DNA Replication & Cell Cycle
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
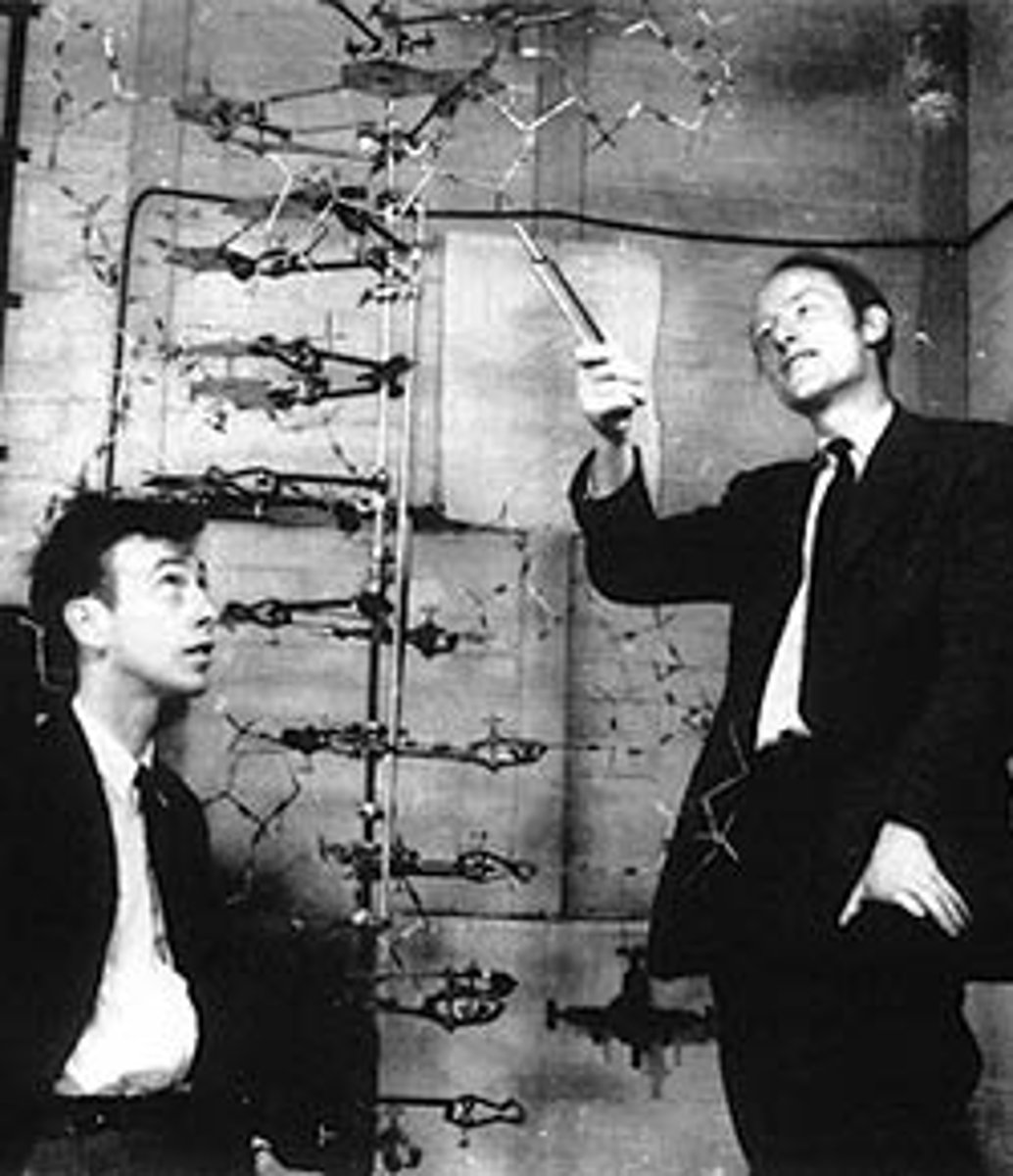
James Watson & Francis Crick
discovered the structure of DNA

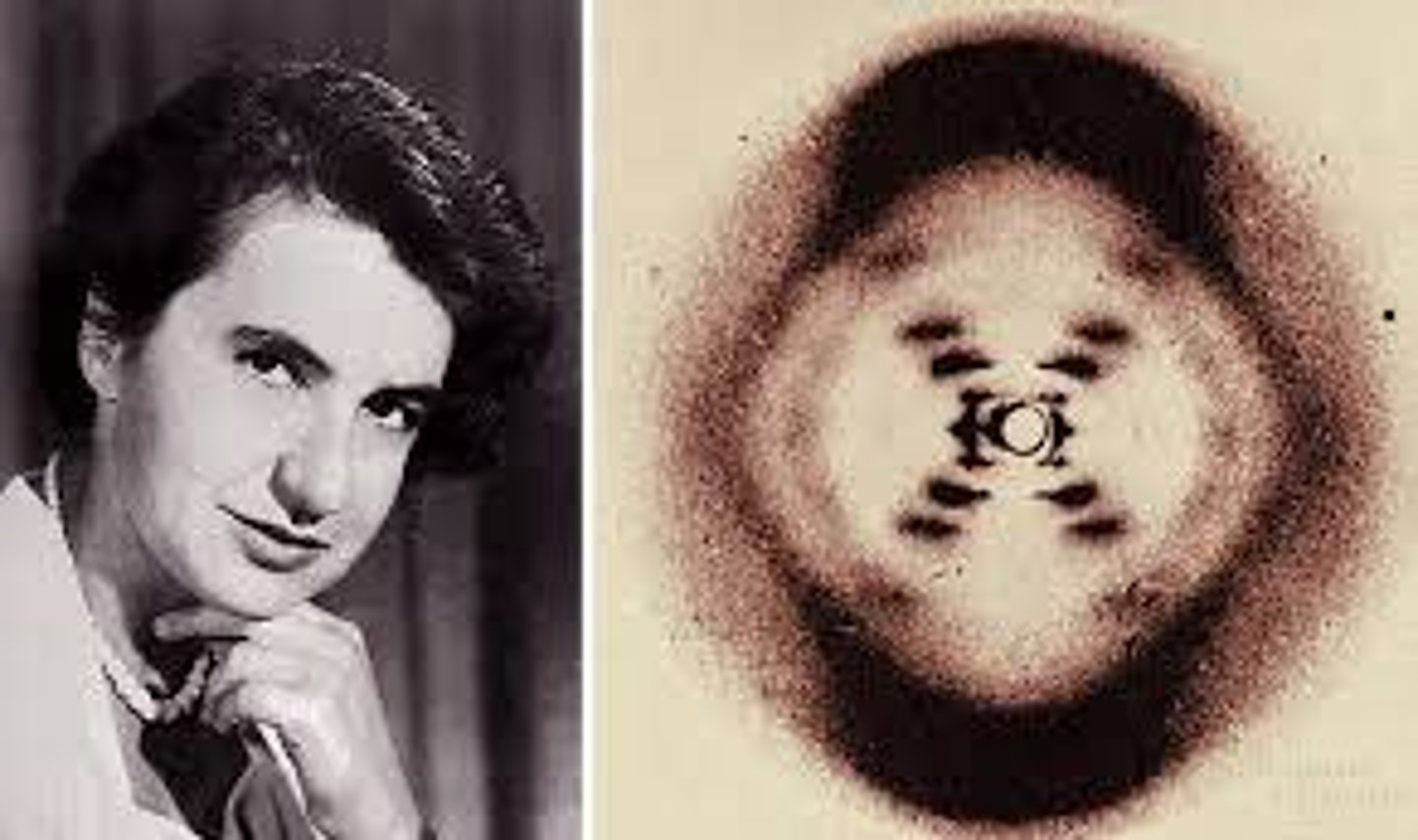
Rosalind Franklin
Took pictures of DNA using X-ray x-ray crystallography. Took Photo 51 which showed DNA was an alpha helix.

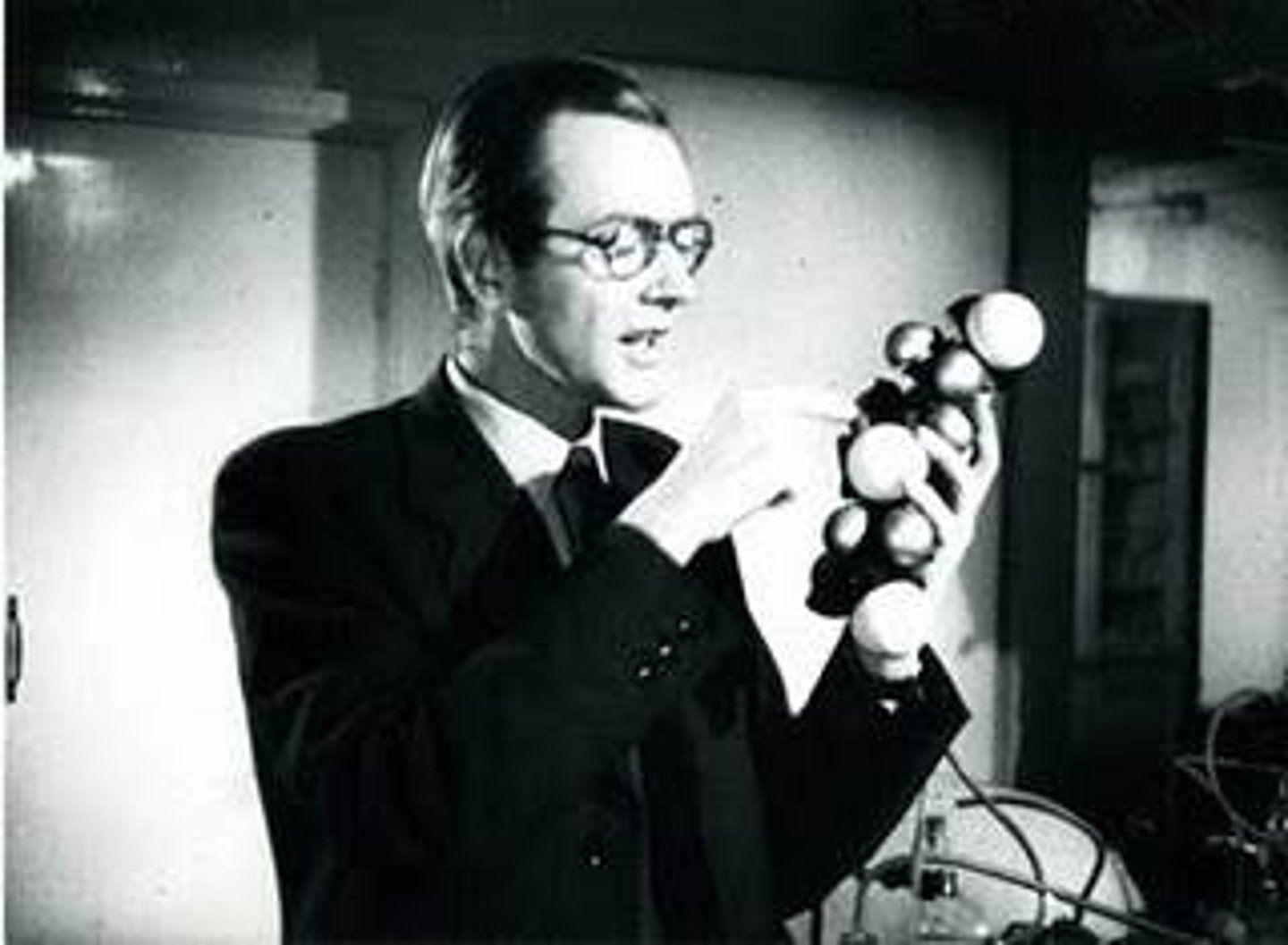
Maurice Wilkins
Used X-ray crystallography to study the molecular structure of DNA. Worked with Franklin (did not collaborate well) to create a picture of the DNA molecule which allowed Watson and Crick to deduce the double helix structure of two strands.

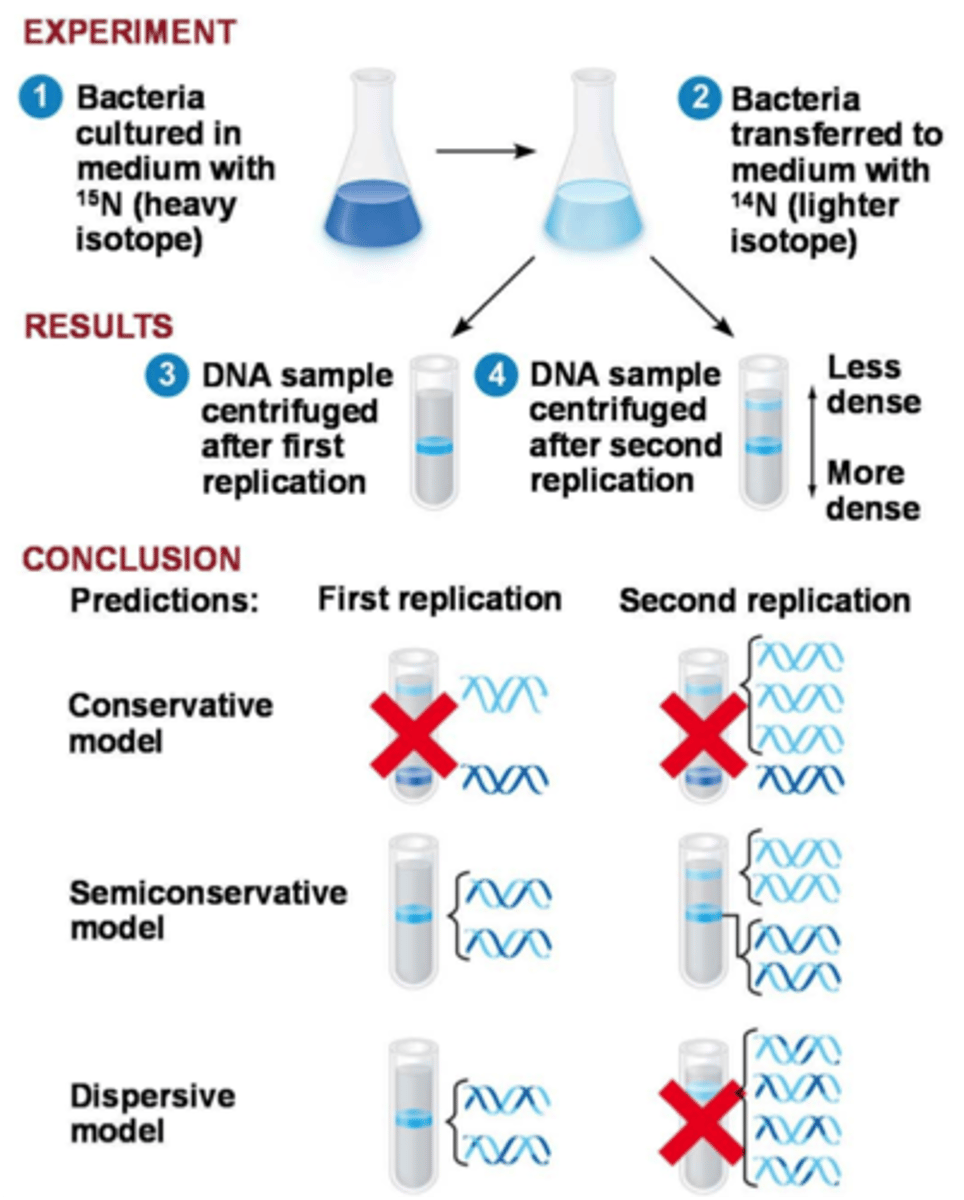
Meselson and Stahl
Determined that DNA replication is semiconservative in experiment using E. coli bacteria
Interphase & Mitotic phase
two phases of the cell cycle
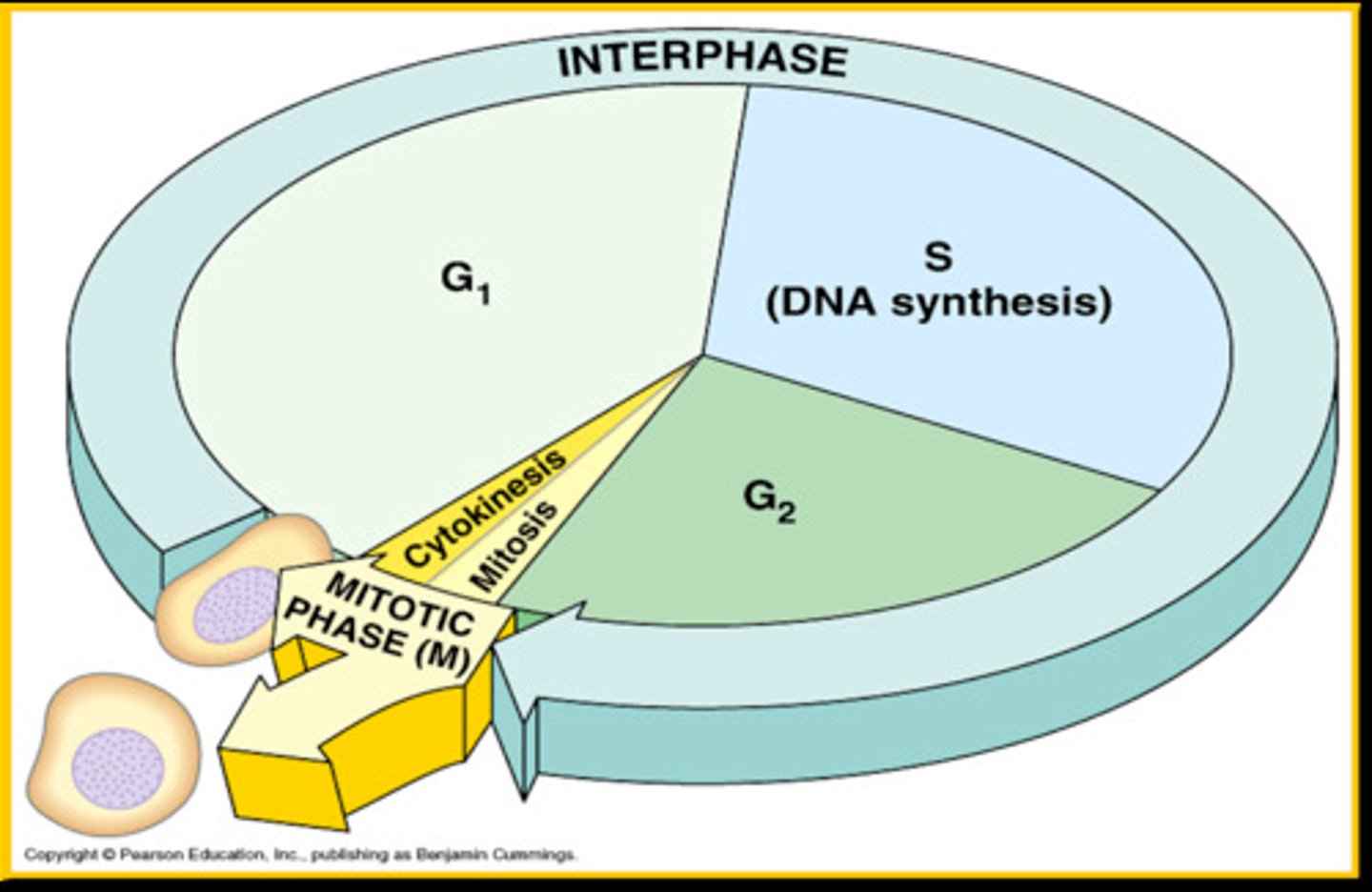
G1, S, G2
stages of interphase
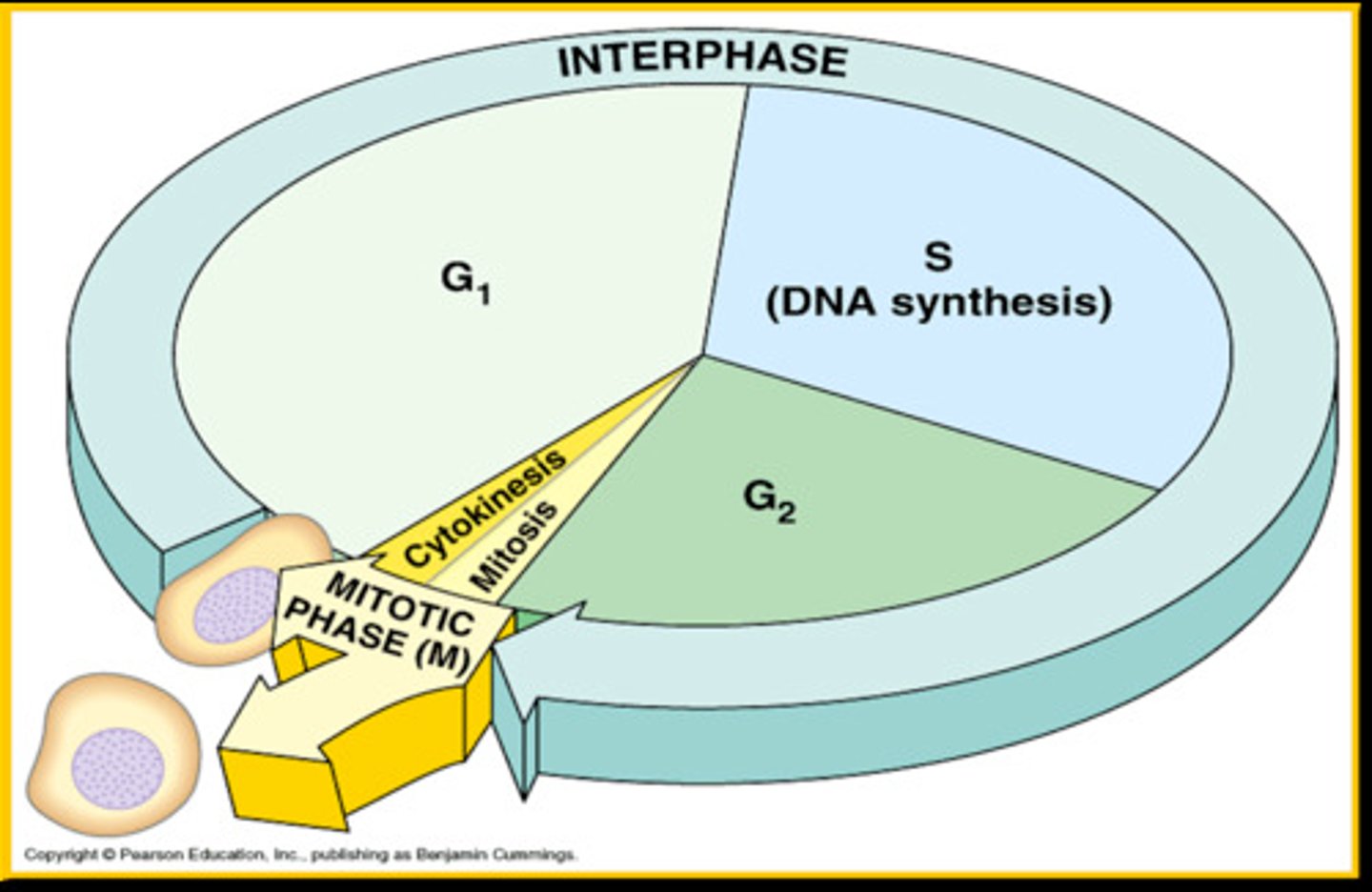
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
G1: Gap 1
Cell growth
G2: Gap 2
preparation for division
Prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis in which the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the chromosomes become visible, nuclear membrane disappears. centrosomes/centrioles move to opposite sides of cell, and spindle forms.

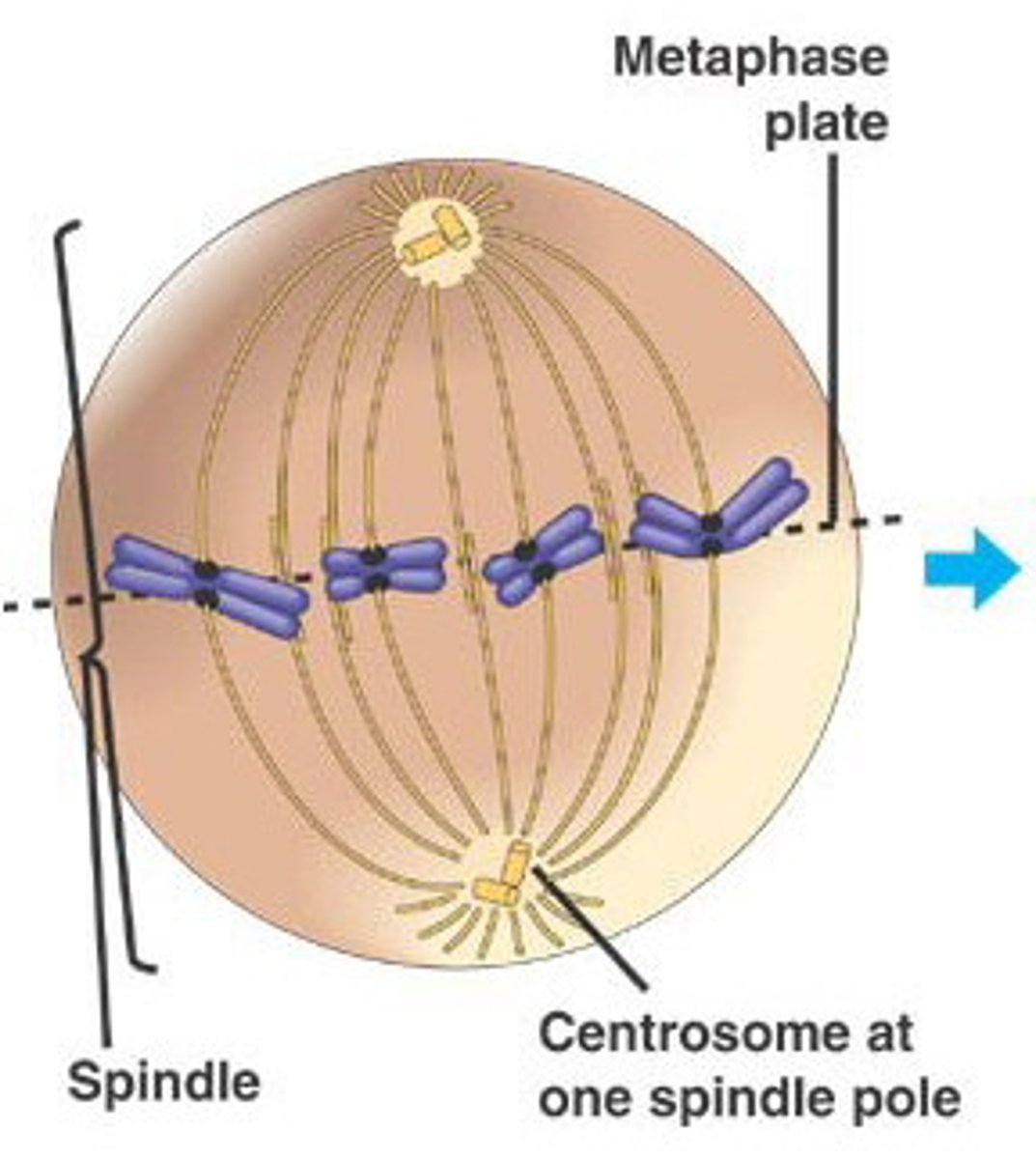
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
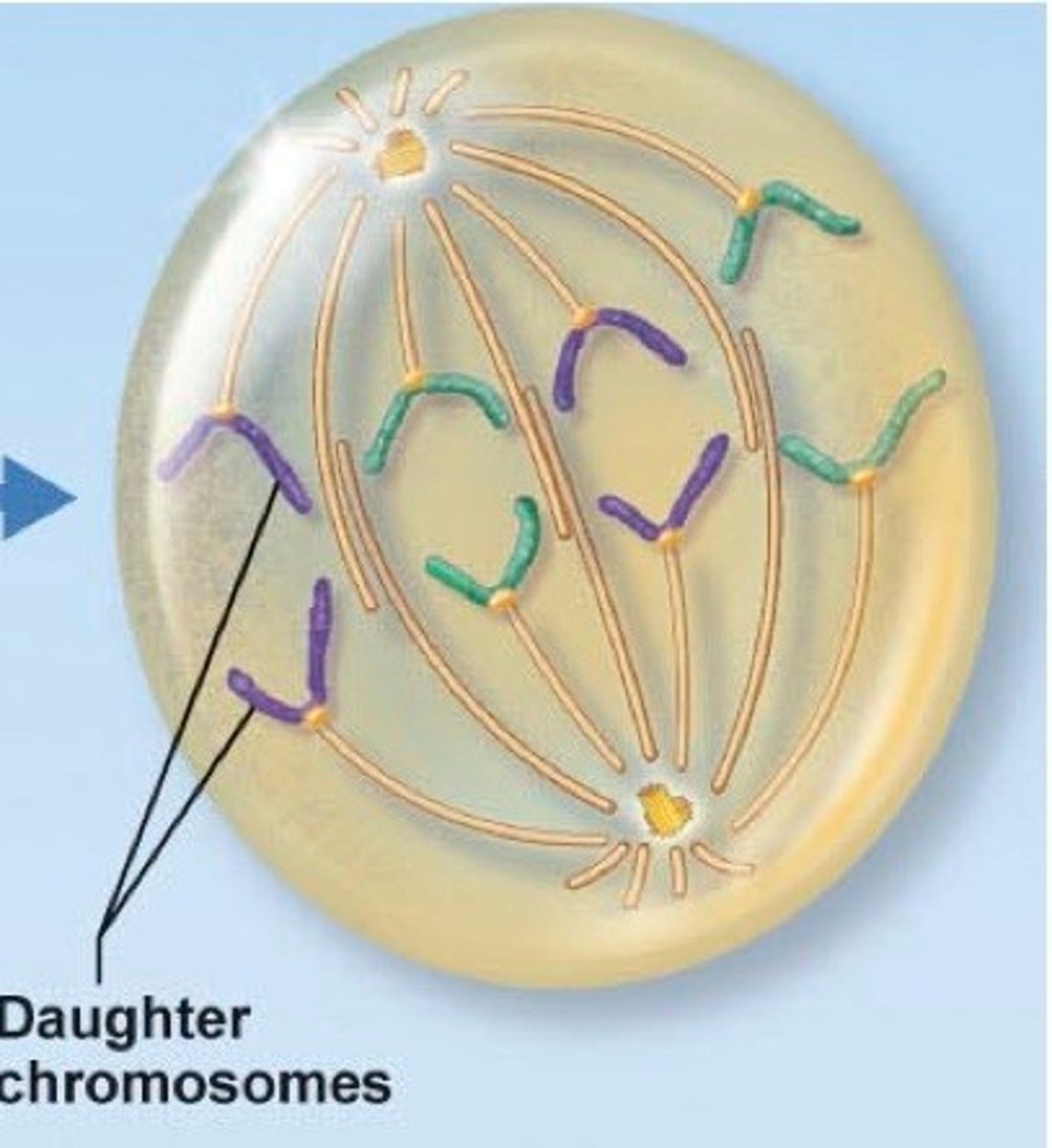
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
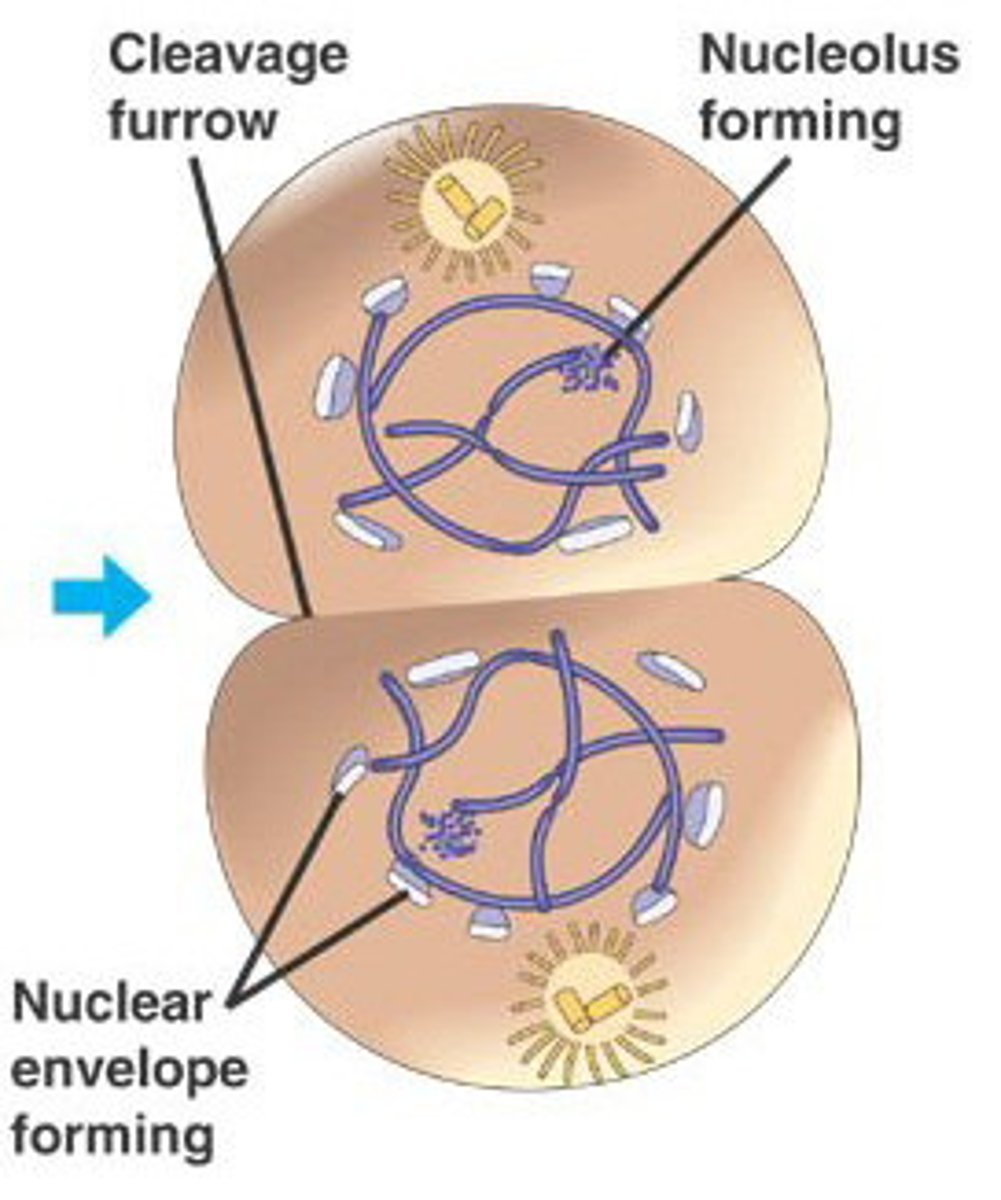
Telophase
Phase of mitosis in which a nuclear membrane reforms around each new set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
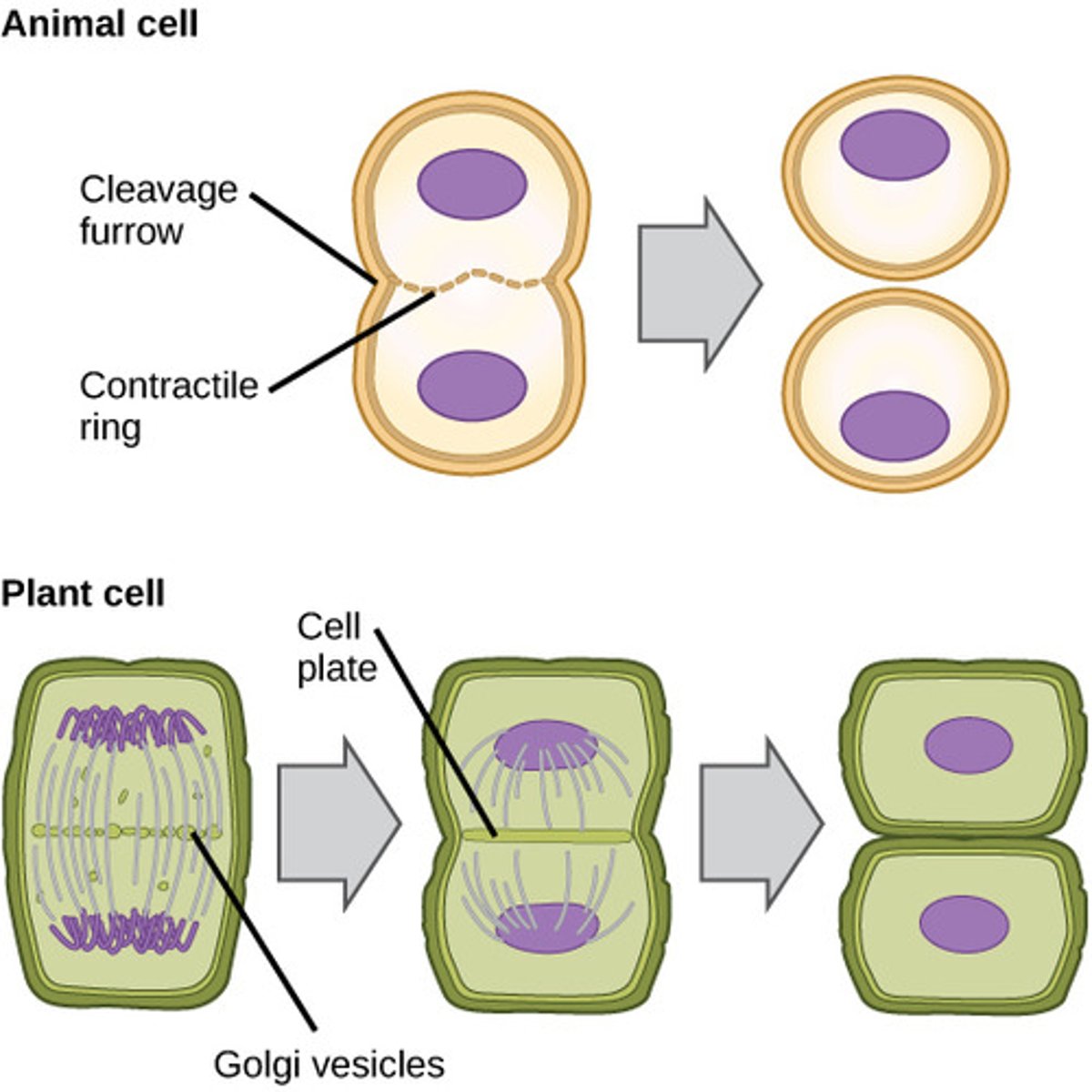
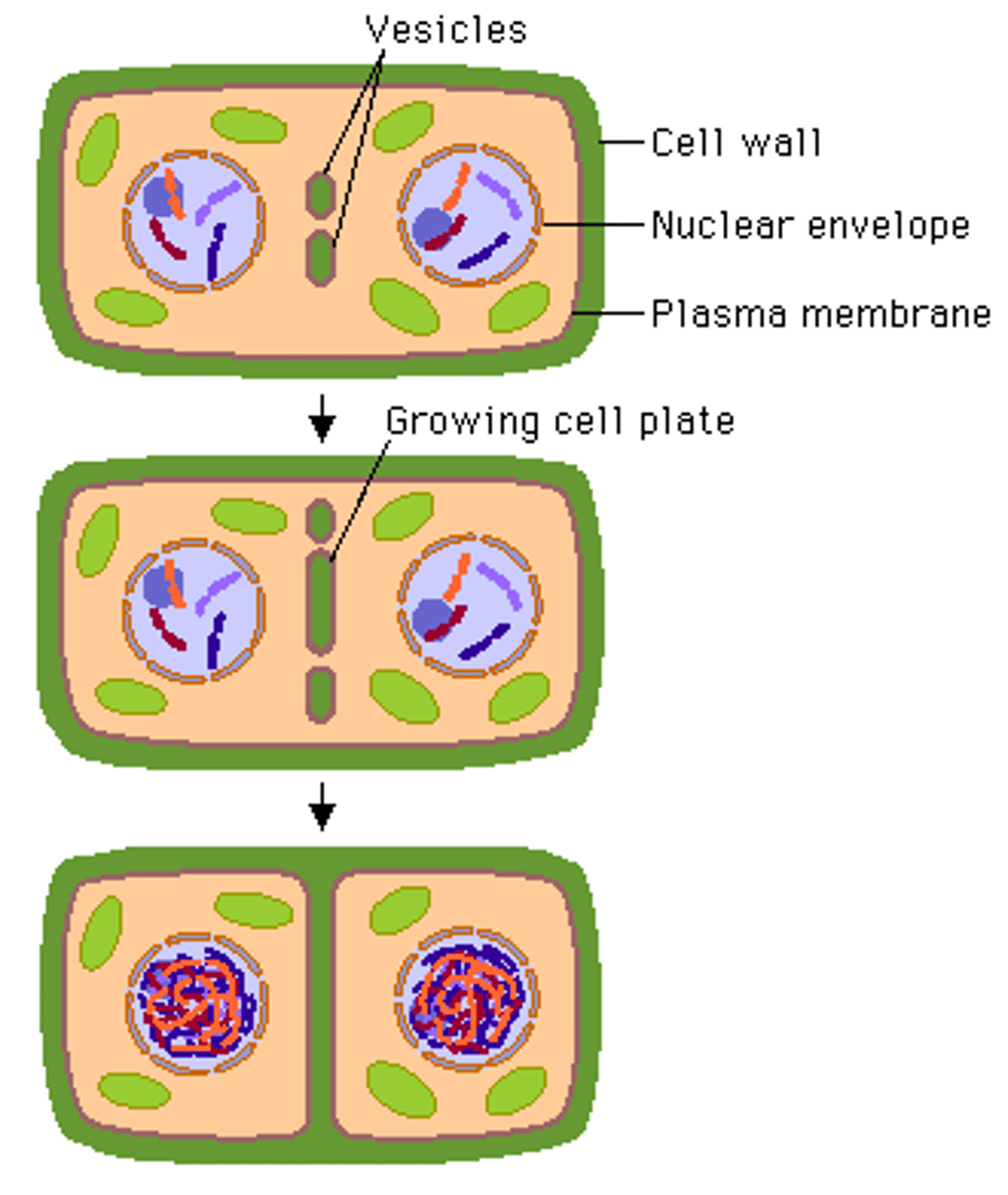
Cell plate
the precursor of a new plant cell wall that forms during cell division and divides a cell into two
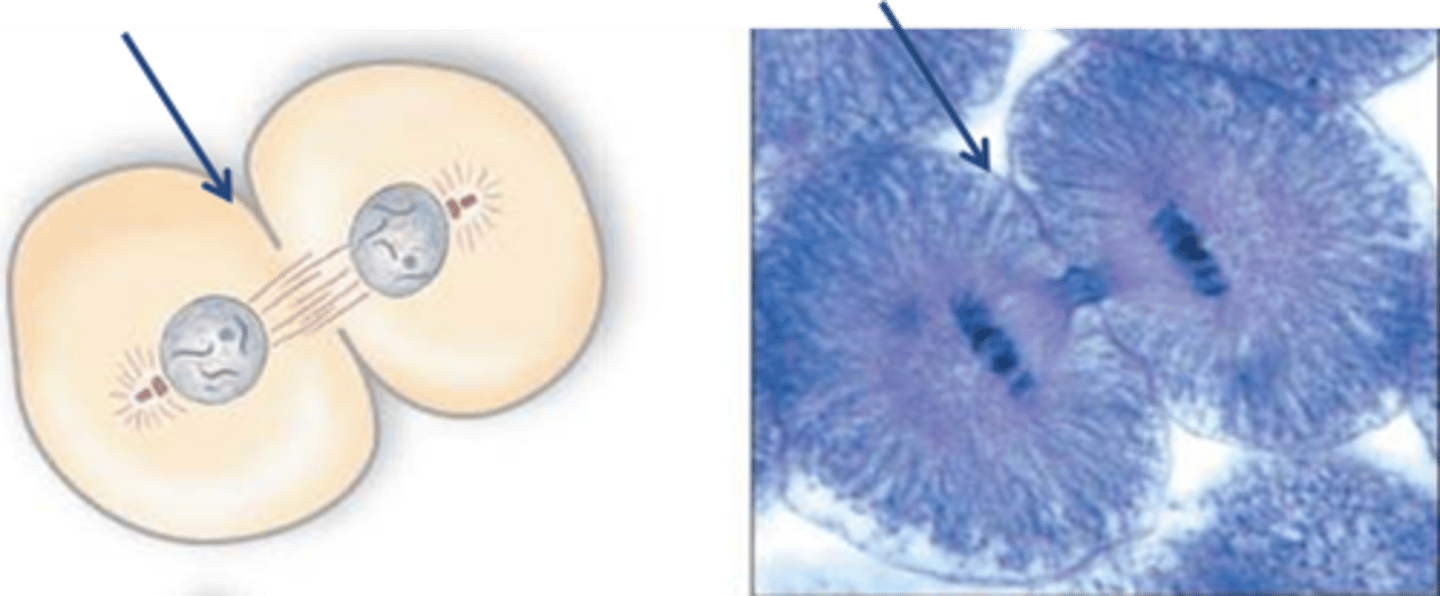
Cleavage furrow
The area of the cell membrane that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell in animal cells.
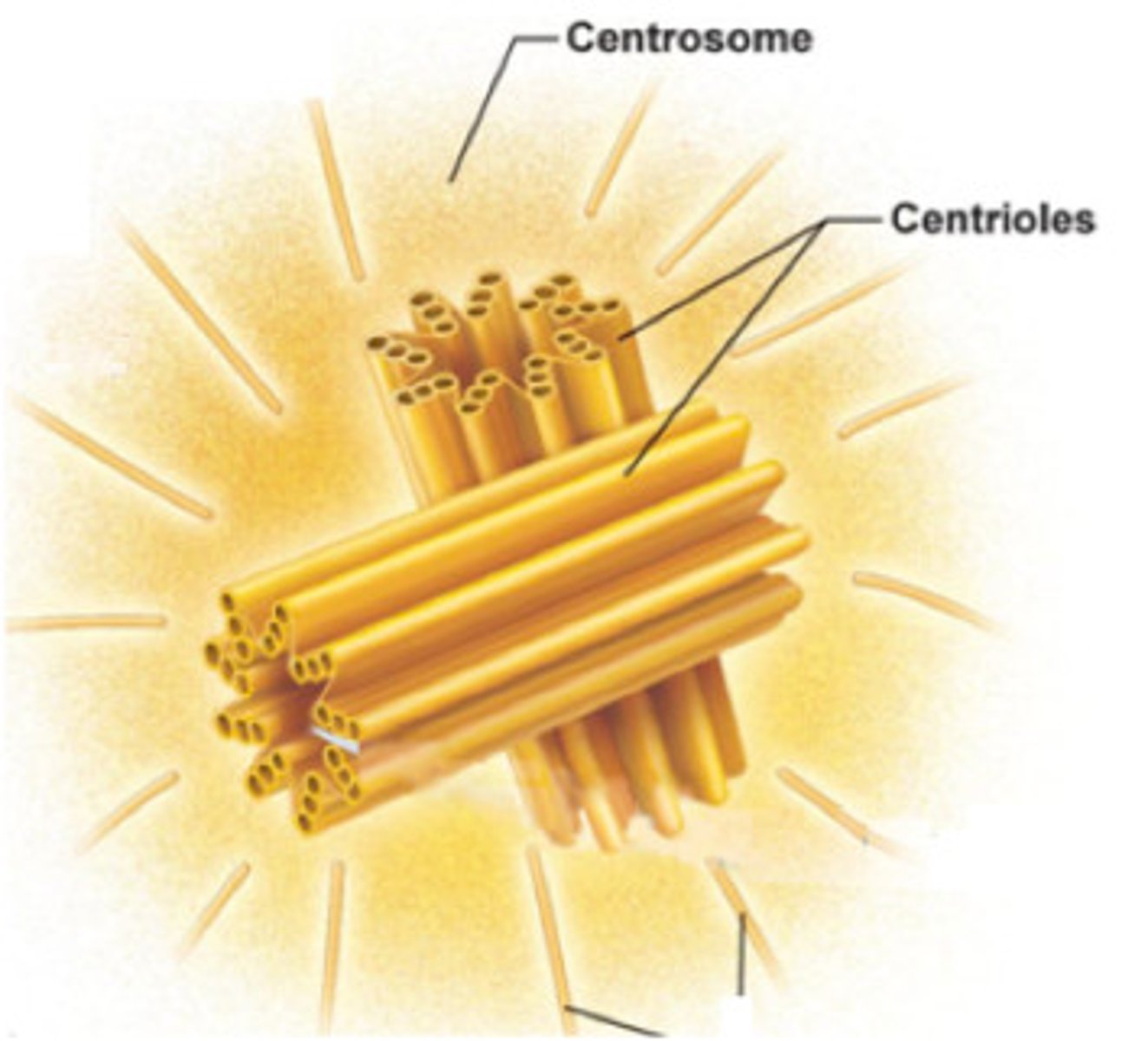
Centrosome
forms mitotic spindle
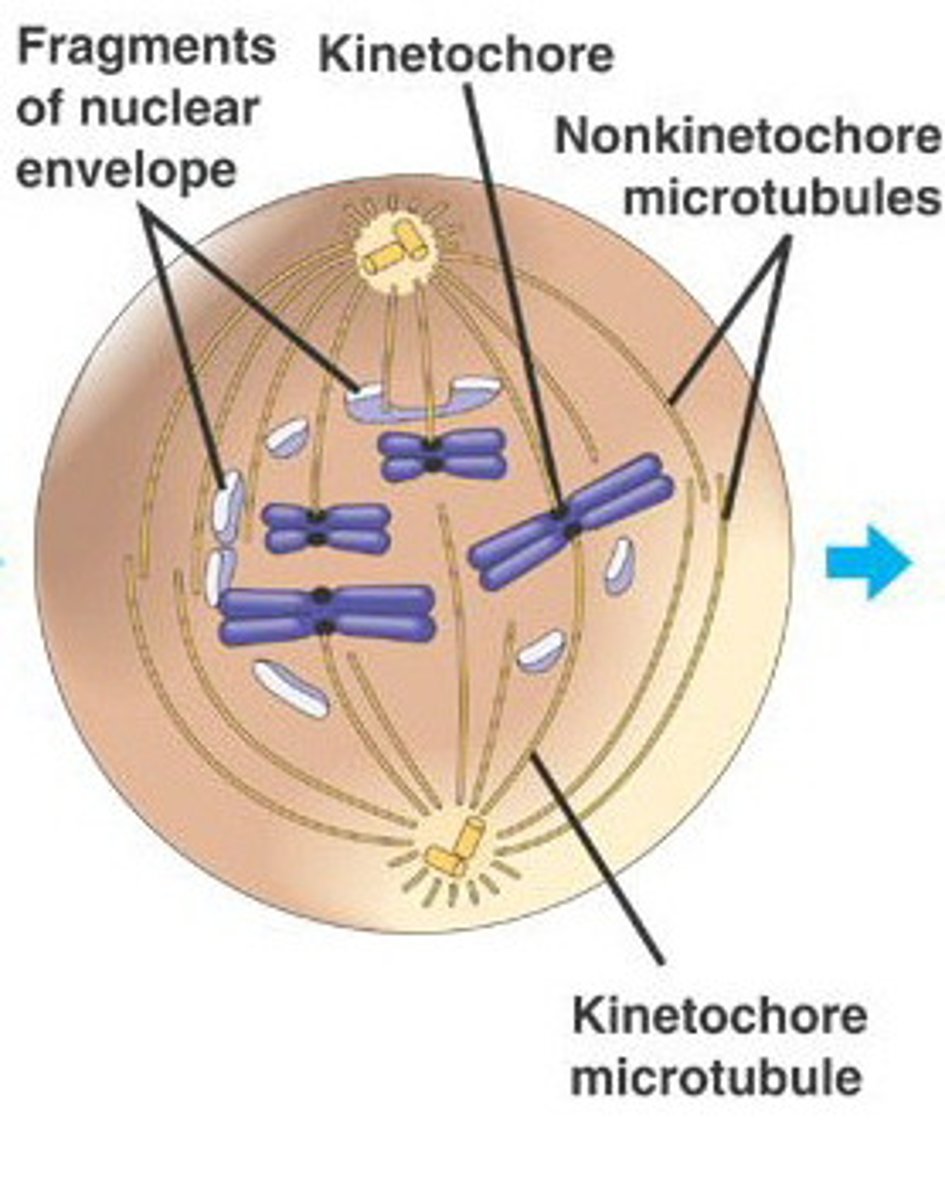
centromere
narrowing region of chromosome, holds sister chromatids together

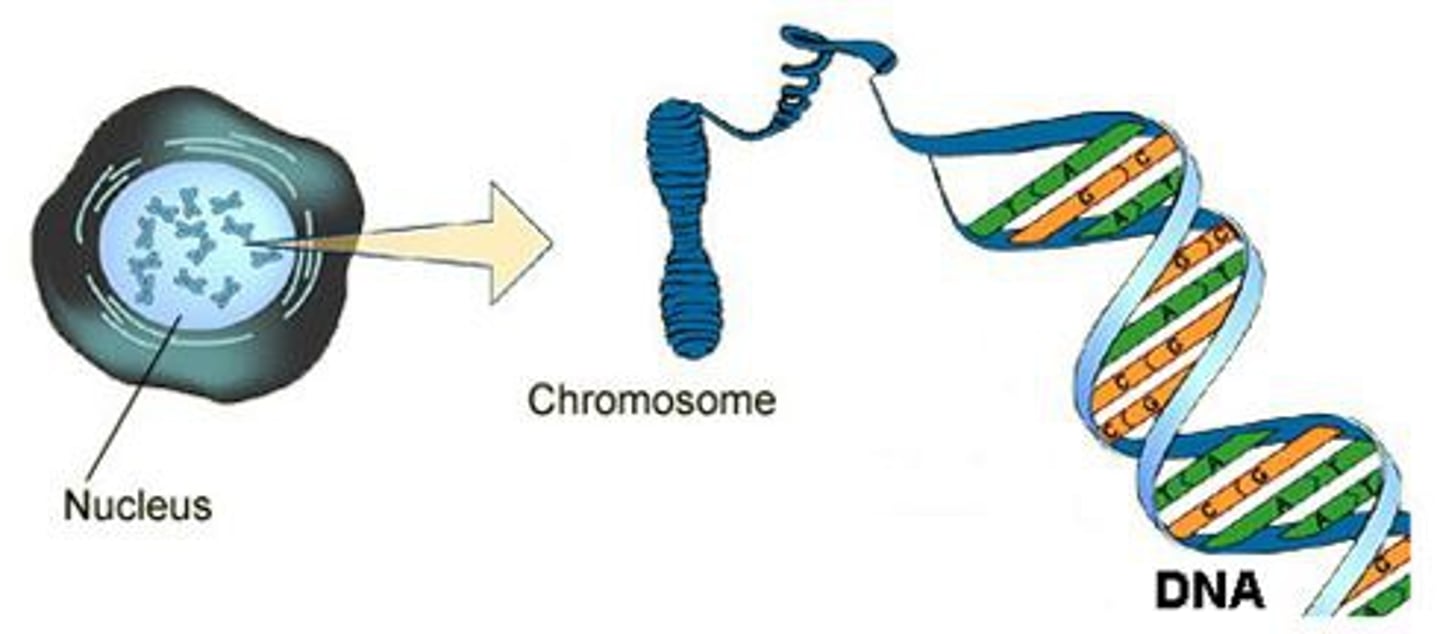
Chromosome
A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
Kinetochore microtubules
spindle fibers that attach to the chromosomes at the kinetochore, they pull chromosomes to the poles of the cell during mitosis
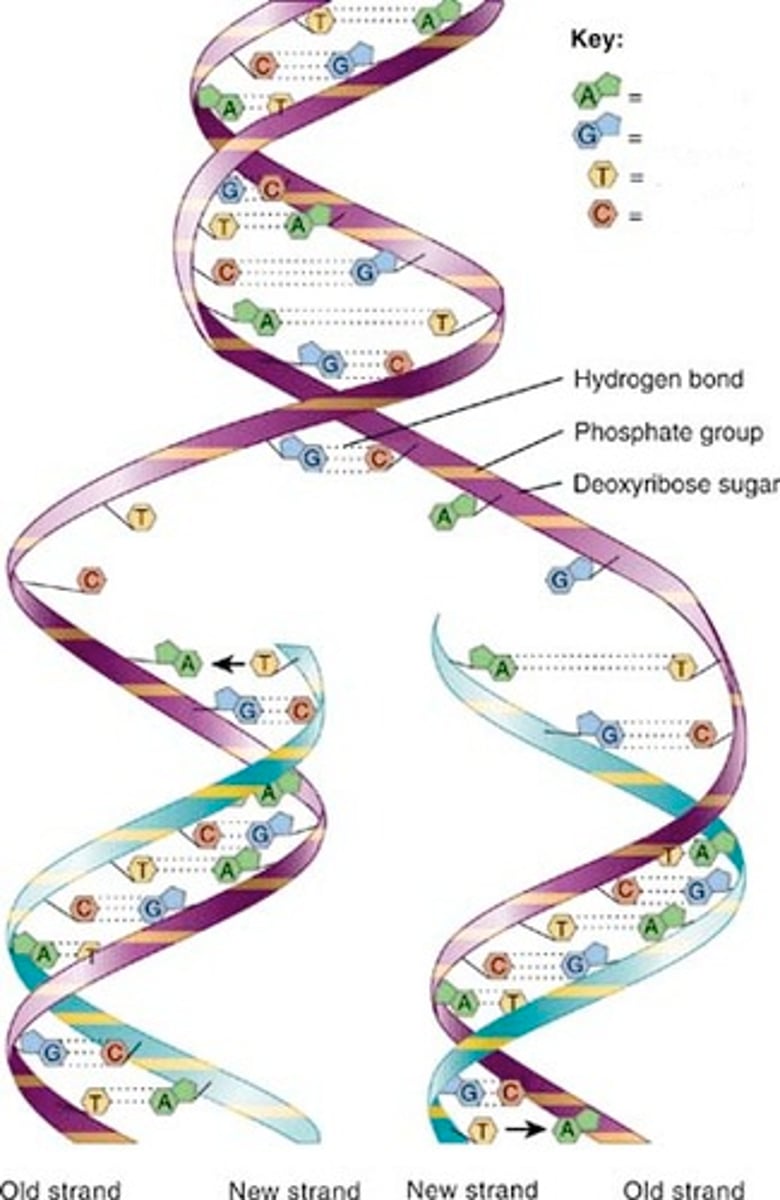
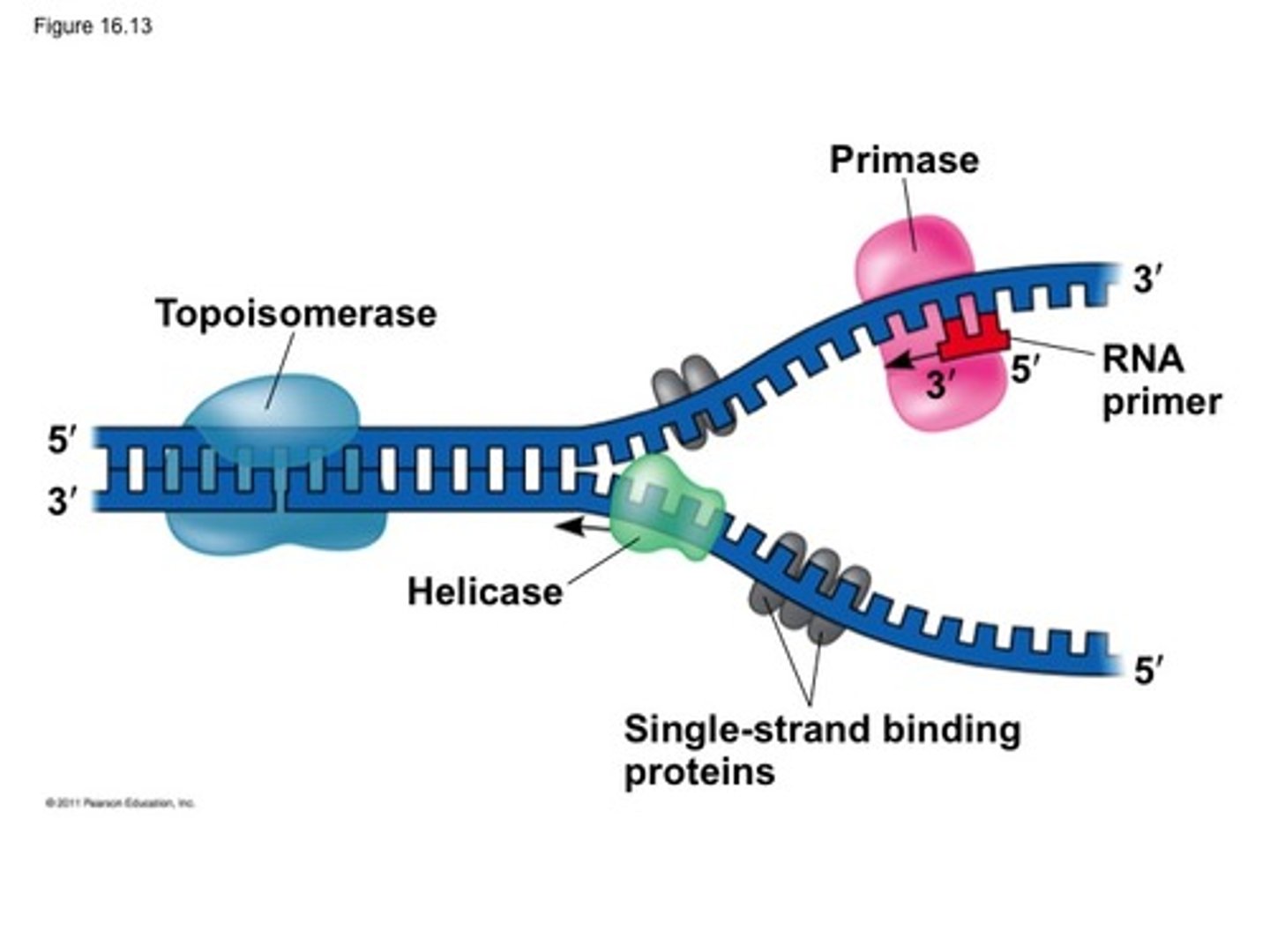
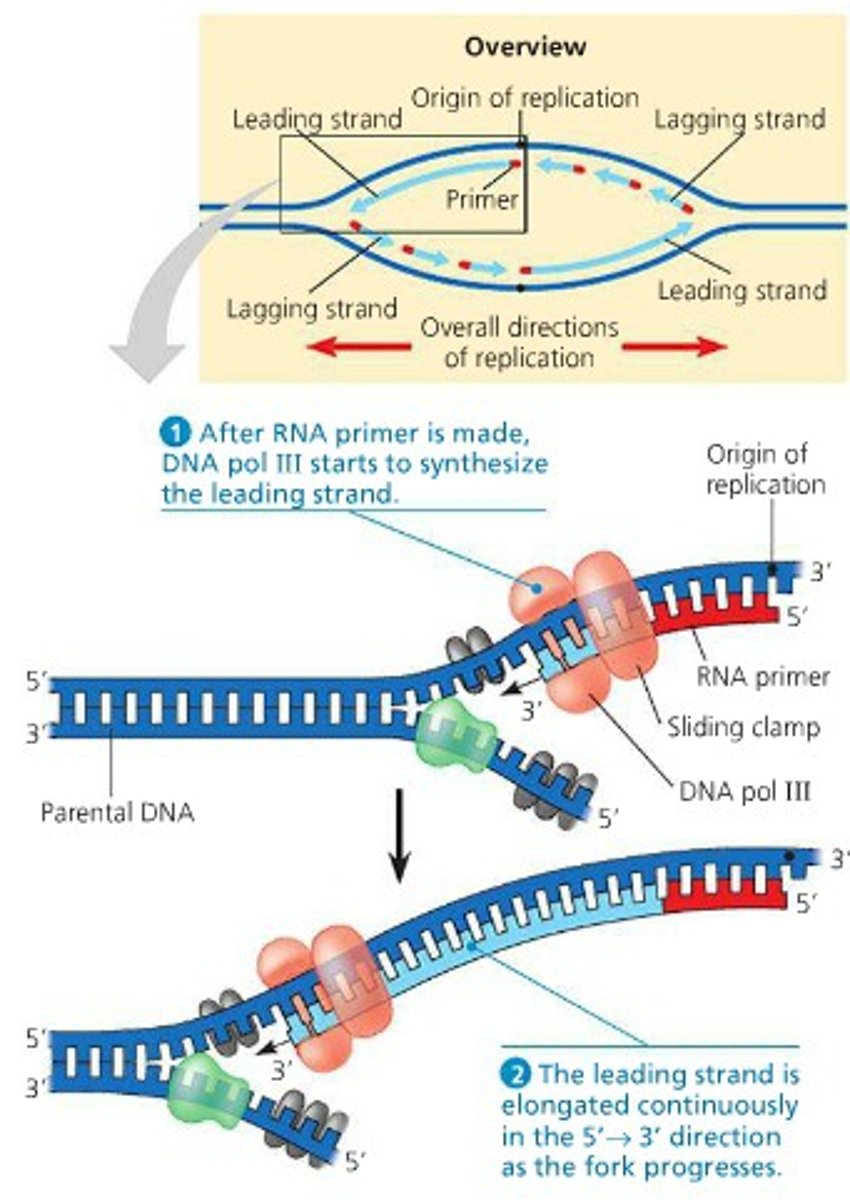
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
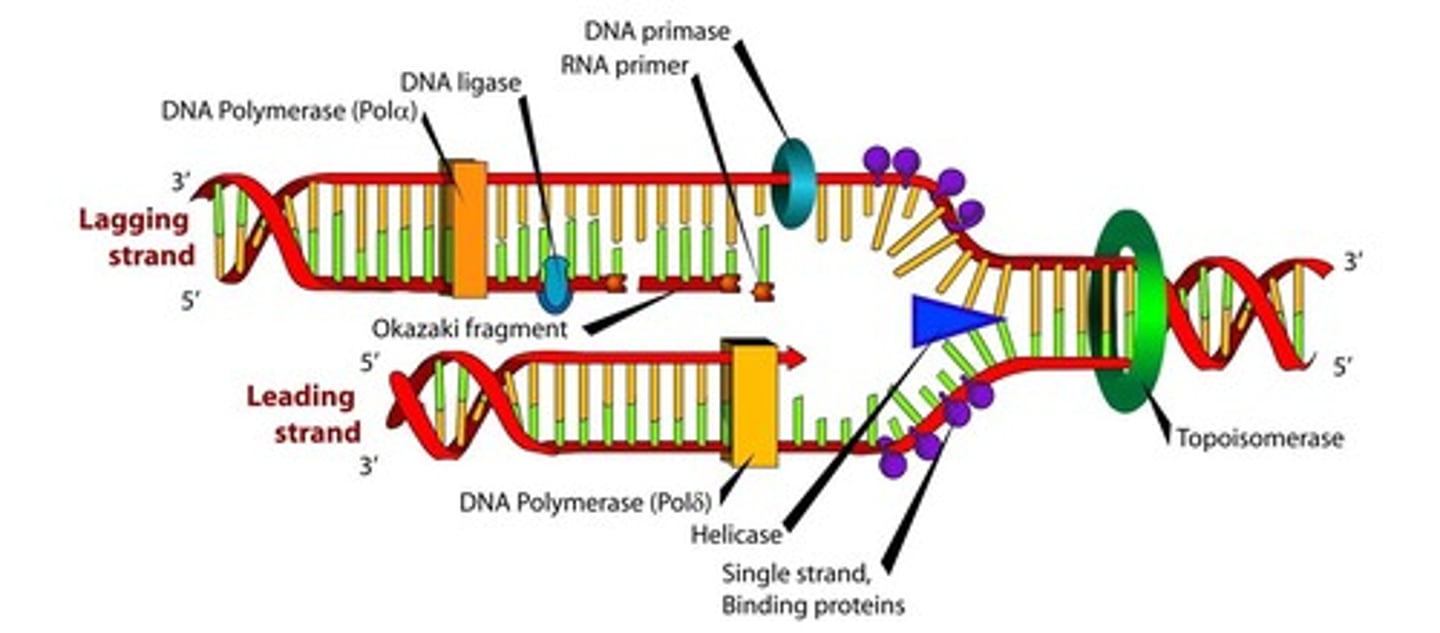
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork.
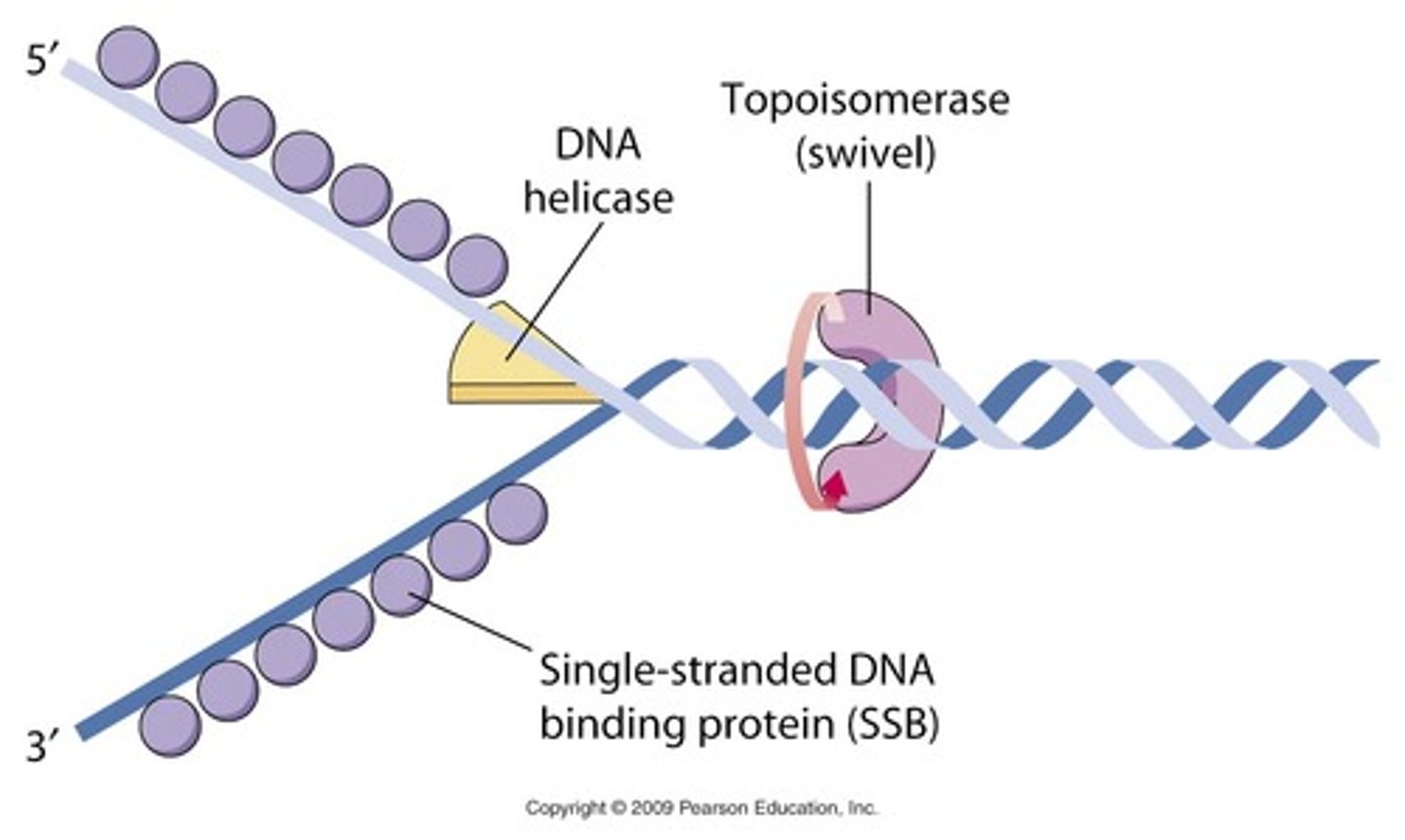
single strand binding protein
binds to the separated strands of DNA to keep Hydrogen bonds from reforming
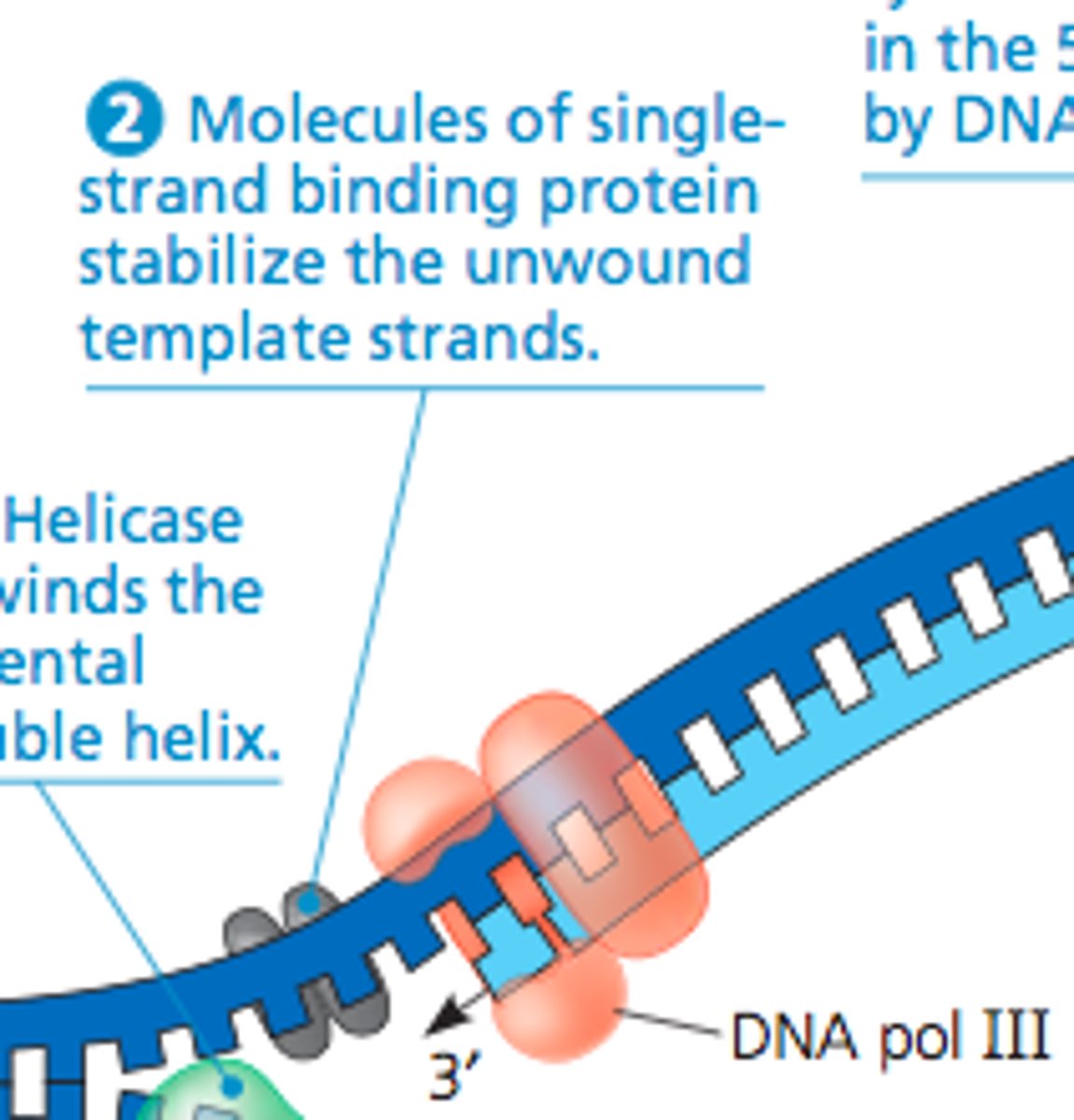
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer to start DNA synthesis.
DNA polymerases
Family of enzymes involved in DNA replication. One copies the DNA by adding complementary nucleotides, another removes & replaces primers, and another proofreads & repairs.

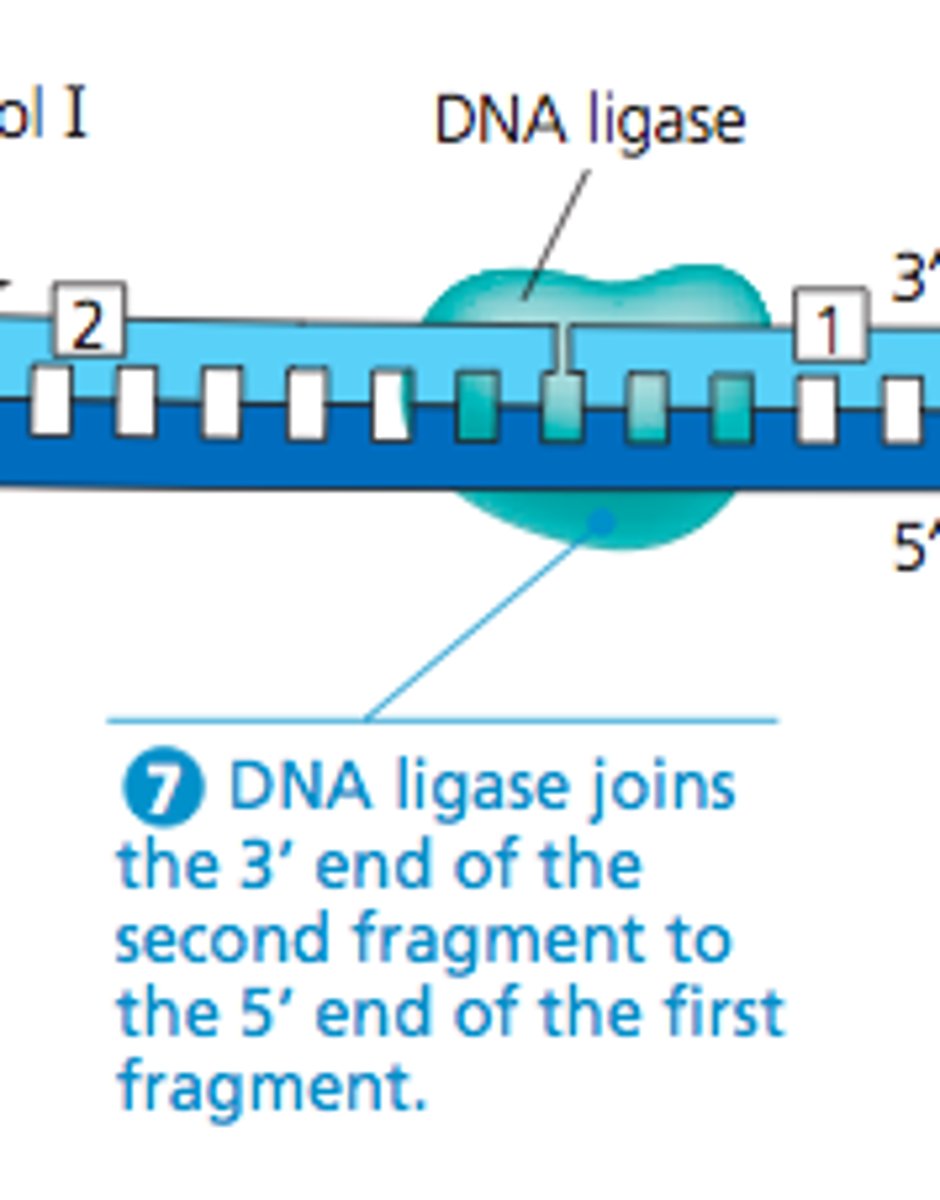
DNA ligase
enzyme that chemically links DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds.
5' to 3' direction
Direction DNA polymerase moves
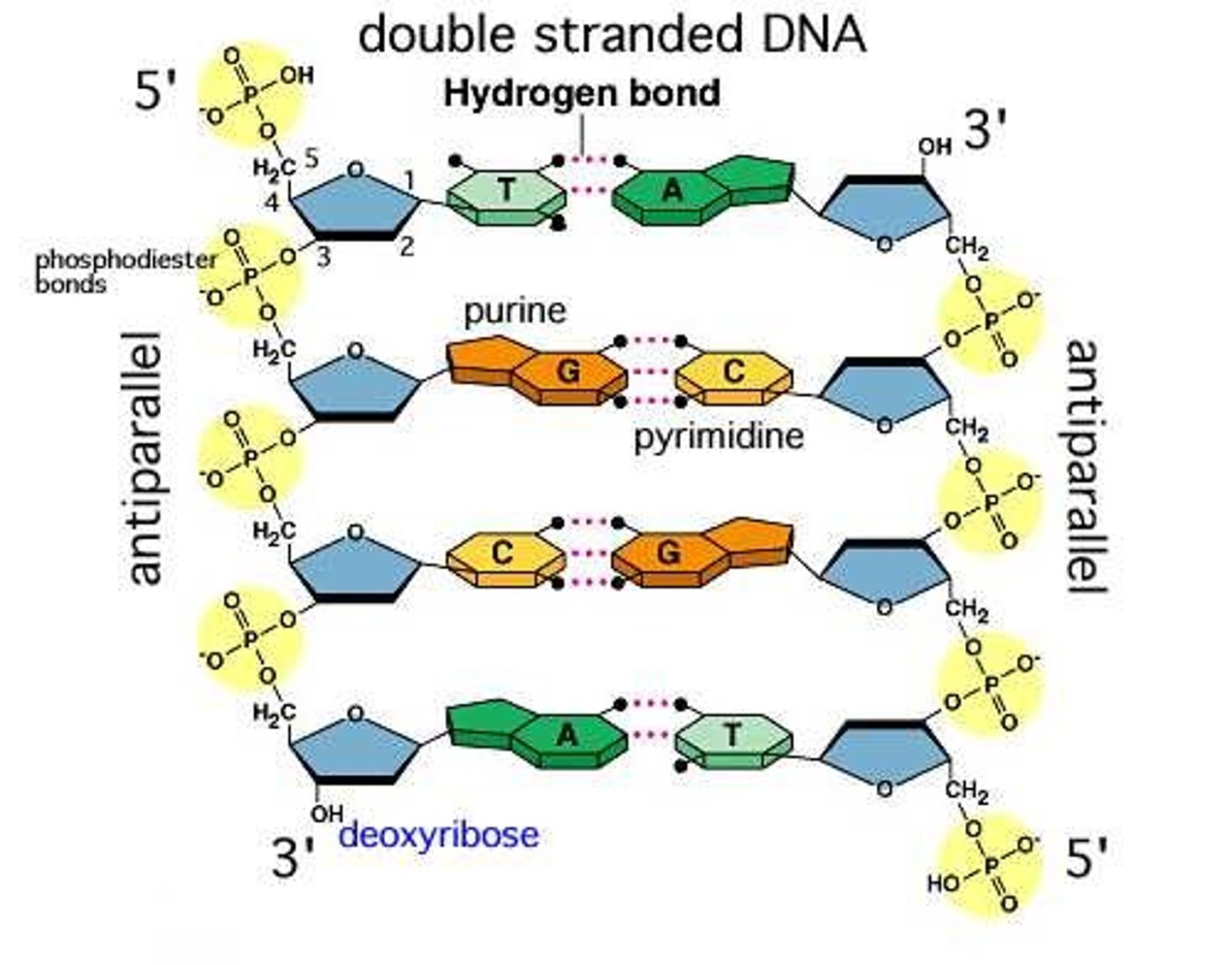
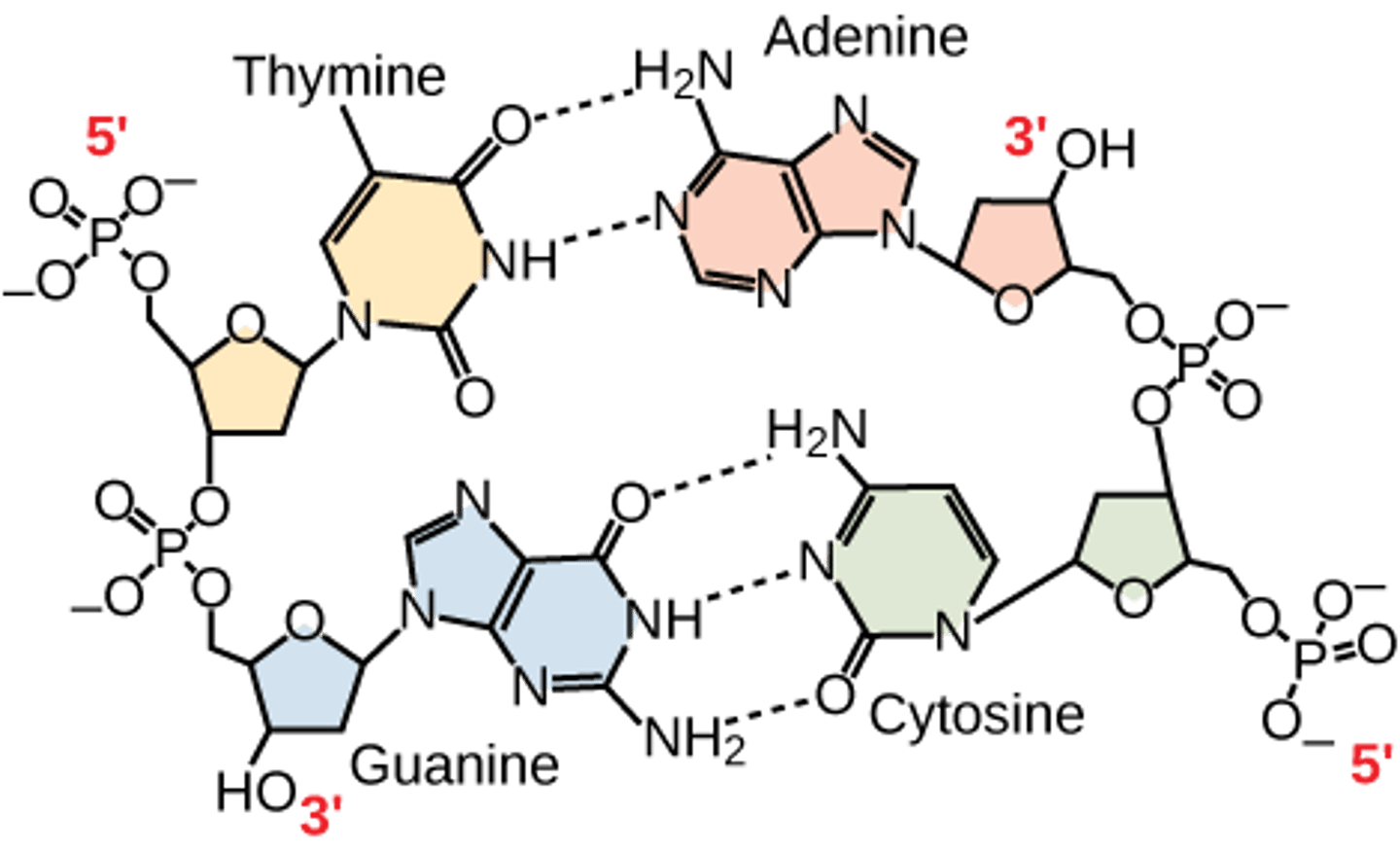
Hydrogen bonds
hold 2 strands of DNA together, Adenine & Thymine form 2, and Cytosine & Guanine form 3.
Leading Strand
new strand of DNA oriented 5' to 3', synthesized continuously
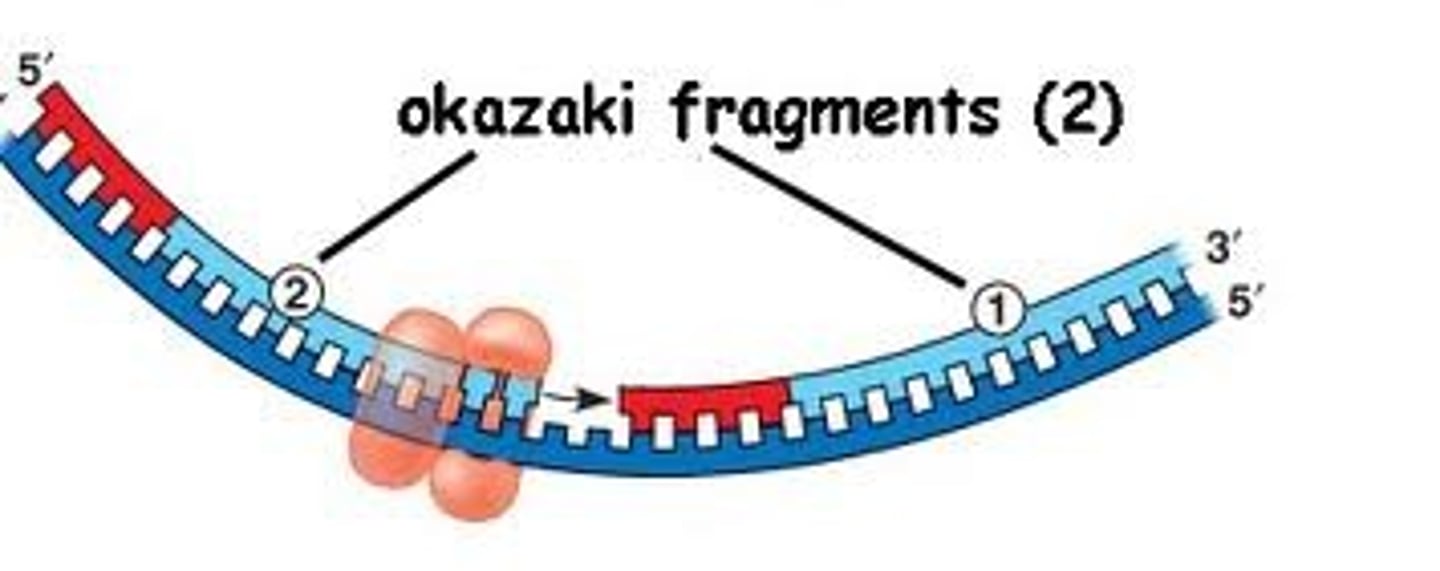
Lagging strand
new strand of DNA that is oriented 3' to 5', synthesized backwards in sections called Okazaki fragments.
Free 3' end
what DNA polymerase attaches nucleotides to
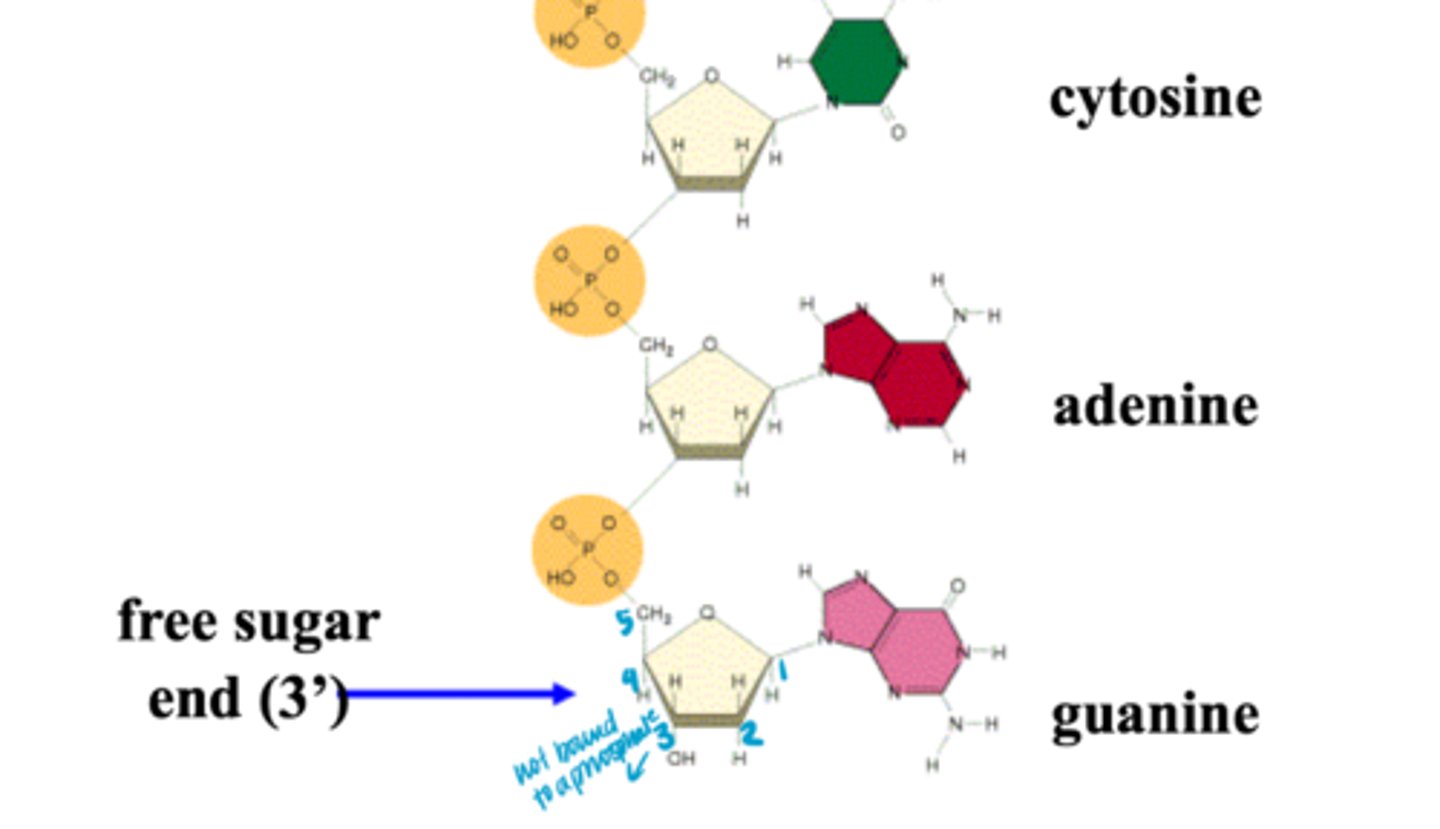
5' end
End of DNA that gets shorter each DNA replication after primers are removed.
Semiconservative
the model of replication that DNA follows when it replicates. Each parent strand serves as template for the formation of a new strand. Replicated DNA consists of 1 old and 1 new strand
sugar-phospate
forms the backbone (sides ) of the DNA.
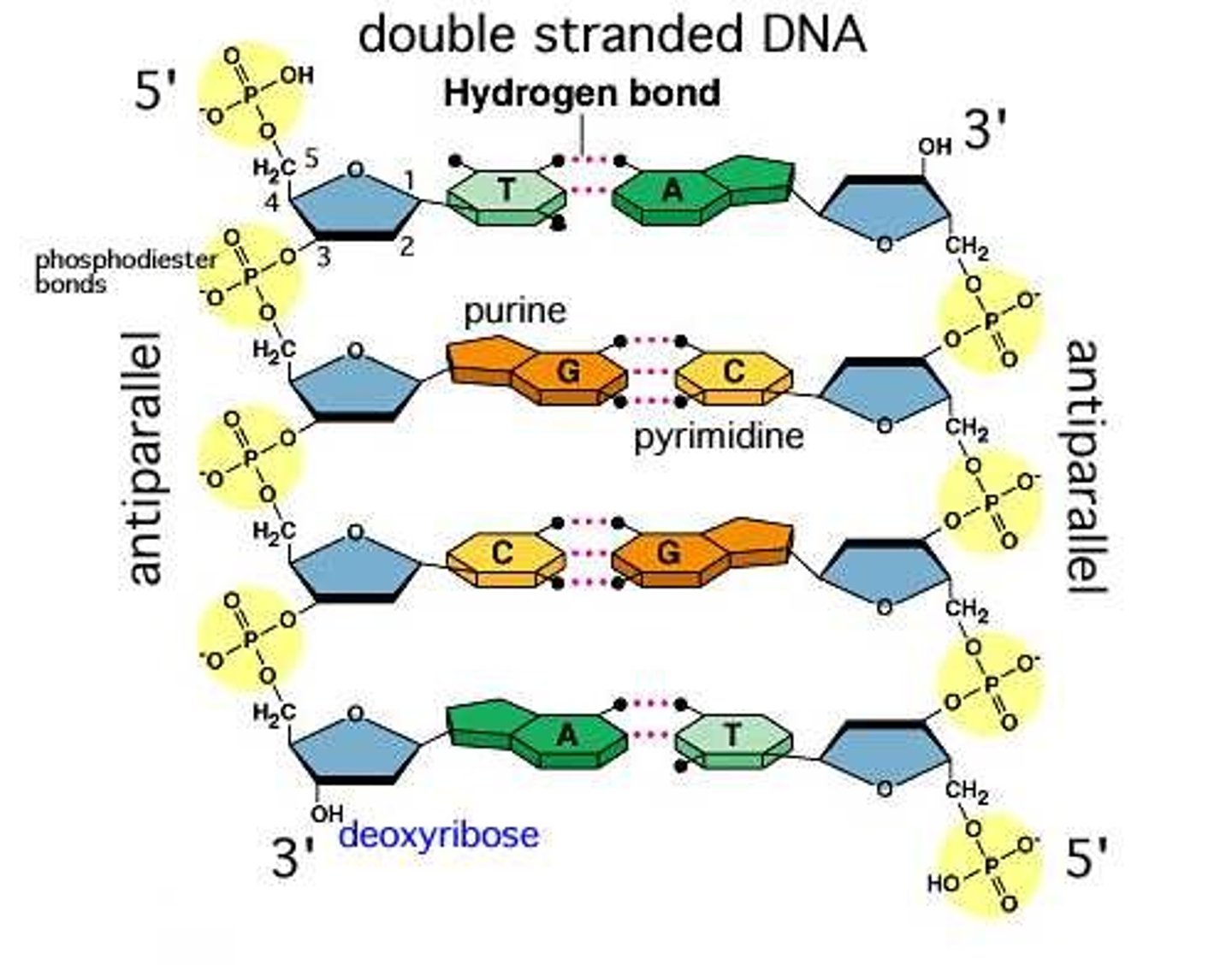
Phosphodiester bond
the type of bond that links the nucleotides in DNA or RNA. joins the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide
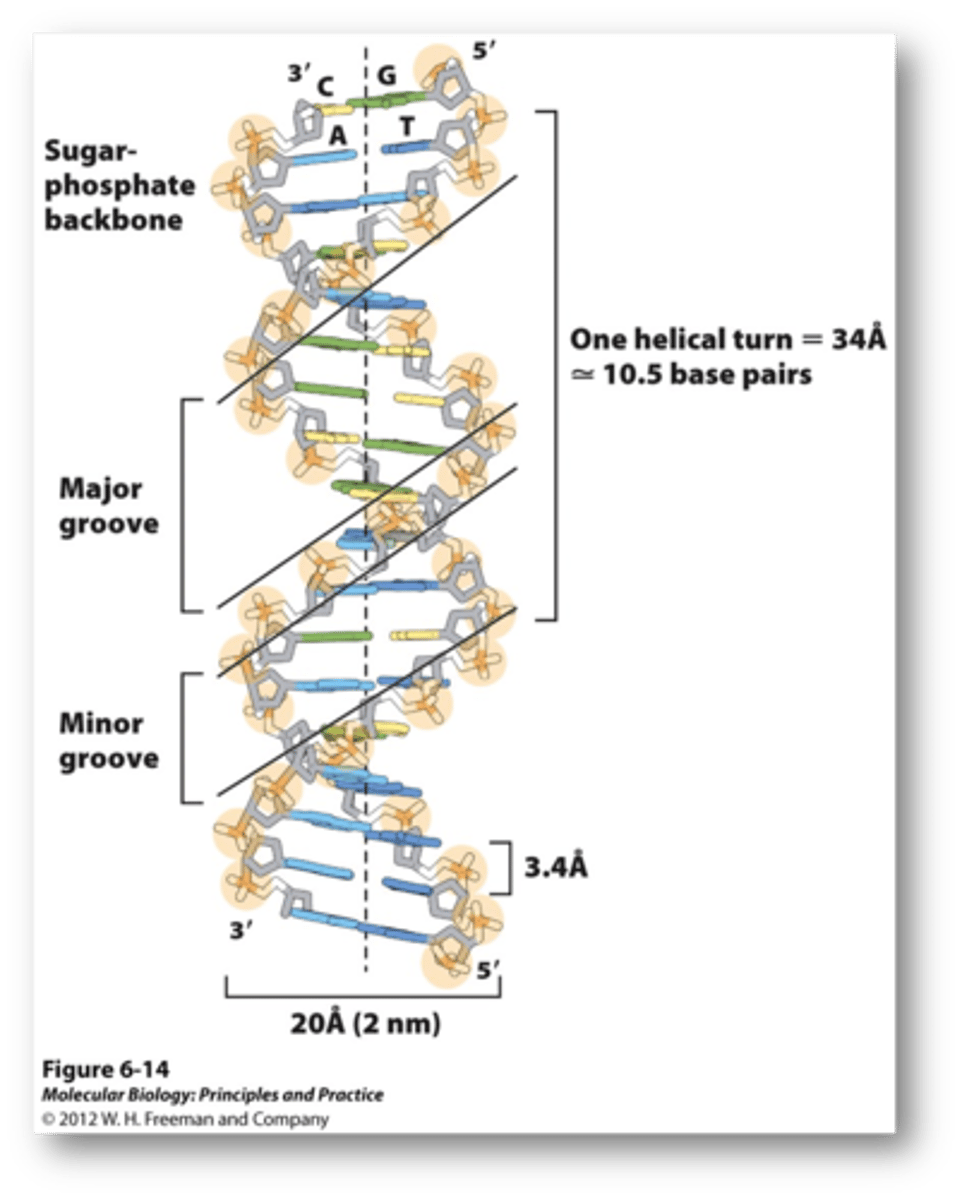
2 nm
diameter of DNA
3.4 nm
distance of 1 complete turn of the DNA, contains 10 nucleotide base pairs
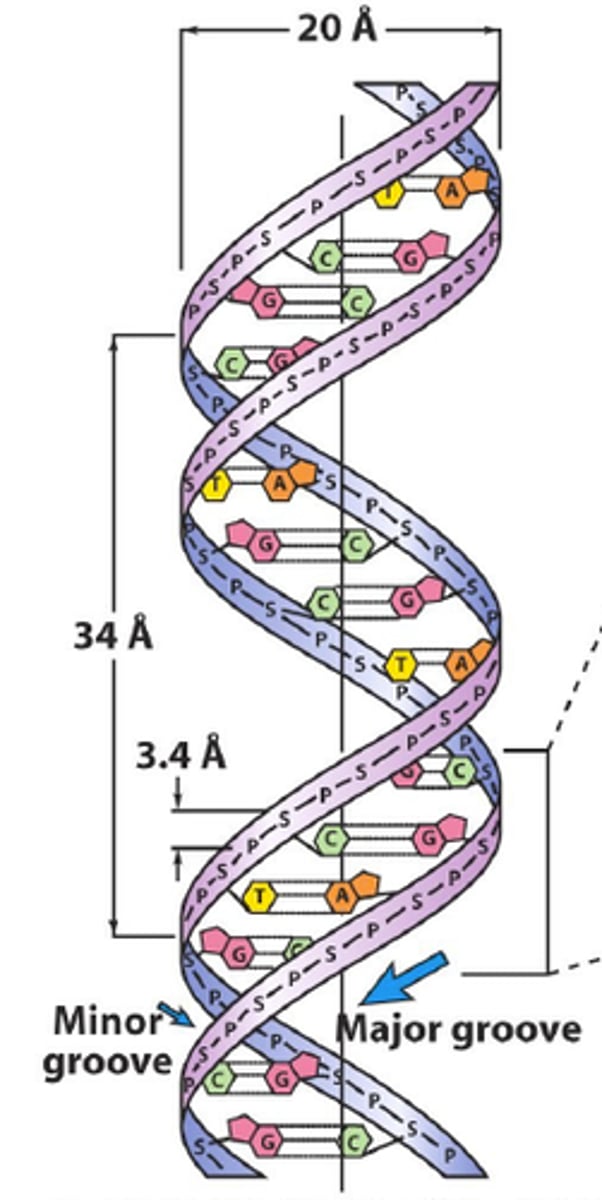
.34 nm
vertical distance between nucleotide base pairs in DNA
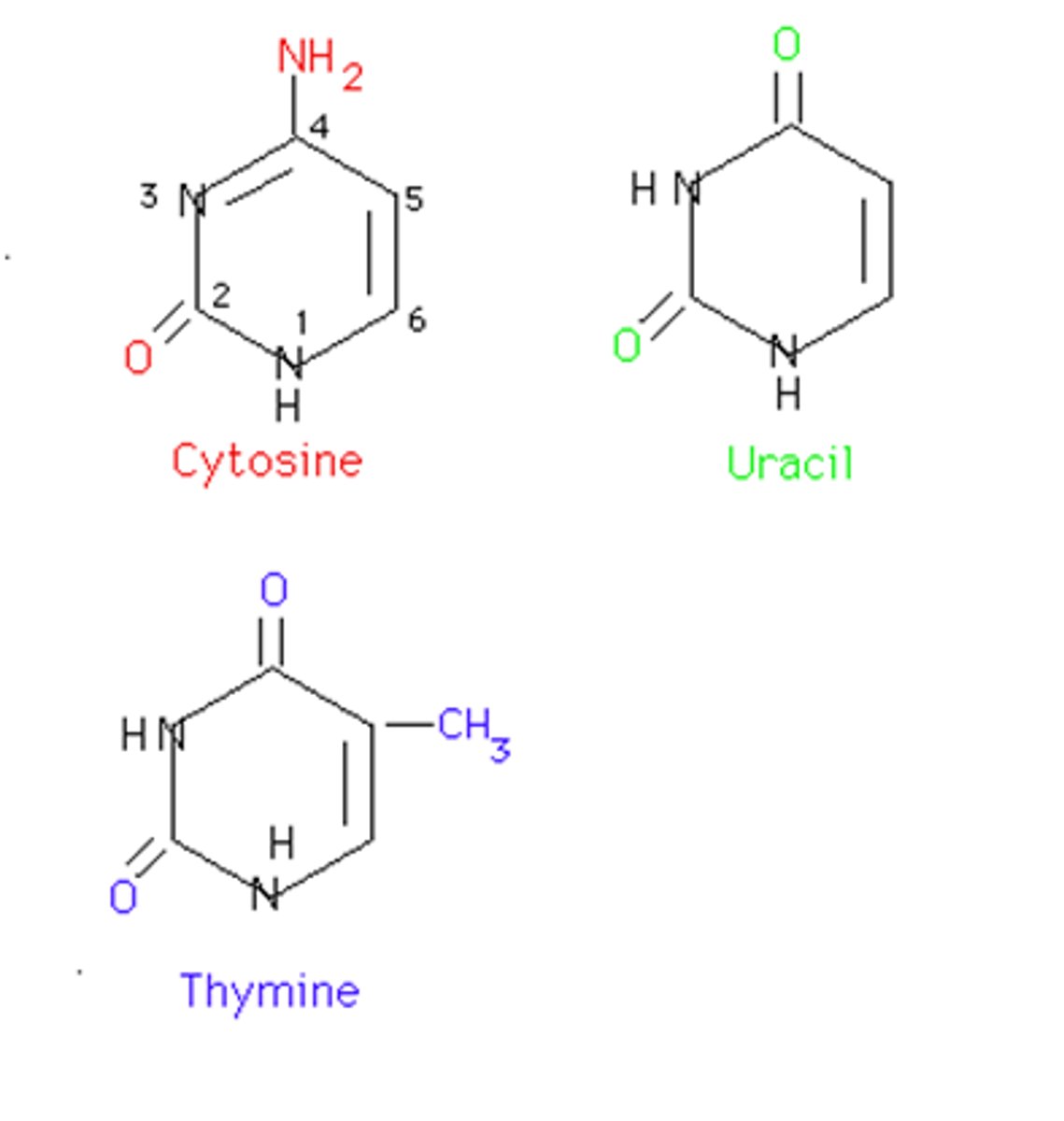
Purine
a nitrogenous base that has a double-ring structure; one of the two general categories of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA; either adenine or guanine
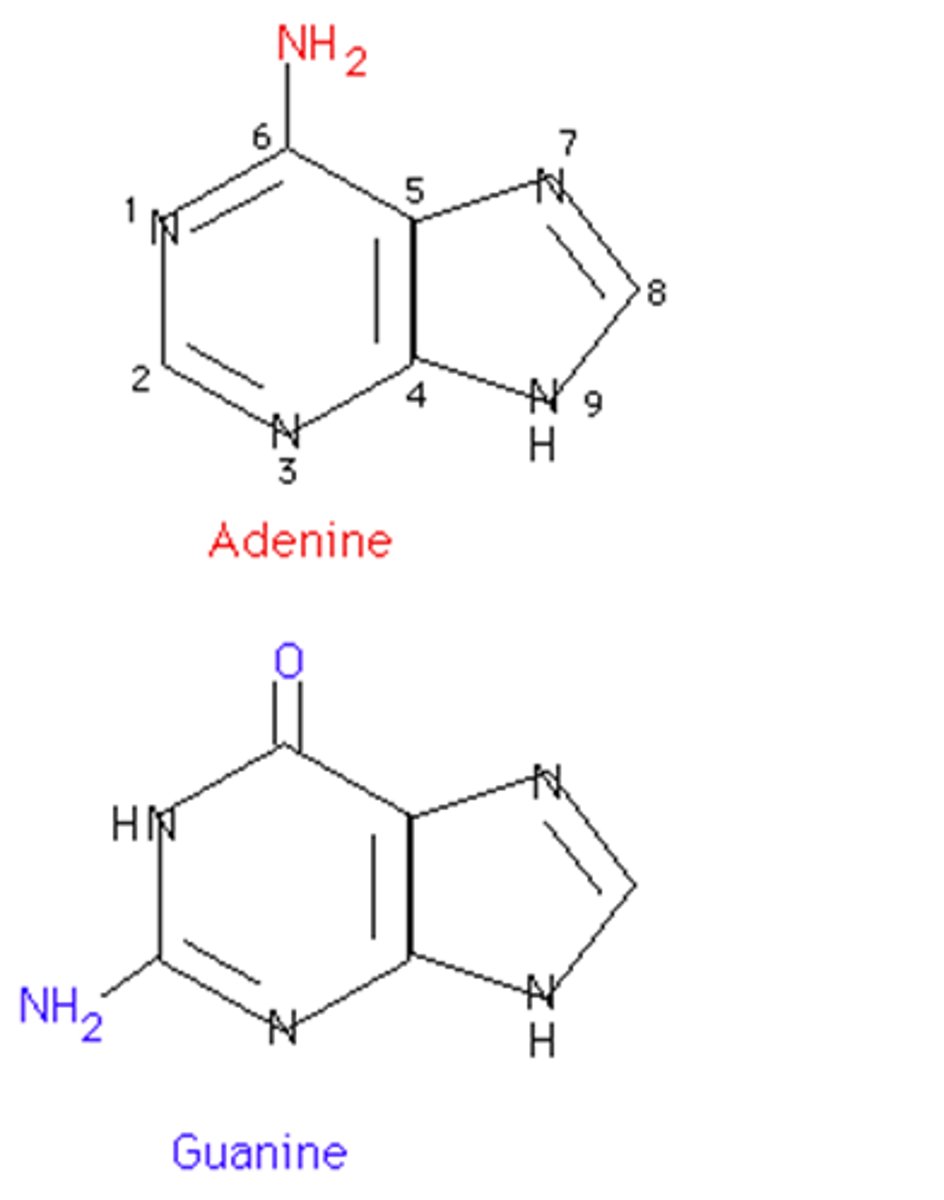
Pyrimidine
a nitrogenous base that has a single-ring structure; one of the two general categories of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA; thymine, cytosine, or uracil
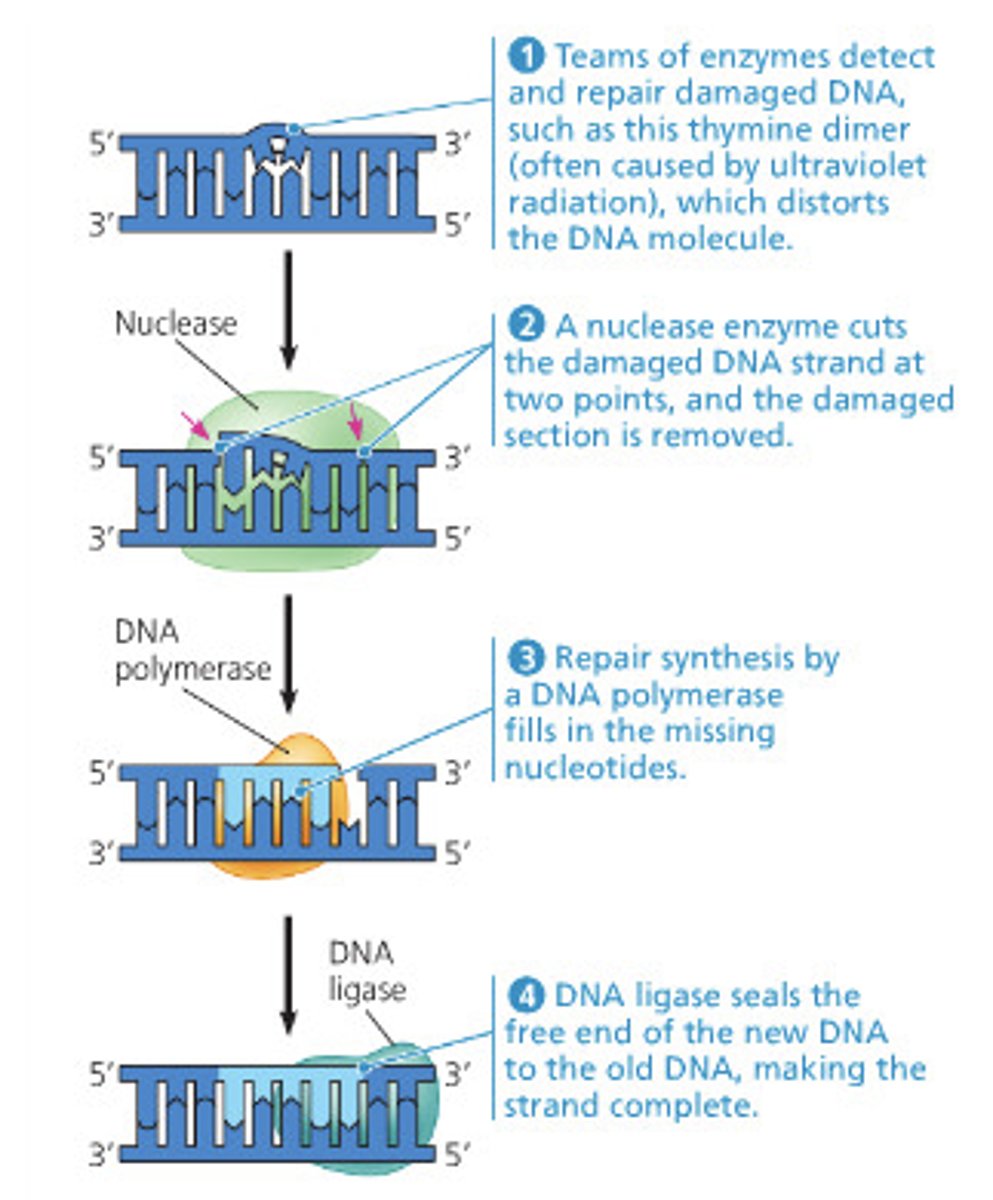
excision repair
a DNA-repair process where enzymes remove a damaged portion of DNA, synthesize a replacement section in place, and attach it to the neighboring DNA segments
mismatch repair
repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing in DNA
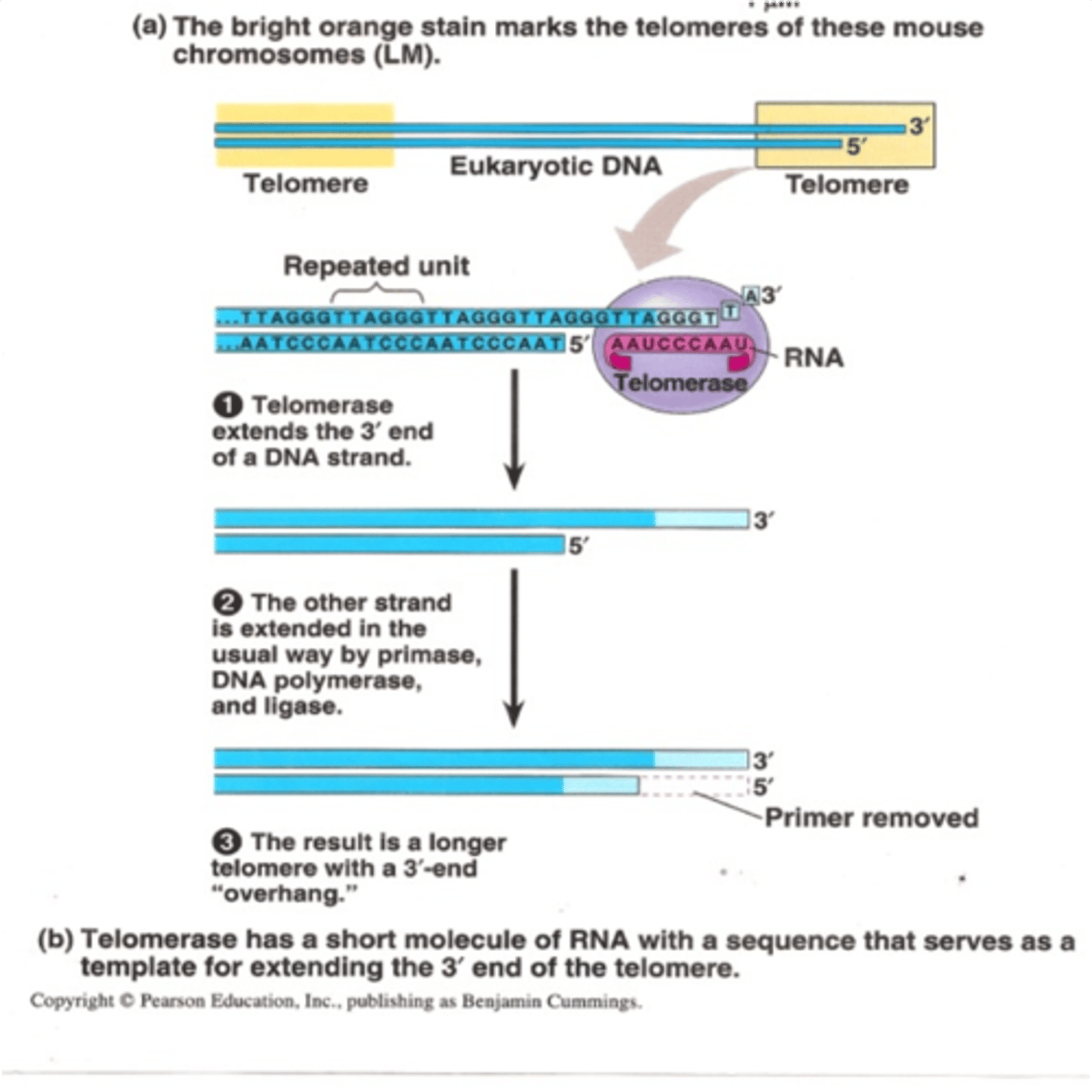
Telomeres
Repeated DNA sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
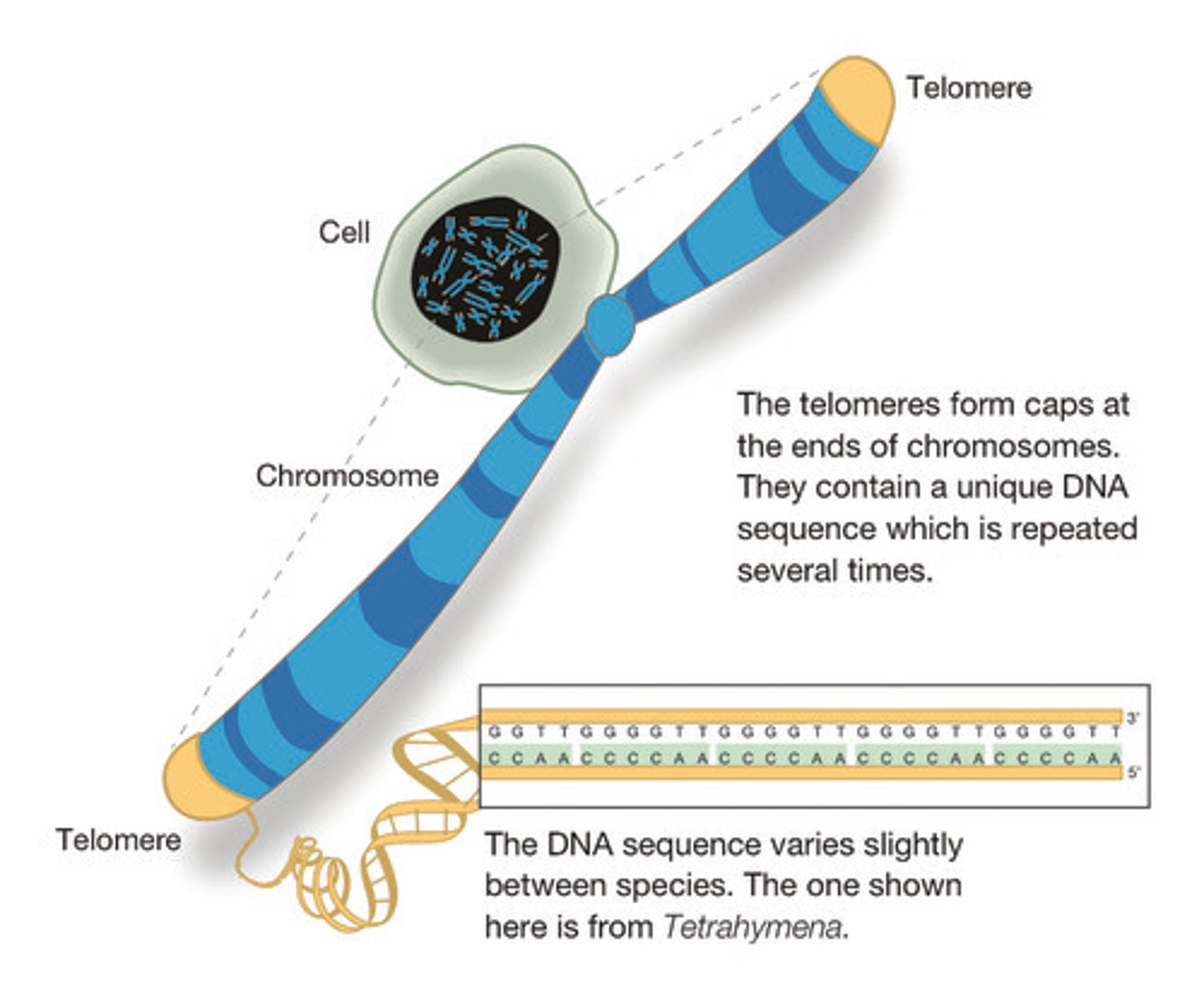
Telomerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells.