GS 16 Convection
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
a type of heat transfer where materials that are warmed become less dense and rise, and materials that are cooler become more dense and sink
what is convection?
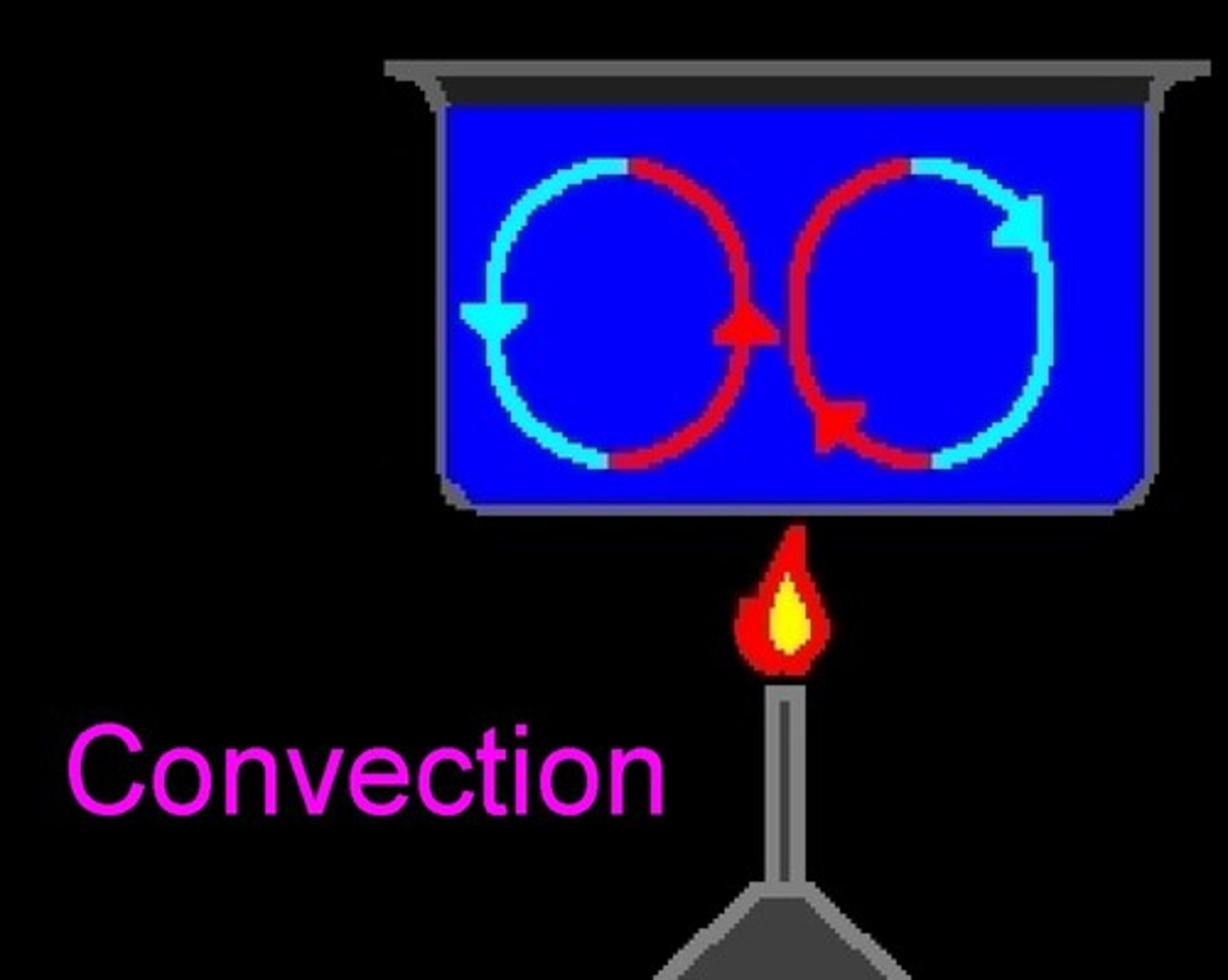
density decreases as materials are warmed
what happens to the density of materials that are warmed?
density increases as materials are cooled
what happens to the density of materials that are cooled?
rock rises/moves upward as it becomes less dense
what happens to rock when it becomes less dense?
rock sinks/moves downward as it becomes more dense
what happens to rock when it becomes more dense?
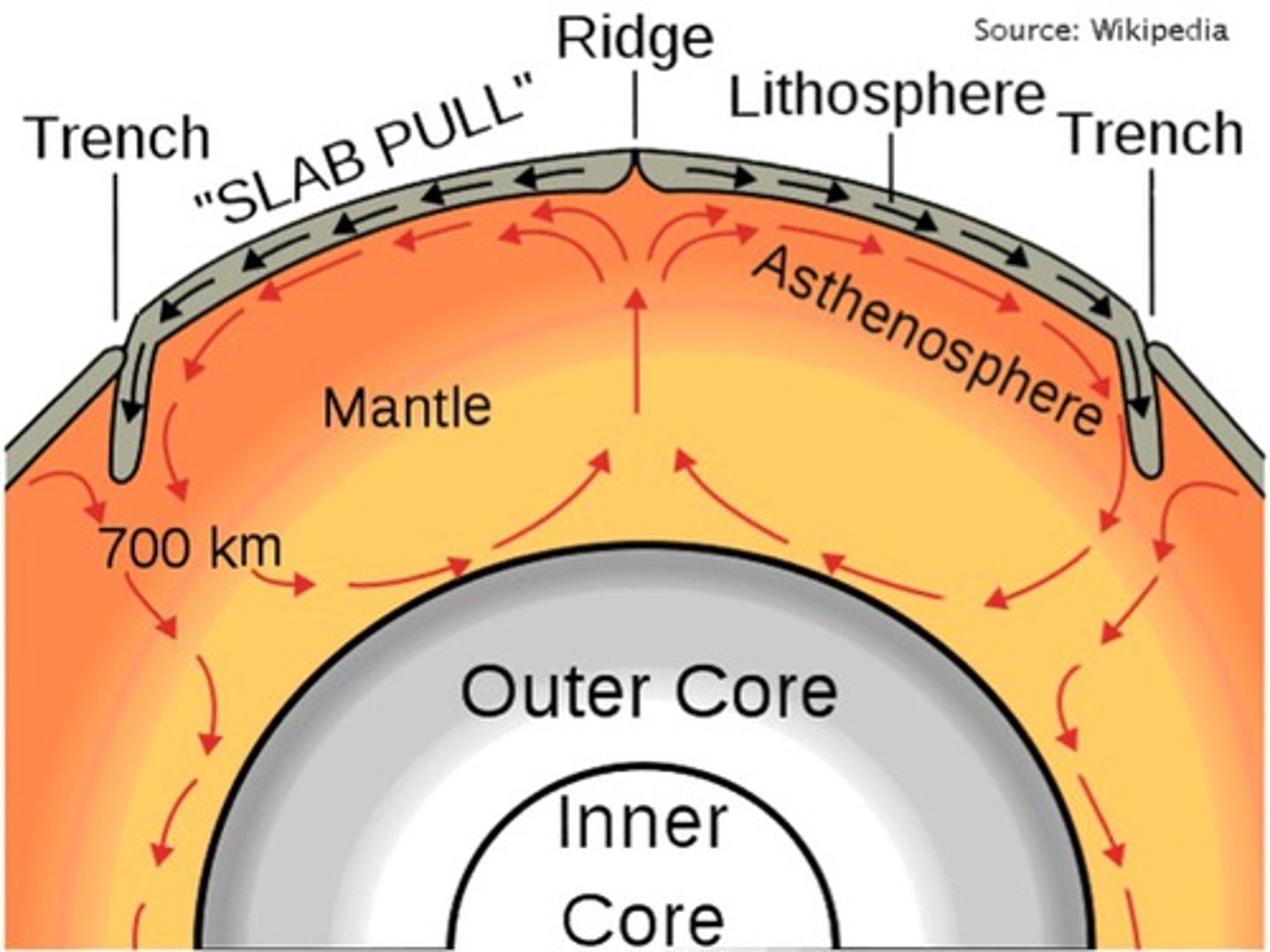
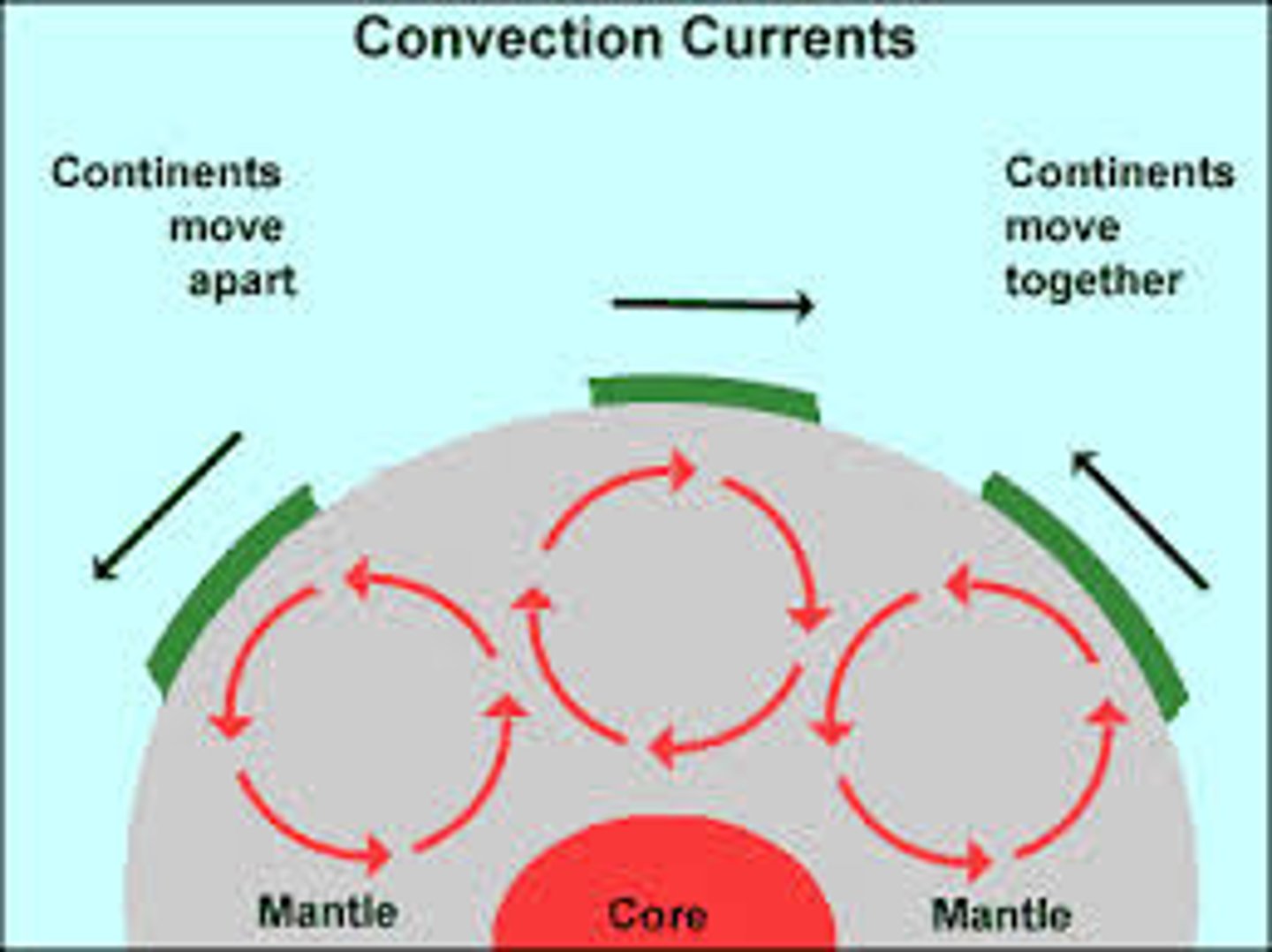
heat from the core powers convection currents
where does the heat come from that powers earth's convection currents?
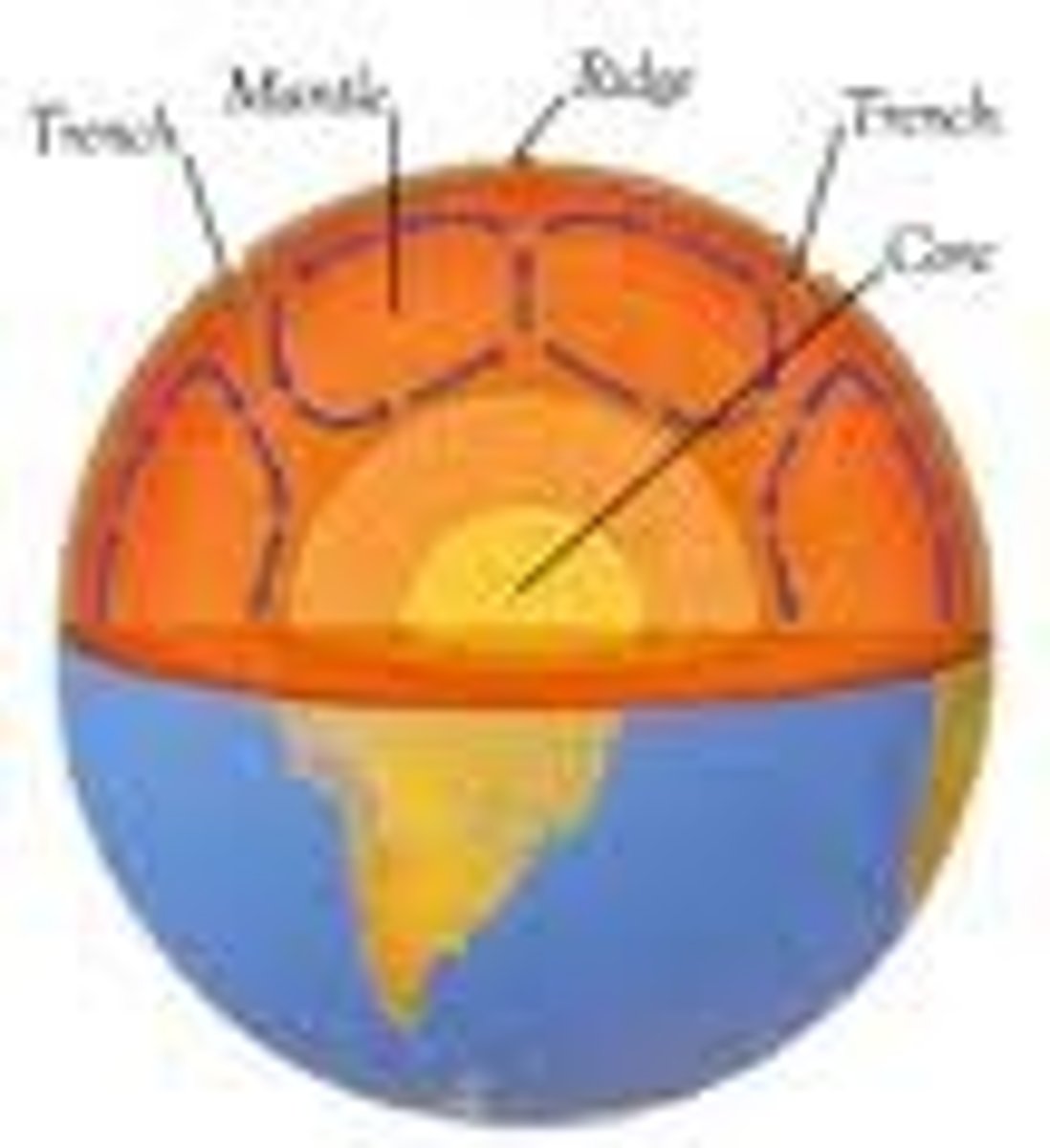
convection primarily occurs in the mantle
in what earth layer (crust, mantle, core) does convection primarily occur?
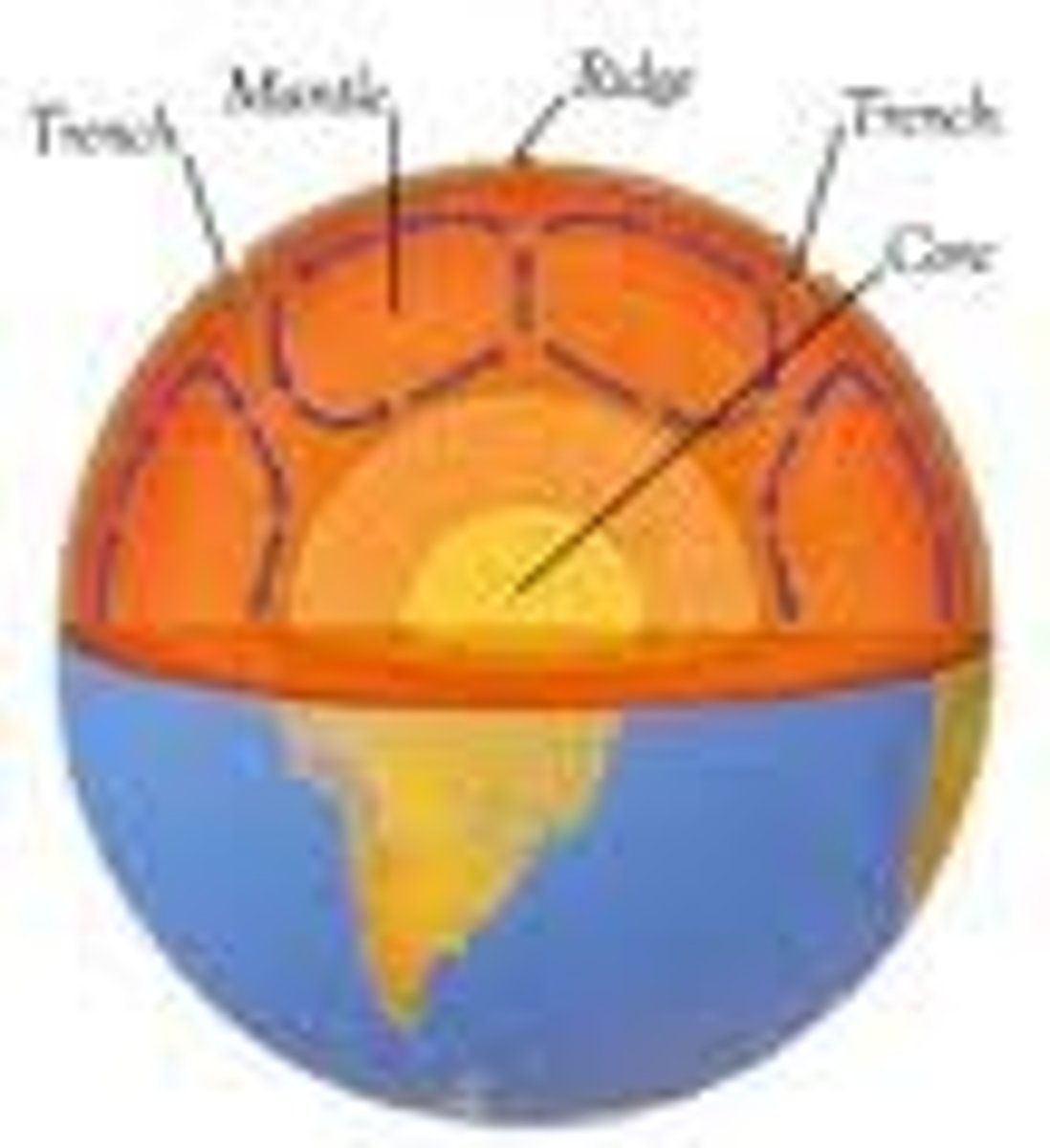
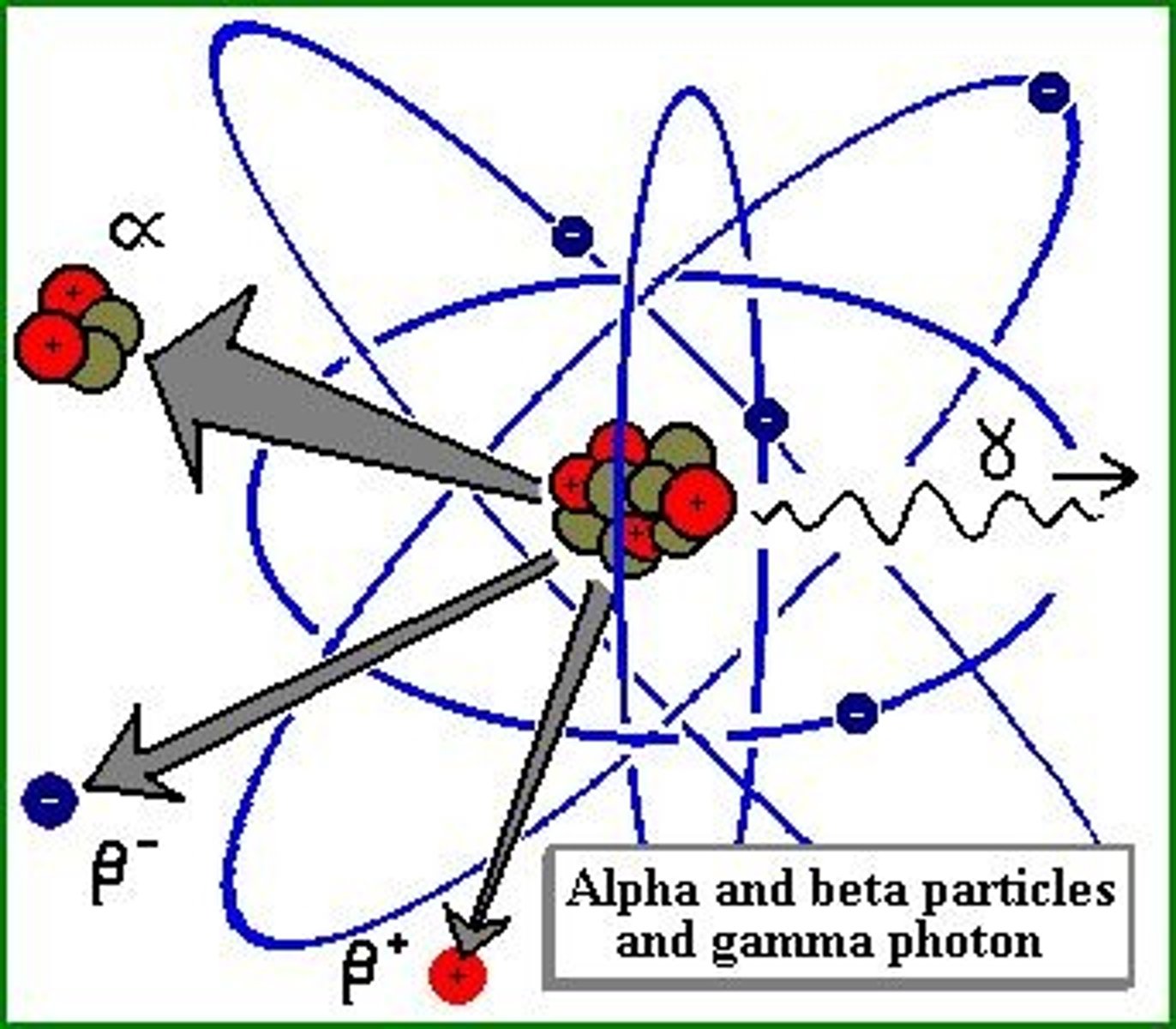
the core's heat comes from (1) radioactive decay and (2) residual heat left over from the formation of the earth
where does the core's heat comes from?
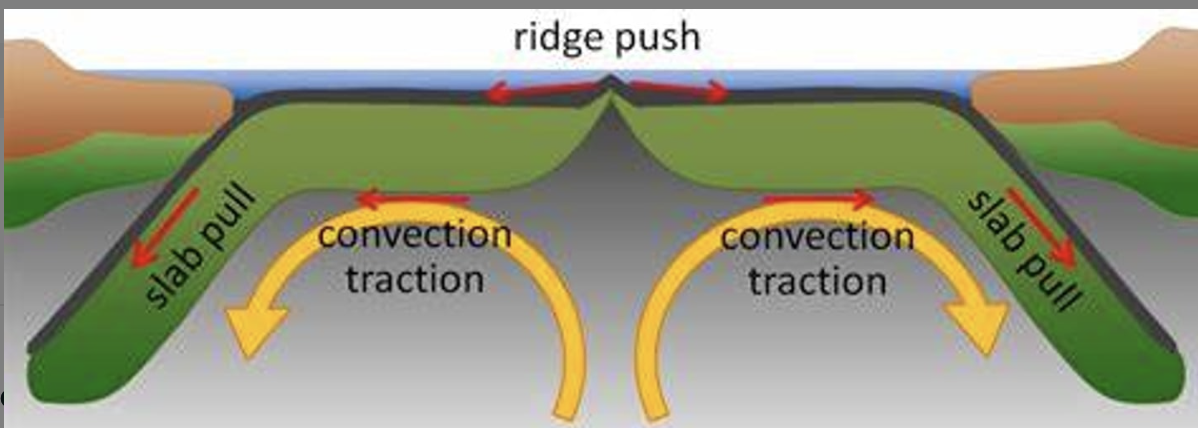
ridge push
what is another name for seafloor spreading?
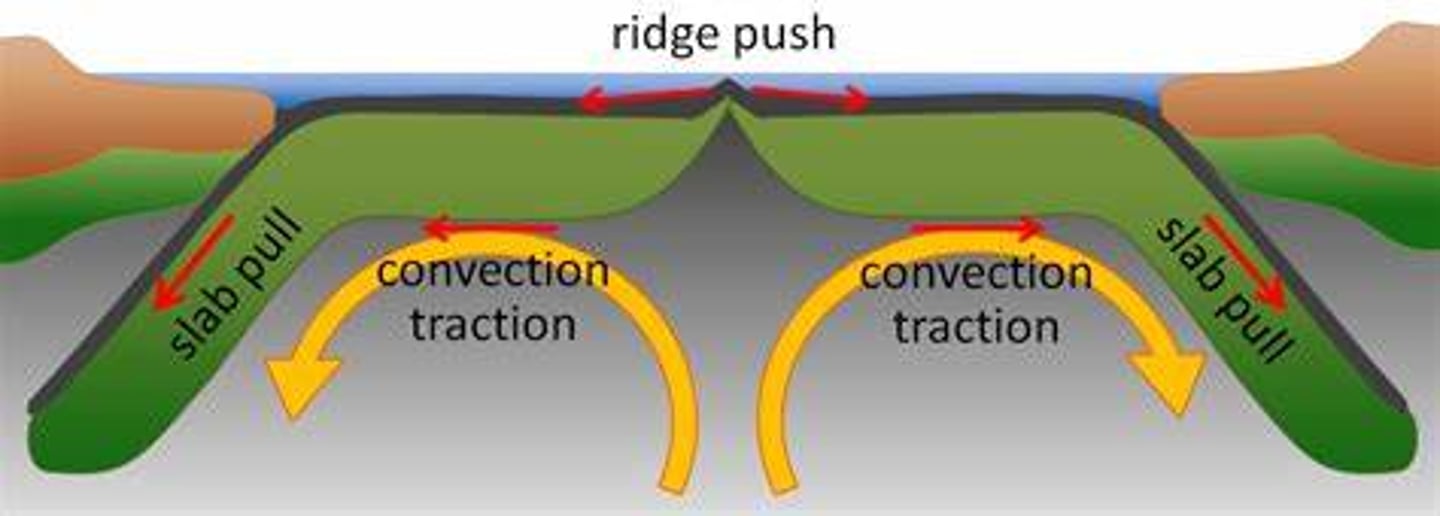
slab pull
what is another name for subduction?
rock gets older, colder, and more dense as you get further away from a MOR
how does the age, temperature and density of rock change as you get further away from a MOR?
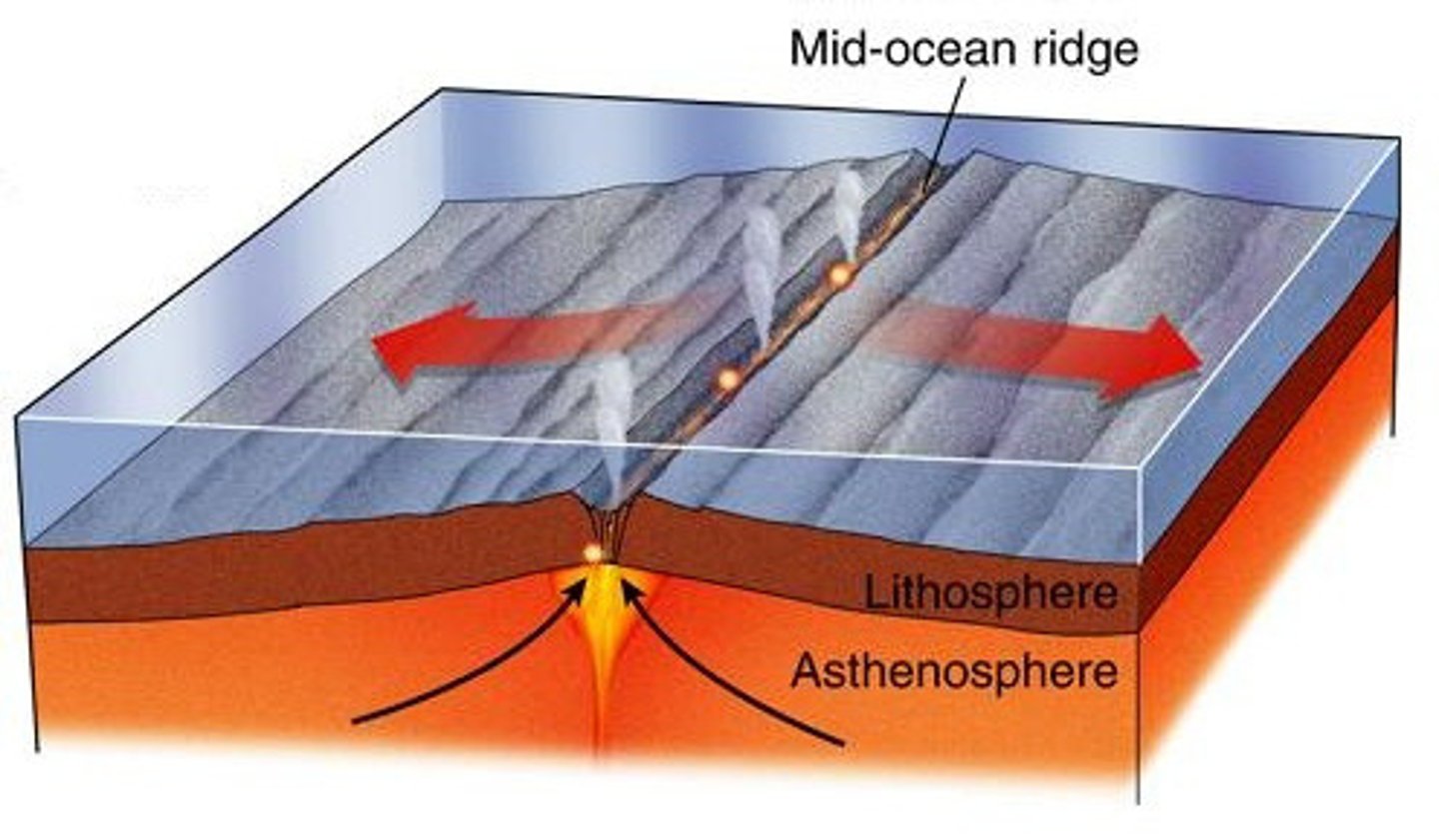
rock gets younger, warmer, and less dense as you get closer to a MOR
how does the age, temperature and density of rock change as you get closer to a MOR?
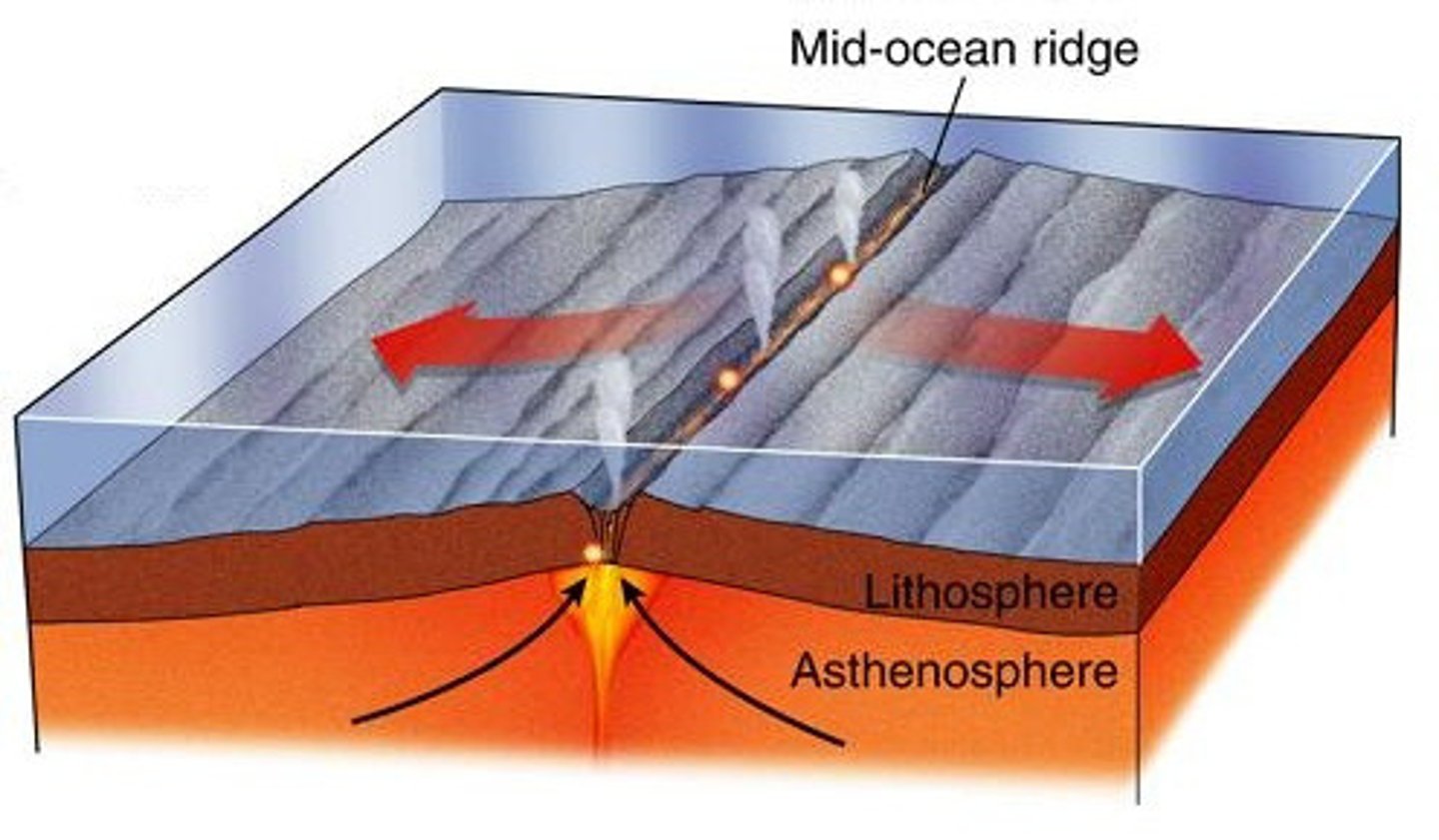
warmer, less dense rock rises and erupts at a mid ocean ridge, and then sinks as it moves farther away from the ridge and cools
how does convection occur at a mid ocean ridge?
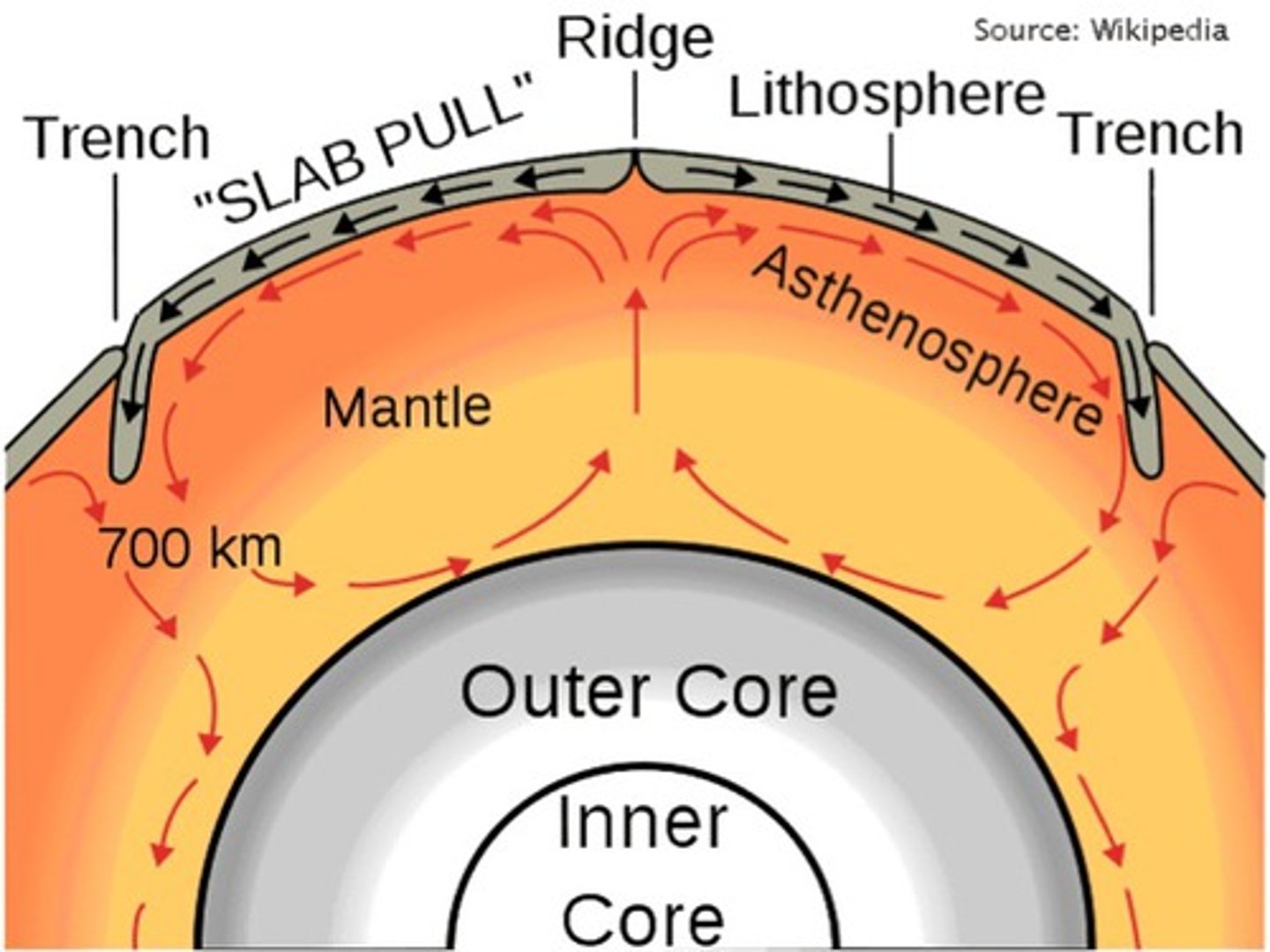
cooler, denser rock sinks at a subduction zone, and then rises as it becomes warmed and erupts out of a volcano
how does convection occur at a subduction zone?
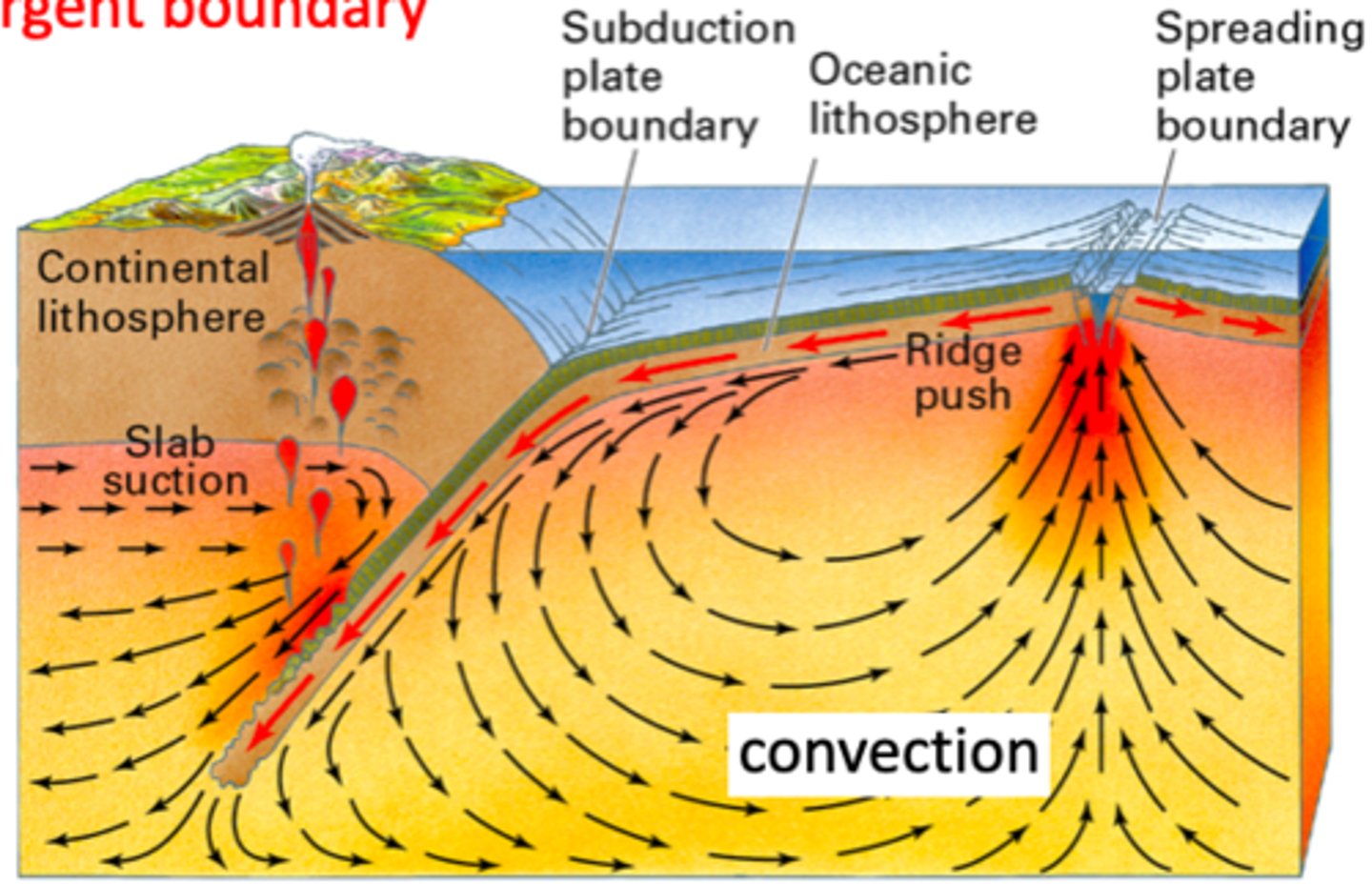
the driving force behind plate tectonics is convection in the upper mantle (asthenosphere)
what is the driving force behind plate tectonics?
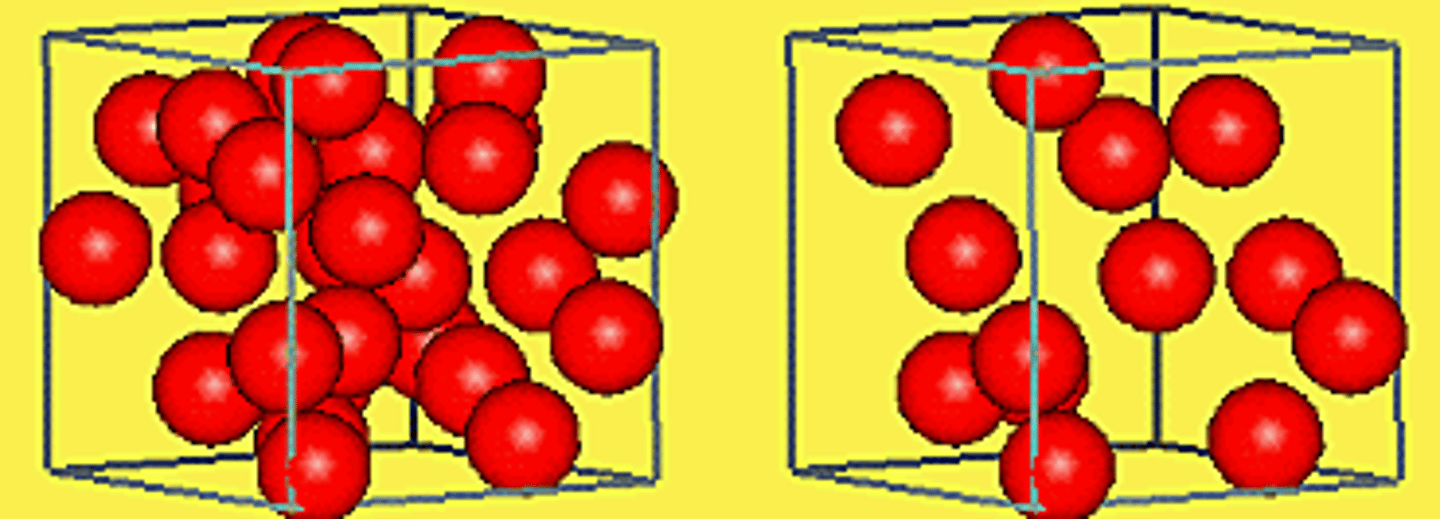
because the molecules they are made of begin to move faster and farther apart
why do things that are warmed become less dense?
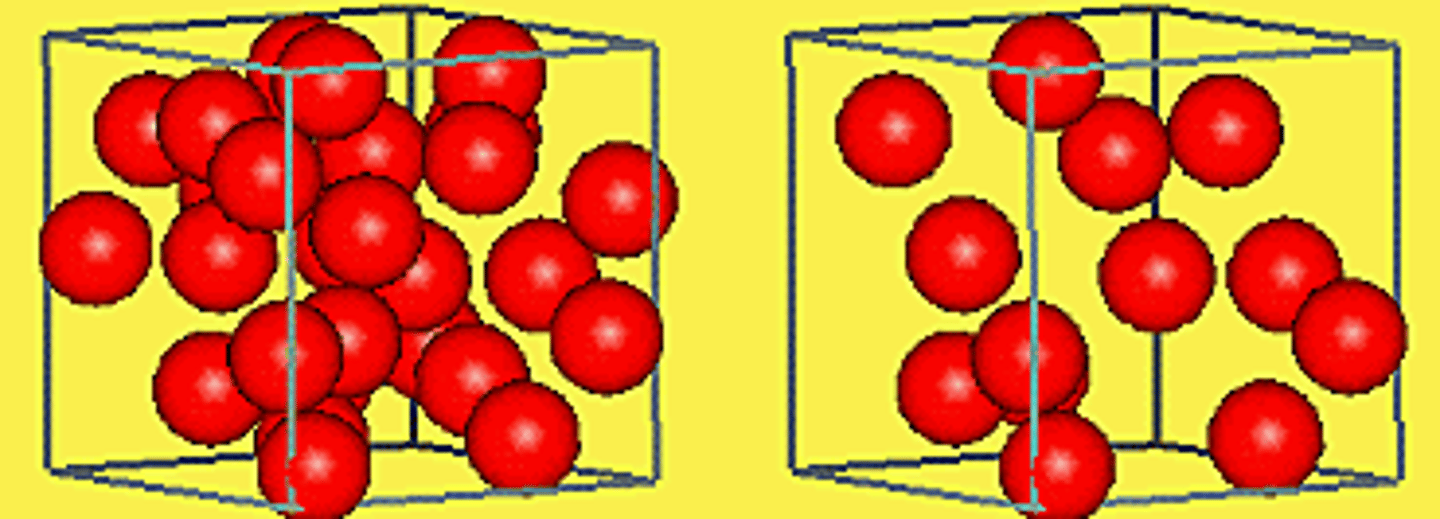
because the molecules they are made of begin to move slower and closer together
why do things that are cooled become more dense?
oceanic crust gets thicker the farther away you get from a mid ocean ridge
how does the thickness of oceanic crust change as you get further away from a mid ocean ridge?
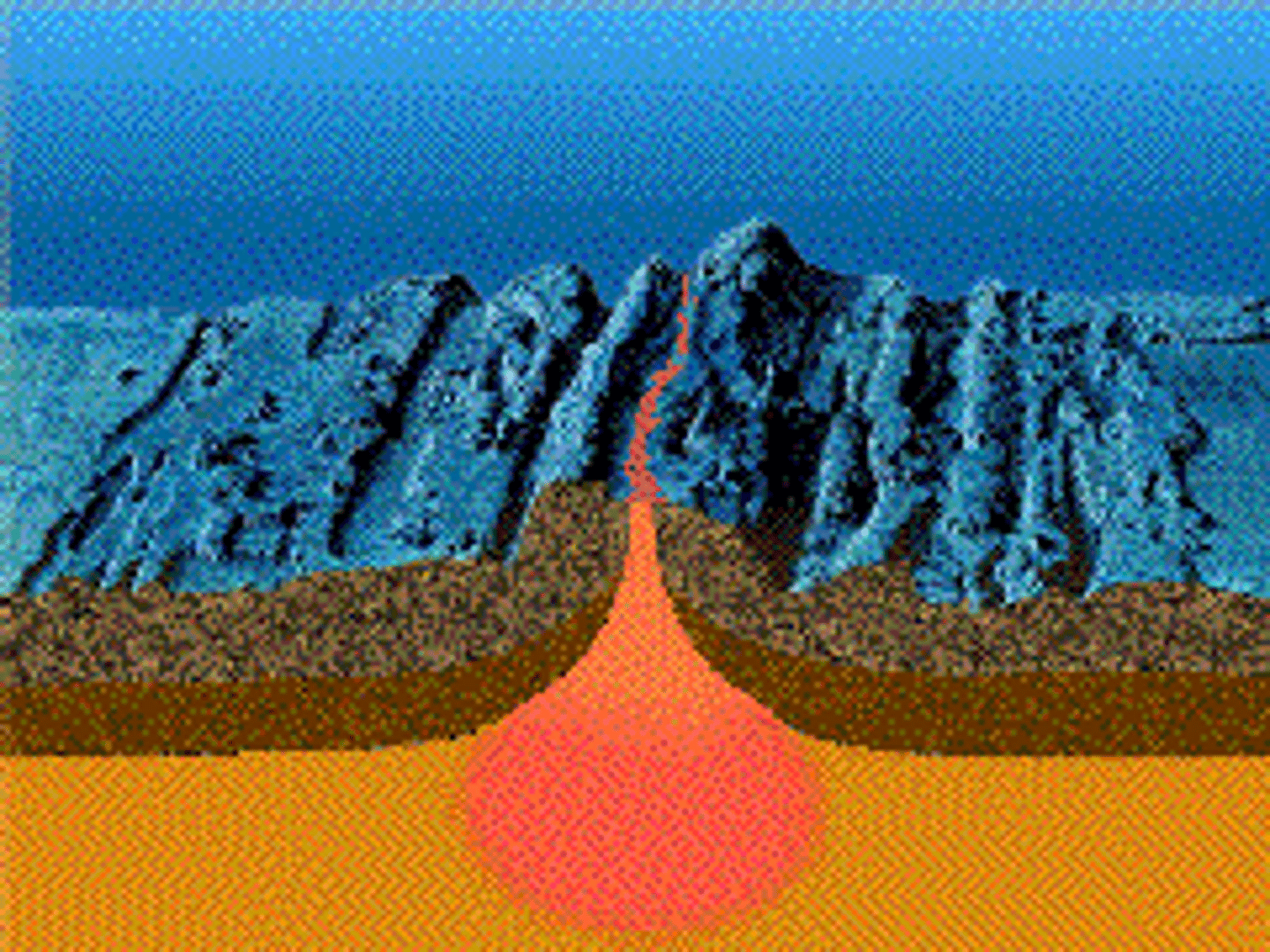
oceanic crust gets thinner the closer you get to a mid ocean ridge
how does the thickness of oceanic crust change as you get closer to a mid ocean ridge?
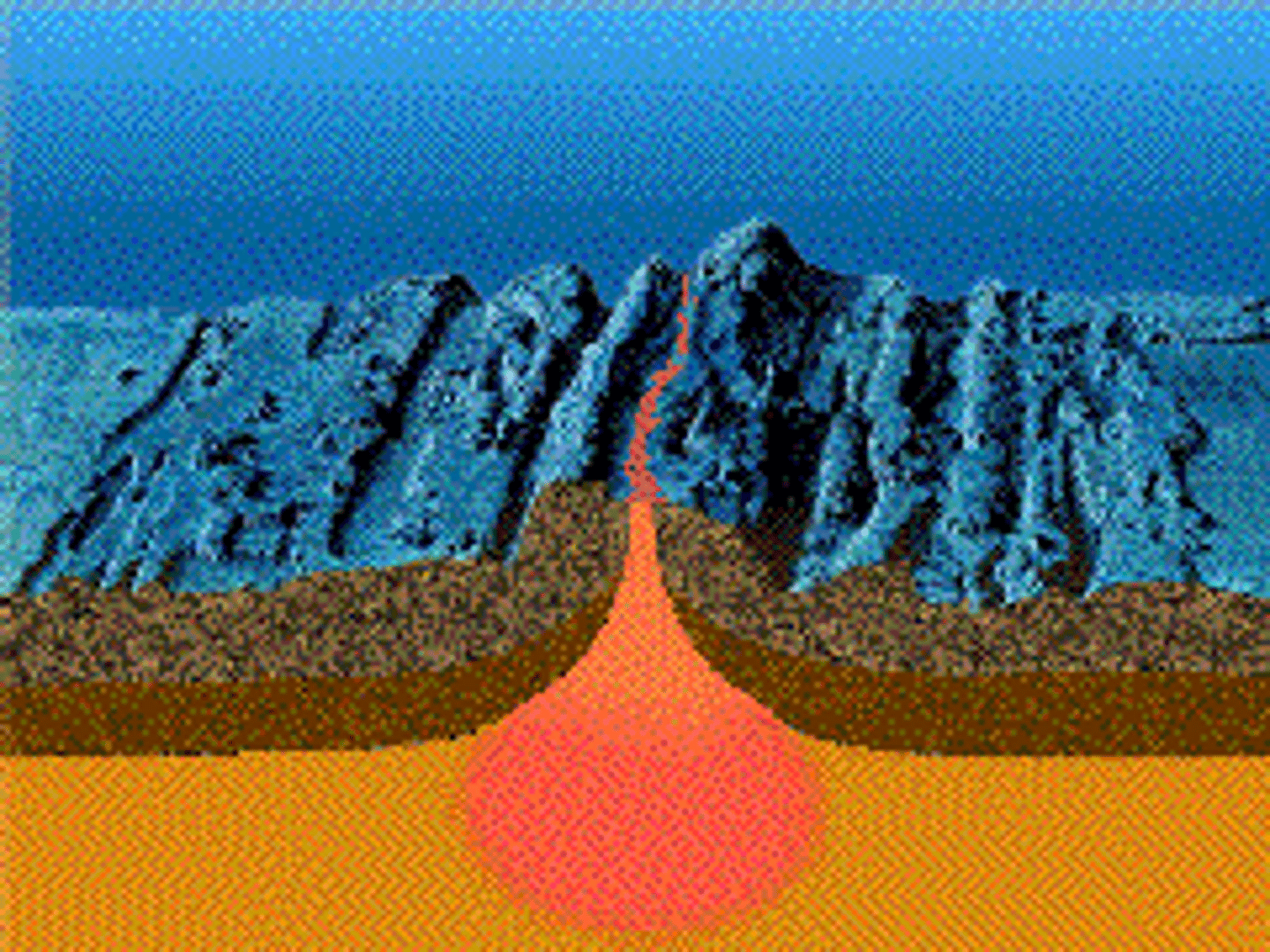
cool rock moves down and away at a convergent boundary, and rises once it is warmed again
how does convection occur at a convergent boundary?
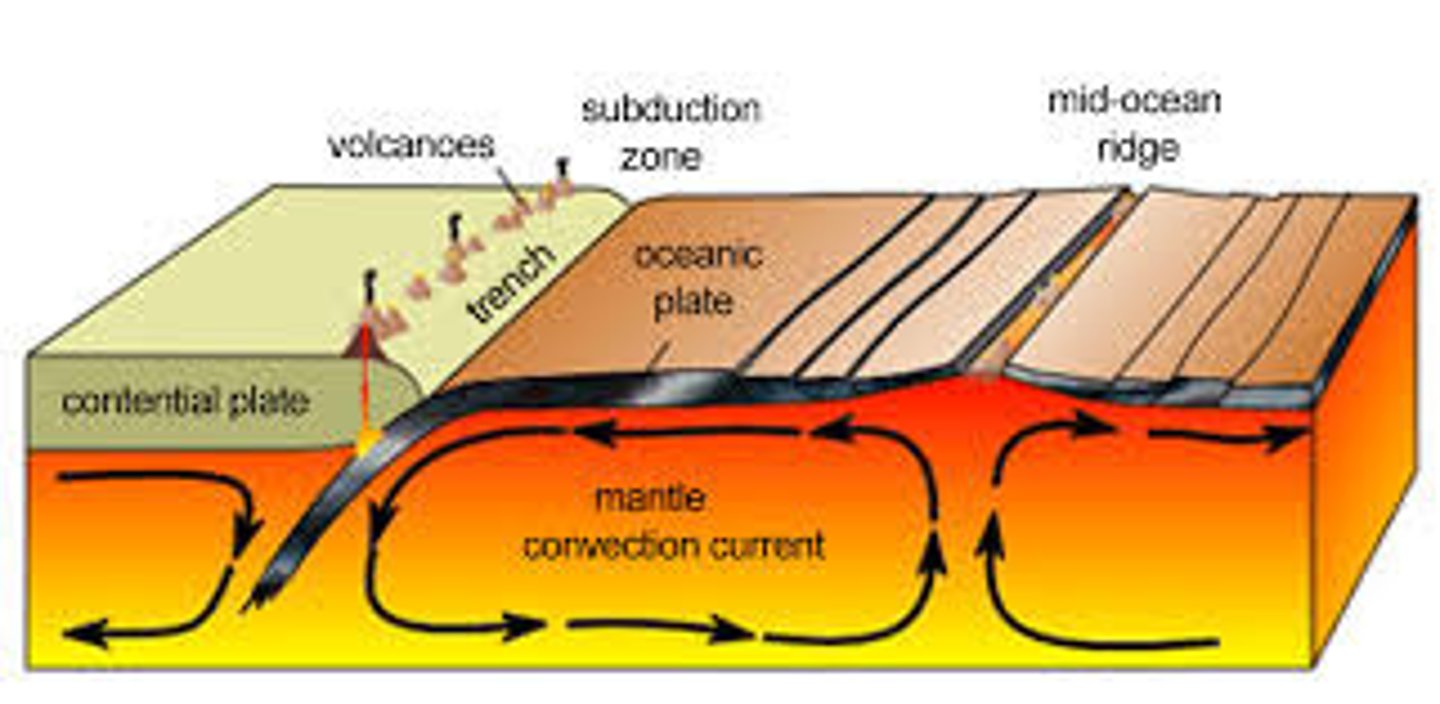
warm rock rises and spreads outwards at a divergent boundary, and sinks once it is cooled again
how does convection occur at a divergent boundary?
the asthenosphere is a semi-solid layer, possessing characteristics of both solids and liquids
what is the asthenosphere like?