APWH: Unit 6 Key Terms (with pictures)
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Nationalism
A political ideology that emphasizes the interests, culture, and identity of a nation or group of people.

Imperialism
A policy or ideology of extending a nation's power and influence over other countries or territories through diplomacy, military force, or economic domination.

Sino-Japanese War
A conflict between China and Japan primarily over control of Korea from 1894 to 1895. The war marked Japan's emergence as a major imperial power, as it defeated the Chinese Empire and forced China to cede Taiwan and other territories to Japan.

Formosa
The former name of the island now known as Taiwan. It was used by the Portuguese in the 16th century, and the island was later colonized by the Dutch, the Spanish, and finally the Qing Dynasty of China.
Phrenologists
Practitioners of phrenology, a pseudoscience claiming that a person's character and mental abilities could be determined by the shape of their skull.
Charles Darwin
An English naturalist best known for developing the theory of evolution by natural selection, outlined in his 1859 book On the Origin of Species.
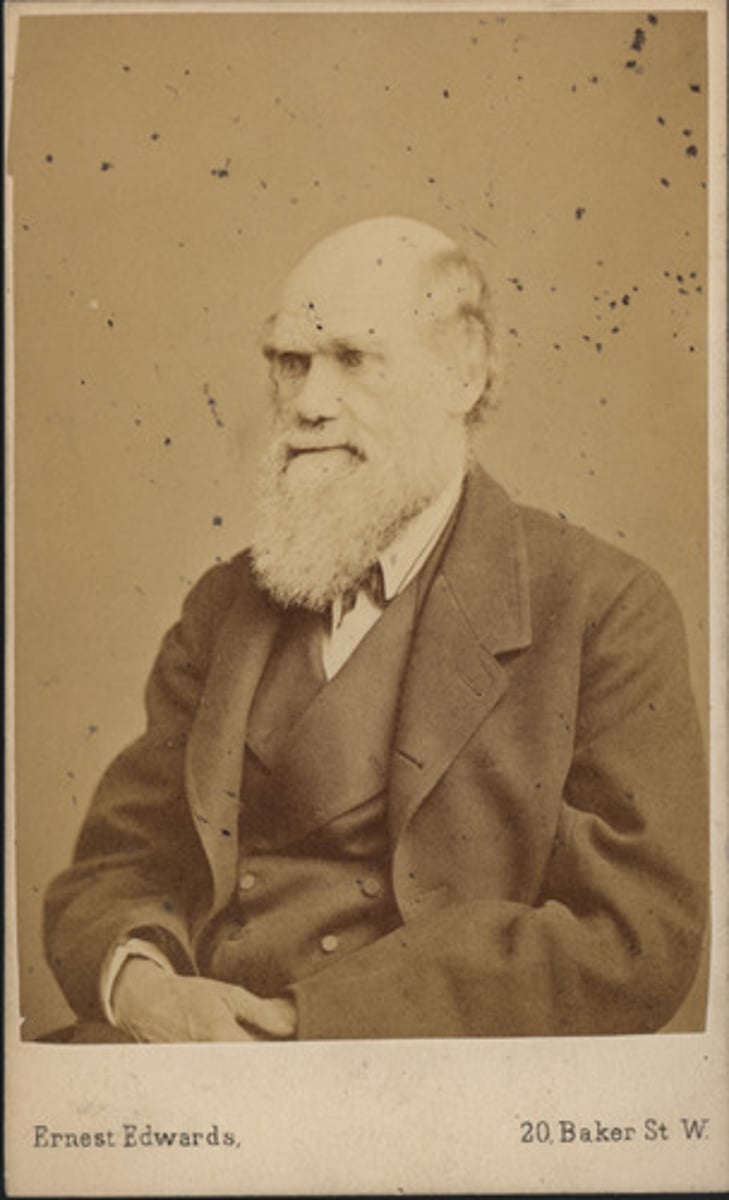

Social Darwinism
A social theory that applied Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection to human societies. It suggested that competition and survival of the fittest explained societal and racial hierarchies, often justifying imperialism, racism, and economic inequality.

David Livingstone
A Scottish missionary and explorer who is best known for his work in Africa. Livingstone explored large parts of Africa, sought to end the slave trade, and promoted Christianity.

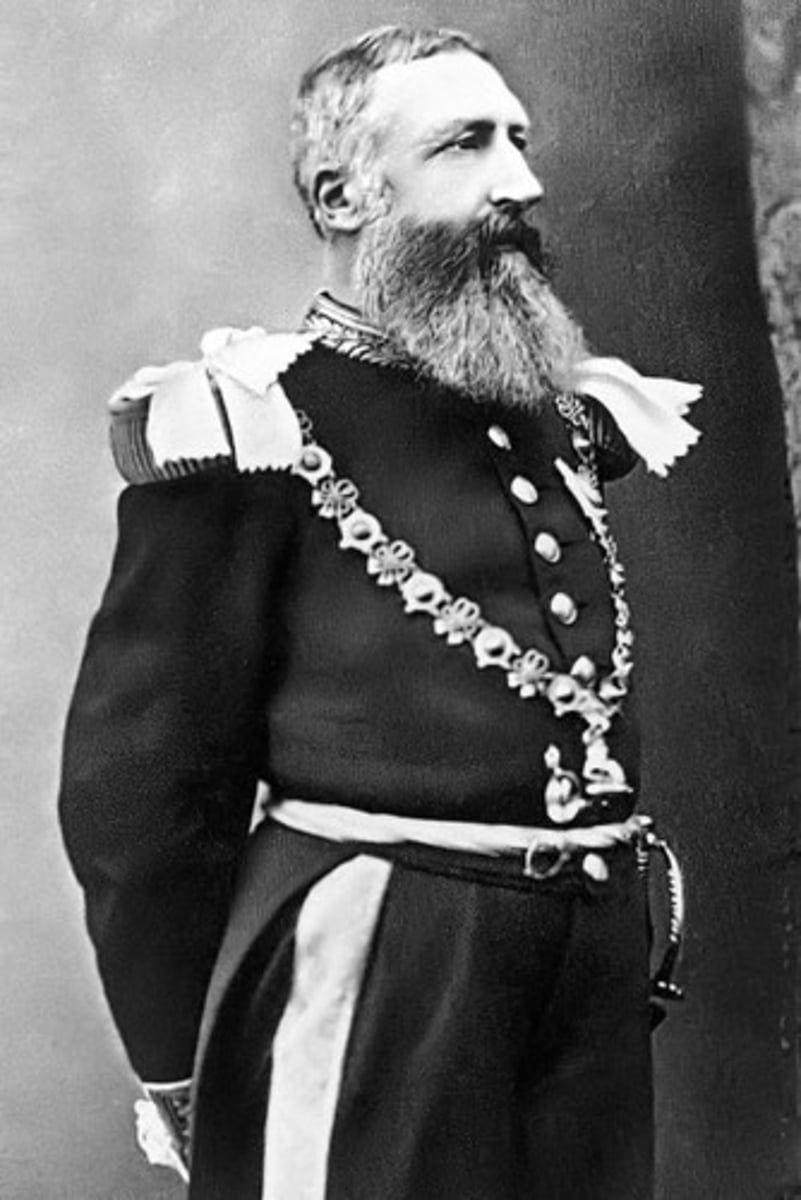
King Leopold II
The king of Belgium, infamous for his personal control over the Congo Free State, where he exploited its resources (especially rubber) using forced labor and brutal methods.

Cixi
One of the most powerful women in the history of China, active from the 1860s into the 1900s

Sierra Leone
A country in West Africa that became a British colony in the 19th century, originally established as a settlement for freed slaves.
Gold Coast
A British colony located in West Africa, which later became the independent nation of Ghana in 1957.
Cape Colony
A British colony located at the southern tip of Africa, founded in 1652 as a supply station for Dutch East India Company ships.
Congo Free State
A large territory in central Africa that was privately controlled by King Leopold II of Belgium, who used forced labor to extract resources, particularly rubber, from the local population.
Abyssinia
The ancient name for Ethiopia, a country in the Horn of Africa.
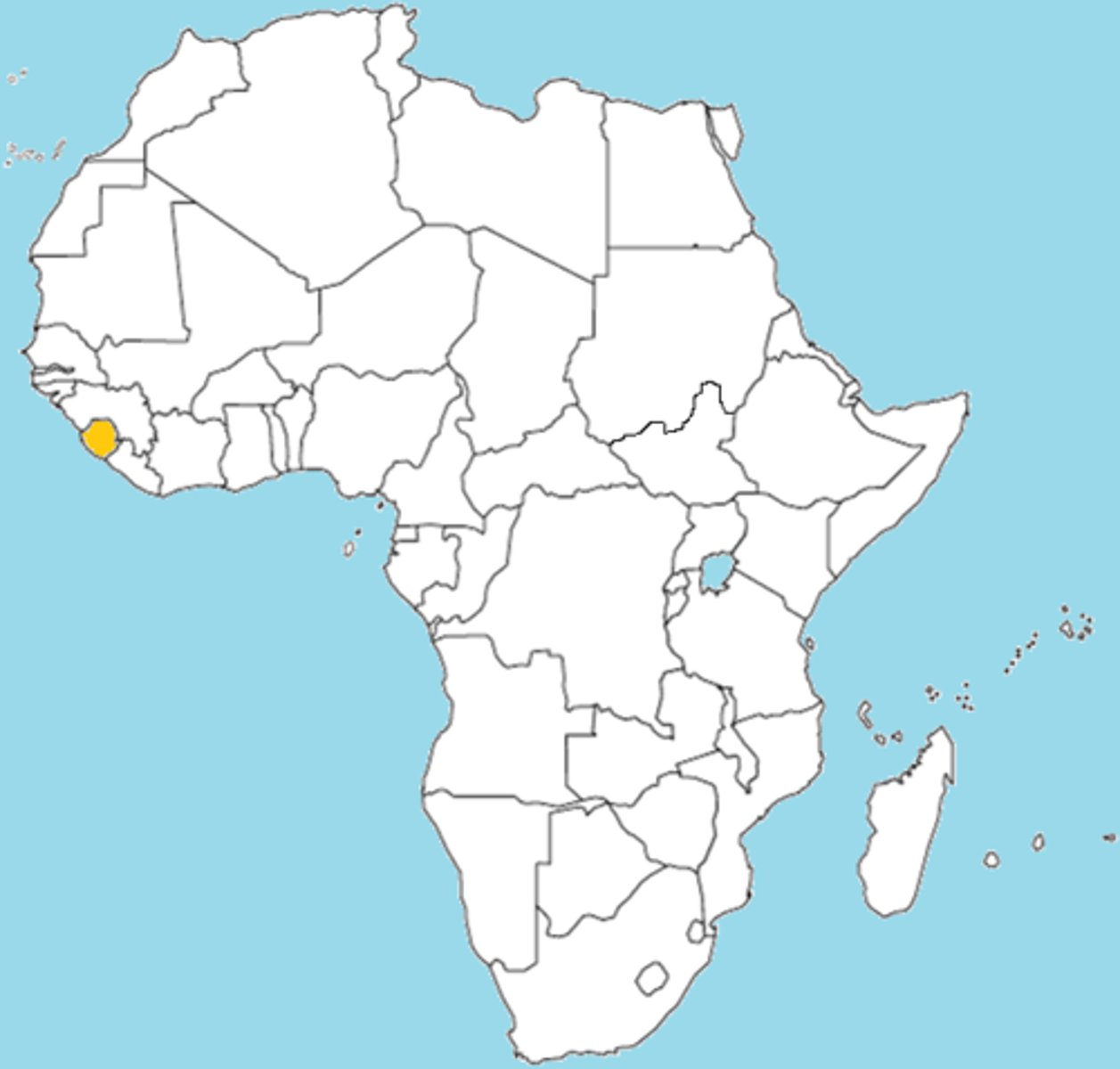
Liberia
A country in West Africa that was founded by the American Colonization Society in the early 19th century as a settlement for freed American slaves.
Ceylon
The colonial name for the island nation now known as Sri Lanka, which became a major producer of tea, rubber, and coconut.
Dutch East Indies
Was a colony of the Netherlands from the 17th century until its independence in 1945.
Indochina
Refers to a region in Southeast Asia, which includes the modern-day countries of Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia.
Malayan Emergency
One of the few successful counter-insurgency operations undertaken by the Western powers during the Cold War.

Siam
The former name of Thailand, a country located in Southeast Asia.
Australia
A continent and country in the Southern Hemisphere, formerly known as New Holland before being claimed by Britain in 1770.
New Zealand
A country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, first settled by the Māori people around 1300 AD. It was claimed by Britain in the 19th century and became a British colony in 1840.
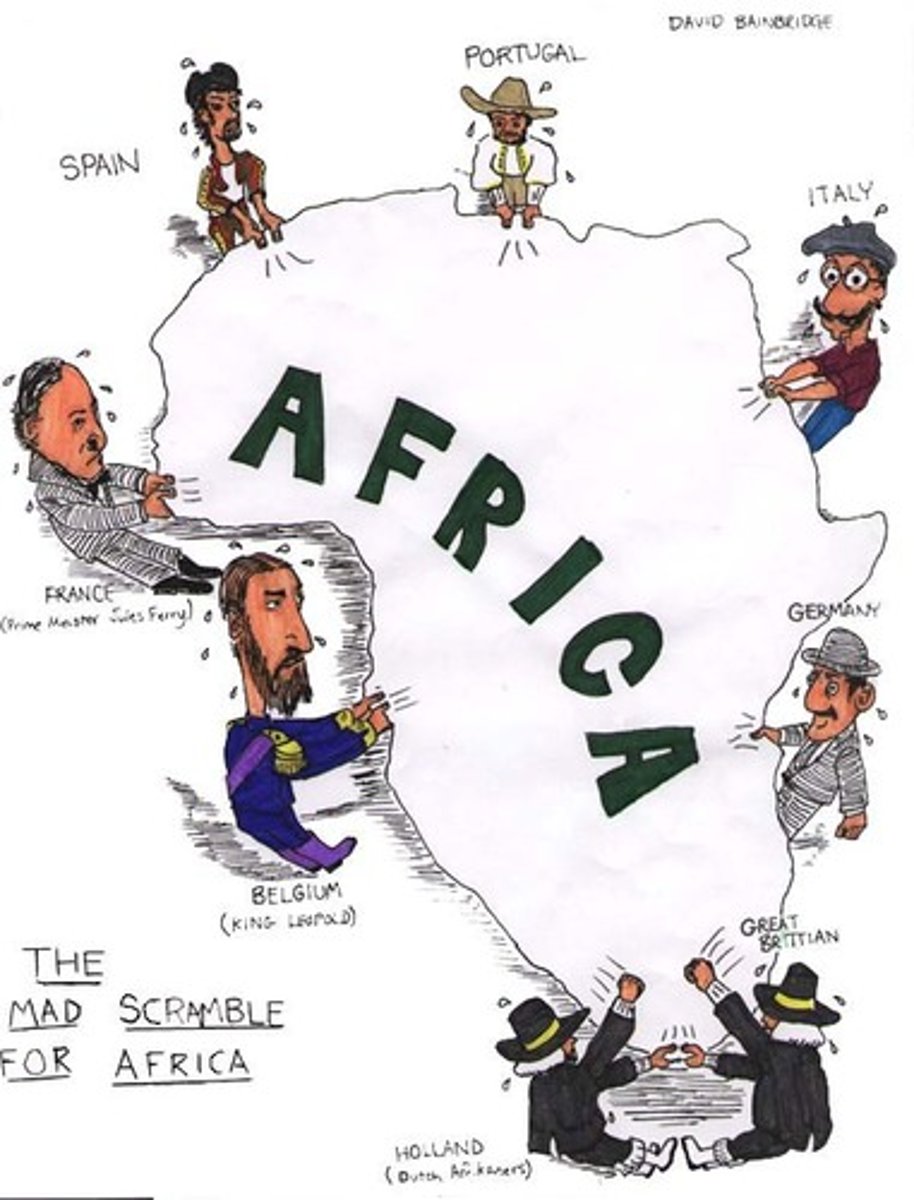
Berlin Conference
A meeting convened by European powers to regulate the colonization and trade in Africa. The conference, which was held in Berlin, Germany, led to the 'Scramble for Africa', where European powers divided African territories without regard for indigenous peoples or pre-existing political boundaries. The conference marked the start of intense European colonial expansion in Africa.
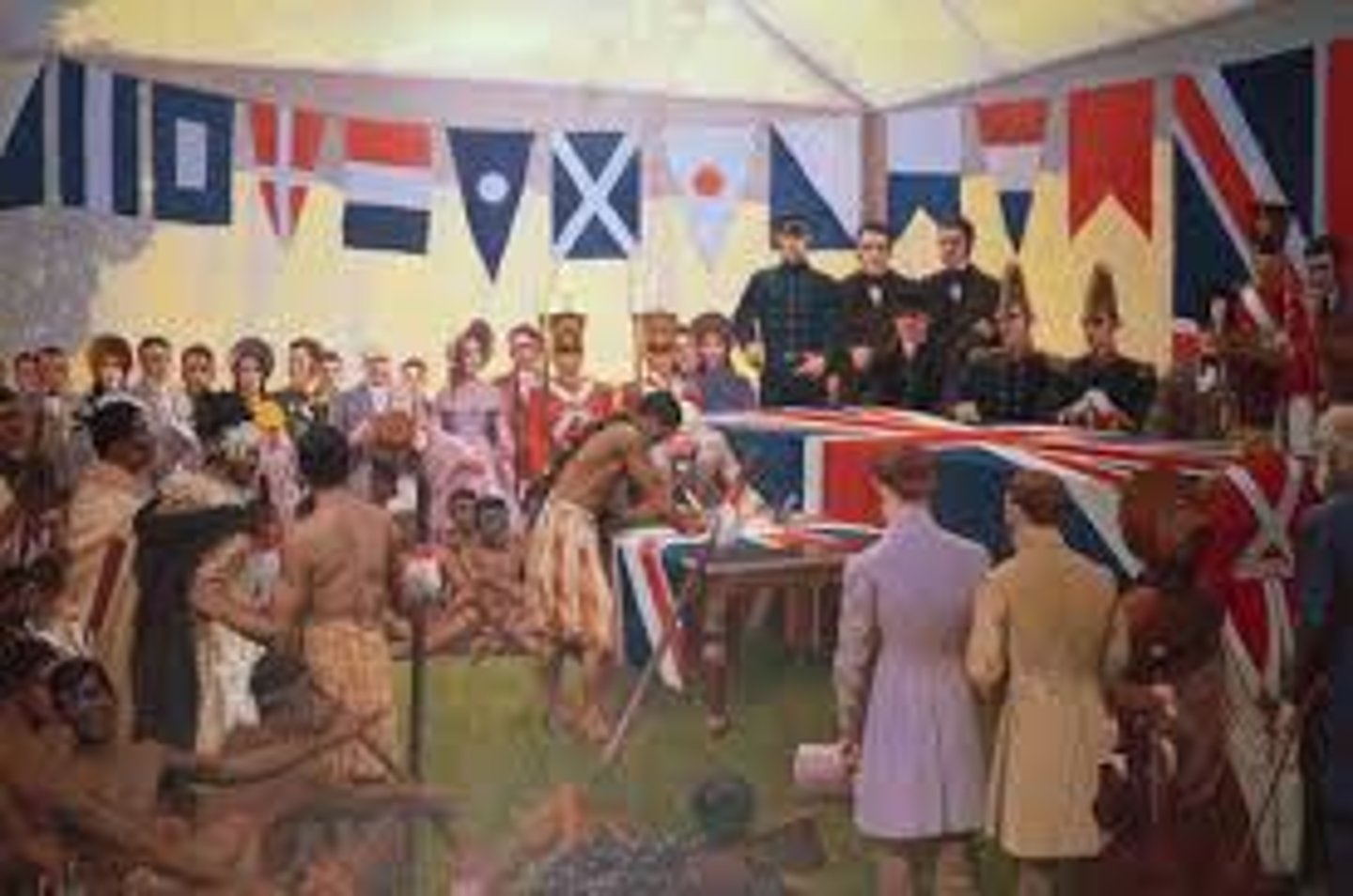
Treaty of Waitangi
An agreement between the British Crown and Māori chiefs, signed in New Zealand in 1840. It was meant to recognize Māori land rights and grant British sovereignty over New Zealand. However, there were discrepancies between the English and Māori versions of the treaty, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts over land ownership and governance.

Scramble for Africa
A term used to describe the period of intense European colonization of Africa between the late 19th and early 20th centuries, culminating after the Berlin Conference (1884-1885). European powers competed to claim territories in Africa for resources, strategic military advantage, and economic opportunities, often disregarding indigenous rights and causing lasting socio-political effects.

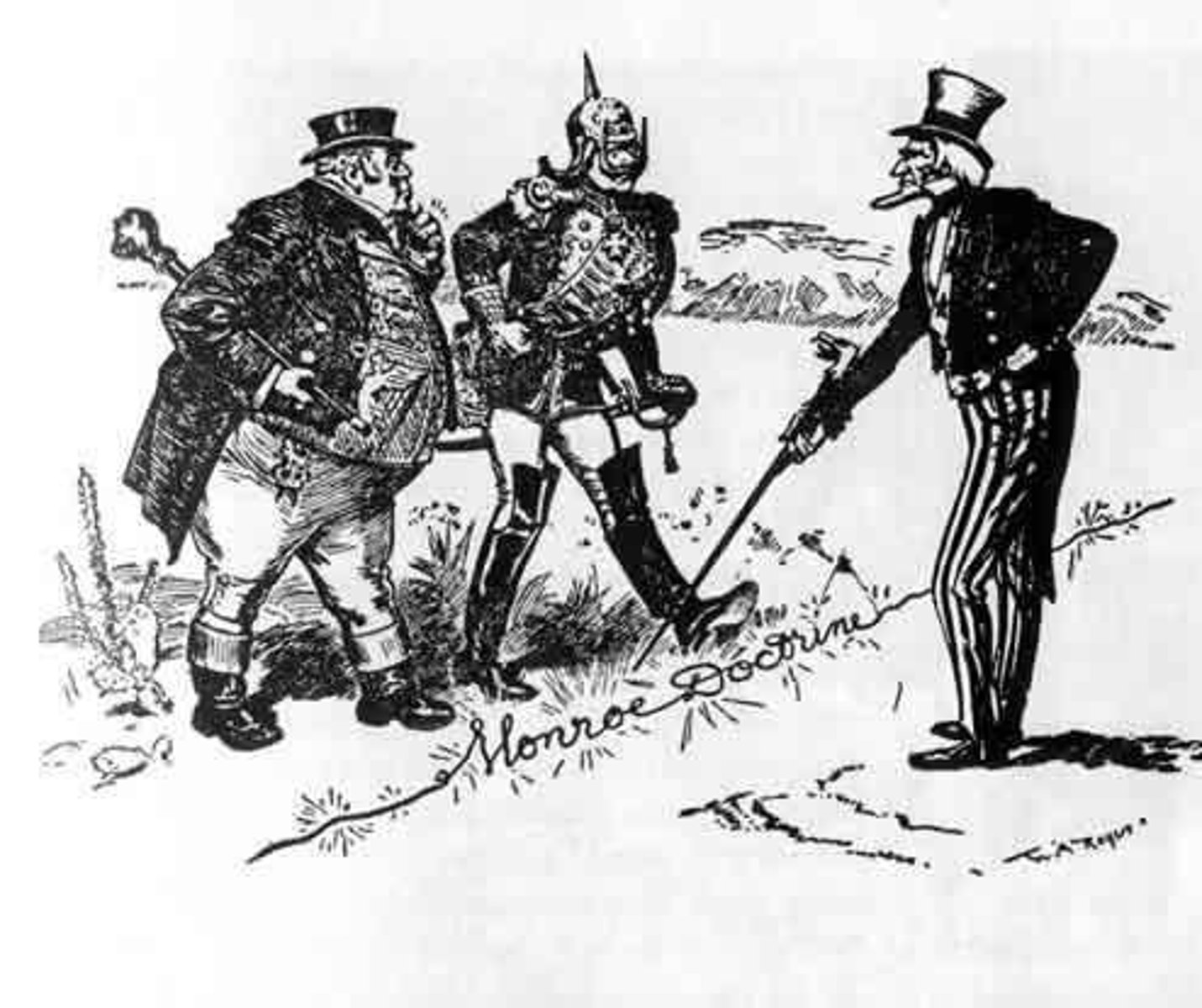
Monroe Doctrine
A principle that declared any European attempts to colonize or intervene in the Western Hemisphere would be considered acts of aggression, requiring U.S. intervention.

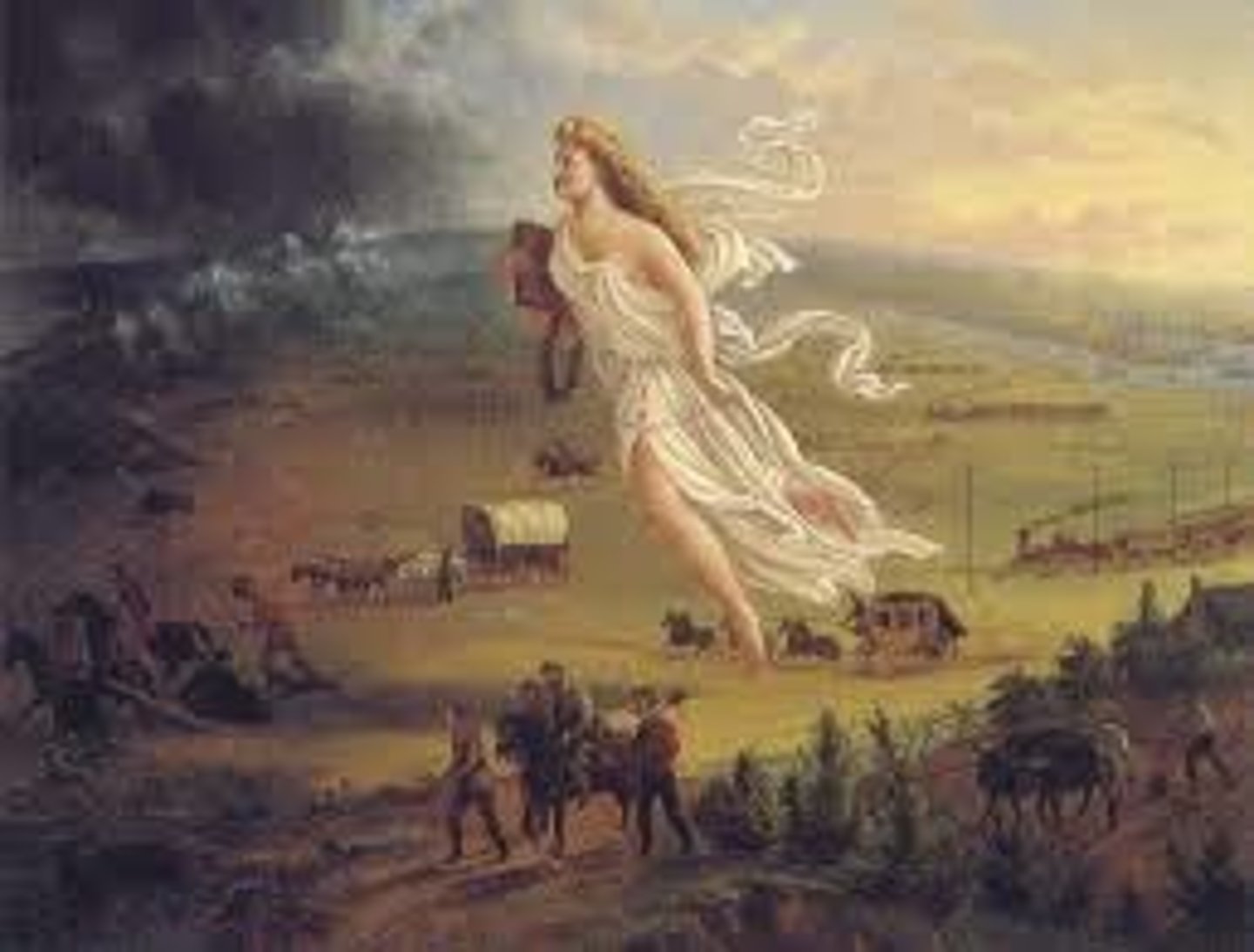
Manifest Destiny
A 19th-century American ideology that believed the United States was destined, by God, to expand its territory across North America, from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean.

Roosevelt Corollary
An addition to the Monroe Doctrine articulated by U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt in 1904, asserting the U.S. right to intervene in Latin American affairs.

The Great Game
A period of geopolitical competition between Russia and Britain for control and influence over Central Asia.

Concentration Camps
Facilities where large groups of people, often civilians or prisoners of war, are confined under harsh conditions, typically without trial.

Penal colony
A settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory.

Boer Wars
Fights between the British Empire and Boer settlers in South Africa.

Seven Years' War
A global conflict involving most of the great powers of the time, often referred to as the first 'world war.'

Taiping Rebellion
A massive civil war in China, led by Hong Xiuquan, who claimed to be the younger brother of Jesus Christ.

Boxer Rebellion
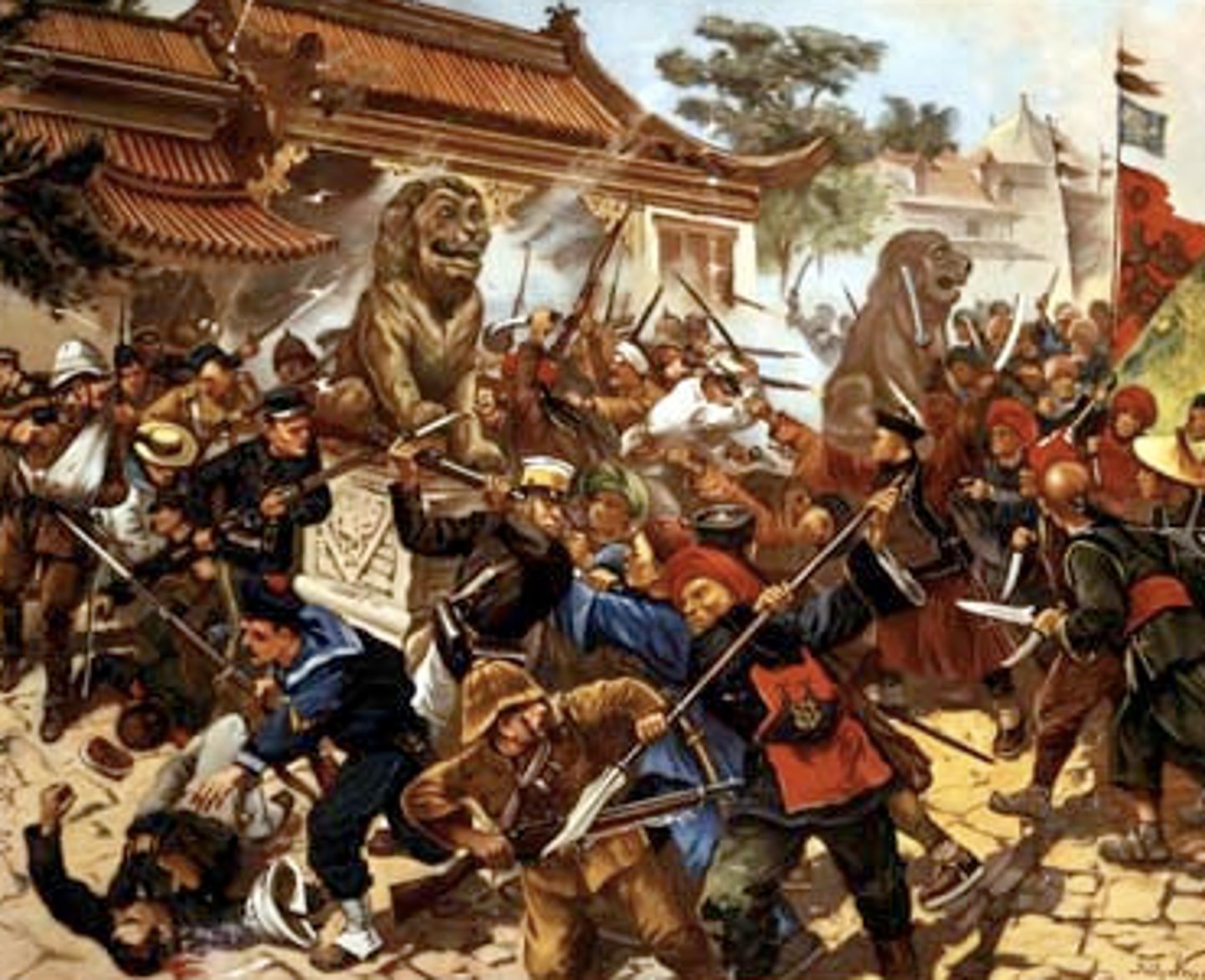
An anti-imperialist, anti-Christian uprising in China, led by a group known as the Boxers.

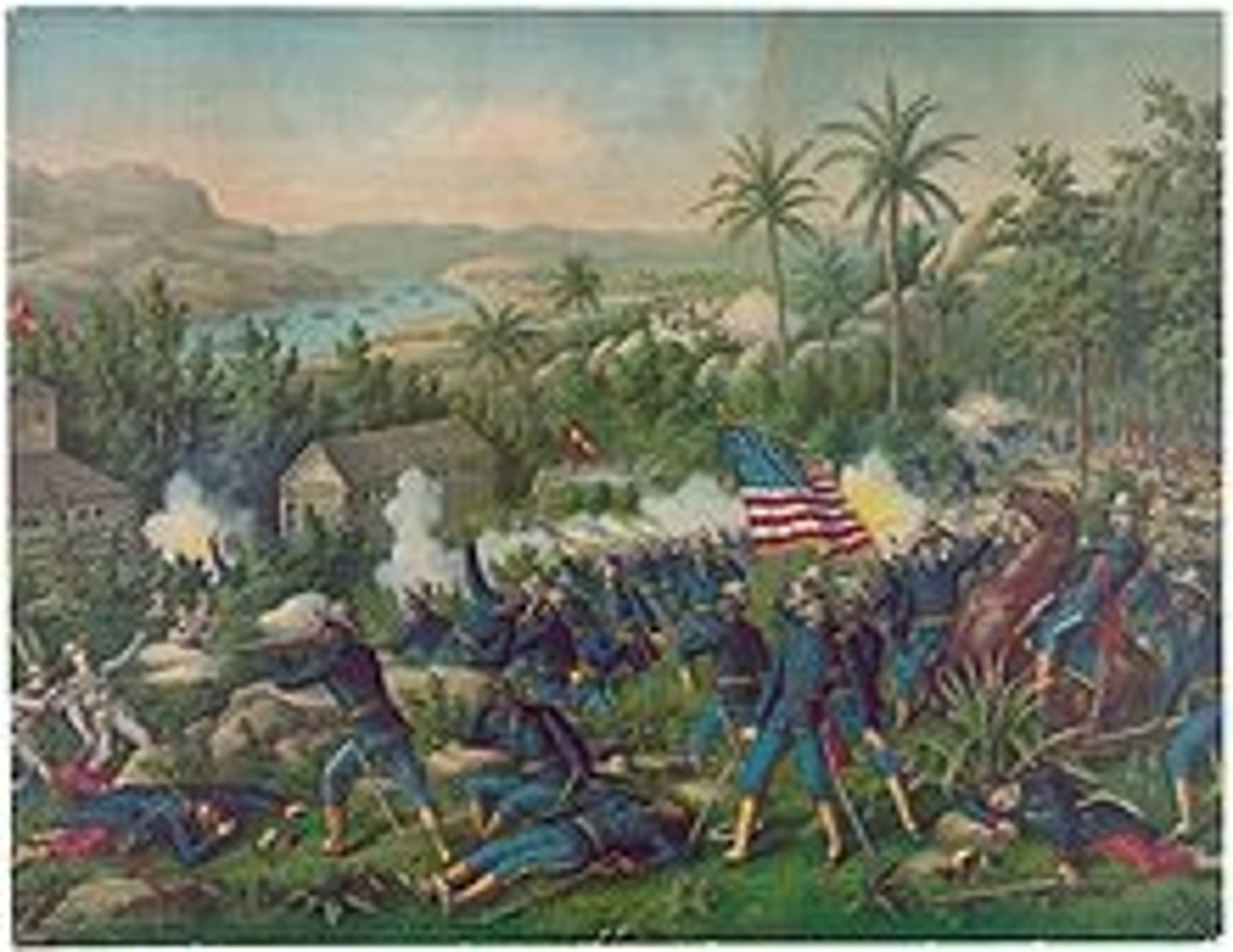
Spanish-American War
A brief conflict between Spain and the United States, triggered by the explosion of the USS Maine in Havana Harbor and U.S. support for Cuban independence.

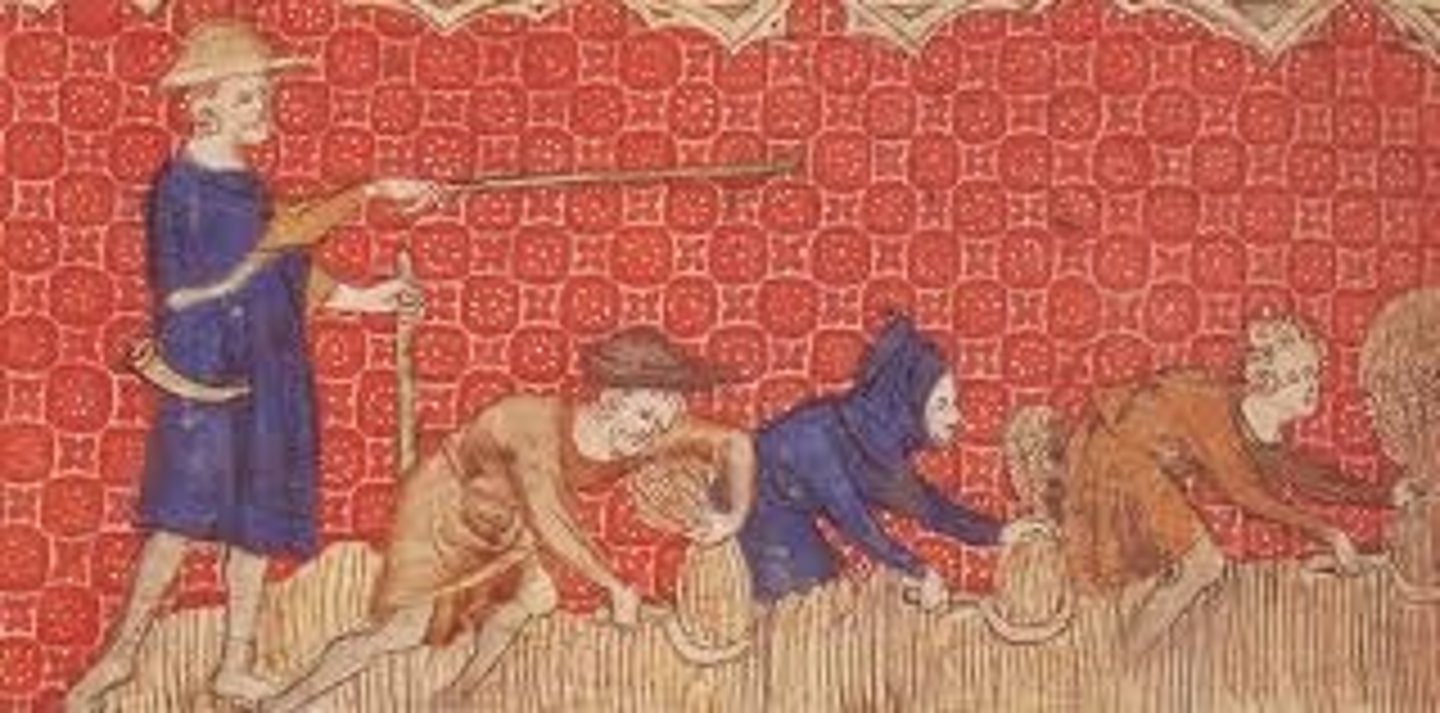
Corvee labor
Refers to a system of unpaid labor required by the government, typically involving forced work on public infrastructure projects.

Spheres of influence
Regions where a particular foreign country holds dominant influence, whether political, economic, or military, but without formal colonization.
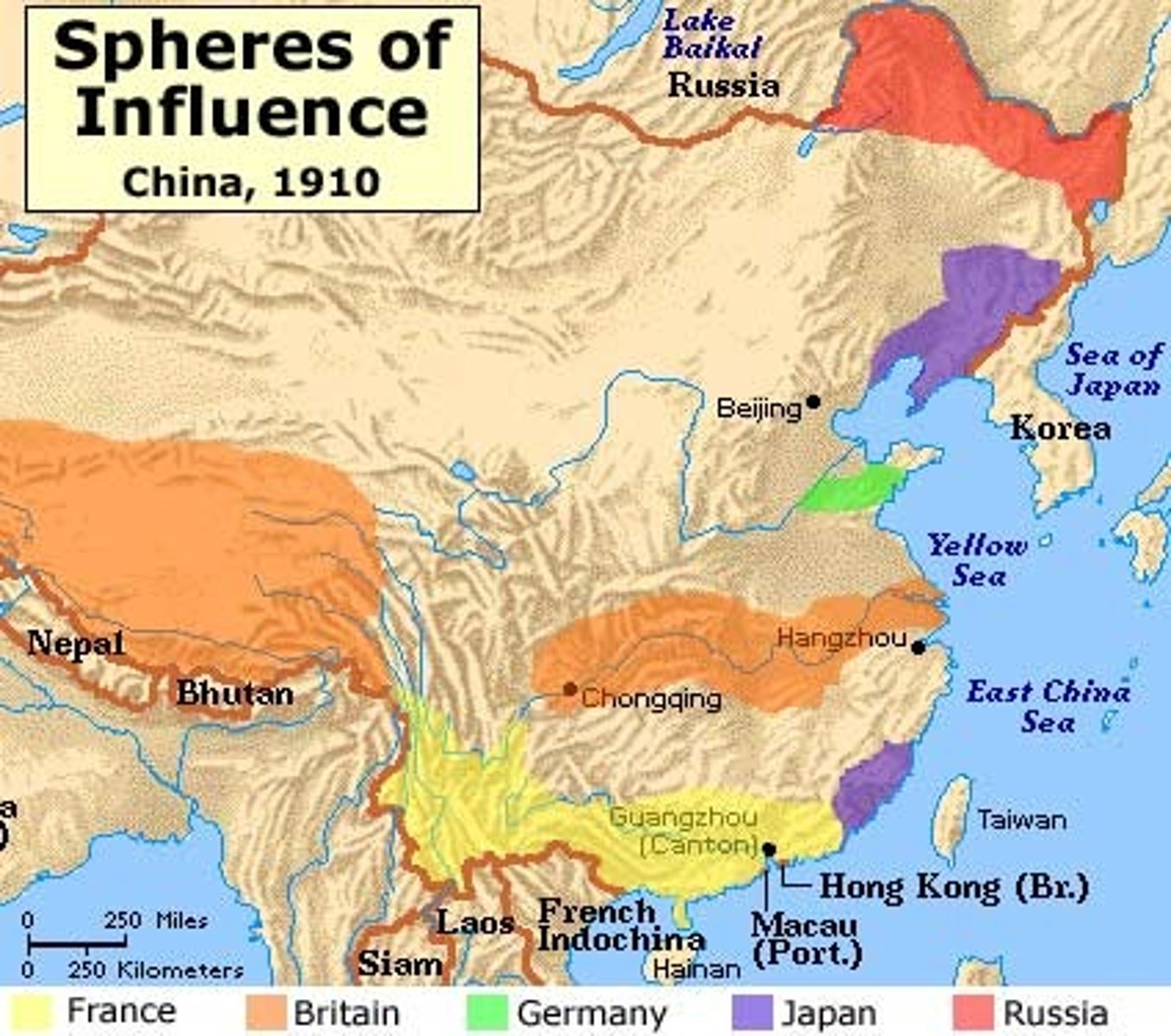
Settler colony
Refers to a type of colonial establishment where large numbers of settlers from the colonizing country move to the colony.

East India Company (EIC)
A private trading company granted a royal charter by the British Crown.

Dutch East India Company (VOC)
A Dutch trading company founded in 1602 to manage trade in Asia.

Afrikaners
A South African ethnic group primarily descended from Dutch, German, and French Huguenot settlers who arrived in southern Africa during the 17th and 18th centuries. They speak Afrikaans, a language derived from Dutch.

Maori
The indigenous Polynesian people of New Zealand.

Colonization Society
Refers to organizations or movements that promoted the colonization of new territories.
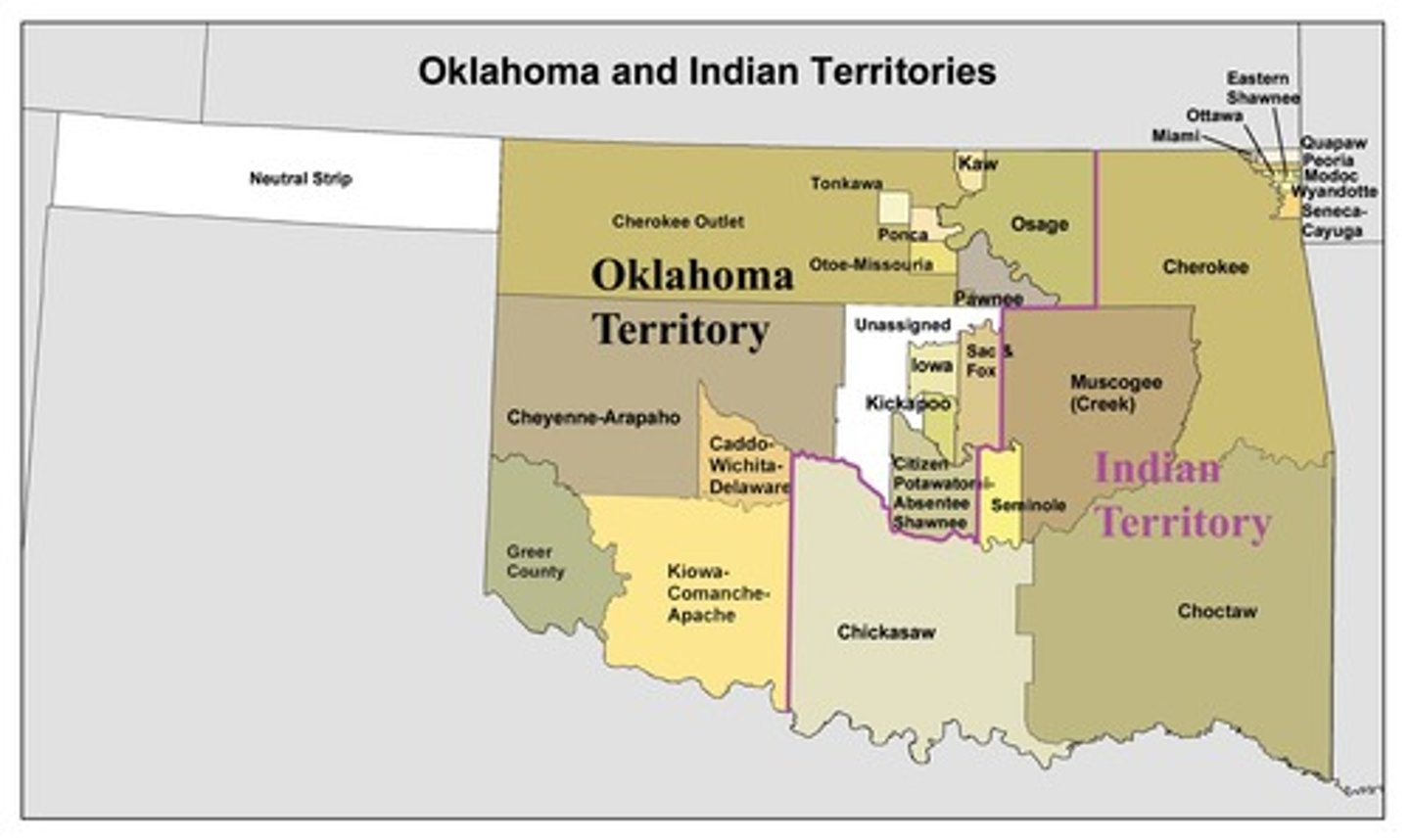
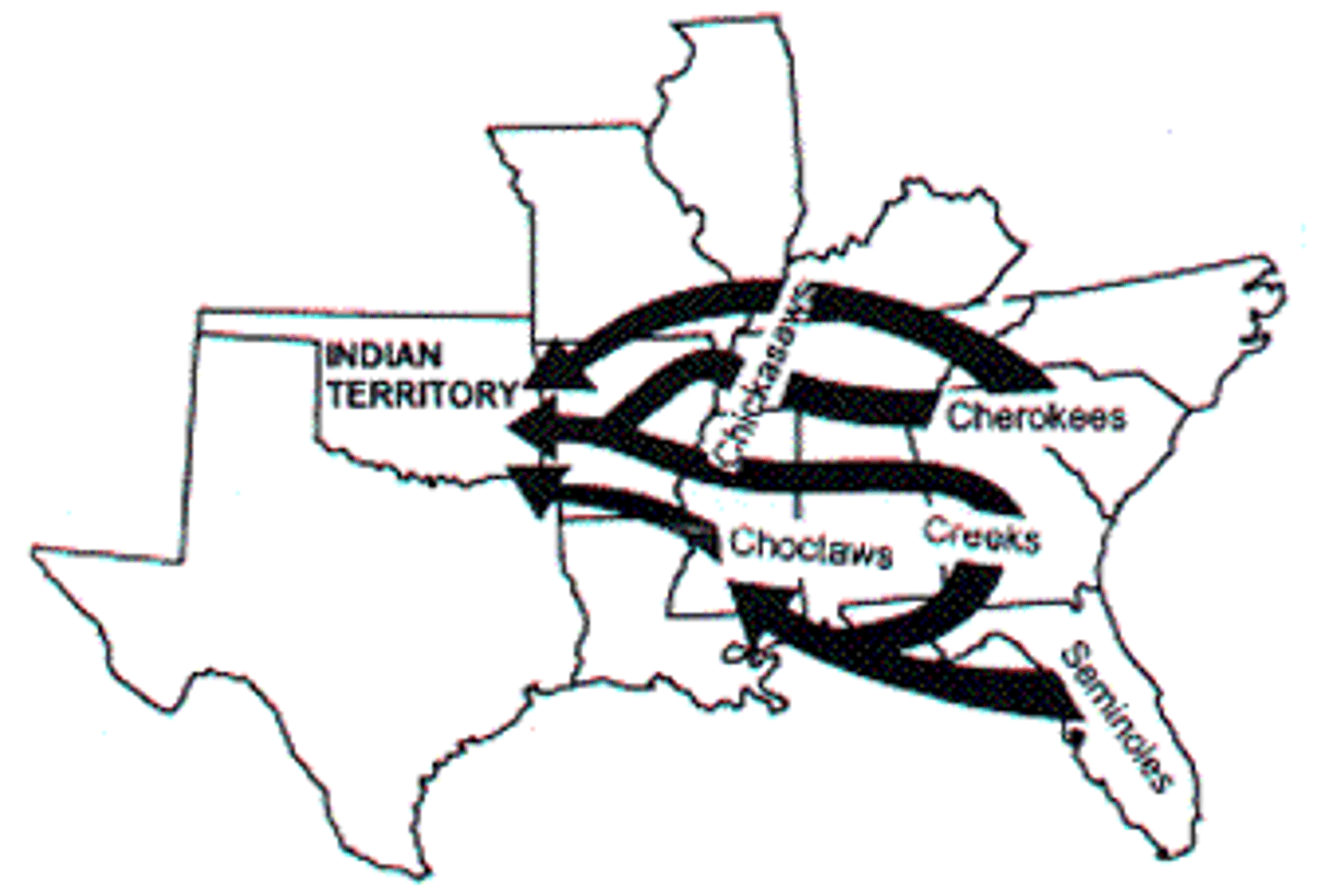
Indian territory
A region in the central United States designated by the U.S. government in the 19th century as land to which Native American tribes were forcibly relocated, especially under the Indian Removal Act of 1830. The territory eventually became part of the state of Oklahoma. It was intended to be a place where Native American tribes could live without interference from European settlers, though it led to significant hardship, including the Trail of Tears.
Trail of Tears
A forced, tragic migration where the U.S. government made Native American tribes leave their ancestral lands in the Southeast and walk over 1,000 miles to Indian Territory (modern-day Oklahoma) in the 1830s.

Quinine
A medicinal compound derived from the bark of the cinchona tree, used primarily to treat malaria.

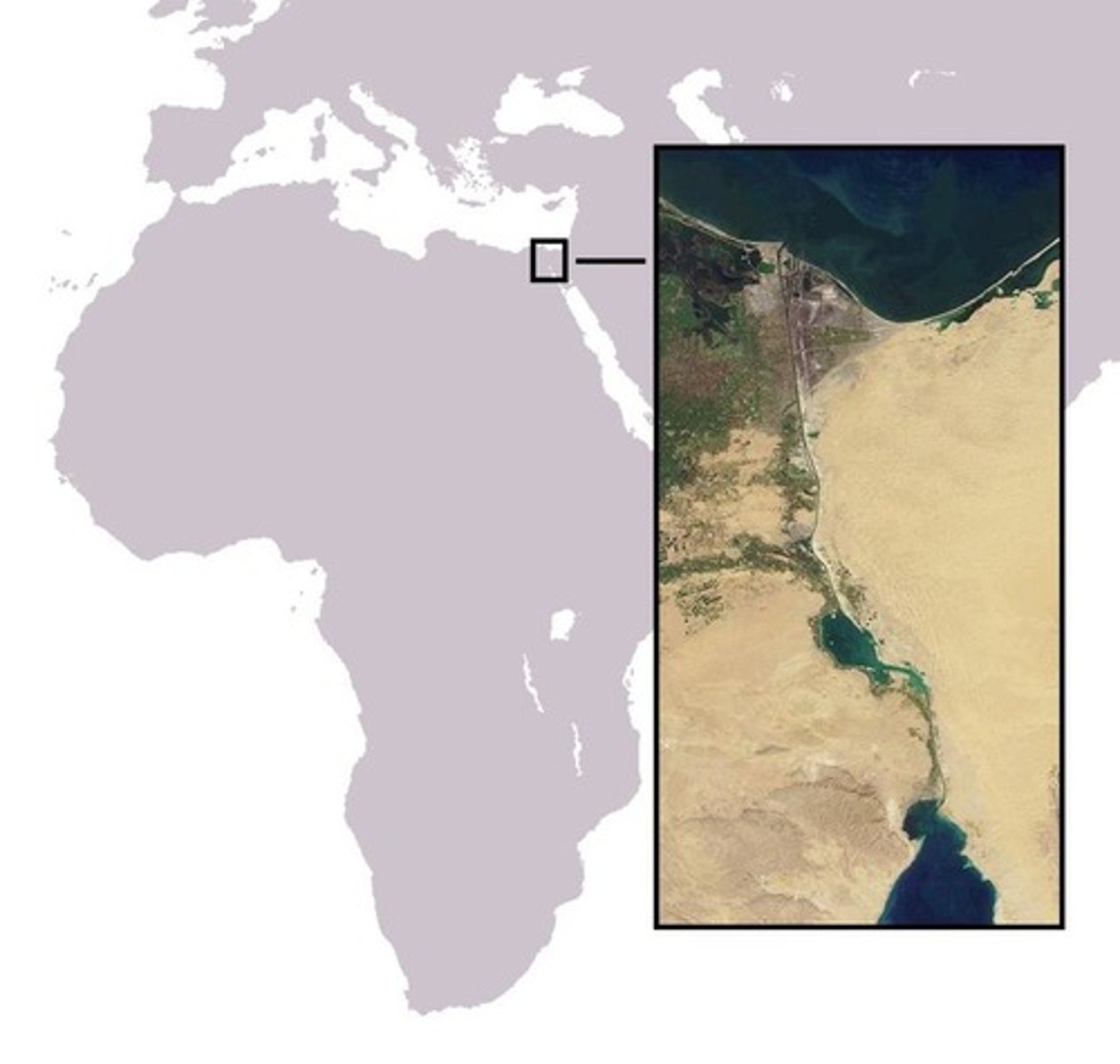
Suez Canal
A man-made waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, completed in 1869 in Egypt.
Tupac Amaru II
The last indigenous monarch of the Inca Empire in Peru who led an indigenous revolt against Spanish colonial rule in the 18th century.
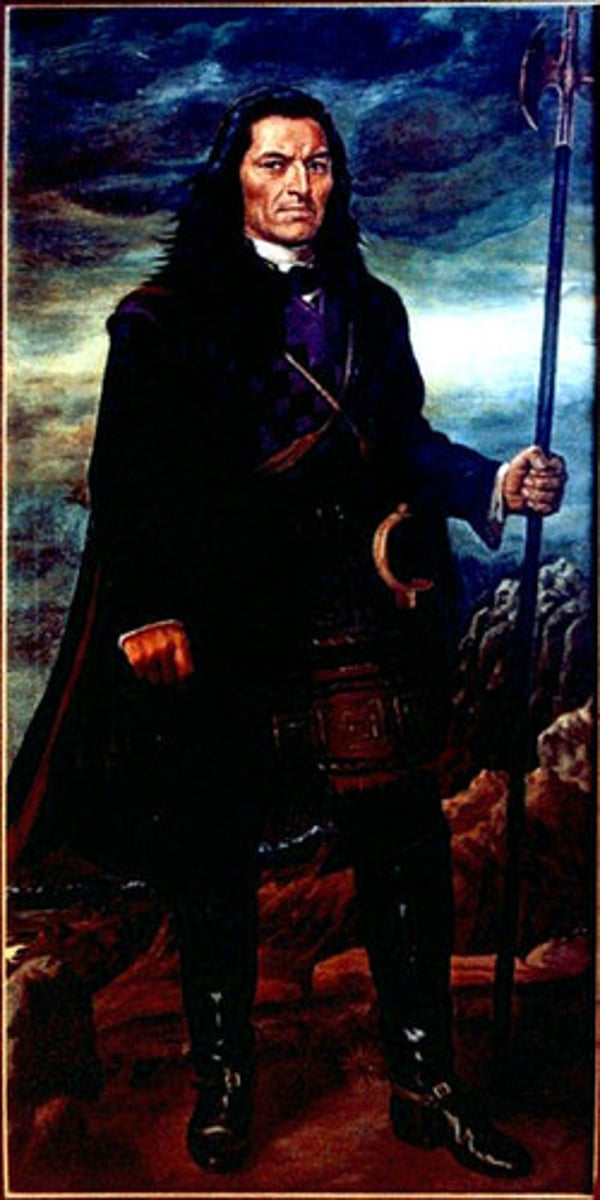

Benito Juarez
A Mexican lawyer and politician who served as the president of Mexico from 1858 to 1872, known for his role in leading the country through the Reform War.
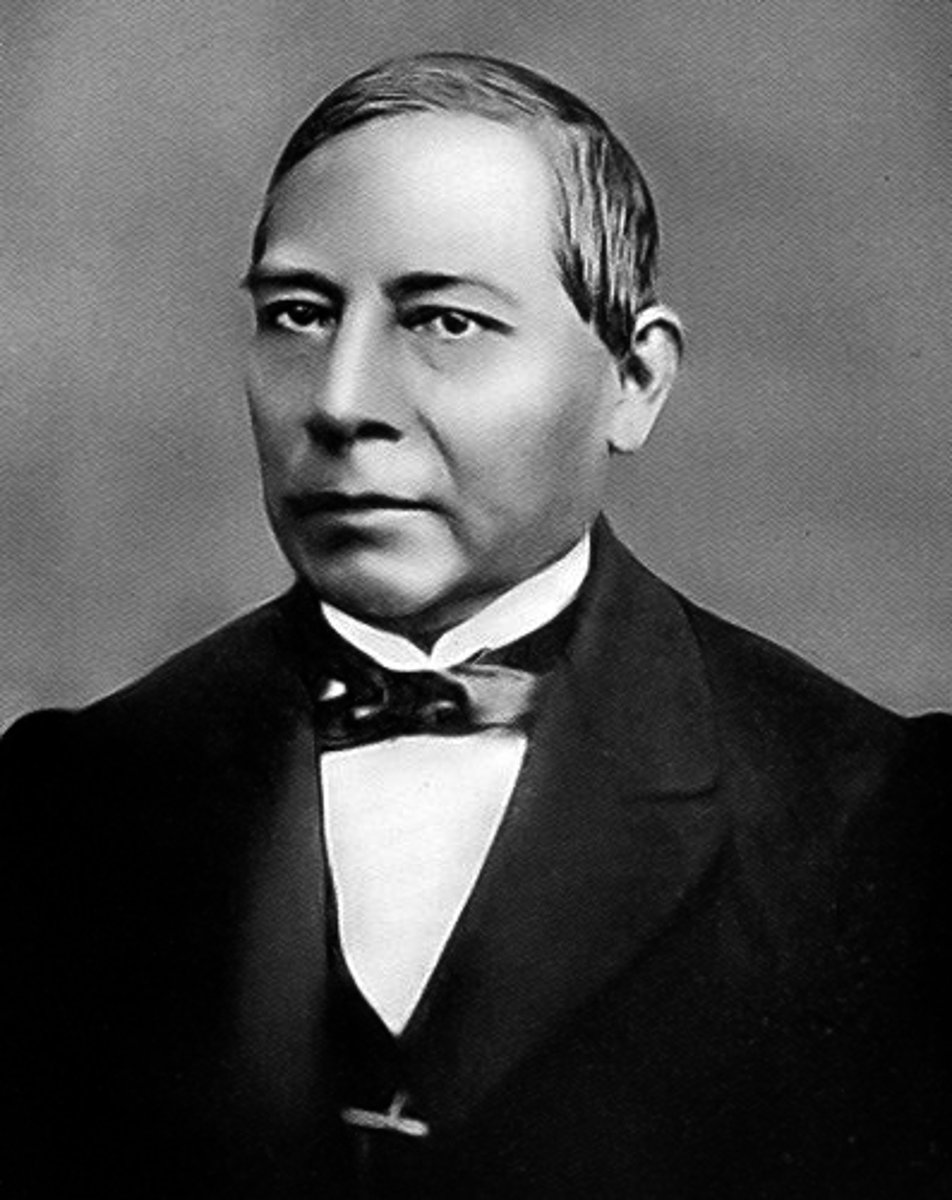

Jose Rizal
A Filipino nationalist and revolutionary, Rizal was a leading figure in the campaign for Philippine independence from Spain.
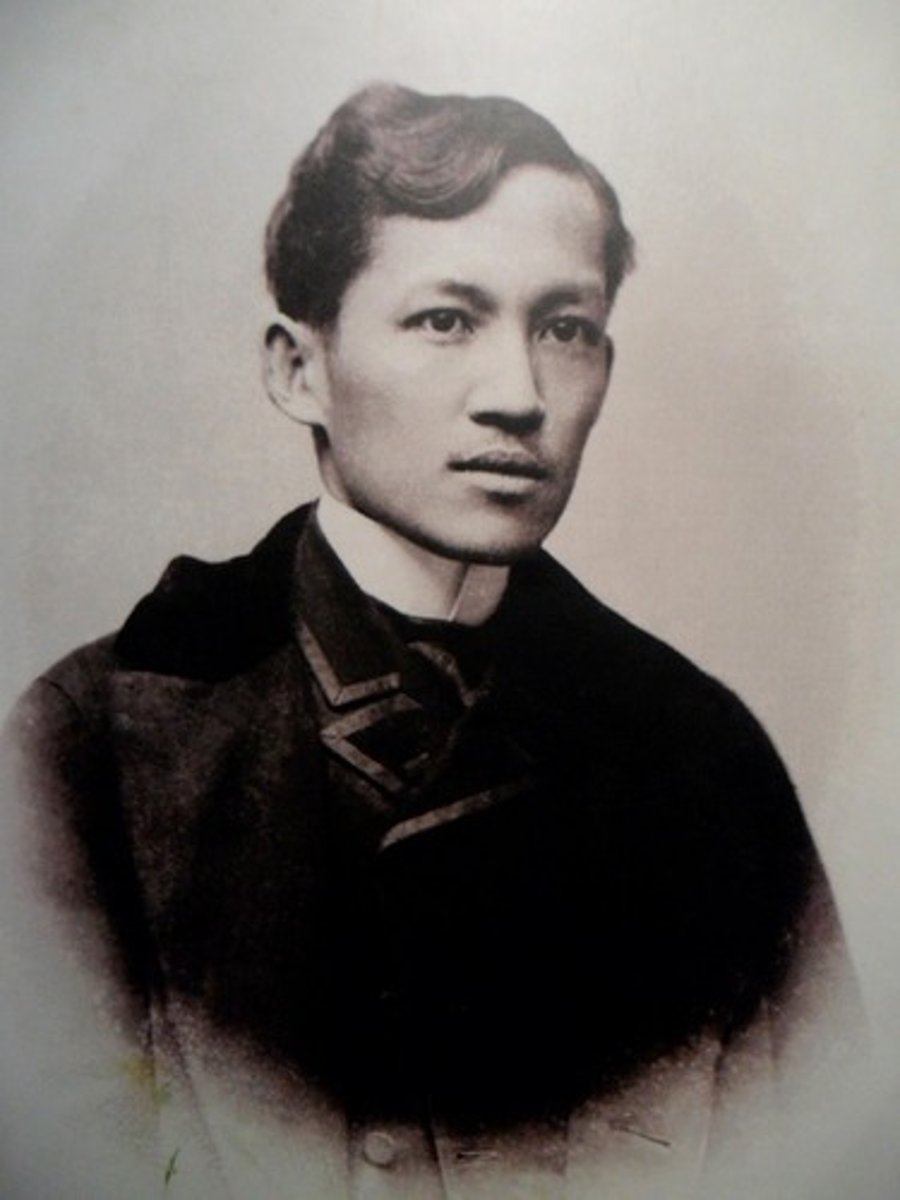

Usman dan Fodio
A Muslim scholar and leader who founded the Sokoto Caliphate in northern Nigeria, leading a religious and political movement against corrupt rulers.
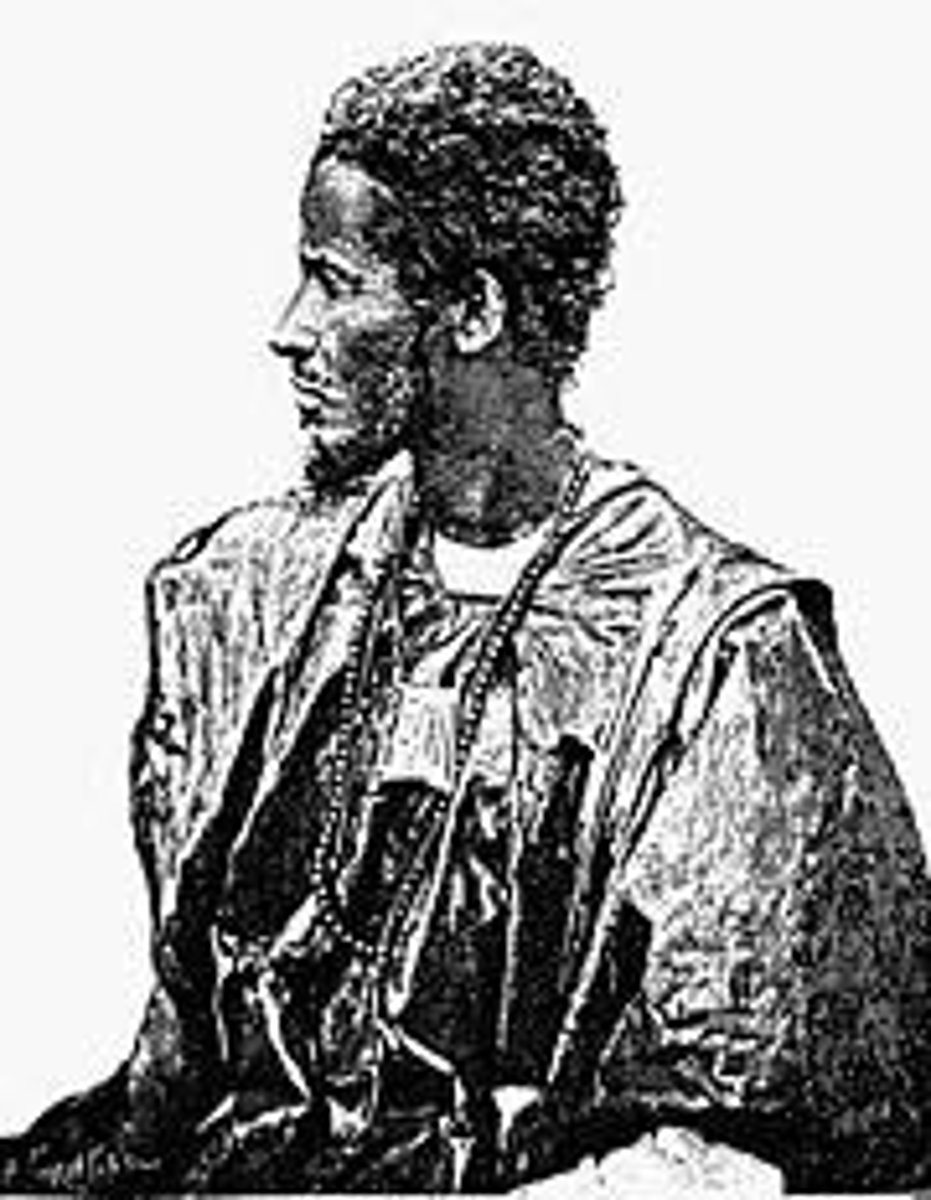

Samory-Toure
African military leader. A Muslim, he began to amass a personal following in the mid-1850s, establishing a military base on the Upper Niger.
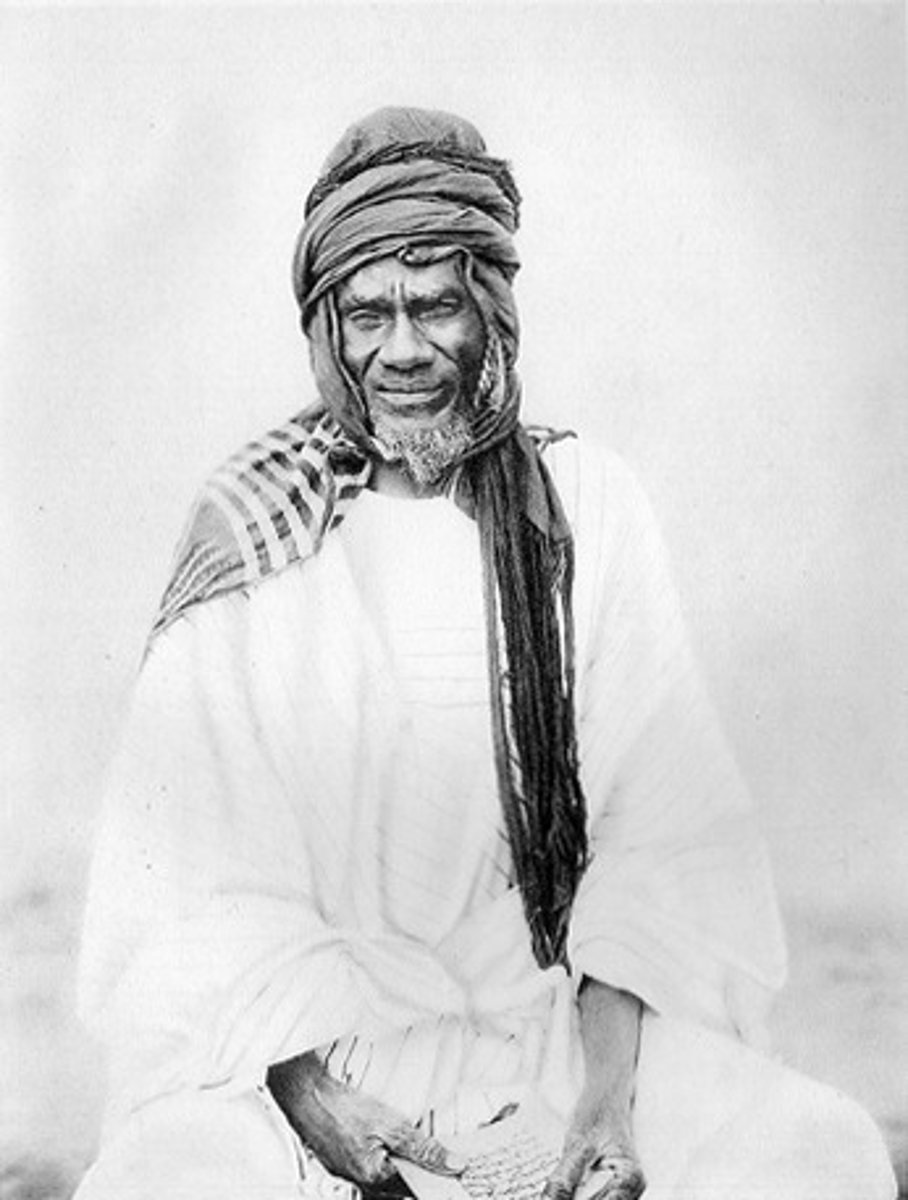

Muhammad Ahmad
A Sudanese religious leader who proclaimed himself the Mahdi and led a successful rebellion against the Egyptian and British authorities in Sudan.
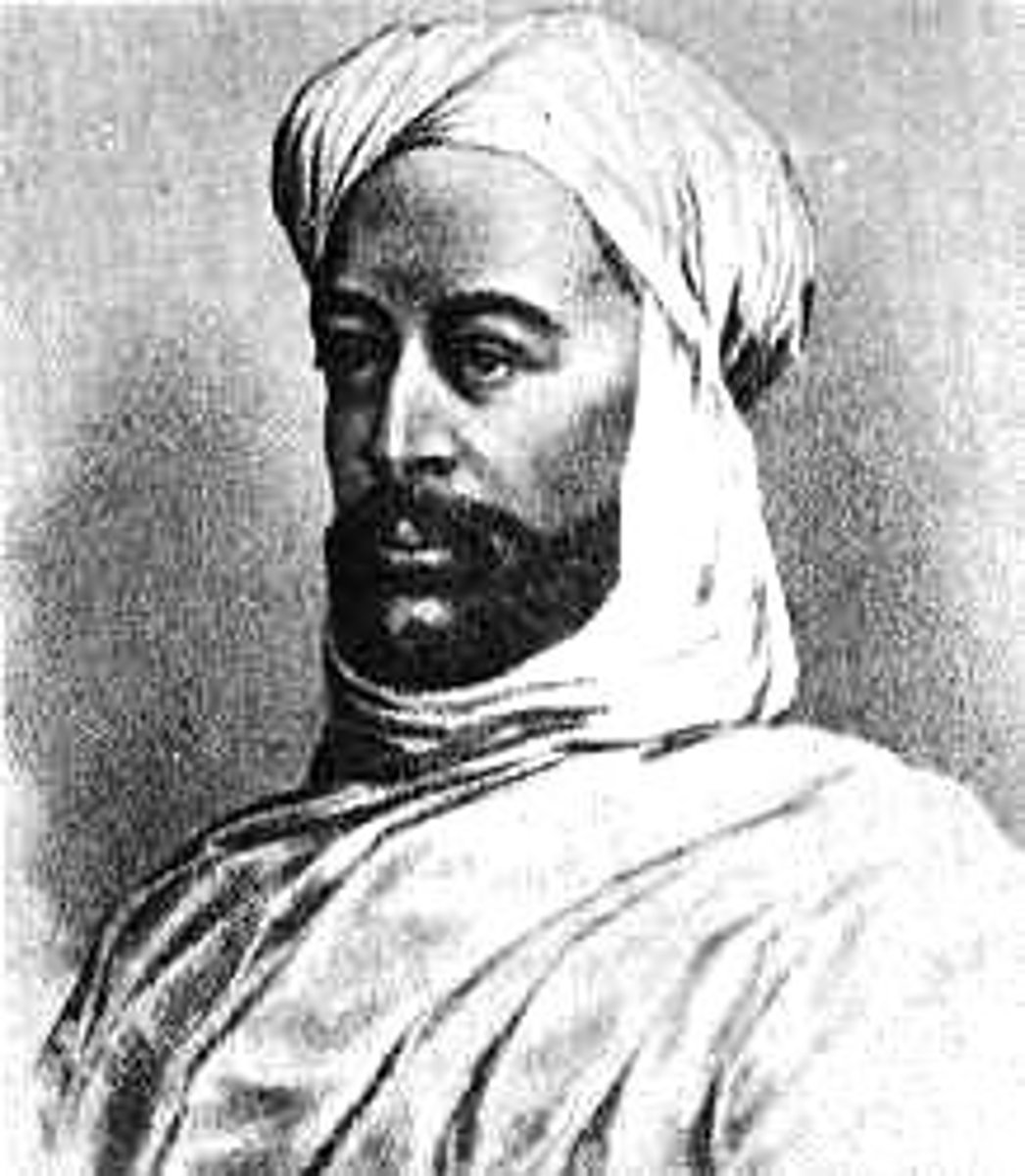

Yaa Asantewaa
The Queen Mother of the Ashanti Empire in West Africa, famous for leading the Ashanti forces in the War of the Golden Stool against British colonial forces.

Balkan Peninsula
A region in southeastern Europe, bordered by the Adriatic, Ionian, and Aegean seas, home to a number of ethnically diverse and historically significant states.
Vietnam
A country in Southeast Asia with a long history of resistance to foreign occupation. It was colonized by France in the 19th century and became part of French Indochina.
Philippines
An archipelago in Southeast Asia, consisting of over 7,000 islands, which was a Spanish colony for over 300 years before being ceded to the United States after the Spanish-American War in 1898.
Sokoto Caliphate
A large Islamic state in West Africa, founded in 1804 by Usman dan Fodio after a successful religious and political revolution against the Hausa rulers.
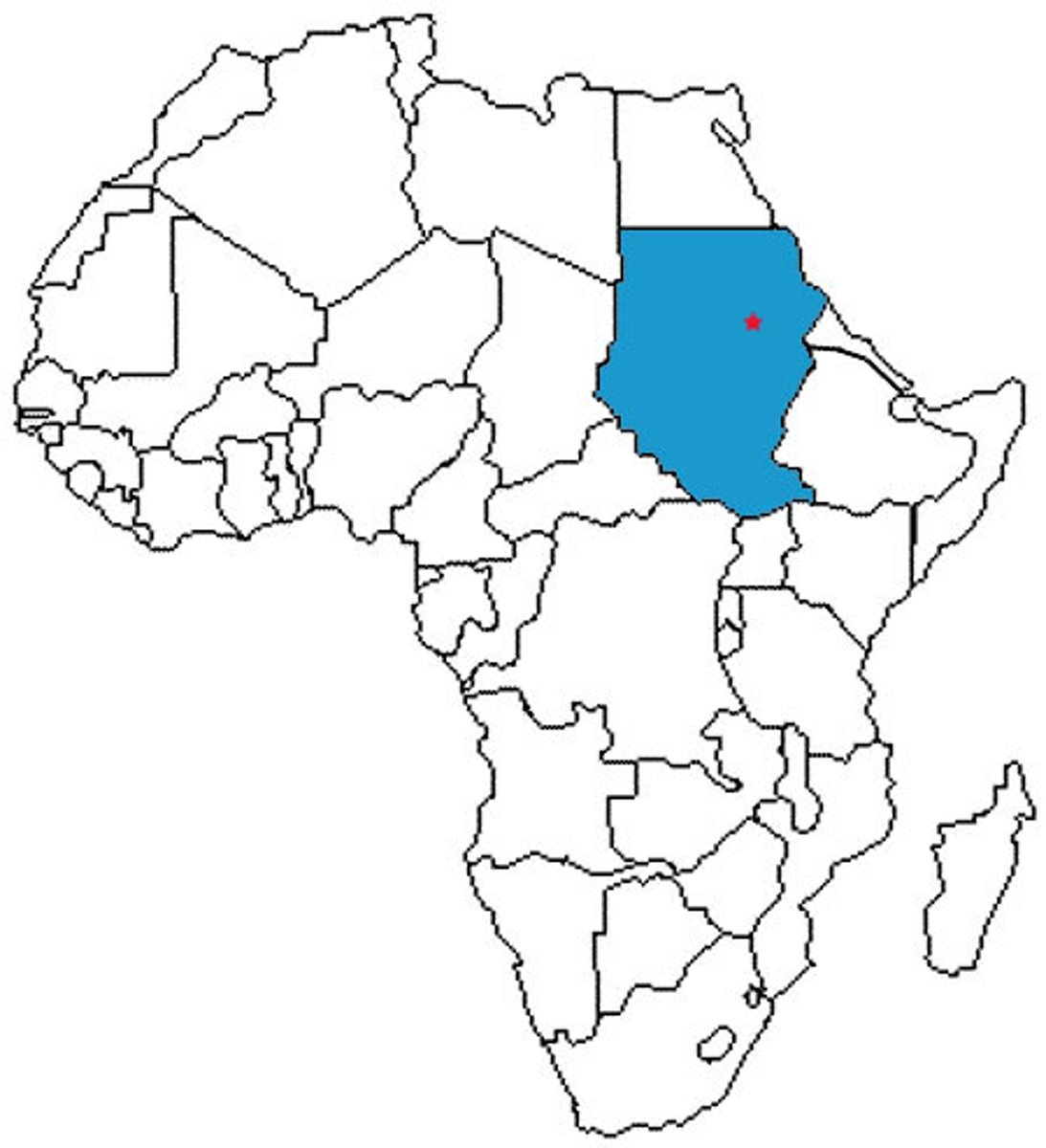
Sudan
A country located in northeastern Africa, historically home to powerful empires such as the Meroitic Kingdom and the Kingdom of Kush.
Asante Empire
a powerful West African state that emerged in the late 17th century, known for its wealth, military strength, and complex political organization.
Indian Rebellion of 1857
Military grievances from sepoys regarding their treatment and pay, economic distress due to oppressive taxation and land revenue policies, as well as cultural and religious insensitivity shown by the British.

Philippine Revolution
Began in 1896 as a rebellion against brutal Spanish rule that spanned over three centuries from the time Ferdinand Magellan led an expedition to the island in the early 1560s to the establishment of a full Spanish colony.

Philippine-American War
Lasted three years and resulted in the death of over 4,200 American and over 20,000 Filipino combatants

Maori Wars
the First Taranaki War (1860-1861) and the Second Taranaki War (1863-1866), each marked by fierce resistance from Māori groups. The outcomes of these wars ultimately led to significant loss of land for the Māori and reinforced British control over New Zealand.

Xhosa Cattle Killing Movement
A significant resistance movement that occurred among the Xhosa people in South Africa during the 1850s. This movement involved the mass slaughter of cattle and the destruction of crops, driven by the belief that this act would cleanse the land and bring about a new era free from colonial oppression.

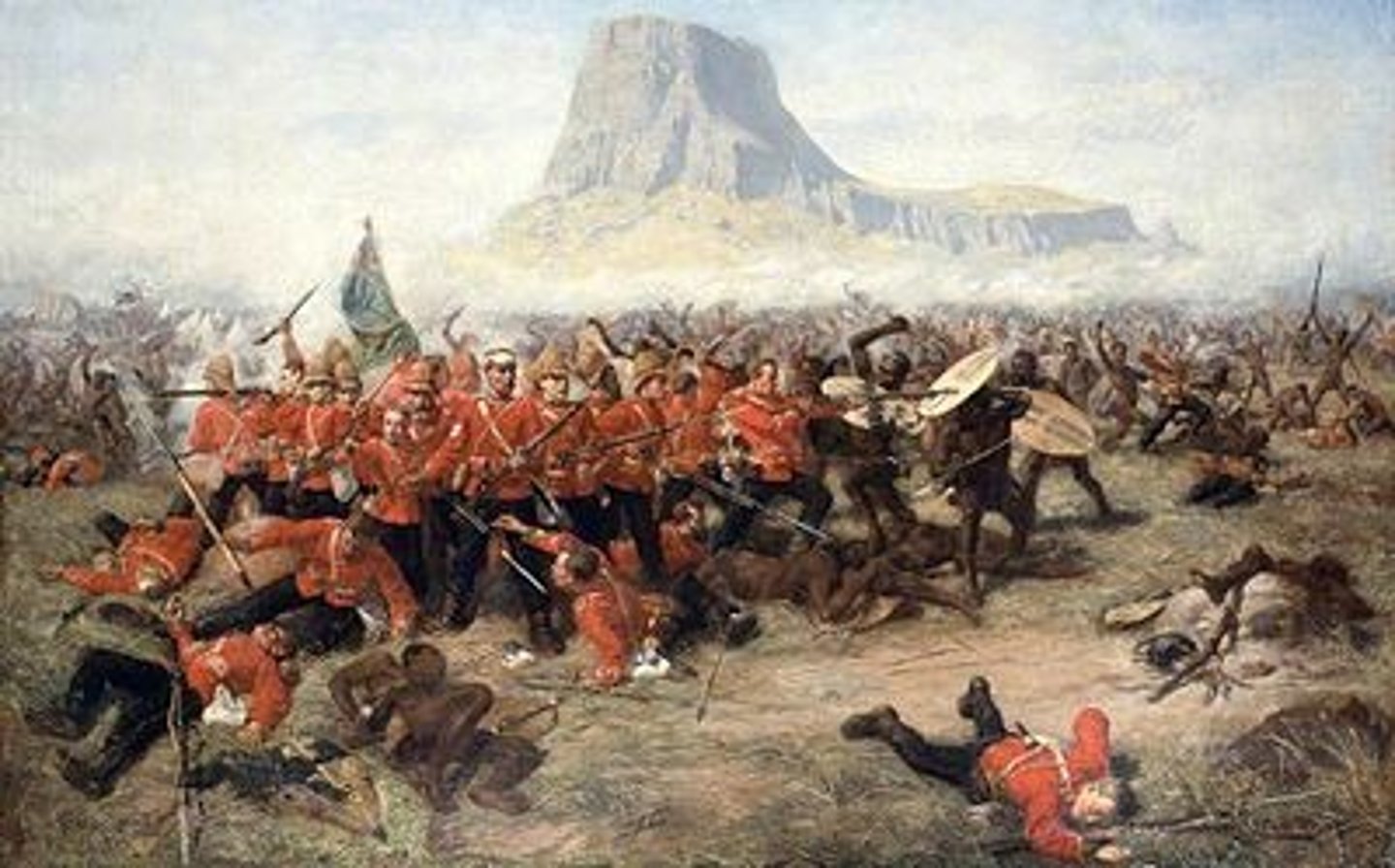
Anglo-Zulu War
A conflict between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom in southern Africa in 1879. The war was sparked by British attempts to annex Zululand. Despite early Zulu victories, the British eventually defeated the Zulus and annexed their territory.

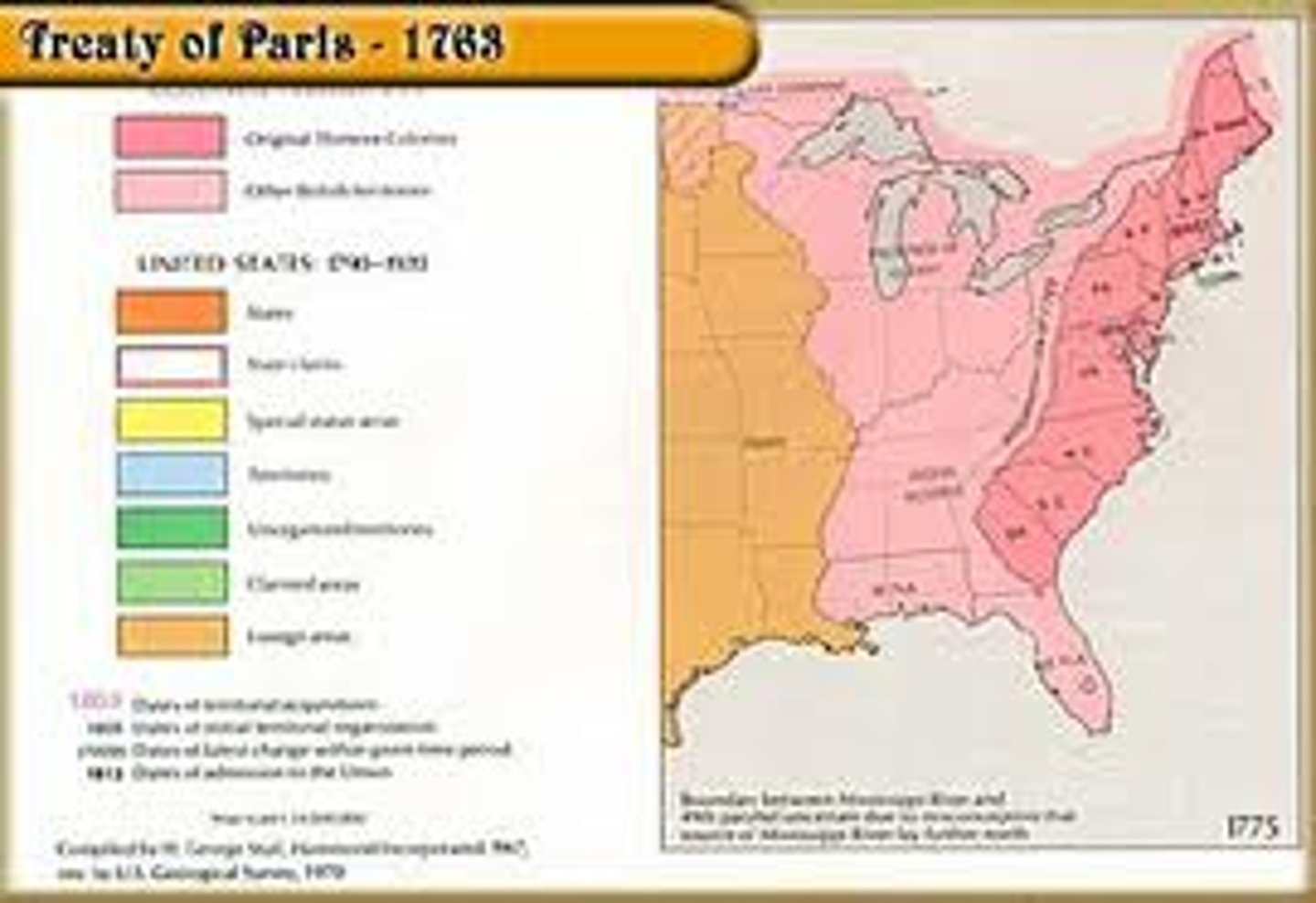
Treaty of Paris
Refers to multiple agreements, but the most famous are the Treaty of Paris (1763), which ended the Seven Years' War (or French and Indian War) between Britain and France, and the Treaty of Paris (1783), which ended the American Revolutionary War and recognized American independence from Britain.
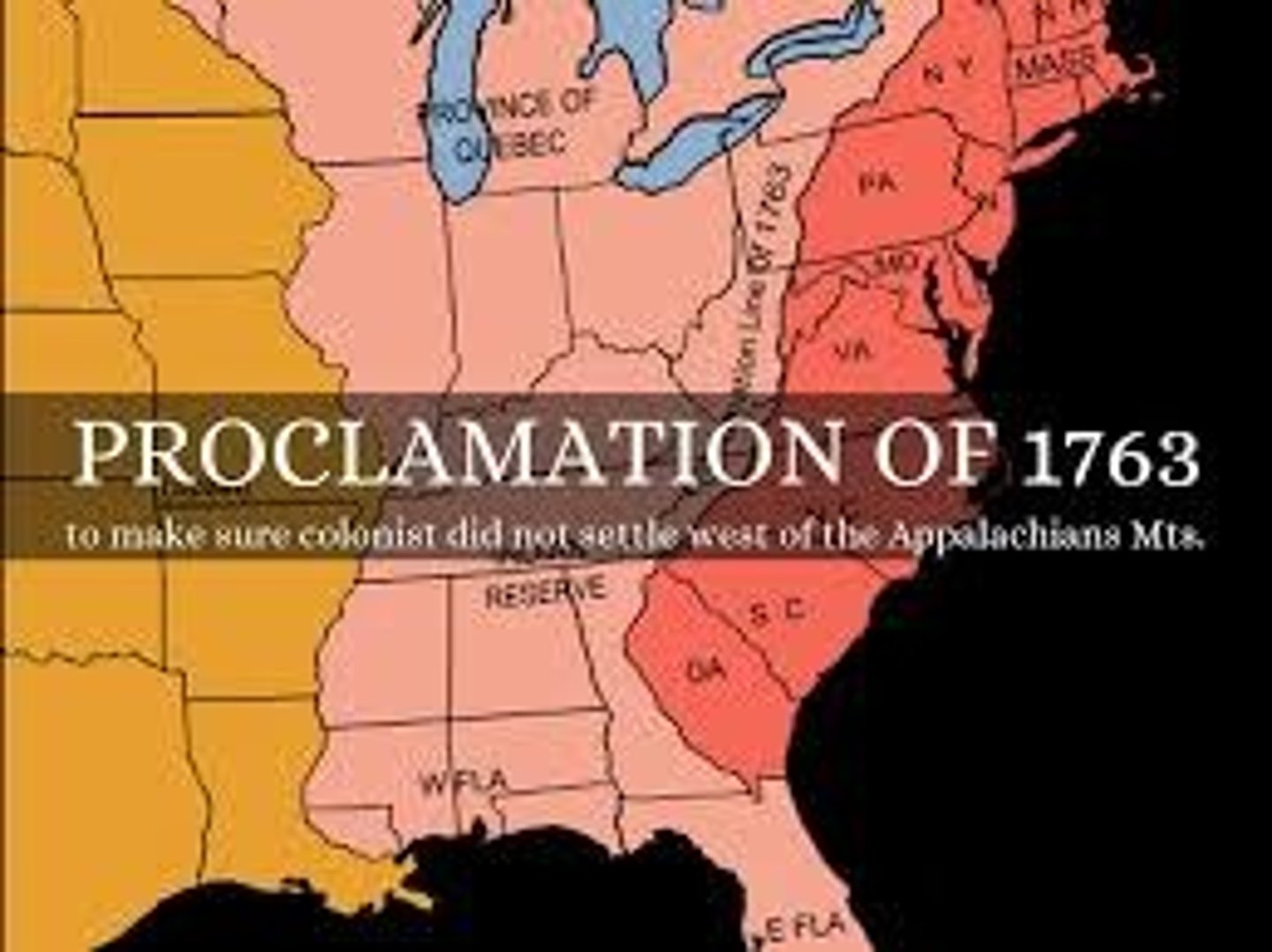
Proclamation of 1763
A British law issued by King George III after the Seven Years' War that prohibited colonial expansion westward beyond the Appalachian Mountains.
Indian Removal Act
A U.S. law signed by President Andrew Jackson in 1830 that authorized the forced relocation of Native American tribes living east of the Mississippi River to lands in the western territories.
Indian National Congress
A political party in India, founded in 1885, which played a crucial role in India's struggle for independence from British colonial rule.

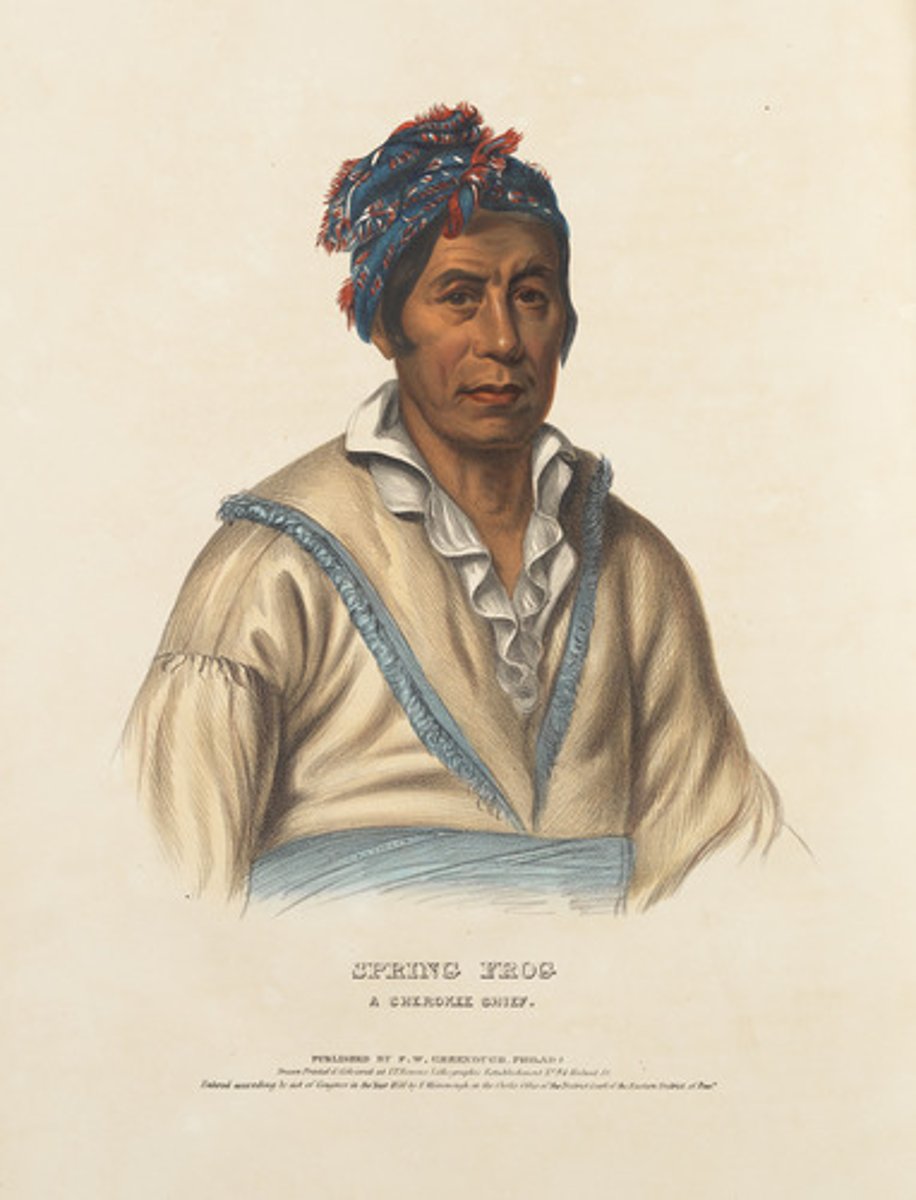
Cherokee Nation
A Native American people originally from the southeastern United States (Georgia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Alabama) who were forcibly relocated to Indian Territory (modern-day Oklahoma) during the Trail of Tears.

Aboriginal
The Indigenous people of Australia, known for their rich cultural heritage, deep spiritual connection to the land, and distinct languages.
Xhosa
An ethnic group in South Africa known for their distinct cultural practices and language, they were significantly affected by European colonization.
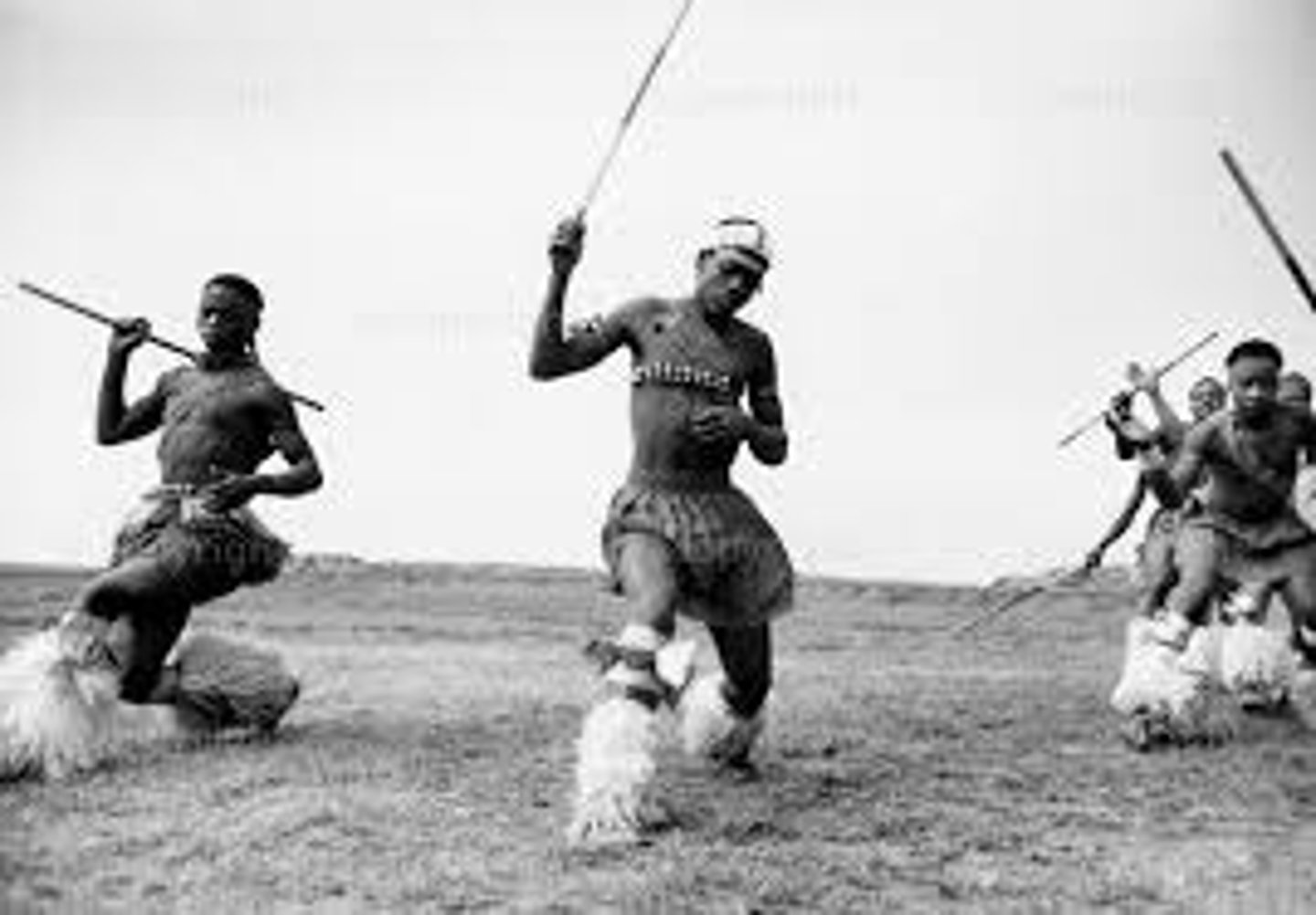

Zulu
The name of a tribe of South Africa people who live in the northern part of Natal. They were the dominate tribe in the late 19th century when European Imperialism began. They resisted both the Boers and the British, but ultimately lost their homeland and freedom by 1879.

Mahdi
A figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the End of Times to rid the world of evil and injustice.

Pan-Africanism
The idea that peoples of African descent have common interests and should be unified.

Sepoys
Infantry soldiers from the Indian subcontinent during India's period of colonization.

Raj
Prince or royalty in Indian languages.

Guano
The excrement of sea- birds

Cotton
A natural fiber harvested from the cotton plant, widely used for making textiles and clothing.

Rubber
A tough elastic polymeric substance made from the latex of a tropical plant or synthetically.

Palm oil
A versatile vegetable oil derived from the fruit of the oil palm tree, primarily found in West Africa, Southeast Asia, and parts of Central America.

Ivory
A dense, white material derived from the tusks and teeth of animals, most notably elephants.

Copper
A reddish-brown metal that has been used by humans for thousands of years, primarily in the production of tools, weapons, and currency.

Tin
A malleable, silvery-white metal that has been used for various applications since ancient times, notably in the production of bronze when alloyed with copper.

Gold
A highly valued precious metal that has been used as a form of currency, a symbol of wealth, and a means of trade throughout history.

Diamonds
Precious gemstones formed deep within the Earth's mantle under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.

Cecil Rhodes
A strong proponent of British imperialism and believed in the superiority of Anglo-Saxon culture, which motivated his expansionist policies.

De Beers Mining Company
A multinational corporation founded in 1888 that specializes in diamond exploration, mining, and marketing.

Cash Crops
An agricultural crop that is purposely made strictly to be sold in a market environment for as much money as possible.

Export Economies
Economic systems that rely heavily on exporting goods and services to generate income and drive growth.
Monocultures
The deliberate cultivation of only one single crop in a large land area.

Railroads
Networks of iron (later steel) rails on which steam (later electric or diesel) locomotives pulled long trains at high speeds. The first railroads were built in England in the 1830s. Their success caused a railroad-building boom throughout the world that lasted well into the 20th century.

Steamships
A vessel that is propelled by steam power, typically generated by burning coal in a boiler. This innovation represented a major advancement in marine technology during the Industrial Age, allowing for faster and more reliable transportation of goods and people across water.

Telegraph
Communication system for transmitting messages over a distance by radio or electrical signals. The telegraph was the first electrical system used for communication in the early days.

Apartheid
A policy of strict racial segregation imposed in South Africa to permit the continued dominance of whites politically and economically.

Spice Islands
A small group of islands to the north-east of Indonesia, between Celebes and New Guinea.
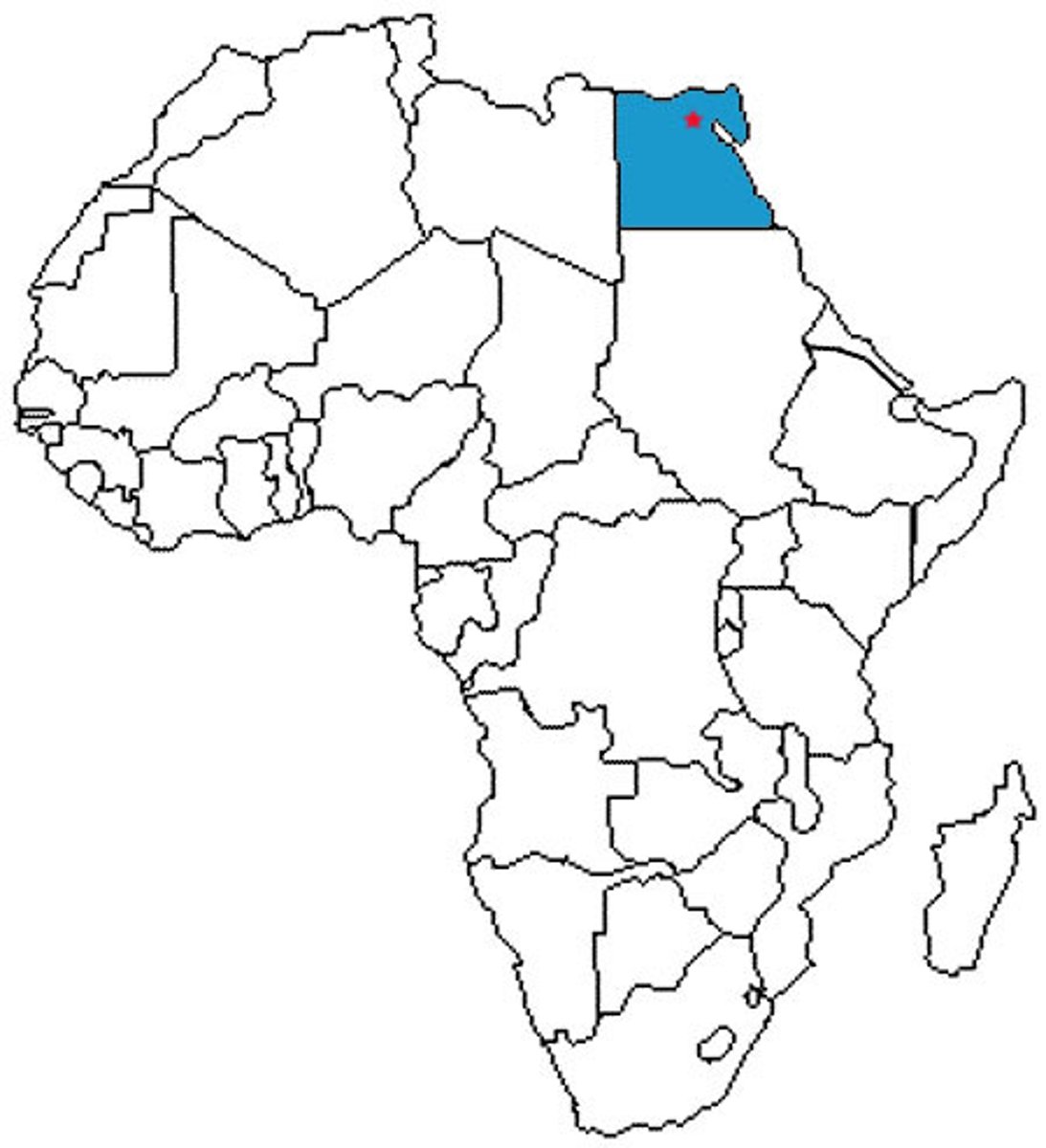
Egypt
A country located in North Africa, known for its ancient civilization and significant cultural, political, and economic contributions to the world.