ZOOL 224 Lepidosauria (Snakes)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Are snakes technically lizards?
Yes. Serpentes are within squamata and are techincally lizards, but they are highly derived and distinctive so we shouldn't think of them as lizards.
What is the diet of all snakes?
Carnivorous
What are 2 theories on the origin of snakes?
-Snakes evolved from a subterranean lineage of limbless lizards
-Snakes evolved from marine aquatic lizards
Describe the fossorial snake origin theory
Snakes evolved from fossorial lizards, similar to primitive typhlopids (blind snakes). One problem with this is that the skulls of snakes are highly derived and flexible, which is the opposite of fossorial species skulls.
Describe the marine snake origin theory
-Varanids are related to mosasaurs (extinct marine lizards)
-Some argue that snakes originated from mosasaurs and made their way back onto land
How can we determine homologies and which features are primitive or derived?
Using a phylogeny.
Why is it so hard to determine snake origins?
Scientists can't agree on a phylogeny. Molecular and morphological analyses can't agree on where to place serpentes.
Describe the general snake body form
-Elongate
-No sternum
-No girdles
-No limbs (some have hindlimb vestiges)
Where does the elongation of snakes come from?
Increased numbers of centra to 141-435. NOT the lengthening of each centrum.
Do snakes have body regions?
No. They do not have any girdles and therefore no body regions.
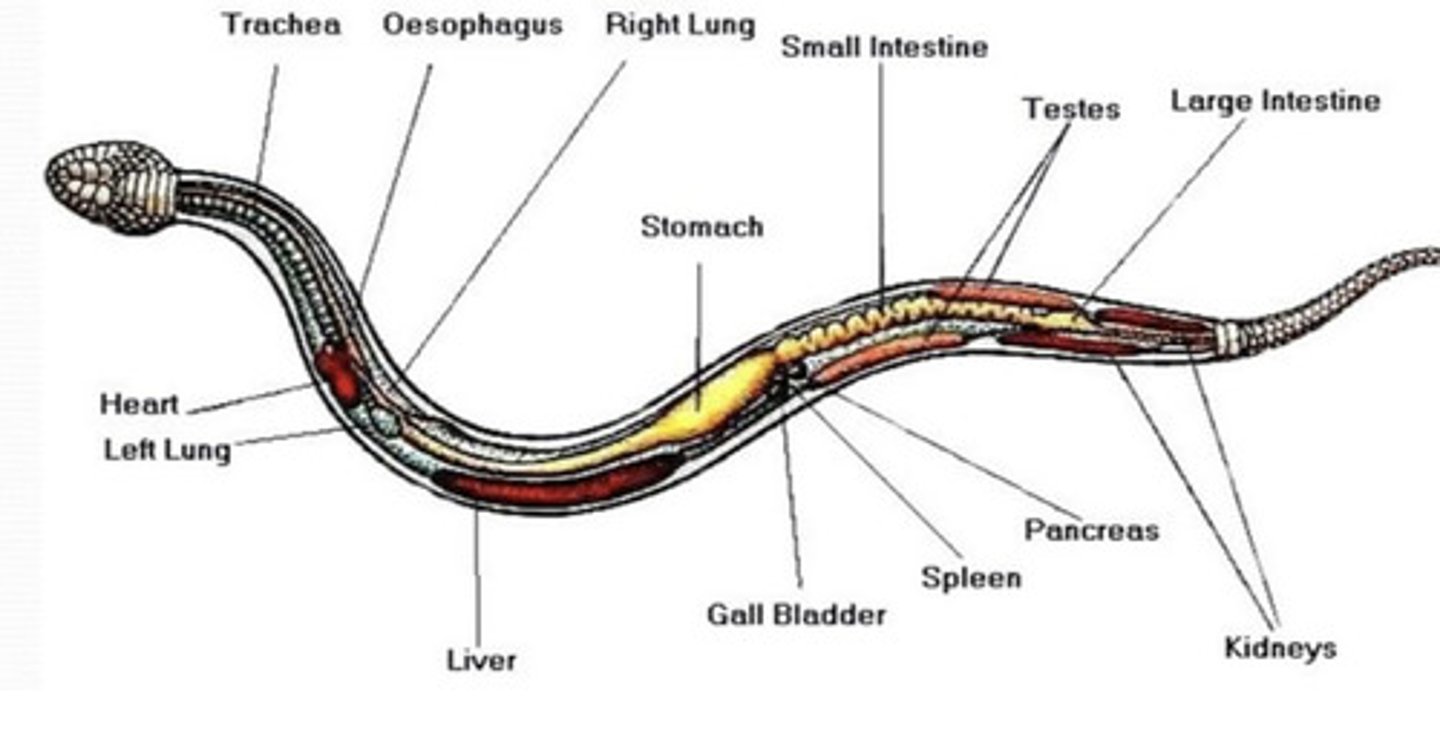
How does snake viscera change because of their elongate shape?
The viscera also becomes elongate. The left lung is small or absent. They also have no urinary bladder.
Describe snake scales
-Large and rectangular
-Scutes ventrally and metameric (same number as vertebrae)
What do snakes lack?
-External ear openings
-Tympanic membrane
-Middle ear
-Eustacian tube
Describe snake eyes
-Immovably fused transparant eyelids (called brille or spectacle)
-NO CILIARY BODIES (ring shaped muscle that change shape of lens)
-Snakes focus by moving the lens back and forth like fish
Describe the male snake reproductive organ
Paired copulatory organs called a hemipenis
Describe the snake tongue
Forked protactile long tongue
How do snakes capture and eat prey?
-Capture prey with mouth and swallow whole
-Hold prey with bortions of body and mouth
-Constriction or venom to disable prey
Describe the skull specialization of snakes
-Jaws loosely joined
-Dentaries not fused
-Left and right upper and lower jaws move independently (can "walk" jaws over food)
What are the 3 types of venomous snakes?
-Opisthogylphous
-Proteroglyphous
-Solenoglyphous
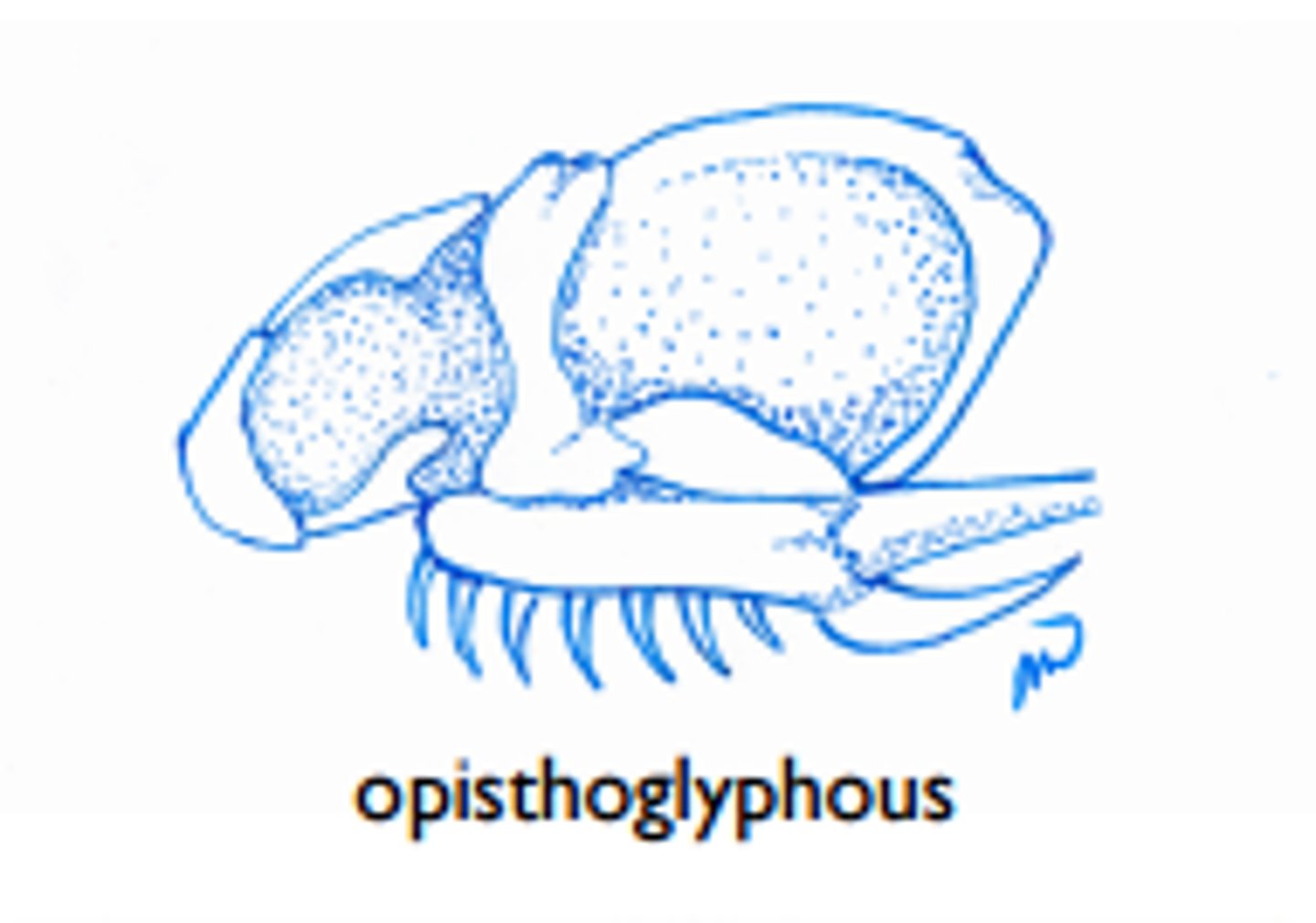
Describe opisthoglyphous snakes
-Rear fanged
-Fangs grooved and placed at back of maxilla
-Eg. Boomslang
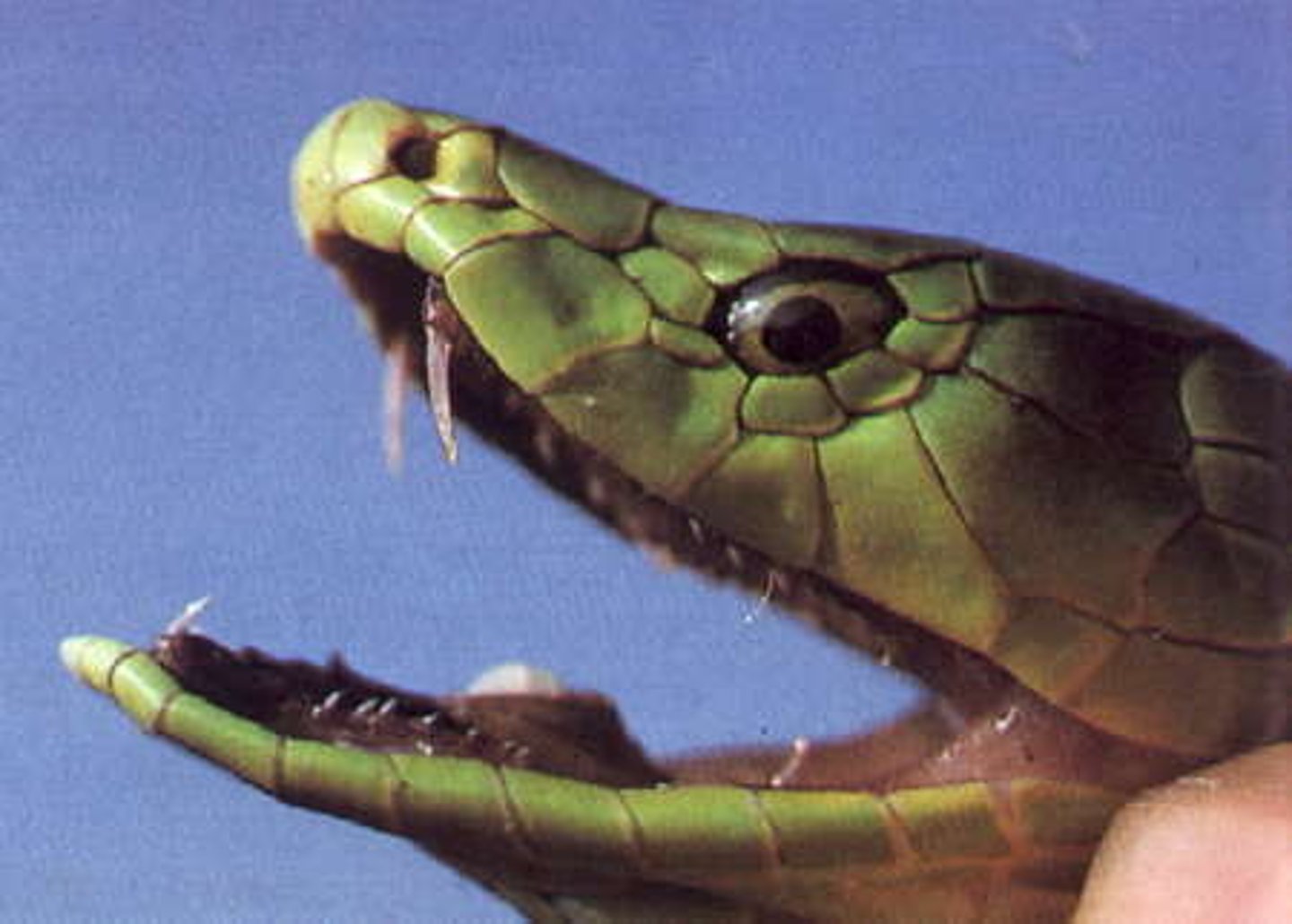
Describe proteroglyphous snakes
-Front fanged
-Fangs fold around venom channel
-Positioned on the front of short maxilla
-Green mamba, cobra

Describe solenoglyphous
-Channel/tube fanged
-Fangs on moveable, very reduced maxilla
-Fangs can fold abck in mouth
-Rattlesnake, viper
What are the 4 types of snake locomotion?
-Serpentine/undulatory
-Sidewinding
-Concertina
-Rectilinear
Describe serpentine snake locomotion
-Body undulates side to side
-Ventral scutes grip ground to move forward while lifting body off ground to reduce friction
Describe sidewinding snake locomotion
-Limits contact with hot sand
-Anchors a few points and pushes off substrate off these points
Describe concertina snake locomotion
-Anchores rear portion of the body and pushes front forward, anchors at front, and pulls rest of body forward
-Used in a restricted environment
Describe rectilinear snake locomotion
-Muscles attach to scutes and gradually lifts and moves them forward
-Very slow
Describe colubridae
-Probably noy monophyletic
-Worldlife, 60% of all snakes
-Aglyphous, proteroglyphous, and opisthoglyphous
-Alberta: garter, wester hog nosed, bullsnake, racer

Describe viperidae
-Worldwide
-Venomous
-Solenoglyphous
-Cranial infrared receptors in loreal pits (crotalines) or beneath scale surface
-Alberta: Crotalis viridis (prairie rattle snake)
