BSCI170: How the Endomembrane System Works
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/6 notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Order of the endomembrane system
Nucleus: RNA is created
Nuclear envelope: RNA leaves nucleus
Rough ER: uses RNA to synthesize and modify proteins
Transport vesicles: transports proteins from rough ER to golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus: further modification, sorting, and packaging
Secretory vesicles: secretes proteins out of the cell
Plasma membrane: releases proteins outside of the cell through exocytosis
*vesicles are always needed for transportation; think of proteins/phospholipids as babies who can’t be trusted to go to places on their own so they needed a truste adult. that trusted adult is the vesicle
Transport vesciles - in depth
inside, polypeptide will turn into glycoprotein, and a part of the rough ER will bud off and turn into vesicle to transport the phospholipid/protein to the golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus: in depth
Cis face: side of golgi facing/closest to ER
transport vesicles fuse w/ cis face bc it’s closer
Trans face: side of golgi facing away/further from ER
things will move from the cis face to trans face
Secretory vesicles
buds off from golgi apparatus and transports proteins/phospholipids from the golgi apparatus to plasma membrane by fusing with it
Plasma membrane
either secretes phospholipids/proteins or it stays inside
Lysosomes function
trashbag organelle; breaks down molecules like proteins, other oranelles, lipids, nucleic acids, etc.
very acidic
has digestive enzymes
What is autophagy
breakdown of damaged organelles
lysosomes aid in this
what is phagocytosis
cells called phagocytes ingest foreign particles like bacteria, viruses, and other dead cells
lysosomes aid in this
Mitochondria: Where is it found, function, and characteristics
Found in:
animal cells
plant cells
Function: generates ATP through aeriobic respiration
breaking ATp produces energy
waste is carbon dioxide
Characteristics:
outer membrane: permeable to lots of molecules
inner membrane: less permeable, has cristae (lots of folds)
has their own DNA and ribosomes
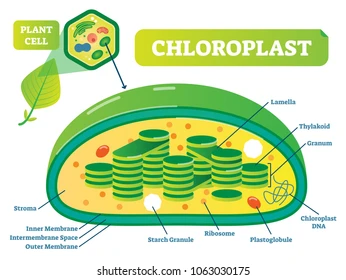
Chloroplasts: Where it’s found, function, and characteristics
Found in:
plant cells
Function:
site of photosynthesis; converts solar energy to chemical energy
Characteristics:
has inner and outer membrane
stroma: space inside inner membrane
thylakoids: inner membrane structure that look like flat discs