Earthquakes - Japan 2011 Earthquake Case Study
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Describe Japan as a developed country + location:
Highly developed country
Advanced infrastructure - buildings are built with earthquakes in mind
Advanced technology & a robust economy
High GDP - 4.97 trillion USD (2018)
Efficient healthcare system, extensive education
Located on Pacific Ring of Fire - prone to earthquakes
When did the 2011 Japan earthquake occur?
11th March 2011.
What caused the 2011 Japan Earthquake?
Japan is located on the eastern edge of the Eurasian plate. The continental Eurasian plate is subducted by the oceanic Pacific plate. This formed a subduction zone, at a destructive plate boundary. Friction causes the Pacific plate to stick, pressure builds & is released causing a rapid shift in the plates - this is the earthquake.
What was the magnitude of the Japan earthquake? How long did it last?
9.0 magnitude, lasted 6 minutes
Where was the epicentre & how deep was it?
Epicentre was 43 miles east of Tohuko at a depth of 20 miles - shallow.
Evaluate Japan’s prediction measures:
Japan Meteeorological Agency (JMA) and local governments
What were the primary effects of the Japan earthquake?
Ground shaking - extensive damage to buildings & infrastructure
Land fall - some coastal areas experienced land subsidence as the earthquake dropped the beachfront in some places by more than 50cm
What were the secondary effects of the Japan earthquake?
Tsunami - reached over 40 metres & caused widespread destruction along the coast
Fatalities - around 16,000 deaths reported, 28,000 people dead or missing, mainly resulting from the tsunami
Injuries - 26,152 were injured, mainly as a result of the tsunami
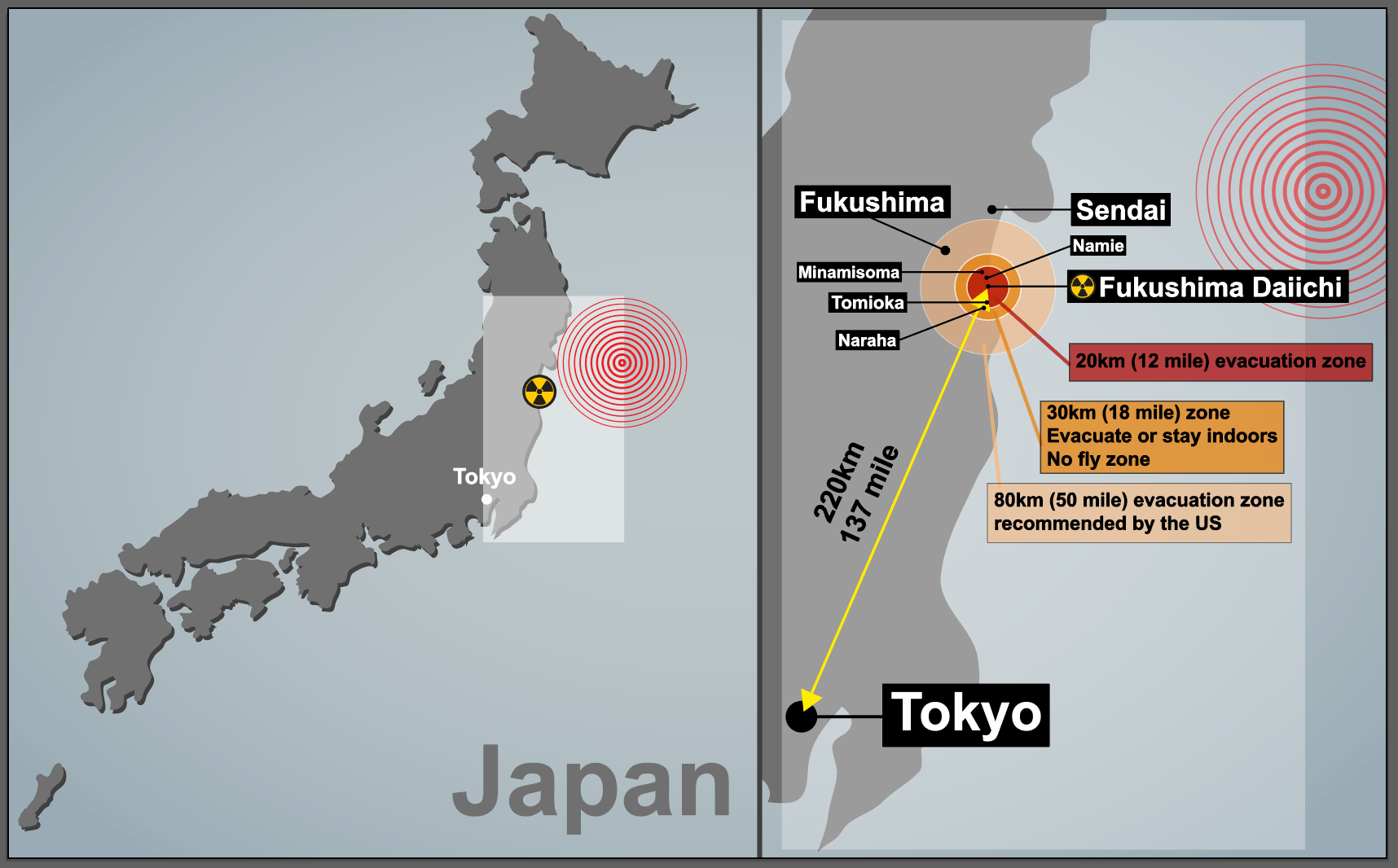
Nuclear crisis - The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant was damaged - lead to radiation leaks & evac of people in 20km radius
Economic loss - estimated over $235bn - most expensive natural disaster in the world’s history, Tokyo’s stocks fell
Displacement - around 340,000 people were displaced from their homes
Damage - tsunami destroyed 332,385 buildings, 2126 roads, 56 bridges & 26 railways, 10% of fishing ports were damaged, 300 hospitals were damaged & 11 destroyed
Environmental damage - Coastal ecosystems were heavily impacted, 400km stretch of coastline dropped by 1.6m
Blackouts - over 4.4mn households were left without electricity in Tokyo & 8 other prefectures
Transport - rural areas remained isolated for a long time because the tsunami destroyed major roads & local trains & buses. Tohoku expressway was damaged, major airports halted flights
Immediate responses to the Japan Earthquake: Tsunami warnings & prediction
Japan Meteorological Agency issued tsunami warnings 3mins after earthquake urging those affected by the earthquake to not return home - helped lower death toll
Scientists predicted where the tsunami would hit using modelling & advanced forecasting technology
Social media gave earlier updates than the media
Immediate responses to the Japan Earthquake: Search & Rescue operations
Rescue workers & 100,000 members of the Japan self-defence force were dispatched within hours
Defence ministry sent eight fighter jets to check damage
Immediate responses to the Japan Earthquake: Radiation protection measures
Government declared a 20km evacuation zone around the Fukushima power plant
Evacuees from the area around the nuclear power plant were given iodine tablets to reduce radiation poisoning risk
Immediate responses to the Japan Earthquake: International assistance
Japan received help from 91 countries - blankets, food, military transport
Japan received help from US military
Search & Rescue teams from New Zealand, India, South Korea, China & Australia were sent
Immediate responses to the Japan Earthquake: Access & Evacuation
Access was restricted to affected areas due to debris & mud, complicating immediate support
Hundreds of thousands were evacuated to temporary shelters or relocated
Long-term responses to the Japan Earthquake: Reconstruction policy & budget
Establishment of the Reconstruction Policy council in April 2011
Approval of a budget of 23 trillion yen (£190 billion) for recovery over ten years
Creation of ‘Special Zones for Reconstruction’ to attract investment in the Tohoku region
Long-term responses to the Japan Earthquake: Coastal protection measures
Implemented coastal protection policies like seawalls & breakwaters designed for a 150year recurrence interval of tsunamis.
Long-term responses to the Japan Earthquake: Transportation & infrastructure repair
Repair & reopening of 375km of the Tohoku Expressway & by the 24th of March 2011
Restoration of the runway at Sendai Airport by the 29th of March, a joint effort by the Japanese Defence Force & the US army
Long-term responses to the Japan Earthquake: Utility Reconstruction
Energy, water supply, and telecommunications infrastructure reconstruction
As of November 2011, 96% of electricity, 98% of water, and 99% of the landline had been restored
How does Japan prepare for earthquakes?
Strict building codes - buildings are constructed to withstand seismic activity
Early warning systems - advanced technology provides early warnings to citizens
Education & drills - regular earthquake drills in schools, offices & public places