BIO 227 EXAM 3 Lecture BSU
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO lecture led by Professor Dr. Workman
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Calcium is one of the minerals stored and released from bone. What are some of its functions within the body?
Muscle contraction, blood clotting, nerve impulse transmission
What are the primary components of thick and thin filaments?
Thick filaments are composed of myosin protein
Thin filaments are composed primarily of actin protein. Tropomyosin and tropic are associated regulatory proteins.
In which band are there thick filaments only, with no thin filament overlap?
H zone
What is a motor unit, and what is the relationship between size and degree of control?
A motor unit is a single motor neuron and the muscle fibers it controls.
There is an inverse relationship between the size and degree of control. Muscles needing greater power but less control have bigger motor units.
What triggers the binding of synaptic vesicles to the synaptic knob membrane to cause exocytosis of ACh?
Nerve signal triggers the entry of calcium into the synaptic knob. Calcium binding to synaptic vesicles triggers the exocytosis of ACh.
What is the function of CA2+ in skeletal muscle contraction?
Calcium released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum hinds to troponin, inducing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. This change exposes the binding sites of actin, allowing crossbridge cycle initiation.
What causes the release of the myosin head from actin? What resets the myosin head?
ATP binding causes the release of the myosin head from actin.
The myosin head is reset from the splitting of ATP into ADP and Pi by ATPase.
What are the various means for making ATP available in a 1500-meter race?
Phosphates system, anaerobic cellular respiration, aerobic cellular respiration.
Which of the following describes a neuron?
ALL the other choices accurately describe neurons
The cells of this type of muscle are branched and striated
cardiac muscle
This type of muscle allows precision in terms of dexterity and force generation.
skeletal muscle
Which of the following accurately contrasts glial cells versus neurons?
neurons transmit signals while glial cells create a supportive habitat for neurons

Which of the following is a true statement about this muscle tissue?
all of the other answers are correct
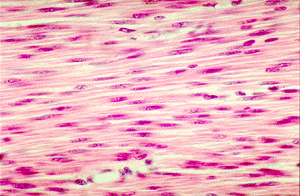
What type of muscle tissue is this?
smooth muscle
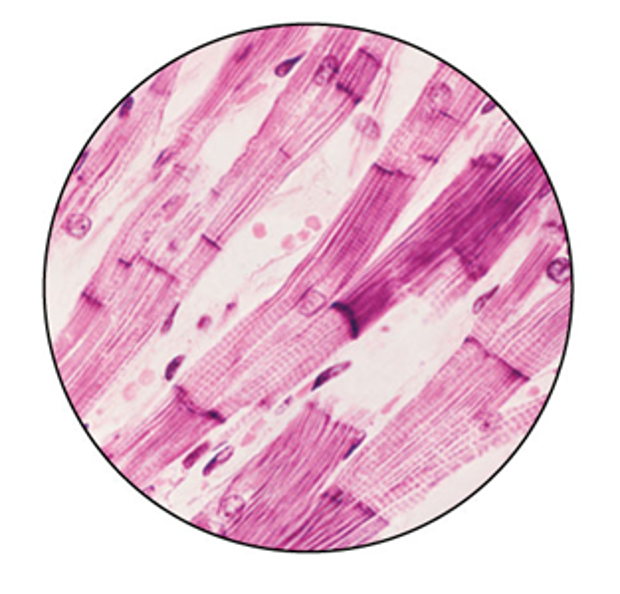
Which of the following is/are true statement(s) about this tissue?
all the other responses are correct
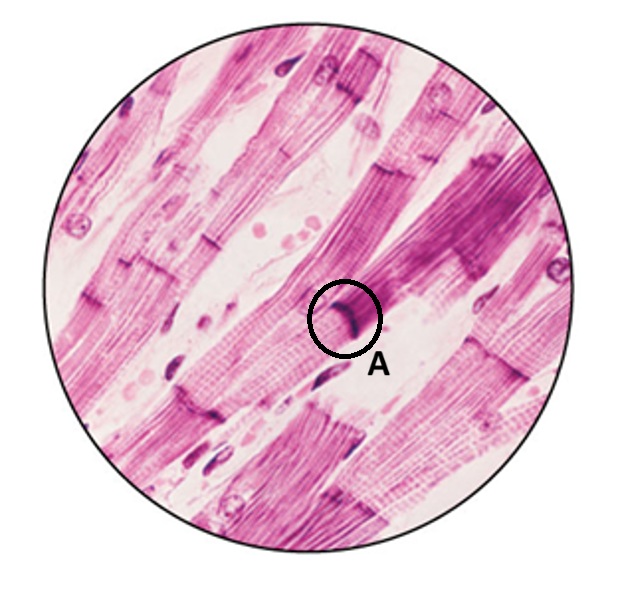
What is the function of the structure labeled in A?
connect neighboring cells with both an anchor and a pore
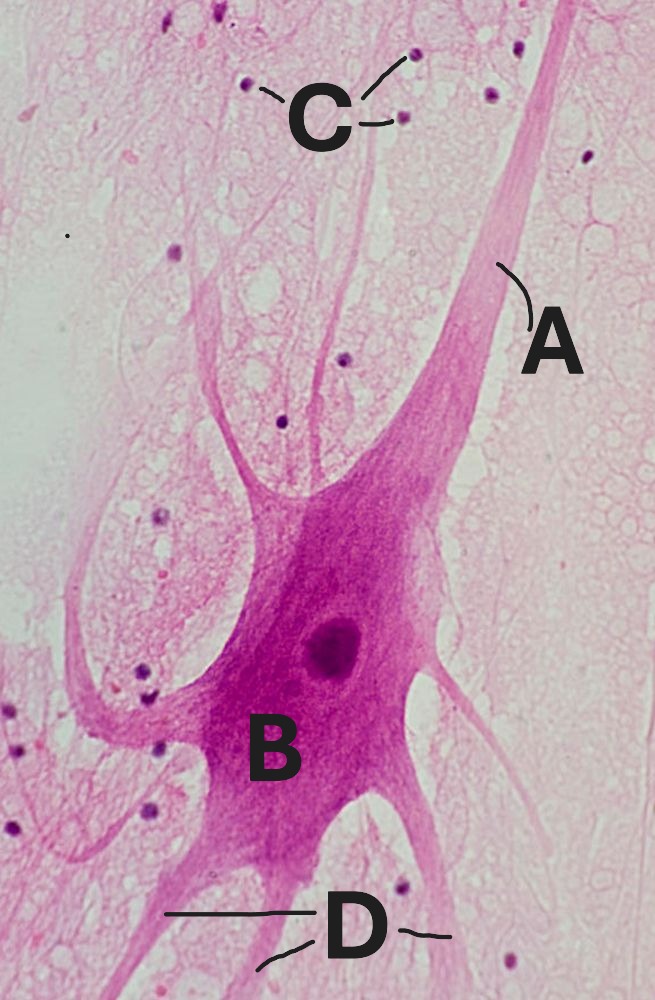
Label “B” points to what structure?
cell body
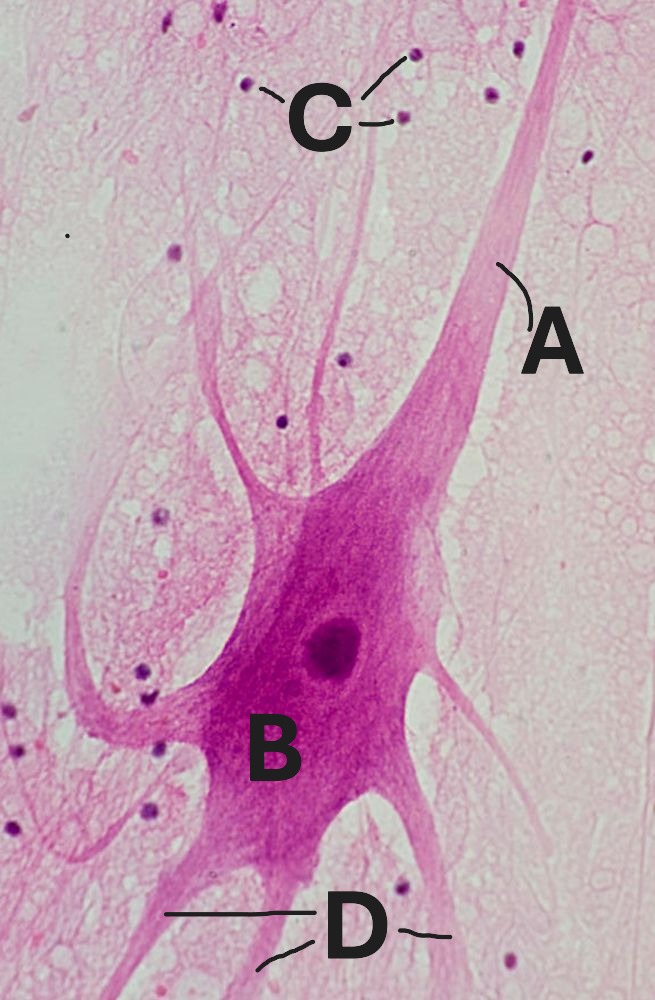
Label “A” points to what structure?
axon
This refers to a single neuron and all the individual muscle cells it controls.
motor unit
Ions flow freely from one cell’s cytoplasm into the next cell’s cytoplasm through this structure, which allows neighboring cardiac muscle cells to contract in synchrony (in other words, in a coordinated way).
intercalated discs
This term describes a neuromuscular adaptation to practice whereby a motor neuron may disconnect from some muscle fibers and/or connect to others, which improves precision, dexterity, and regulates how much force is generated.
muscle memory
Which of the following muscles has the largest motor unit?
quadriceps
These structures connect the muscle cell membrane to the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows an action potential to penetrate deep into the muscle cell.
t-tubules
This term describes a neuromuscular adaptation to practice whereby a motor neuron may disconnect from some muscle fibers and/or connect to others, which improves precision, dexterity, and regulates how much force is generated.
muscle memory
Ions flow freely from one cell’s cytoplasm into the next cell’s cytoplasm through this structure, which allows neighboring cardiac muscle cells to contract in synchrony.
intercalated discs
The main function of this organelle is to store calcium ions (Ca2+).
sarcoplasmic reticulum
The region of a muscle cell from one Z-line to the next, this is the unit of contraction.
sarcomere
Because the cell membrane of a muscle cell contains structures not found in other cell membranes, it has a special name. It is called the ________.
sarcolemma
During contraction, the “heads” of this myofilament tug along the other myofilament, bringing Z-lines closer together.
myosin
This refers to a single neuron and all the individual muscle cells it controls.
motor unit
During which phase of cross-bridge cycling is ATP used?
ATP helps myosin disconnect from actin
Which of the following defines "voltage-gated ion channel?"
A transport protein that facilitates movement of ions ONLY WHEN the cell membrane potential nearby reaches a certain voltage
The period where no stimulus, not even a greater-than-threshold strength stimulus, can initiate another action potential is called the:
absolute refractory period
What ion movement is responsible for repolarization and hyperpolarization during an action potential?
efflux of potassium (K+)
A resting membrane potential...
results from a local difference in charges concentrated on opposite sides of a plasma membrane
What is the resting membrane potential of an animal neuron?
-70 mV
Which of the following is INCORRECT about acetylcholine (ACh)?
ACh causes sodium ions (Na+) to move out of the muscle cell
Which of the following metabolic pathways yields the most ATP per molecule of glucose?
oxidative phosphorylation
Which of the following metabolic processes can human cells perform without oxygen?
lactic acid fermentation
What enzyme produces ATP during oxidative phosphorylation?
ATP Synthase
In the electron transport chain, what do the active transporters pump across the mitochondrial inner membrane?
Protons (H+)
The energy currency of cells, this molecule stores and releases energy like a rechargeable battery.
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
What muscle is the antagonist of biceps femoris?
all the other choices are correct
Which pair of muscles is involved with chewing?
masseter & temporalis
Which of the following is a muscle that manipulates your facial expressions?
all the choices are correct
Which of the following is FALSE about muscles?
muscles push and pull
Which of the following is a muscle involved with breathing?
all are correct
True or False: The foramen magnum is a hole in the skull through which the brain physically connects with the spinal cord.
True
List the layers from deepest to most superficial.
Myofibril, muscle fiber, fascicle
What layer does the perimysium cover?
muscle fascicle
What layer does the epimysium envelop
the whole muscle
what does the sarcolemma cover?
myofibril
what does the endomysium cover?
muscle fiber
A single myofiber is a ______, it’s wrapped with _____ connective tissue known as ______
muscle cell; loose areolar; endomysium
When many cells are clustered together we have a _____ that is encased in ______ connective tissue with the name_______.
muscle fascicle; dense irregular; perimysium
The clusters (fascicles) group as a _____ surrounded with_____ made of _____ connective tissue.
whole muscle; epimysium; dense regular
Myosin and actin are both ______
contractile proteins
Tropomyosin and troponin are both _______
regulatory proteins
titin and dystrophin are____
structural proteins
A ______ is a protein strand that comes in two forms- thin and thick- that slide along one another during contraction.
myofilament
When the myofilament strands overlap and unite they become a _______
myofiber
Functional unit of muscles
sarcomeres
What is when non-gated channels are dominant and voltage-gated channels are closed?
Rest
_____ is when excitatory synaptic input nudges the neuron to become more positive to -55mV.
Threshold
Response to becoming -55mV is usually due to sodium or calcium entering neuron through _____ channels
ligand-gated
When do voltage-gated sodium channels open and an influx of the ion occurs?
Depolarization
Voltage-gated sodium channels opening is mediated by a _____ loop that requires an off-switch
positive feedback
_____ is When sodium influx is blocked by an off-switch known as______
Repolarization; inactivation
During repolarization slow voltage gated _____ channels finally open leading to efflux of the ion.
potassium
When voltage gated potassium channels remain open and potassium continues to leave even though the potential goes below -70mV
Hyperpolarization
Resting state of hyperpolarization
-90mV
Phenomenon that every time a somatic motor neuron fires here, events occur that guarantee a myofiber response.
High Fidelity
Three feature of the NMJ synapse that contribute to high fidelity are high concentration of ______released by the motor neuron, high number of _____ embedded in sarcolemma, and synaptic insulation by _____ cells
ACh; nAChR; Shwann
involves a neuron communicating with a myofiber, first stage in muscle contraction
excitation phase
Second stage of contraction that occurs when electrical events are couples to mechanical events
excitation-contraction coupling phase
Third stage of contraction, which is the action part of the event
Contraction phase
Final stage of relaxation when all the previous steps reverse
relaxation phase
When voltage-gated calcium channels open how is the neurotransmitter transferred?
via exocytosis
Deep infoldings of the sarcolemma that a muscular action potential travels down
T-tubules
Thick edges of the sarcolemma in which calcium channels are embedded in
terminal cisternae
TRUE or FLASE: Calcium ions binding to troponin cause tropomyosin to move away from the binding sites of actin.
True
Myosin head activates when it is…..
phosphorylated
Interaction between actin and myosin
crossbridge
Crossbridge breaks when myosin binds a new____molecule
ATP
When contraction ends what pumps the calcium back into the SR?
SERCA
isolated contraction response
twitch
Elastic filament that contributes to a muscle’s ability to recoil following a stretch event.
Titin
What does ATP become when it is hydrolyzed?
ADP and phosphate
Two examples of energy usage in the muscle
Crossbridge dissociation and SERCA pumping calcium into SR
Most efficient at replenishing ATP
aerobic cellular respiration
In glycolysis glucose is converted to “two whats” first?
two pyruvates
In glycolysis what happens to NAD+?
It is reduced to NADH as a way to hold electrons freed from glucose
Process that transforms pyruvate into lactate.
fermentation
What happens to NADH during fermentation?
NADH drops off electrons forming NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue
Glycolysis and Fermentation represent what type of substrate to energy ratios?
one-to-two
What enzyme catalyze energy production in aerobic cellular respiration?
ATP synthase
In the electron transport chain what is required to grab and move the electrons?
Oxygen
What is the the ETC’s substrate to energy ratio?
one-to-many