Clinical Medicine - Neurology
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
337 Terms
Lesion
area of tissue which has been damaged by disease or injury
Localization
process of determining where the lesion exists through H&P and diagnostics
Type localization
what dysfunction is present? - focal, multifocal, diffuse, specific system, or mixed
Grey matter
majority of neuronal somas
extends from brain (outermost/cortex) to the cord (central horn-like structure)
Cord grey matter sections
anterior grey column
posterior grey column
lateral gray column
Grey matter throughout the CNS allows
control movement, memory, and emotion
White matter
myelinated fiber tracts
in brain - connects various parts of cortex for processing and integration
in cord - sensory and motor pathways to and from brain
In skeletal muscle innervation, release of _____ by axon terminal causes transmission of impulse
acetylcholine
Parasympathetic vs sympathetic neurotransmitter
parasympathetic - ACh
sympathetic - NorEpi
Dura mater
outermost, dense fibrous membrane
provides protection against acceleration/deceleration via reflections: falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli
supports venous sinuses
Arachnoid mater
delicate impermeable membrane
separated from dura by subdural space and from pia by subarachnoid space
all cerebral arteries and veins as well as cranial nerves in subarachnoid space with CSF
Pia mater
vascular membrane
most closely adherent to brain and spinal cord
Brain stem
compromised of the medulla oblangata, the pons, and midbrain
reflex centers for respiration, CV, and control of consciousness
contains important nuclei of CN 3-12
contains vomiting and swallowing centers
Cerebellum
timing of motor activities and rapid, smooth progression of movement
coordinates posture, balance, and speech
Basal ganglia
assists in control of complex movements
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
Cerebrum
frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes
Cerebral cortex - frontal
complex problem solving, personality, judgement, and voluntary movement
Broca's area - motor speech
Cerebral cortex - parietal
perception of sensation at primary somesthetic area, located on postfrontal gyrus
Cerebral cortex - occipital
primary visual area
Cerebral cortex - temporal
primary auditory area
Wernicke's area - sensory speech/understanding of written and spoken language
"Spino-" tract
sensory tract
"-spinal" tract
motor tract
3 main sensory systems in spinal cord
pain-temperature
proprioception-stereognosis
light touch
Pain-temperature pathway
enters cord and crosses over immediately
spinothalamic
Proprioception-stereognosis pathway
initially remains on same side then crosses over at brainstem
spinocerebellar
Light touch pathway
combines features of 2 previous tracts
some crosses at lower levels and some at brain stem
med lemniscus
spinothalamic
Motor pathway
down through brainstem and crosses over at junction with cord
Upper motor neuron lesions
weakness
increased reflexes
increased tone
no atrophy or fasciculations
Lower motor neuron lesions
weakness
atrophy
fasciculations
decreased reflexes
decreased tone
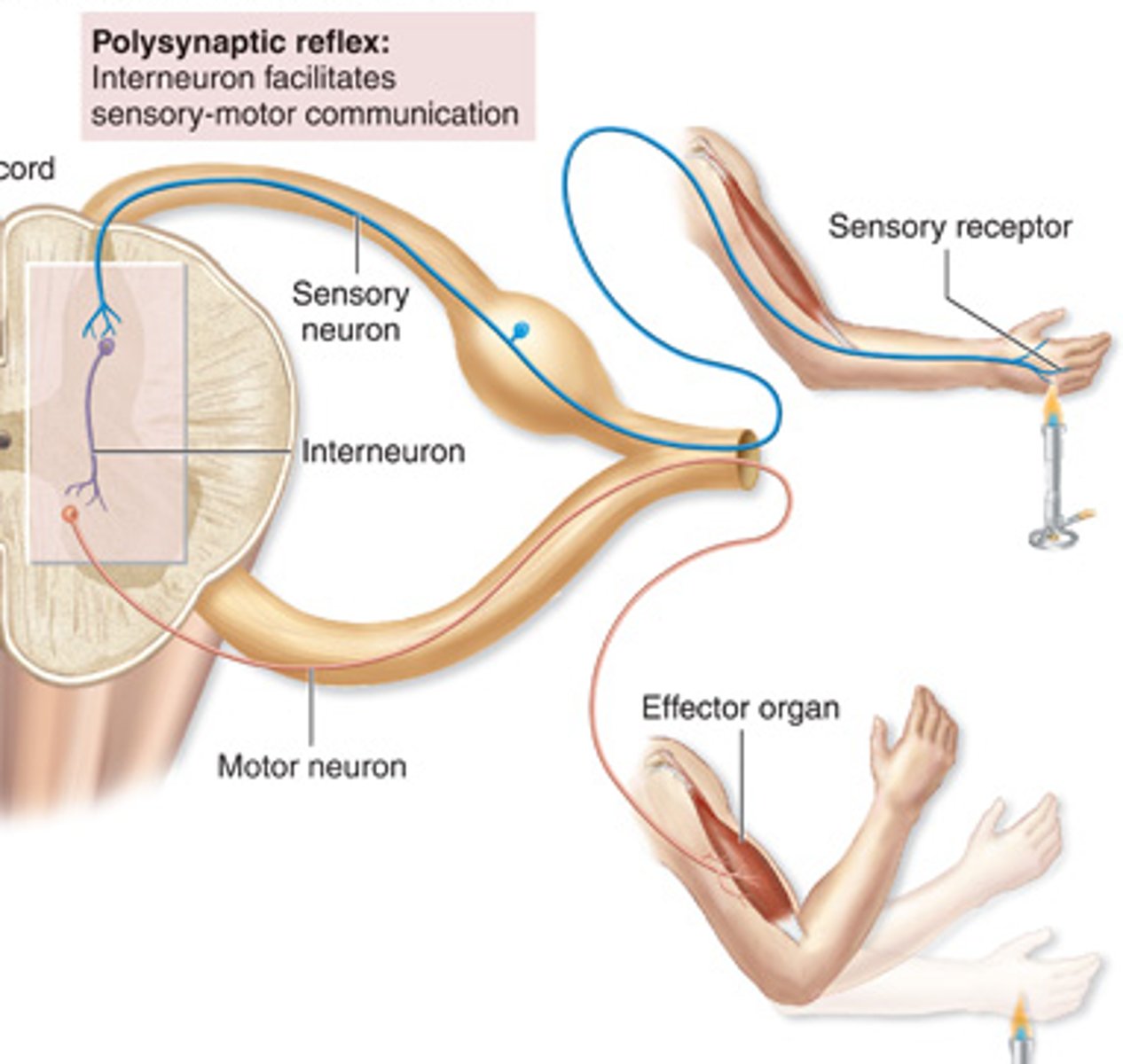
Reflex arc
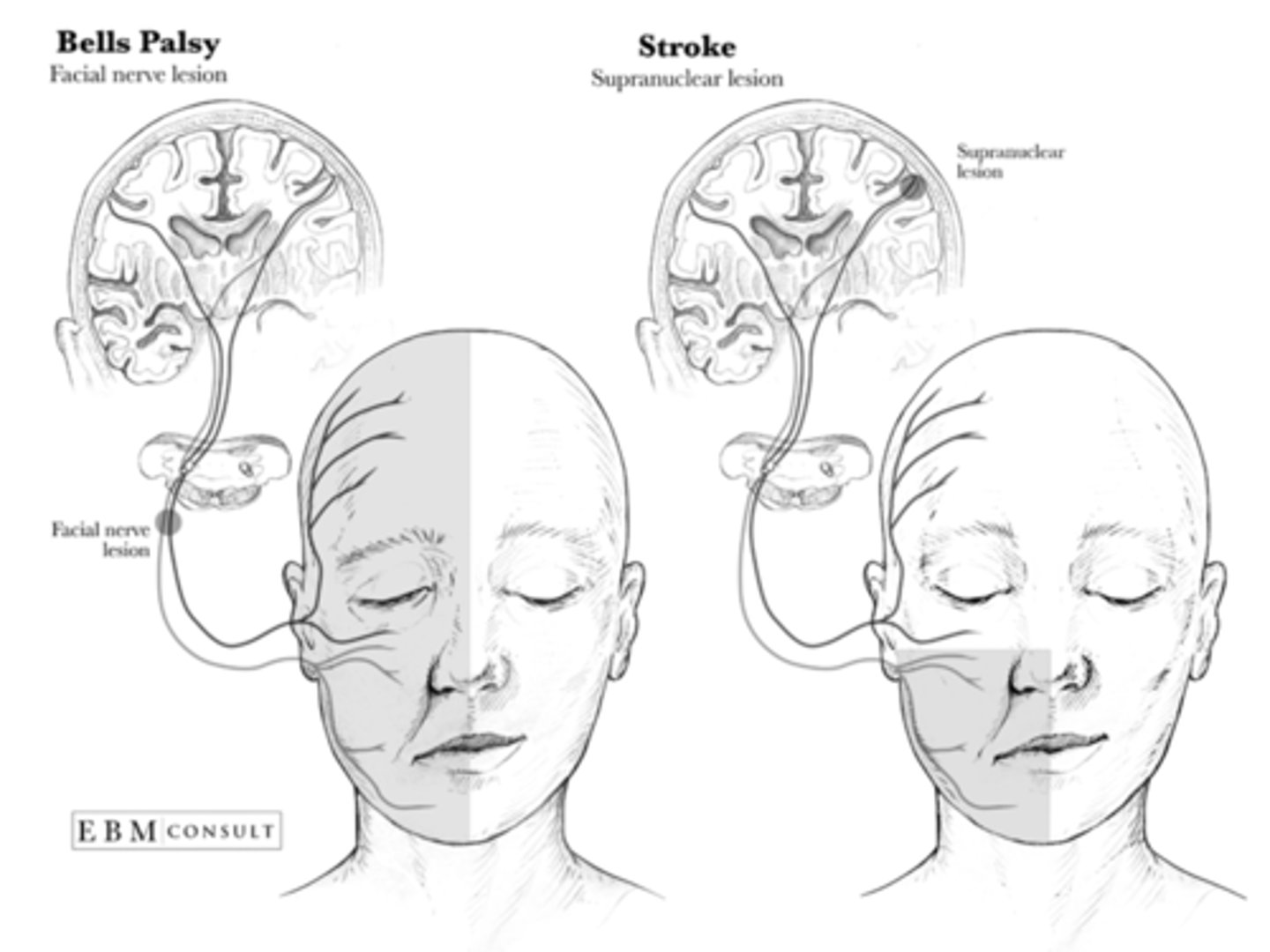
Bell Palsy
sudden onset of facial paresis caused by an inflammatory response involving the facial nerve
idiopathic
MC in DM and pregnancy
Bell Palsy S&S
abrupt facial paralysis that gradually worsens
ear pain on affected side
numbness
difficulty eating
excessive tearing
difficulty closing ipsilateral eye
poor fine facial movements - inability to wrinkle forehead
Bell Palsy vs Stroke
Bell Palsy management
further workup unless suspicion for herpes zoster, Lyme, HIV, or tumor
Bell Palsy treatment goals
improve facial nerve function
prevent complications like corneal damage
minimize long-term sequelae
Bell Palsy treatment
self-limiting and benign with full resolution in up to 6 months
if within 72 hrs: corticosteroids - high dose prednisone
antiviral therapy - acyclovir or valacyclovir
eye drops, patches, moisture chambers
facial exercises
Trigeminal neuralgia
MCC of neuralgic pain in face
unilateral pain involving 2nd, 3rd, or both branches
Trigeminal neuralgia S&S
sudden onset, severe facial pain lasting seconds
sharp, stabbing, or burning
may be precipitated by touch or movement
daily attacks
Trigeminal neuralgia diagnostics
MRI w/ and w/o
Trigeminal neuralgia pathophysiology
ecstatic vascular loop of superior cerebellar artery that compresses and demyelinates the trigeminal nerve
Trigeminal neuralgia treatment
carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine
phenytoin, gabapentin, or topiramate
topical anesthetics
if refractory - injections or surgery
Herpes zoster
reactivation of dormant varicella zoster secondary to immune response
painful vesicular rash in single dermatome
Herpes zoster S&S
stereotypical rash preceded by 2-3 days of burning, tingling, or pain in dermatomal distribution
may be followed by fatigue, malaise, low grade fever, and HA
if pain persists past 1 month --> post herpetic neuralgia
Herpes zoster opthalmicus
distribution of CNV and may involve cornea
Herpes zoster oticus
aka Ramsay Hunt syndrome
involves facial nerve causing facial paralysis or severe ear pain
Herpes zoster diagnostics
Tzanck smear or clinical dx
Herpes zoster treatment
antiviral therapy with initiation within 72 hrs - acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir
analgesic - NSAID, narcotic, anticonvulsants (gabapentin or pregabalin), TCAs (amitriptyline or nortriptyline)
topical analgesics - lidocaine or capsaicin
prevent secondary bacterial infections
Spongiform encephalopathy
group of progressive, fatal neurodegenerative disorders characterized by spongiform changes in brain tissue triggered by prions
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
Variant CJD (vCJD or BSE)
Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Syndrome (GSS)
Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI)
Kuru
most often diagnosed post-mortem
Spongiform encephalopathy etiology
sporadic, genetic, or acquired
Spongiform encephalopathy S&S
rapidly progressive dementia
myoclonus
visual disturbances
cerebellar dysfunction (ataxia)
behavior changes
Spongiform encephalopathy diagnosis
clinical
MRI - hyperintense signals in putamen and caudate nucleus
definitive - biopsy or autopsy
Spongiform encephalopathy treatment
supportive
death typically within 1 year
Hashimoto encephalopathy
rare, potentially treatable autoimmune encephalopathy associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis
linked to anti-thyroid antibodies (anti-TPO and anti-thyroglobulin)
Hashimoto encephalopathy S&S
cognitive impairment
seizures
myoclonus
psychosis
ataxia
stroke-like episodes
Hashimoto encephalopathy diagnostics
elevated anti-TPO and anti-Tg
normal-mildly abnormal thyroid function tests
r/o other causes (infections, metabolic disturbances, and neoplasms)
response to corticosteroid treatment supports diagnosis
Hashimoto encephalopathy - diagnostic criteria
need all 6:
1. encephalopathy with seizures, myoclonus, hallucinations, or stroke-like episodes
2. subclinical or mild overt thyroid disease
3. brain MRI normal or non-specific
4. presence of serum thyroid antibodies
5. absence of well-characterized neuronal antibodies in serum and CSF
6. reasonable exclusion of alternative cases
Hashimoto encephalopathy treatment
corticosteroids - high dose prednisone or IV methylprednisolone
alternative immunosuppressive therapies - azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, or rituximab if refractory
supportive care
Wernicke encephalopathy
acute neuropsychiatric syndrome resulting from thiamine (B12) deficiency
Wernicke encephalopathy etiology
MCC - alcoholism
malnutrition or malabsorption
hyperemesis gravidarum
prolonged IV feeds w/o B12 supplements
Wernicke encephalopathy S&S
triad - ocular abnormalities, gait ataxia, mental status changes
hypotension, hypothermia, peripheral neuropathy
Wernicke encephalopathy diagnostics
H&P
low serum thiamine levels
MRI with bilateral lesions in thalami, mammillary bodies, periaqueductal area
Wernicke encephalopathy treatment
high dose thiamine IV
then oral thiamine supplementation
Wernicke encephalopathy progression
Korsakoff syndrome - amnesia and confabulation
Hepatic encephalopathy
neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver dysfunction leading to accumulation of neurotoxins in blood
acute liver failure, chronic liver disease
precipitating factors - GI bleeding, infection, high protein intake, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, certain meds
Hepatic encephalopathy S&S
cognitive changes
neuromuscular abnormalities - asterixis, hyperreflexia, rigidity
behavioral changes
stupor or coma
Hepatic encephalopathy diagnostics
elevated blood ammonia levels
LFTs
exclusion of other AMS causes - intracranial or metabolic issues
Hepatic encephalopathy treatment
treat underlying cause
lactulose
rifaximin
dietary management
Questions to ask with headaches
onset
location
precipitating events
progression
provocative
quality
radiation
severity
timing
Headache classification
primary - no structural or metabolic etiology
secondary - related to underlying condition
Headaches requiring immediate intervention
vascular
infections
mass lesions
pre-eclampsia
CO poisoning
Headache imaging indications
"worst headache ever"
sudden pattern change
over 50
positional
seizure
fever
head injury
pulsatile sounds
focal signs
history of CA or HIV
related to exercise, sex, coughing, sneezing, urination, or defecation
refractory
severe patient anxiety
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
sentinel headache
MCC - trauma
if spontaneous - most often 2nd to aneurysm rupture
Subarachnoid hemorrhage S&S
"worst headache of my life"
NV
meningismus
alteration of consciousness
focal deficits often absent
Subarachnoid hemorrhage workup
non-contrast CT stat!
LP if scan negative or ambiguous
cerebral angiography - if negative CTA after 2 weeks
Headache types
sinus - behind forehead and/or cheekbones
cluster - in and around 1 eye
tension - hat band pain
migraine - pain, nausea, visual changes
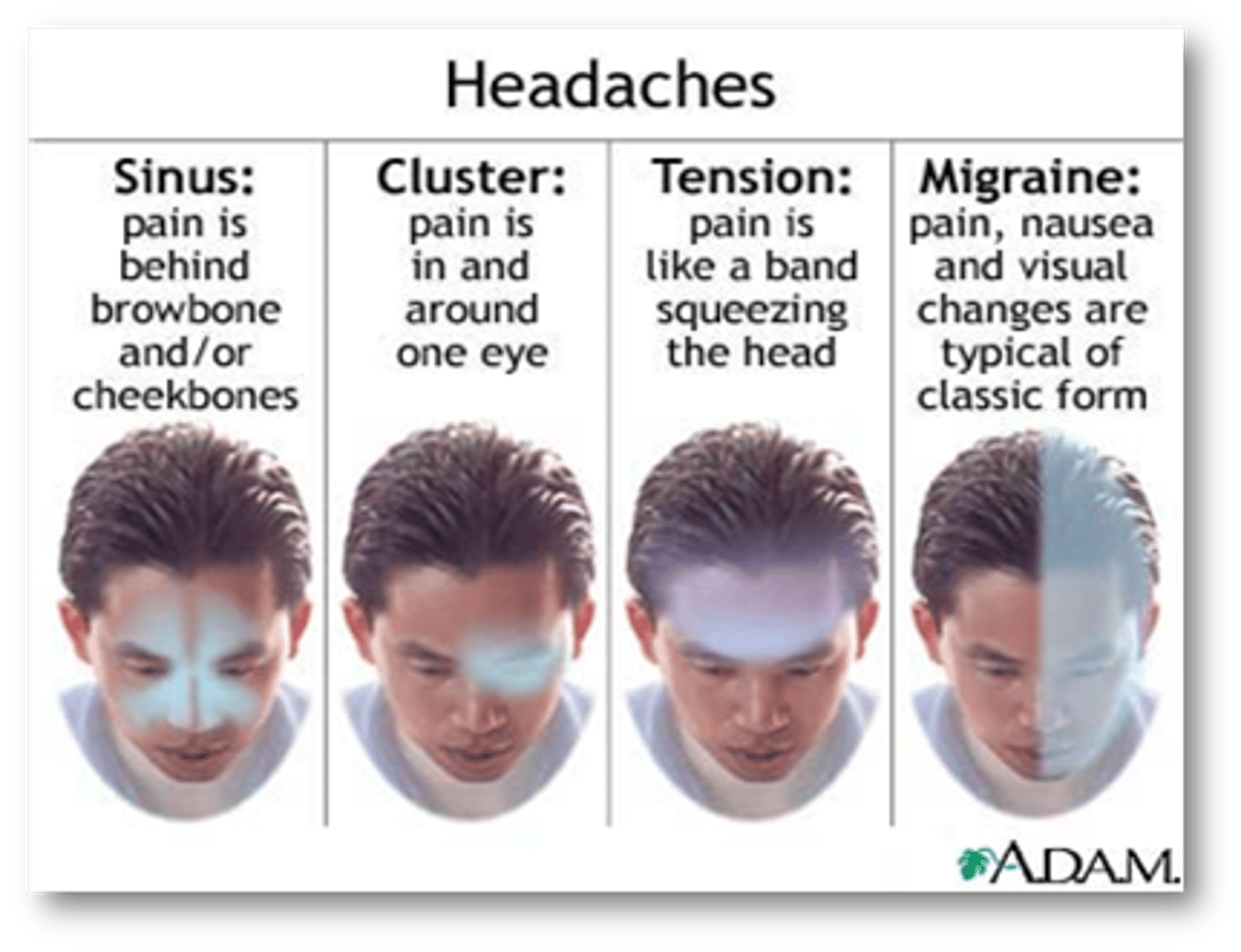
Tension headaches
MC type of headache
hat band formation but can also be generalized
no nausea or vomiting
Tension headaches management
regulate sleep and meals
exercise
stress management
biofeedback and CBT
acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, ASA, caffeine
if chronic - TCA or anticonvulsants
Episodic tension-type headache diagnostic criteria

Migraine headaches
at least 5 attacks lasting 4-72 hrs
at least 2: unilateral, pulsating, mod-sev, aggravation by walking
at least 1: NV, photophobia, and phonophobia
w or w/o aura
focal deficits may occur - disequilibrium, paresthesia, aphasia
Basilar artery migraine
blindness or binocular visual disturbances
dysarthria, tinnitus, perioral and distal paresthesia precede HA
occipital HA
Ophthalmoplegic migraine
periorbital pain and diplopia
4th or 6th CN palsy
may outlast HA by weeks
Migraine equivalent
neuro or somatic complains occurring in isolation
"migraine w/o HA"
Migraine treatment
avoidance of triggers
abortive therapy
prophylactic therapy
Precipitating factors of migraines
stress
foods
+/- sleep
light
noise
menstrual cycle
OCP
Precipitating factors of cluster HAs
alcohol
stress
light
foods
Migraine - abortive treatment
OTC analgesics
Rx NSAIDs - diclofenac, etodolac
ergotamines - DHE (spray or injection) or cafergot PO
Triptans - first line
CGRP inhibitors
monoclonal antibodies - Aimovig, Ajovy, Emgality
Gepants - Ubrelvy or Nurtec
Ergotamines are contraindicated in
vascular disease, NV, diarrhea
Triptans are contraindicated in
vascular disease or complex migraine
Triptans
sumatriptan
Imitrex
Maxalt
Relpax
Zomig
Amerge
Axert
Frova
Treximet
Triptans in pregnancy
pregnancy category C
Migraine prophylaxis indications
3 or more episodes per month
significant impact on daily activity
abortive medications ineffective, contraindicated, overused, or giving adverse effects
patient preference
Migraine prophylaxis meds
beta blockers
CCBs
anti-depressants (SSRIs/Tricyclics)
seizure meds (topamax, depakote, neurontin, zonisamide)
Botox injections
Cefaly headband
Cluster headaches
short, severe, unilateral occurring in clusters (1-many/day for 2 weeks to months)
episodes last 15 min - 3 hrs
extended pain free intervals
periorbital
lacrimation
rhinorrhea or nasal congestion
eyelid swelling
fatigue
Cluster headache treatment
oxygen via non-rebreather
sumatriptan injection
zolmitriptan nasal spray
viscous lidocaine intranasally
DHE IM
Verapamil - first line for preventative
Occipital neuralgia
chronic pain in upper neck, posterior aspect of head, and/or retroorbital pain
Occipital neuralgia etiology
trauma to back of head
compression of occipital nerves
inflammation or irritation of occipital nerves
medical conditions
muscle tension and strain
poor posture
Occipital neuralgia S&S
sharp, shooting, or electric-shock like pain at base of skull radiating to scalp
pain behind eyes
photophobia
scalp tenderness
Occipital neuralgia diagnostics
H&P
diagnostic nerve blocks
Occipital neuralgia treatment
rest, heat, PT, NSAIDs
muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants, antidepressants
nerve blocks and steroid injections
Botox
surgical decompression
neurostimulation