Lecture 20: Radioactivity
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
recap from last lecture

radioactive decay law
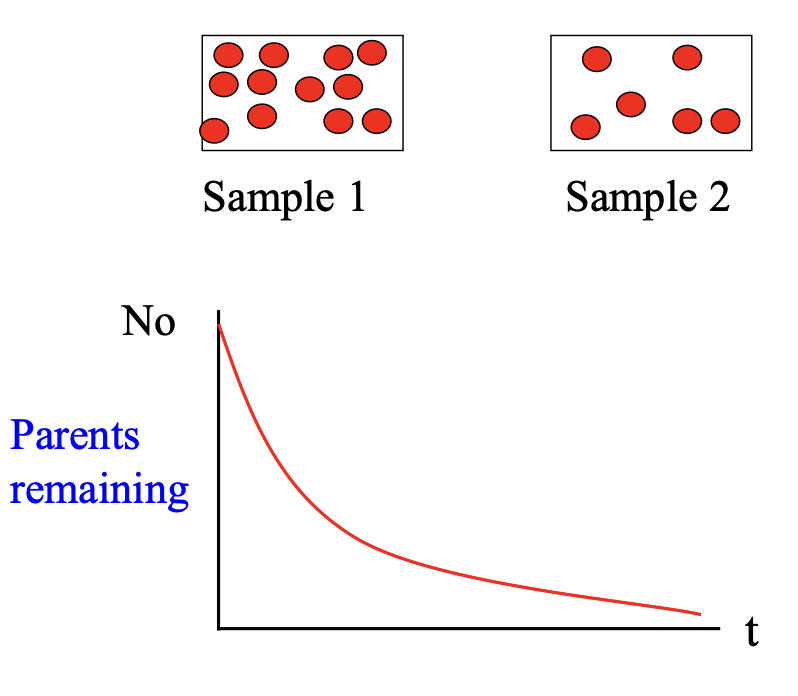
any radioactive isotope contains a vast number of radioactive nuclei
they do not all decay at the one time, rather ONE AT A TIME
this process is RANDOM
we can predict how many nuclei in a sample will decay over a given time period
The number of decays ΔN that occur in a very short time interval Δt is then proportional to Δt and to the total number N of radioactive (parent) nuclei present
A given unstable nucleus has a definite probability of decaying in a given time, this probability is called the
decay constant (same symbol as wavelength)
characteristic of a particular radionuclide
radioactive decay is a statistical process
the number of nuclei decaying per unit time is proportional to the unit of nuclei present at the time
the decay process thus follows an exponential law
radioactive decay law formula
∆N = −λN∆t
λ = decay constant
N = number of nuclei present in a sample
∆N = decay in a given time interval.
∆t = time interval during which decay occurs.
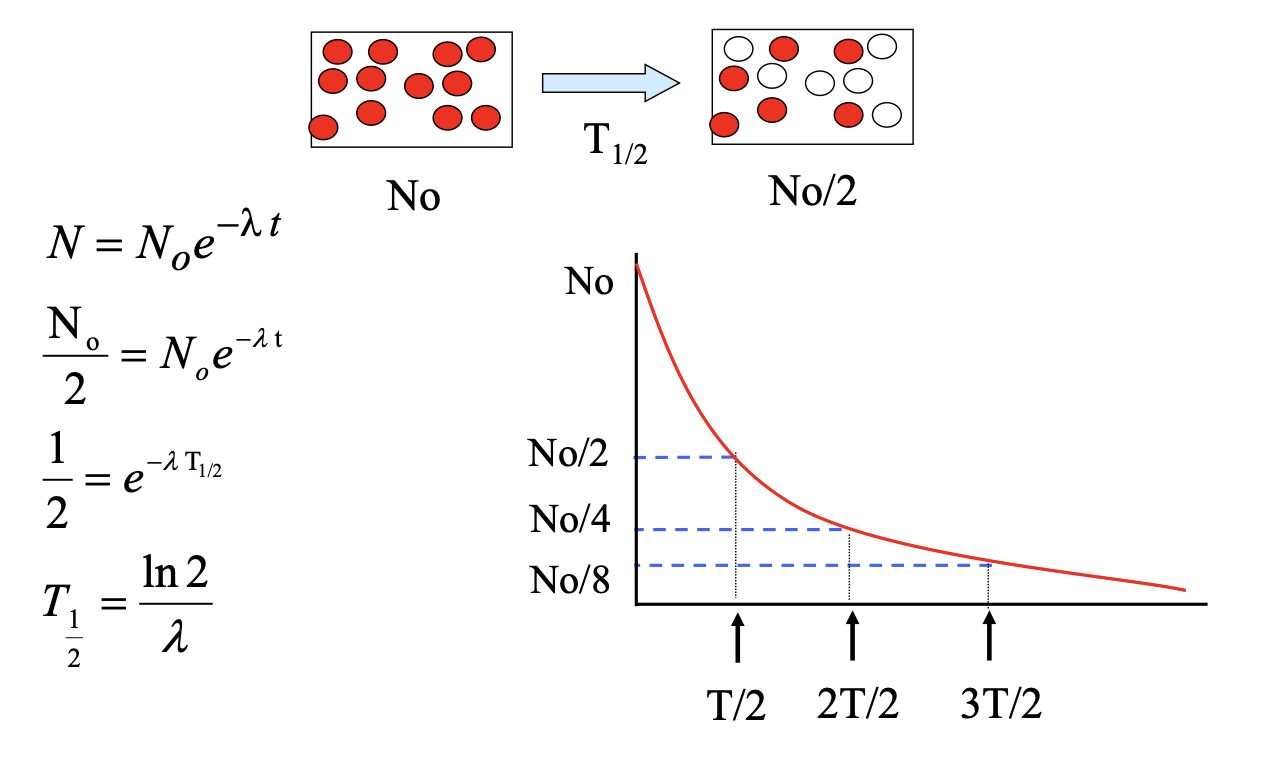
N = N0 e^(−λt)
N = nuclei remaining
N0 = original nuclear
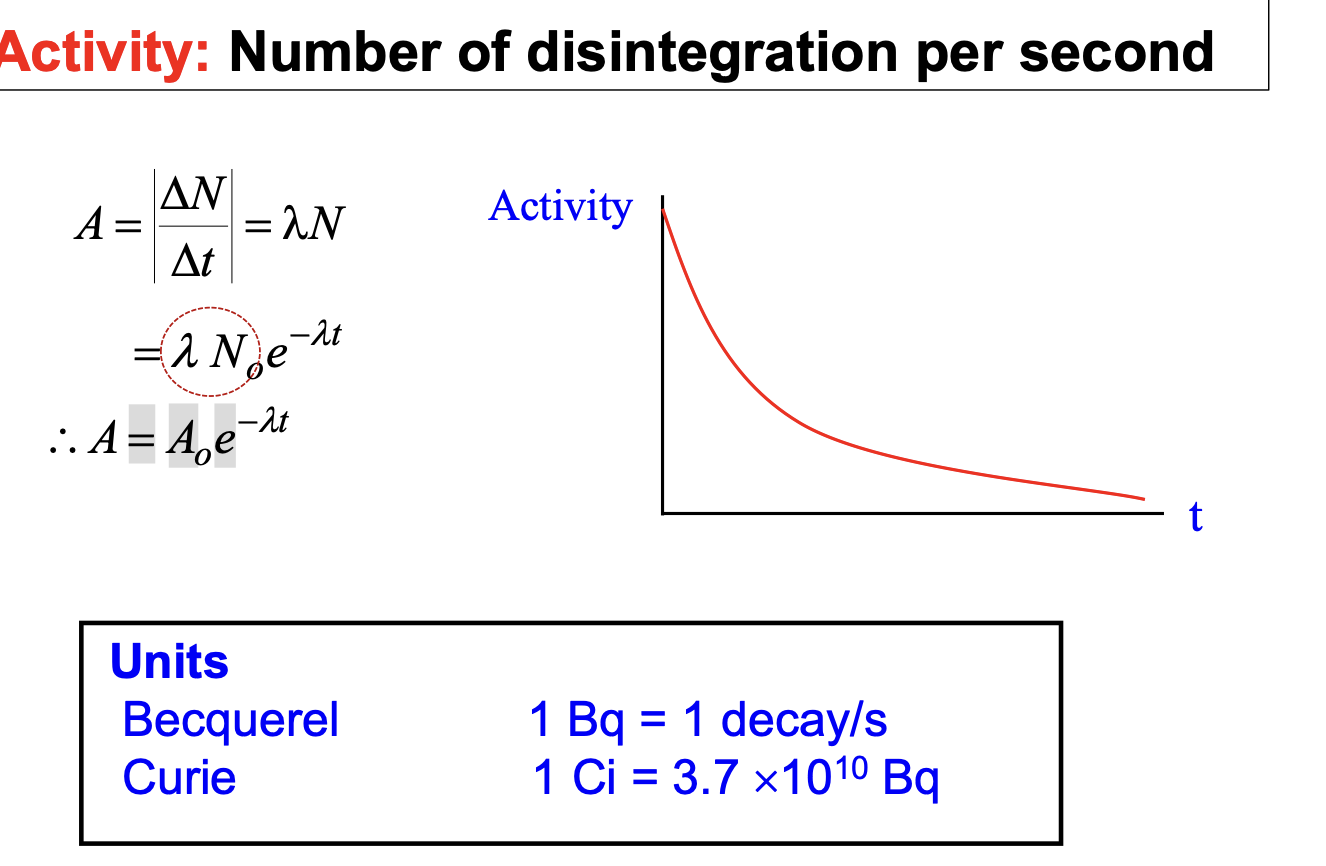
Number of disintegration per second
half life formula: time taken for half the radioactive nuclei to decay
Suppose you have 1g of 238U (T1/2 = 4.5×109 y) and 1g of 226Ra (T1/2 =1.6×103 y)
What is the activity of each:
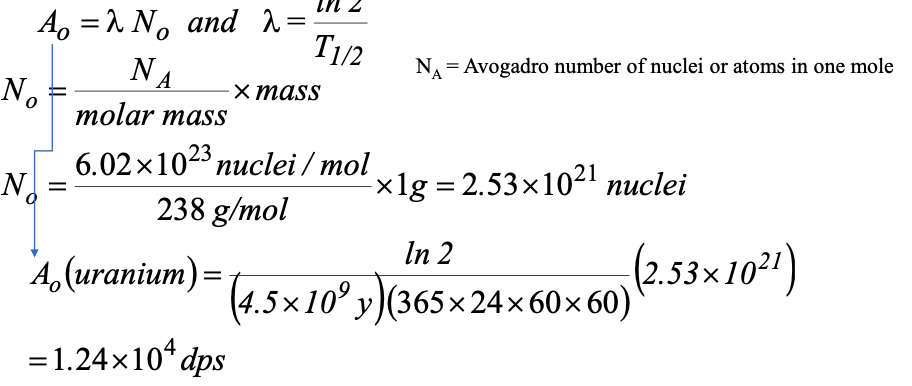

An ancient wooden club is found to contain 290 g of carbon and has an activity of 8.0 decays/s. Determine its age assuming that in living trees the ratio of
14C/12C = 1.3×10-12
T1/2 = 5730 y. (Prob 56/30)
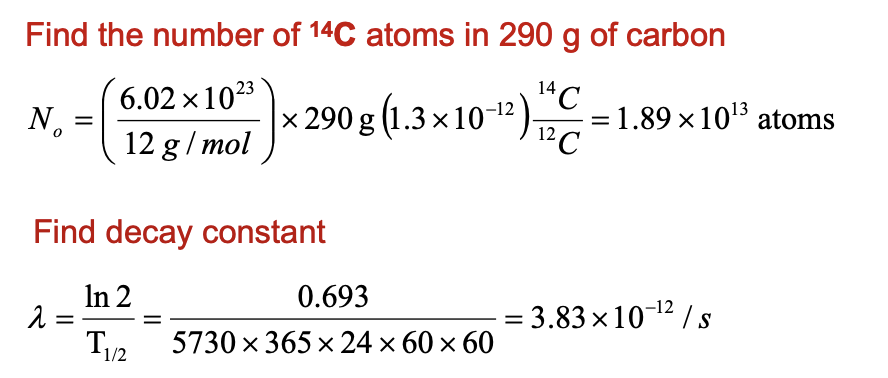

Decay graph for two radioactive samples X and Y are shown
a) Which has a higher probability of decay?
b) What is the half-life of each sample?
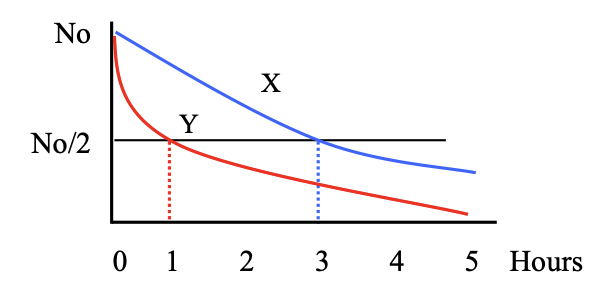
a = Y has a higher probability of decay
b = 1h and 3h