Understanding Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
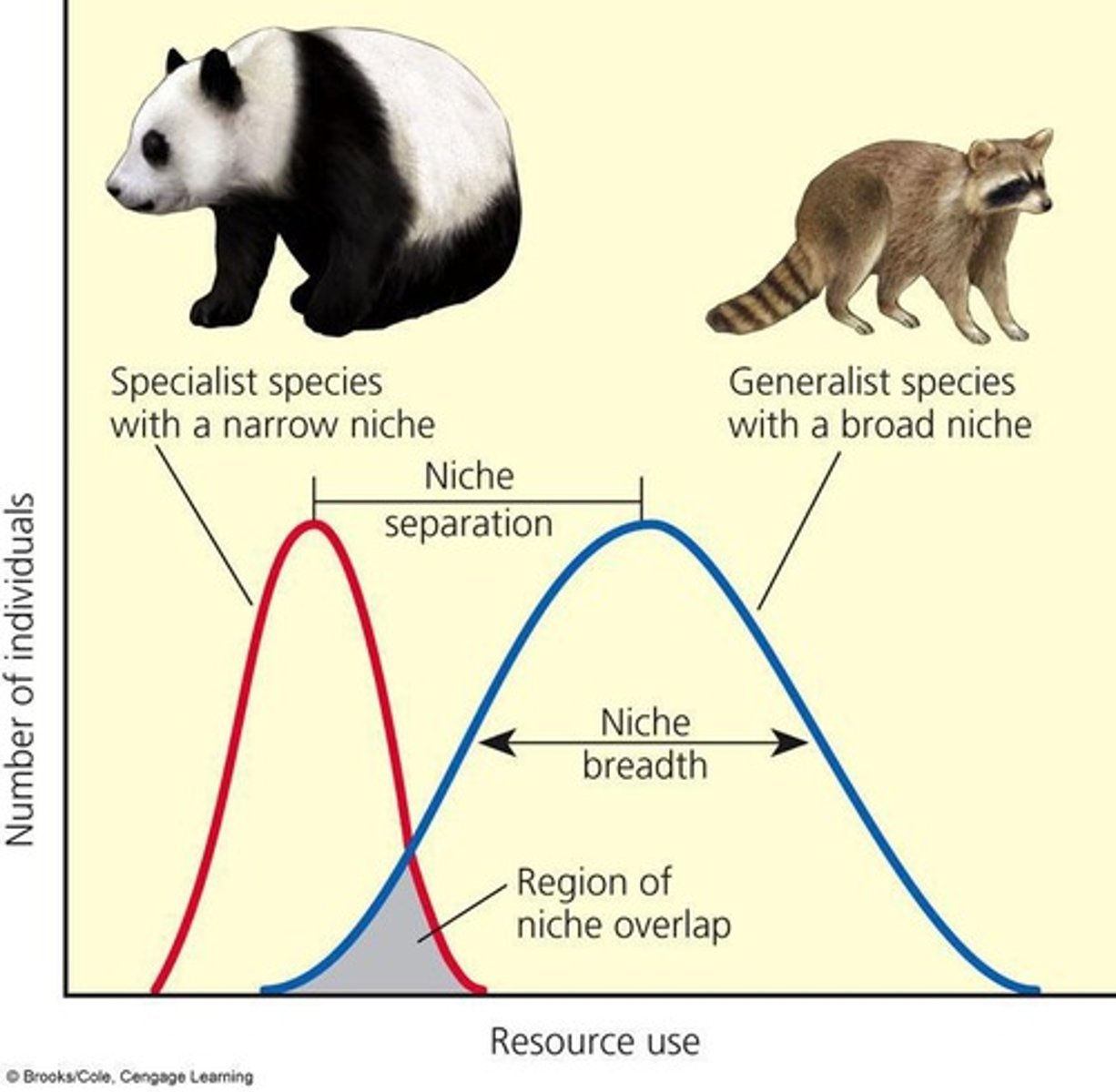
Generalist species
Broad niche, eat a variety of foods, live in different places, tolerate variety of conditions.
Specialist species
Narrow niche, eat just a few foods or only inhabit one small range of conditions.
Keystone species
A plant or animal that plays a unique and crucial role in the way an ecosystem functions.
Density-independent factors
Things and events that limit the size of a population regardless of the density of the population.
Density-dependent factors
Where the effects on the size or growth of a population vary with the density of the population itself.
Ecosystem diversity
The number of different habitats available in a given area.
Species diversity
The number of different species in an ecosystem and the balance or evenness of the population sizes of all species in the ecosystem.
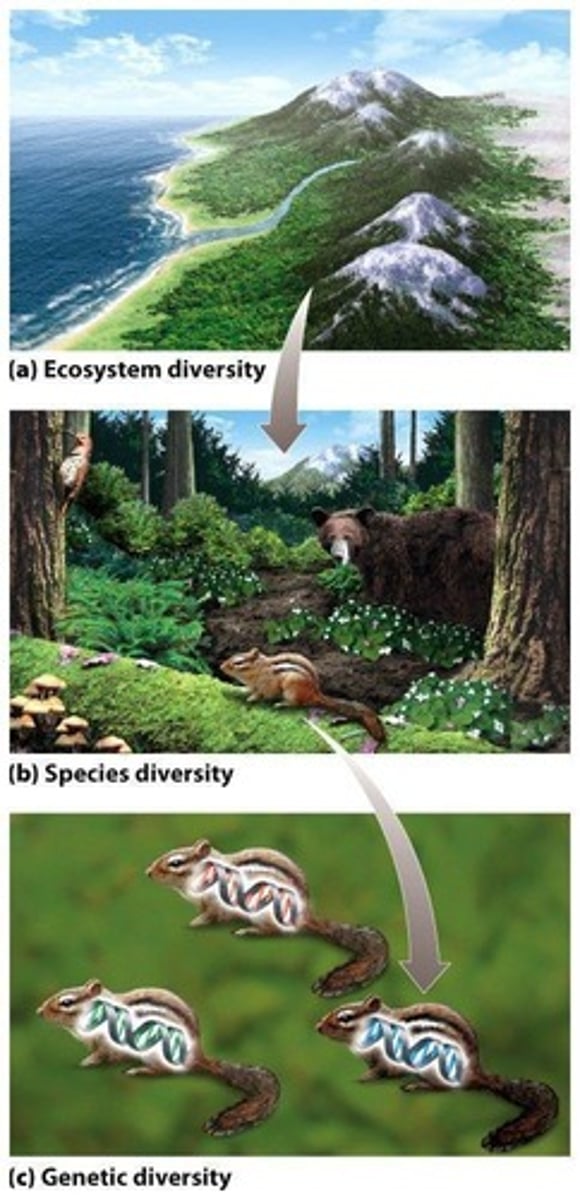

Genetic diversity
How different the genes are of individuals within a population (group of the same species).
Species richness
The total number of different species found in an ecosystem.
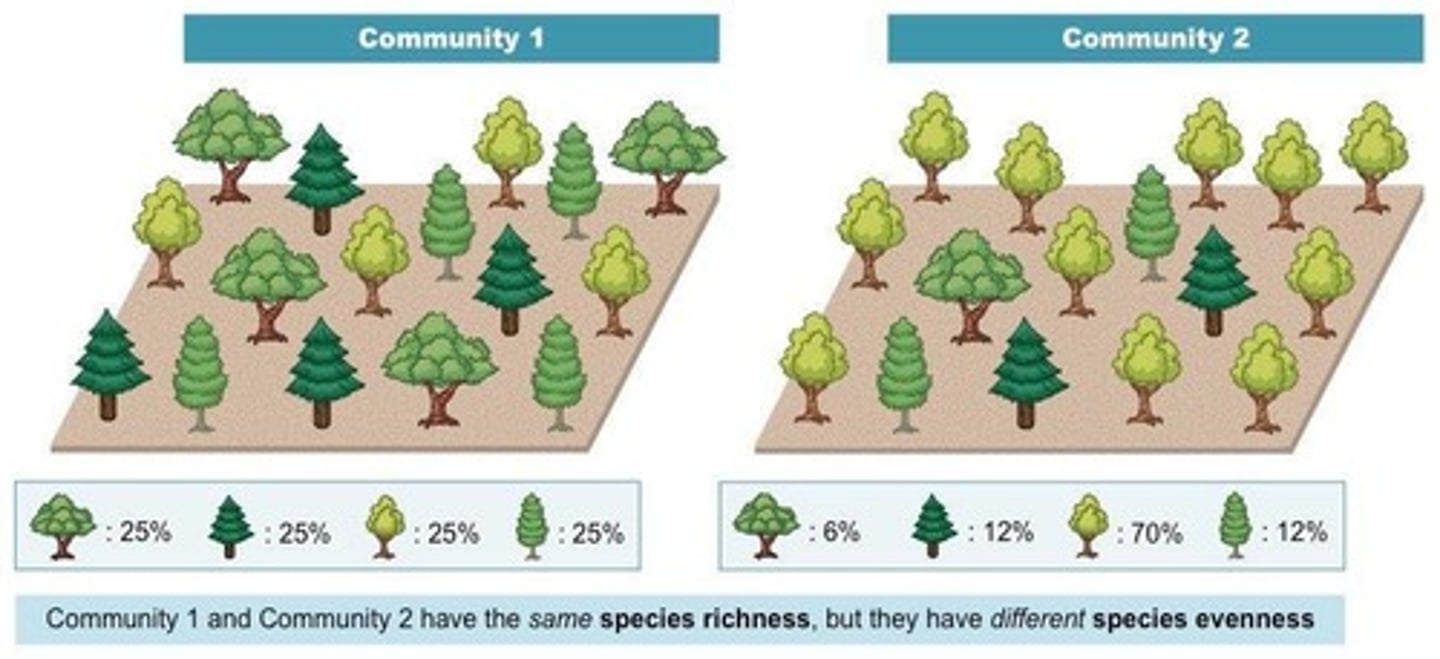

Evenness
A measure of how all of the individual organisms in an ecosystem are balanced between the different species.
Genetic diversity benefits
The more genetic diversity in a population, the better the population can respond to environmental stressors like drought, disease, or famine.
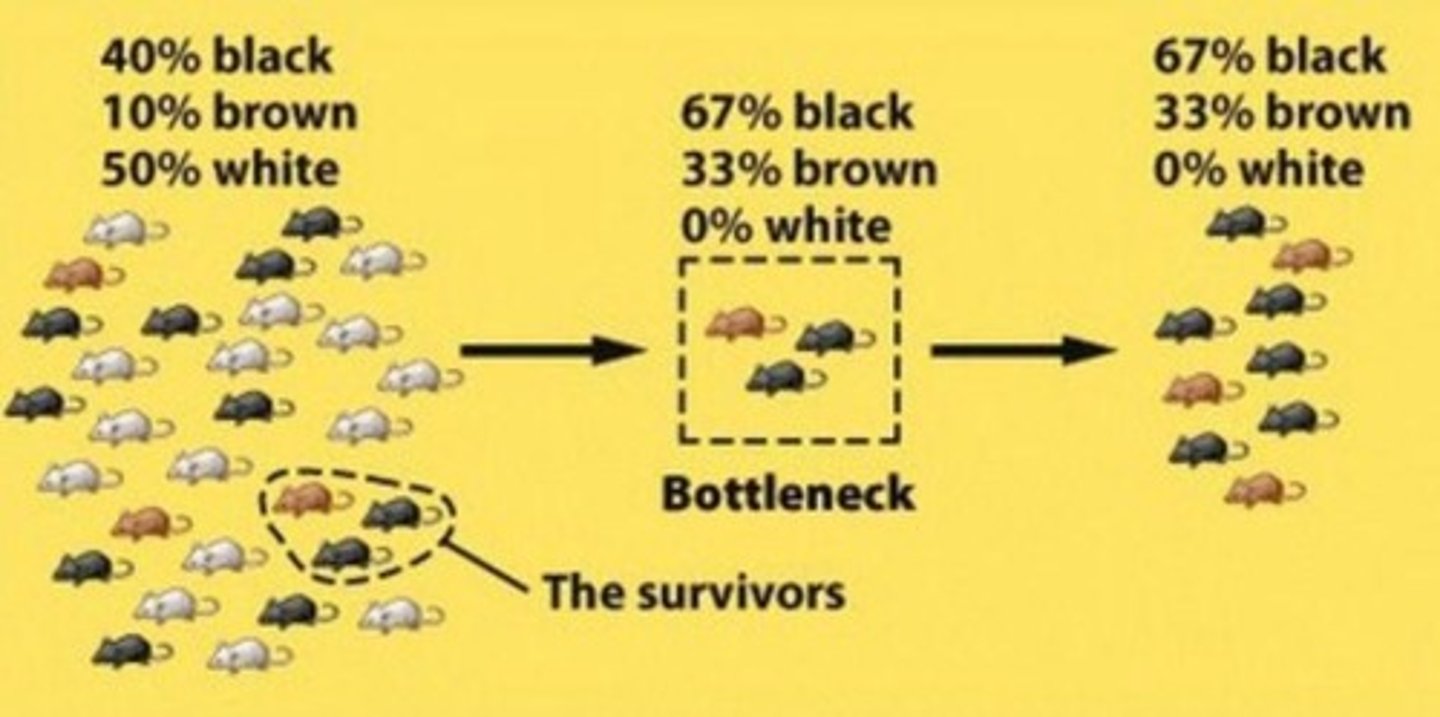
Bottleneck event
An environmental disturbance that drastically reduces population size & kills organisms regardless of their genome.
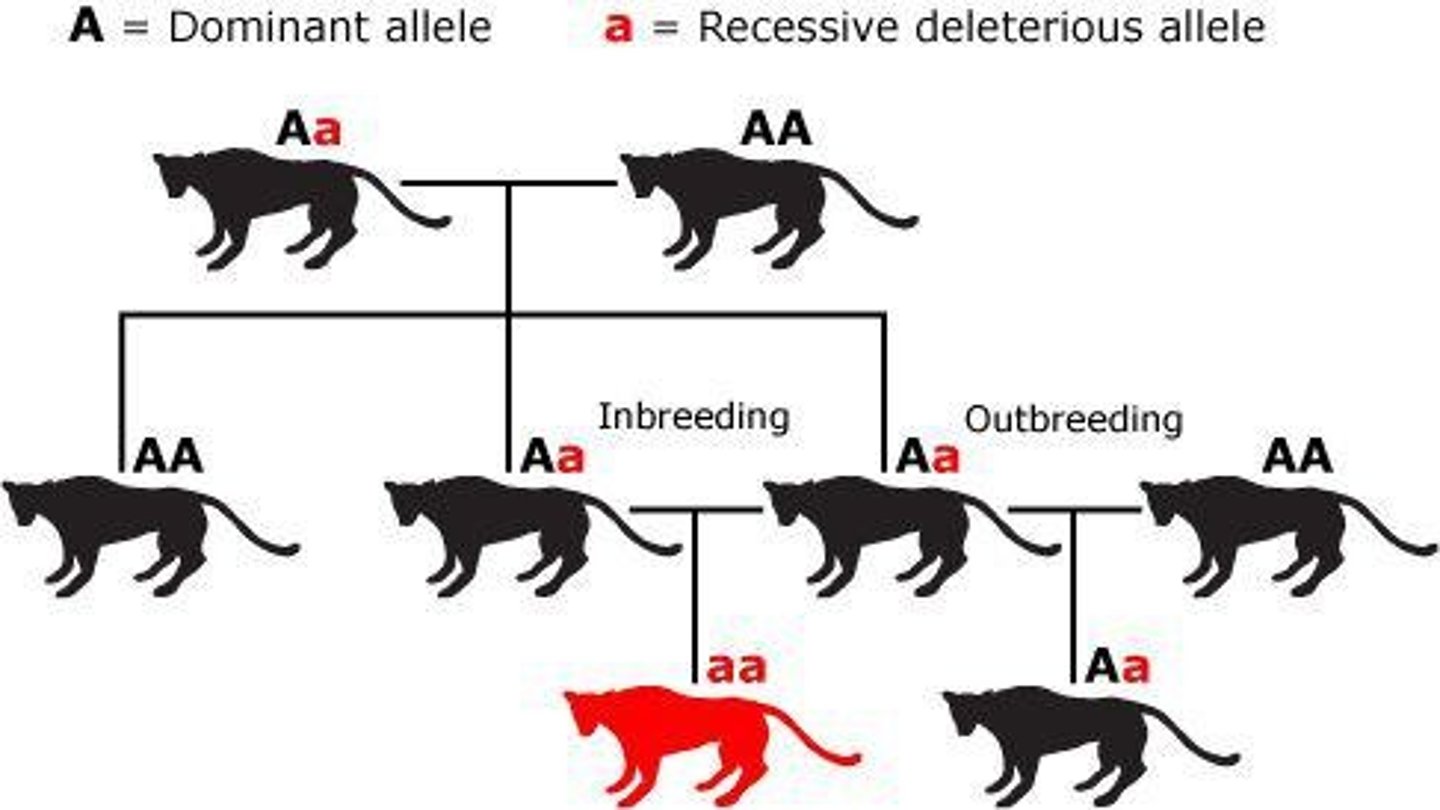
Inbreeding depression
When organisms mate with closely related 'family' members, leading to a higher chance of offspring having harmful genetic mutations.
Ecosystem resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to return to its original conditions after a major disturbance.
Biodiversity
The variety of plant and animal species in an ecosystem.
Ecosystem Services
Goods and services provided by natural ecosystems that are beneficial to humans (often monetarily of life-sustaining).
Cultural Services
Revenue from recreational activities (hunting/fishing licenses, park fees, tourism-related spending) & profits from scientific discoveries made in ecosystems.
Provisioning Services
Goods/products directly provided to humans for sale/use by ecosystems.
Regulating Services
Benefit provided by ecosystem processes that moderate natural conditions like climate and air quality.
Supporting Services
Natural ecosystems support processes we do ourselves, making them less costly and easier for us.
Anthropogenic Activities
Human activities that disrupt the ability of ecosystems to function, decreasing the value of ecosystem services.
Overfishing
The act of catching too many fish at once, leading to fish population collapse and economic consequences.
Deforestation
The clearing of trees, which disrupts regulating services like CO2 sequestration and air quality filtration.
Pollinator Habitat Loss
The loss of habitats for bees and other insects, disrupting supporting services like crop pollination.
Wetland Plant Roots
Roots that filter pollutants, leading to cleaner groundwater and reducing costs for water purification.
Trees in a Forest
They sequester CO2 through photosynthesis, reducing the rate of climate change and lessening damage from rising sea levels.
Beautiful Landscapes
Natural features that attract tourists, generating revenue through park fees and local spending.
Scientific Discoveries
Knowledge gained from ecosystems that can lead to the creation of new medicines sold for profit.
Natural Resources
Materials provided by ecosystems, such as wood, paper, food, and medicinal compounds.
Ecological Consequences
Natural impacts resulting from disruptions to ecosystem services.
Economic Consequences
Monetary impacts resulting from disruptions to ecosystem services.
Recreational Activities
Activities such as camping and tours that generate money and are supported by natural ecosystems.
Health Care Costs
Expenses related to treating diseases that can be reduced by regulating services provided by ecosystems.
Late 1990s
The period when the concept of ecosystem services was developed.
US EPA's Website
An online resource that describes ecosystem services.