LBBBION Long Exam 1
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
Main objective of scientific papers
To inform
Parts of a scientific paper
Title
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Results and discussion
Conclusion
References
How many words do abstracts have?
150 - 200 words
Tenses used in introductions
Past or present; never future
Tenses used in method
Active voice in past tense
Reference according to the worksheet (kind of citations)
CSE
Reference according to the format (kind of citations)
APA 6th
Stand that supports the microscope
Base
A short piece of metal that supports the microscope. it attaches to one end of the base
Pillar
Used for holding the microscope
Handle or arm
Tilting the microscope
Inclination screw
Holds dust shield and nosepiece
Body tube
Upper end of the body tube that bears the eyepiece or ocular lens
Ocular tube/draw tube
Permits the shifting of the objective lenses
Revolving nosepiece
Above the nosepiece to protect objective lenses
Dust shield
Adjusts LPO in focusing
Coarse adjustment knob
Delicate focusing in HPO and OIO
Fine adjustment knob
Where slides are placed
Stage
Found below stage and attached to the pillar; holds the mirror in place
Mirror rack
Eyepiece magnification
10x
LPO magnification
10x
Scanner magnification
4x
HPO magnification
40x
OIO magnification
100x
Below the stage; regulates entry of light
‘ diaphragm
Types of diaphragms
Ins, plate, fan
Lens found immediately below the nose of the stage; concentrates light rays on the specimen
Condenser
Function of a field diaphragm
Also known as Iris diaphragm; regulates entry of light in the condenser
Why use oil in OIO?
Gives higher resolution) prevents blurs
How to store the microscope?
Scanner lens in place
Lower stage
Turn off light source
View in the microscope
Inverted
Does the view in the microscope move to the left if you move the slide to the left?
No, it moves in the OPPOSITE direction
Relationship between magnification and field of view
As magnification increases, field of view decreases
How to calibrate the scanner lens using the stage micrometer
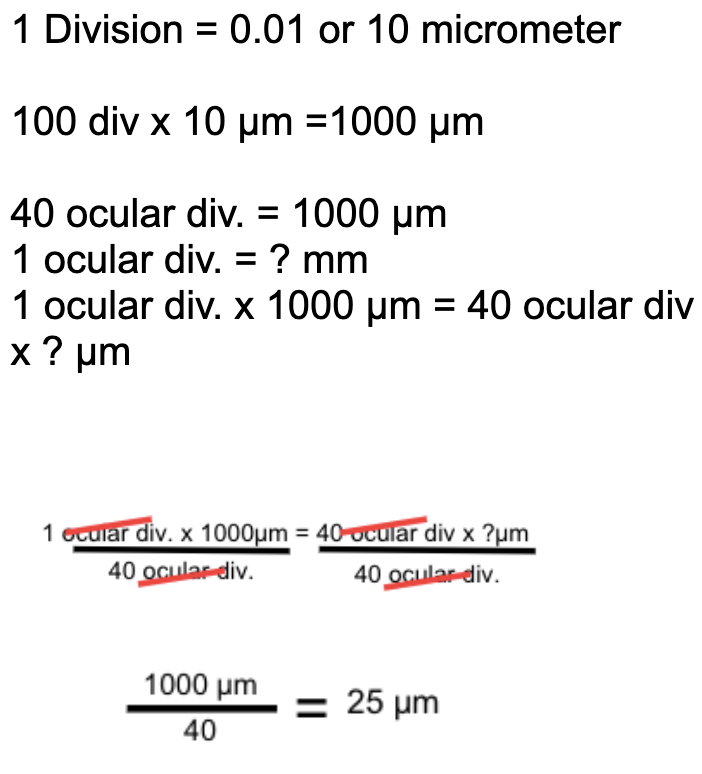
How to calibrate the LPO using the stage micrometer

How to calibrate the HPO using the stage micrometer
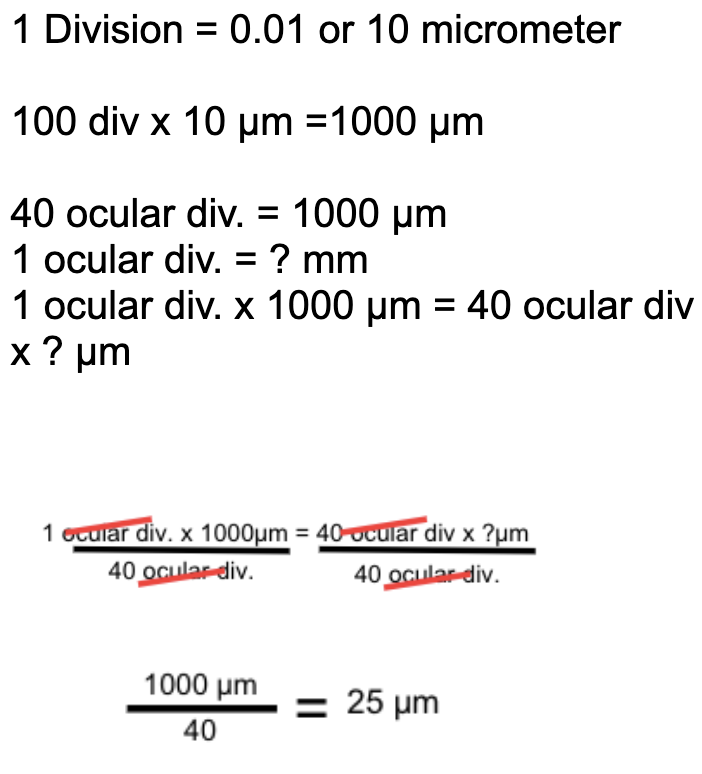
How to calculate the size of the cell without a stage micrometer?
Size = field of view (in mm)/number of cells across
How to compute the magnification of drawing from the size of the drawing and its actual size?
Size of drawing/actual size
Compare magnification, contrast, and resolution
Magnification: small objects are seemingly larger
Resolution: ability to distinguish two objects from each other
Contrast: lightness or colorless or transparent specimens relative to the darkness in the background
How to compute for the percent water or moisture
[(fresh weight - dry weight)/fresh weight] x 100
How to compute for percent organic matter
[(dry weight - ash weight)/fresh weight] x 100
How to compute for percent inorganic matter
(actual weight / fresh weight) x 100
Why determine the percent composition of water, organic and inorganic constituents in a living plant?
These results can be important in various fields of plant science, including agriculture, nutrition, and environmental studies, as they provide insights into the composition of living plants and their nutritional content.
What is the Benedict’s test used for?
To determine the presence of reducing sugars.
What are reducing sugars?
The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively donate electrons to some other molecule by oxidizing it. All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars
What sugars in the experiment exhibited a positive result for the Benedict’s test?
Glucose, fructose, maltose, and very low/faint positive result for starch
How to interpret Benedict’s test results
The "hotter" the final color of the reagent, the higher the concentration of reducing sugar. In general, blue to blue-green or yellow-green is negative, yellowish to bright yellow is a moderate positive, and bright orange is a very strong positive
What does the Barfoed’s test assess?
Monosaccharides
What hints at a positive result for the Barfoed’s test?
Dark red precipitate formed
What does the Iodine test prove?
The presence of starch
What signifies a positive result for the Iodine test?
Dark blue in color
What tests the presence of proteins?
The Biuret Test
What signifies a positive result for the Biuret test?
Pink/purple/pink-purple hue from light blue color
What is the test for starch?
Iodine Test
What are predatory journals?
Journals that ask you to shell out a large amount of money to have your article published in their journal
Why is peer-reviewing necessary in scientific papers?
Increases validity and accuracy by having other experts in the field review your paper
What signifies a positive result for the Iodine test?
Dark blue color from its transparent state
Will evaporated milk test positive in the Biuret test?
Yes, since milk contains protein
Will tryptophan and phenylalanine test positive for the Biuret test?
No, because these are amino acids, not proteins
What does the lipid test (residue test) assess?
Used to detect the presence of lipids within substances
Will glycerol test positive for the residue test?
No, since glycerol is an alcohol. It may be important in the formation of lipids, but is not a lipid in itself
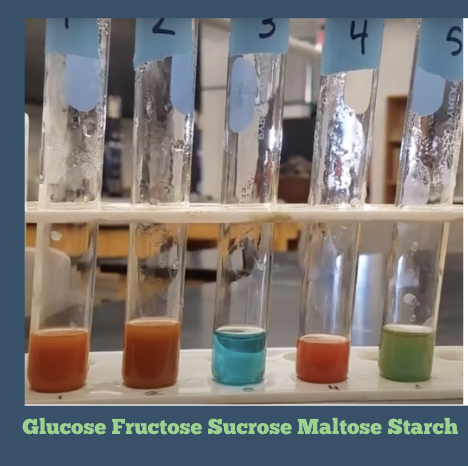

Which of these is positive? (Benedict’s Test)
Glucose
Fructose
Maltose

Which of these is positive? (Barfoed’s Test)
Glucose
Fructose

Which of these is positive? (Iodine Test)
Starch
Sudan Test is for what?
If it contains lipids

Is this positive? (Sudan Test)
Yes, the fat is incorporated and mixed well in the solution

Is this a positive result for Sudan Test?
Yes, it clearly split into separate layers

Which are positive?
All
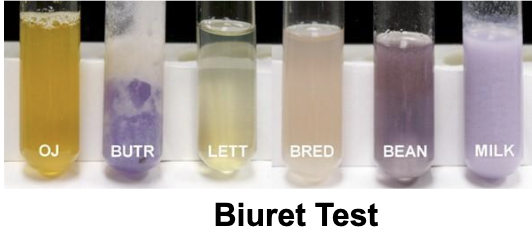
Which are positive?
Almond butter, beans

Which are positive?
Bread, beans
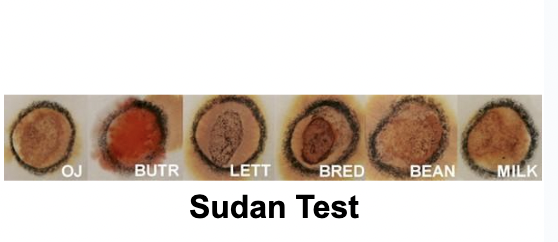
Which are positive?
All
How did the cell came to be?
Robert Hooke studied the cork under a microscope, where he named it as “cells” after he noticed how they resembled the cells that monks used to reside in
Rigid structure that supports the cell
Cell wall
The cell wall is made up of what?
Cellulose, pectin, hemicellulose, and. glycoproteins
Cytoplasm is__________
a gel-like mixture that fills the cell, excluding the nucleus
it is surrounded by the cell membrane
What is the cell’s command center?
Nucleus
This contains the genetic information of the cell
Nucleus
Why is staining important?
Increases contrast
Why is adding oil in OIO important?
Increases resolution
Creates rRNA to make ribosome and sends mRNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis
Nucleolus
What helps maintain the cell wall’s structure and shape?
Structural proteins
Threads of cytoplasm that passes through cell walls of adjacent cells
Plasmodesmata
What enables communication between adjacent cells?
Plasmodesmata
What glues cells together and is made of calcium and magnesium pectates?
Middle Lamella
Structure of the cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer that has a fluid mosaic model
What prevents the cell from bursting due to pressure?
Cell walls
Permeability of the plasma membrane
Selective permeability/semi-permeable
Functions of the plasma membrane
Transport of molecules
Maintains cell homeostasis
Sends and receives signals to/from other cells
What kind of molecules does the plasma membrane allow to pass through?
Gases (such as O2 and CO2), hydrophobic molecules (such as benzene), and small polar but uncharged molecules (such as H2O and ethanol) are able to diffuse across the plasma membrane
Responsible for the production of food within plant cells
Plastids
Contain photosynthetic pgments
Plastids
Kind of plastid that has the main function of photosynthesis.
Chloroplast
Green color of chloroplasts come from ________
chlorophyll
How many chloroplasts can plant cells hold?
300 chloroplasts
Circular movement of organelles around the vacuole which can be counter or clockwise
Cyclosis
What process enables better exchange of materials around the cell?
Cyclosis
Oblong-like bodies that hold carotenoid pigments that exude a bright yellow, orange, or red color
Chromoplasts
Responsible for signaling other organisms in the environment when it’s ripe or ready to pollinate
Chromoplasts
What are the types of plastids?
Chloroplasts
Chromoplasts
Leucoplasts
These do not contain photosynthetic pigments and is often found in plants or parts of plants that require storage for materials
Leukoplasts