Biology - B1.1 Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Monomer
single units, one molecule that can be used to form dimers and polymers
e.g. amino acid, glucose (monosaccharide), fatty acid
Dimers
Two single units, two monomers bonded together
For carbohydrates, it’s disaccharides, and for proteins, it’s dipeptides
Polymers
Three or more single units, three or more monomers bonded together. Can be different monomers bonded together
For carbohydrates, it’s polysaccharides, and for protein, it’s polypeptides
Why is life based on carbon?
all biological molecules require carbon (e.g. DNA and enzymes)
carbon is useful because it requires four covalent bonds and then an enormous variety of molecules can be formed (rings, chains or branches)
Macromolecules
Very large molecules, they are all polymers so they are made up of many monomers. The official limit for a macromolecule is more than 10,000 atomic mass units.
What is a condensation reaction?
The joining of two molecules together with the release water by removing a hydroxyl group and an extra hydrogen.
Energy is required for this reaction in the form of ATP, endothermic reaction
Anabolic reactions
Reactions that build up larger molecules from smaller molecules
Why is water made during a condensation reaction?
The available elements are H2 and O2, and H2O2 is toxic, whilst H2 would make the cells too acidic.
The water formed usually turns into the cytoplasm or exits through osmosis.
Hydrolysis reaction
Literally means ‘water split’
Opposite of condensation reaction
A water molecules is used and split to provide the hydroxyl group and hydrogen that are needed to form new bonds.
Exothermic reaction because energy is released in the form of ATP or thermal energy
Function of hydrolysis reactions
Used to deconstruct polymers into monomers as an energy source or to create new molecules. Mainly used during digestion.
Catabolic reactions
Destruct bonds
Hydrolysis reactions are catabolic
What bond is made after condensation for carbohydrates?
1→ 4glycosidic bonds, covalent bonds, because they are made between two glucoses and between the 1st and 4th carbon
What are the monomers of carbohydrates called?
Monosaccharides
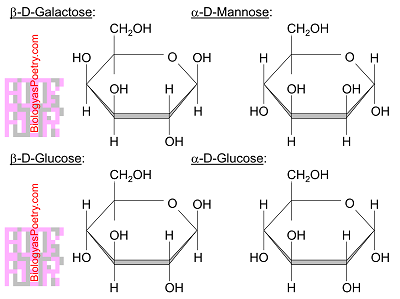
What is a hexose monosaccharide?
A monomer of carbohydrates with 6 carbons, in the shape of a hexagon, with oxygen in the top right angle and the sixth carbon added on the top left.
e.g. glucose or fructose
Pentose monosaccharide
A monomer of carbohydrates with 5 carbons, in the shape of a pentagon, with oxygen in the top center angle and the sixth carbon added on the top left.
e.g. ribose or deoxyribose
Functions of monosaccharides
soluble and then easily transportable
chemically stable so can be stored easily without changing form
good source of energy for aerobic or anaerobic respiration
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates with many monosaccharides joined together
Function of polysaccharides
They are insoluble and are then incredibly good energy sources
Two types of starch
Amylose and amylopectin
What is starch?
Polymer of glucose
Used as storage of glucose for energy because of it’s compact storage and insolubility
Found in plants
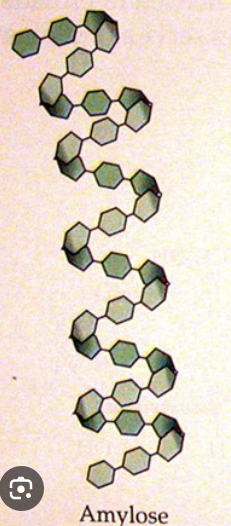
Amylose
Monomer: alpha glucose
Bonds: 1→ 4 glycosidic bonds
Shape: unbranched chain of alpha glucose with a helical shape due to the 1→ glycosidic bonds because they cause an angle between the two monomers
Function: energy storage in plants
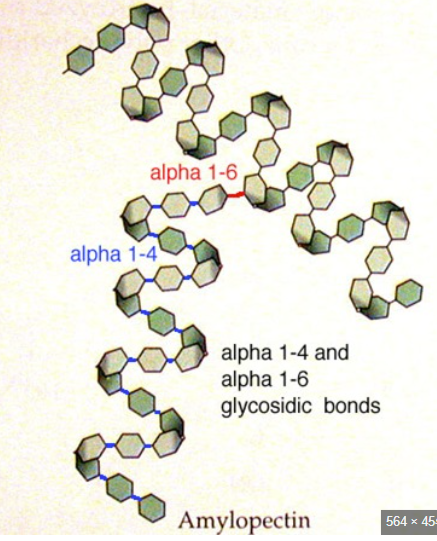
Amylopectin
Monomer: alpha glucose
Bonds: 1→ 4 glycosidic bonds and some 1→ 6 glycosidic bonds
Shape: chain of alpha glucose with a helical shape and some branches
Function: energy storage in plants. the branches make it the glucose more accessible because there are more ends
Glycogen
Monomer: alpha glucose
Bonds: 1→ 4 glycosidic bonds and (1 in 10) 1→ 6 glycosidic bonds
Shape: chain of alpha glucose with a helical shape and many branches
Function: energy storage in animals. the many branches make the energy easily accessible
Function of cellulose
Strong structure/material for cell wall
What is the monomer for cellulose?
beta glucose
What is the structure of beta glucose?
Beta glucose is different from alpha glucose because the hydroxyl groups are on opposite structures for beta glucose. The OH and H are reversed at the first carbon.
Why does the structure of cellulose help its function?
Cellulose is made up of beta glucose so every other beta glucose has to flip in order to maintain the 1→ 4 glycosidic bonds
As the monomers flip, the angles of the bonds cancel out and result in a straight chain.
The straight chains can then easily be stacked on top of each other and hydrogen bonds are created between the OH and H of the beta glucose monomers.
These hydrogen bonds make cellulose stronger than any other polysaccharide, helping its function.
Glycoprotein
Def: molecules with both a carbohydrate and a protein part
Particularly common in animal cell membranes
The carbohydrate part sticks out of the cell membrane and acts as a recognition site for other cells
Oligosaccharide
3-15 monosaccharides
What are the three types of glycoproteins?
A, B and O
Structure of A, B and O glycoproteins
A has 5 monosaccharides with the first four being the same base as the other glycoproteins
B has 5 monosaccharides with the first four being the same base as the other glycoproteins, different than A
O has 4 monosaccharides, all four being the same base as with A and B
Antigens
The glycoproteins A and B are called antigens as they stimulate an immune response (depending on the blood type of the person)
How are A, B and O glycoproteins useful during blood transfusions?
The A, B and O glycoproteins show what type of blood would be rejected by the body as it is foreign.
O is the universal donor as it has the same base as A & B. If the blood type is O, only O can be transfused.
If someone has blood type AB, any blood can be given; no glycoproteins will be considered foreign.
What are the types of lipids?
Fats, oils, waxes and steroids
Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
They are said to be hydrophobic however, they solely prefer non-polar substances, and then mostly dissolve in non-polar substances.
This is because lipids contain less oxygens which are slightly electronegative meaning they have less polarity.
What is the melting point for oils?
Around 18 degrees Celsius or below room temperature
What is the melting point for fats?
Above room temperature but below 37 degrees Celsius
What is the melting point of waxes?
Above 37 degrees celsius
What is the structure of steroids?
They have four fused carbon rings (characteristic four-ring structure)
Structure of triglycerides
One glycerol and three fatty acids though the structure of the fatty acid can vary
Are formed by condensation reactions as the OH of a the carboxyl group of the hydrocarbon chain can react with one of the hydroxyls of the glycerol
3 waters molecules are produced
Ester bonds are the bonds connecting the fatty acids to the glycerol
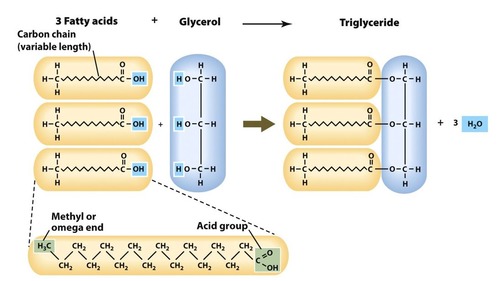
Structure of fatty acids
Carboxyl group at one end (COOH) and then a hydrocarbon chain and a methyl group at the end (CH3)
COOH(CH2)nCH3 is the general formula of a fatty acid
variations with the presence, position and number of double bonds and the length of the hydrocarbon chain
Compare and contrast the bond formed between the fatty acid and the glycerol with the bond between two monosaccharides
Ester bond vs. glycosidic bond, both are made through a condensation reaction
What are the two categories of fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acid vs. unsaturated fatty acid (cis or trans fatty acids)
Saturated fatty acid
Fatty acids that have single bonds between every carbon on the hydrocarbon chain
General formula of CnH2nO2
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with one or more double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
Either cis or trans depending on where the hydrogens of the carbons that have the double bond are positioned
Cis unsaturated fatty acids
The hydrogens connected to the carbons of the double bond are on the same side
So they bend at the double bend
So they are less easy to stack and have a lower melting point and are liquid at room temperature, oils
What type of fatty acids do animals store their lipids as?
Saturated fatty acids
What type of fatty acids do animals store their lipids as?
Unsaturated cis fatty acids
Unsaturated trans fatty acids
The hydrogens connected to the carbons with the double bond are on the same side
So they are straight-chained and have a higher melting point and are solid at room temperature
They are produced artificially
Monounsaturated vs. polyunsaturated fatty acids
Monounsaturated fatty acids have one double bond whilst polyunsaturated fatty acids have two or more
What group of cells are triglycerides stored in in animals?
Adipose tissue, which is located beneath the skin and around organs
What are the advantages of triglycerides being stored in adipose tissue?
Chemically stable, so the lipids don’t get involved in reactions
The lipids don’t dissolve so don’t have any effect on the solute concentration and osmosis
Lipids release twice as much energy per gram than carbohydrates so double the energy can be stored in half the body-mass
Poor conductors, so excellent thermal insulators
Liquid at body temperature so they can absorb shock
Compare and contrast carbohydrates and lipids as energy storage compounds
Both are used in energy storage
Carbs is short term while lipids is long term
Carbs can be mobilized easily while lipids takes longer to mobilise
Carbs are soluble and then easily transportable while lipids are insoluble and harder to transport
Carbs release less energy per gram while lipids release double the energy per gram
Carbs can be used in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration while lipids can only be used in aerobic respiration
Phospholipids
Structure: have a section that is hydrophobic (the fatty acids, the tail) and a section that is hydrophilic (the phosphate group and the glycerol, the head)
Therefore, amphipathic, although the hydrophobic part has more effect as the tails are longer in comparison to the head
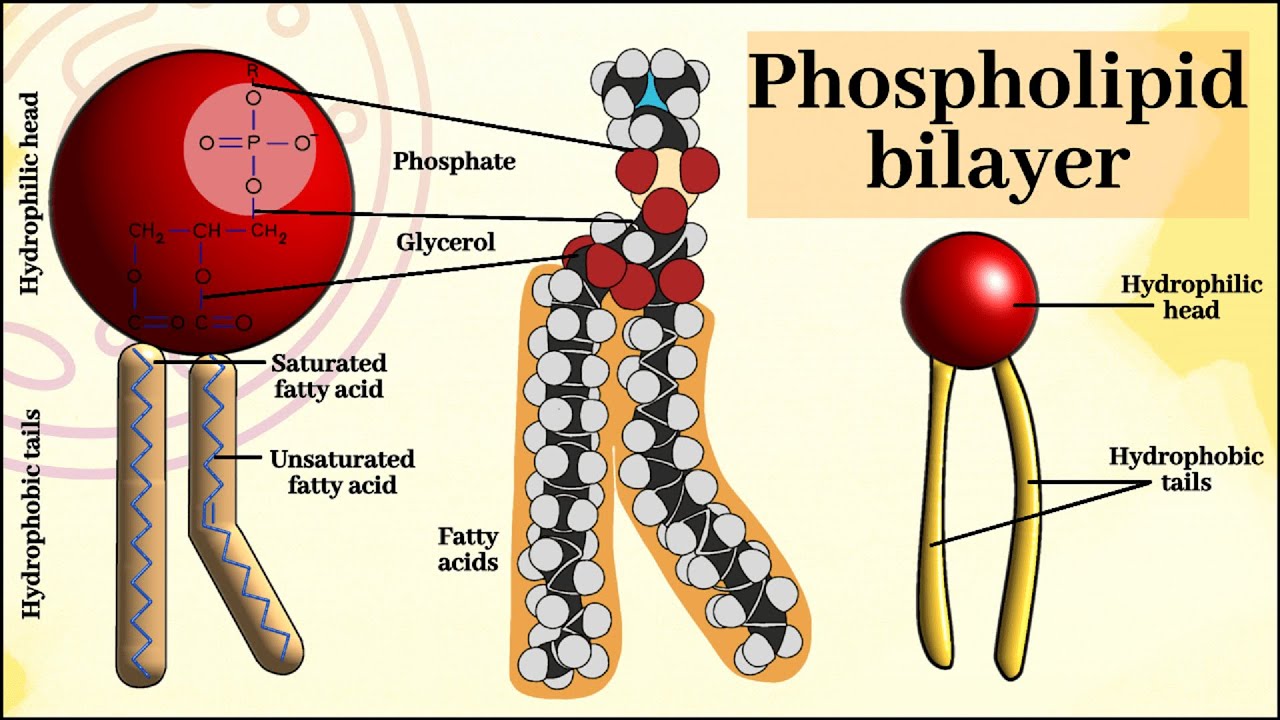
Amphipathic
When one part of a molecule is hydrophobic while another is hydrophilic
Structure of cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer with phospholipids arranged in two layers, the heads are faced towards the inside the cell and towards the solution outside, the tails are all pointing inwards
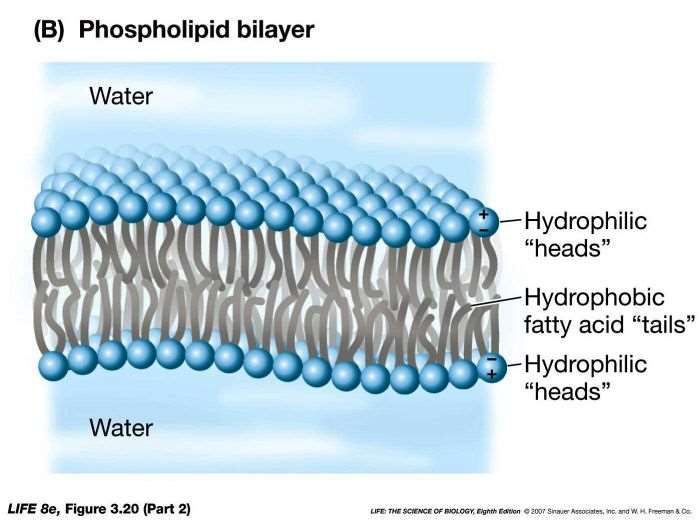
Phospholipid bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids, both hydrophobic and hydrophilic with the hydrophobic tails facing inwards
Steroids easily passing through a cell membrane
They can easily pass through a cell membrane because they are considered hydrophobic because they are made of mostly hydrocarbons
This is useful as steroids regulate many levels and reactions