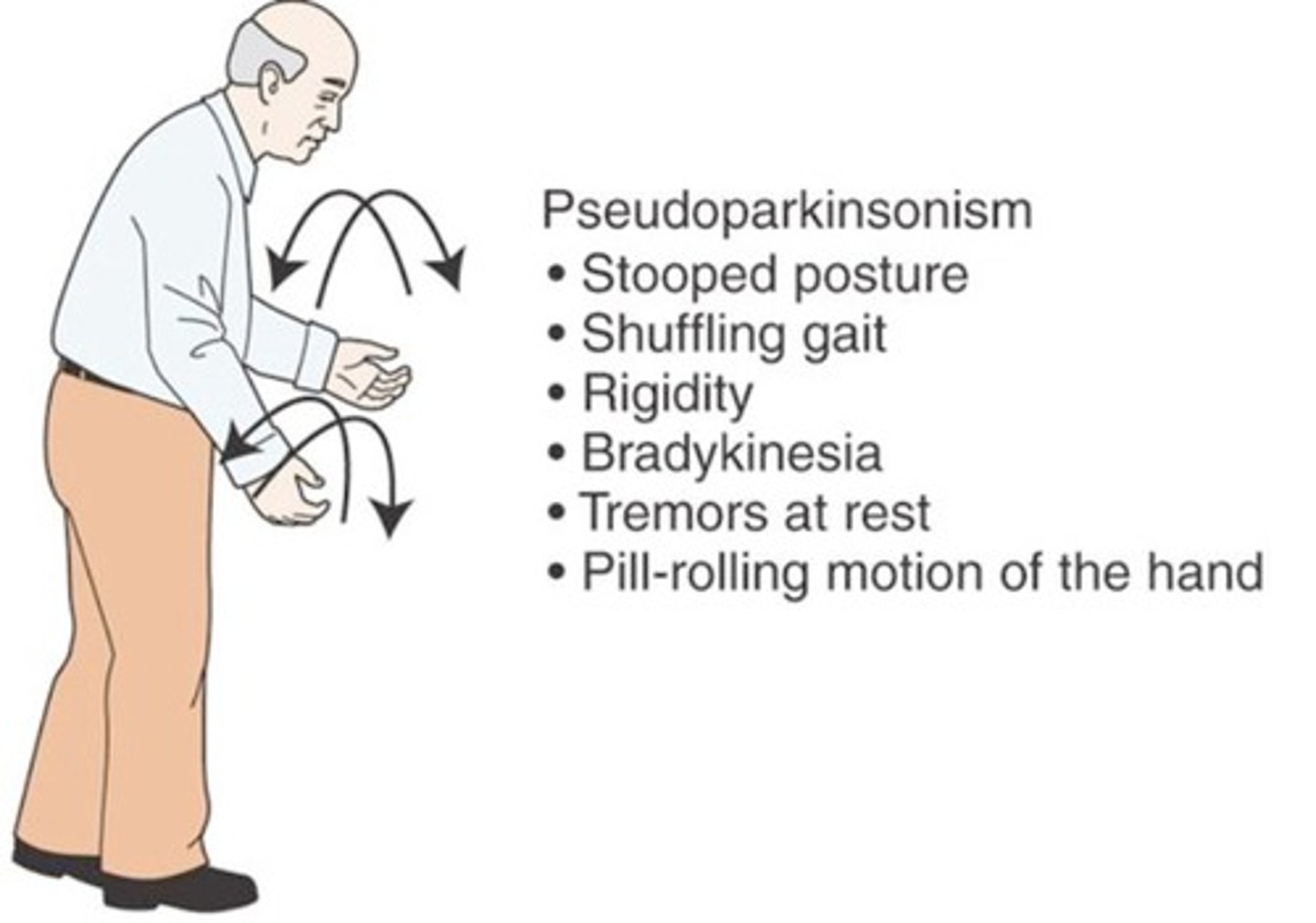
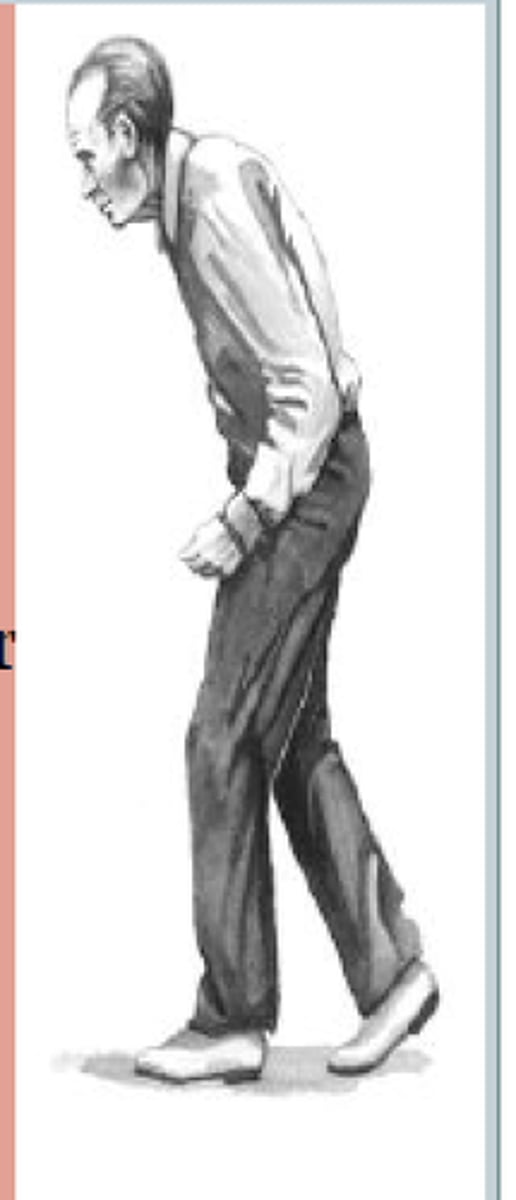
Shuffling Gait
Stooped posture with small shuffling steps of low ambulatory efficiency.

Biomarkers of Parkinson's Disease
Decreased dopamine production in the substantia nigra, which produces dopamine to permit proper functioning of the basal ganglia.
Levodopa
Used to treat Parkinson's disease.