Eukaryotes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are some shared derived characteristics of eukaryotes?
nucleus
endomembrane system (organelles)
cytoskeleton
mitochondria
cytoskeleton
network of fibers;
functions as support and shape change
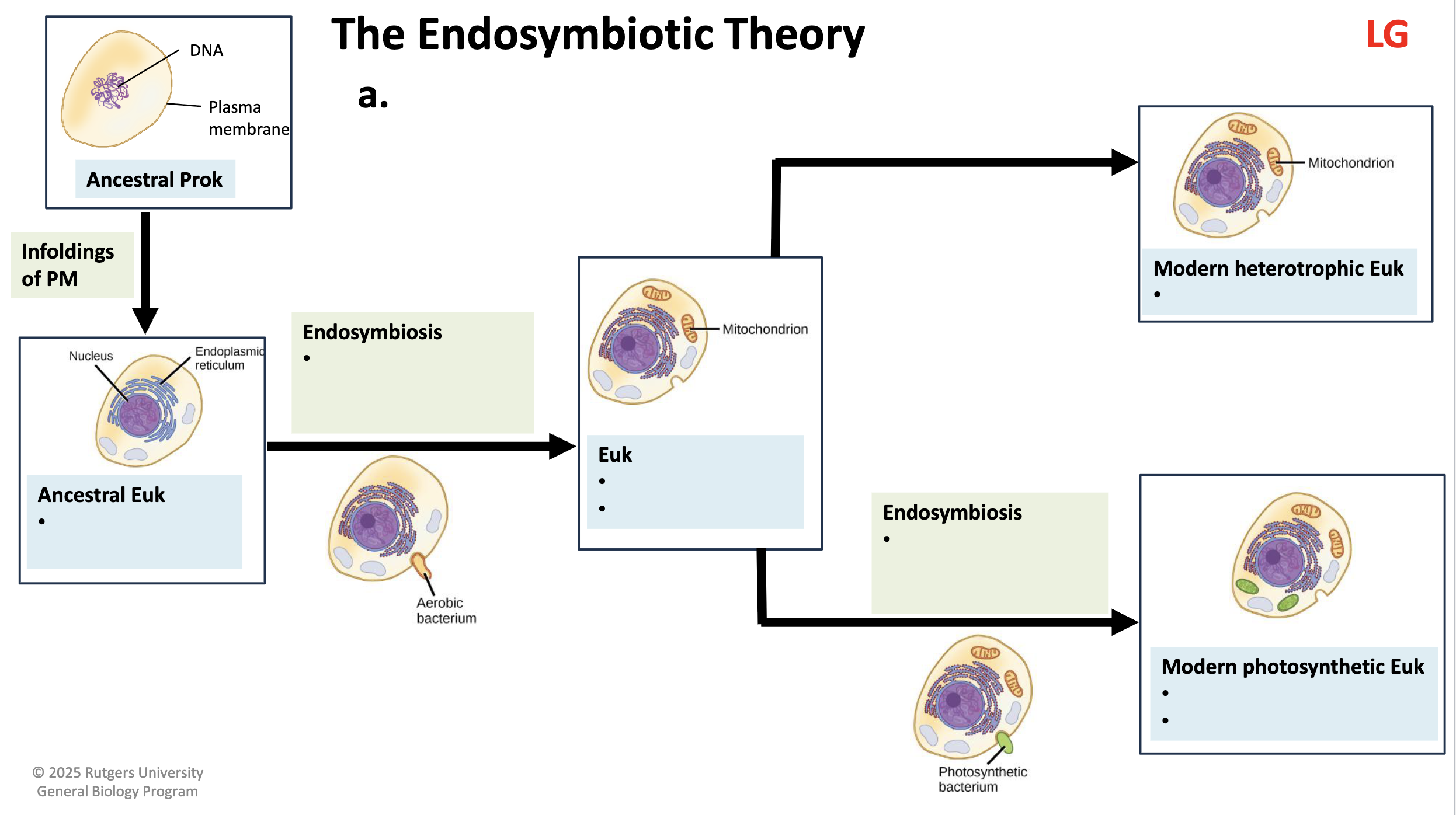
serial endosymbiosis
one cell engulfs another and both benefit
primary endosymbiosis
a prokaryote was engulfed by another cell
proteobacteria →
mitochondria
cyanobacteria →
plastids (chloroplasts)
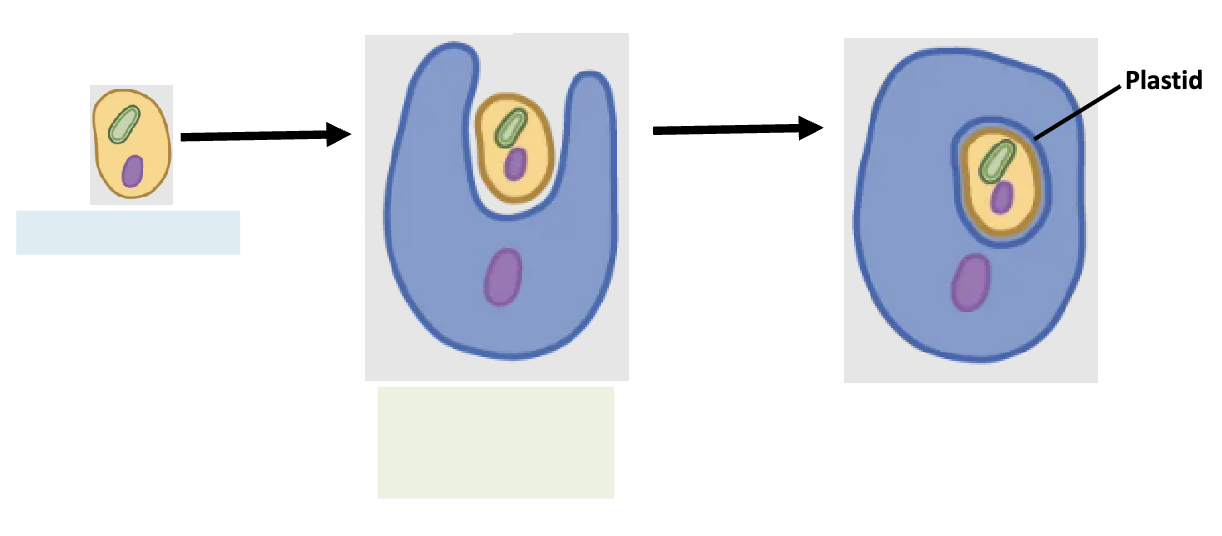
secondary endosymbiosis
a eukaryote was engulfed by another cell
draw primary endosymbiosis
draw secondary endosymbiosis
All eukaryotes are protists except…
land plants, fungi, and animals
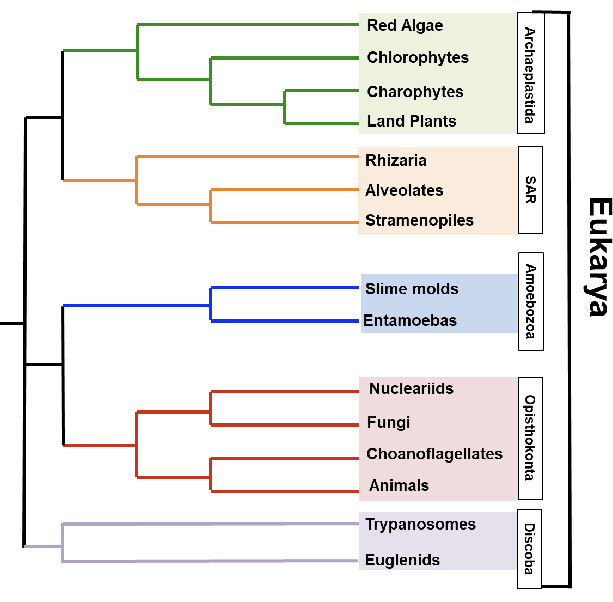
5 supergroups
archaeplastida
SAR
amoebozoa
opisthokonta
discoba
Most protists are multicellular or unicellular?
unicellular
protists
first eukaryotic cells
What are three possible nutritional strategies of eukaryotes?
photoautotrophs
heterotrophs
mixotrophs
Photoautotrophs get energy using…
chloroplasts
Heterotrophs get energy using…
organic molecules
Mixotrophs get energy using…
photosynthesis & heterotrophic
archaeplastida branches
red algae
chlorophytes
charophytes
land plants
archaeplastida shared derived character
chloroplast from primary endosymbiosis of a cyanobacterium
Is all of archaeplastida photosynthetic?
yes
red algae
phycoerythrin
multicellular and highly branched
warm tropical oceans
phycoerythrin
red photosynthetic pigment that absorbs blue & green light (deep into water) → deep habitats
green algae
chlorophytes & charophytes;
chloroplasts very similar to land plants
What is most closely related to land plants?
charophytes
SAR branches
rhizaria
alveolates
stramenopiles
SAR shared derived character
secondary plastid from red algae
stramenopiles shared derived character
2 paired flagella: long hairy + short smooth
3 main groups of stramenopiles
diatoms
golden algae
brown algae
wall of diatom
silicon dioxide → glass-like
2 overlapping parts
protection
diatomaceous earth
filters, absorbs, medicinal
features of golden algae
yellow & brown carotenoids
most are unicellular
tiny scales of silica or CaCO3
Where is golden algae found?
freshwater & marine biomes
Golden algae are nanoplankton, meaning that they are…
2 - 10 um
diverse group
cannot swim against the current
features of brown algae
most complex protists
multicellular
large (few cm to 75 m)
seaweed
Where is brown algae found?
cold marine waters;
form kelp forests, which inhabit a variety of other organisms
What is the commercial importance of brown algae?
some edible
algin
algin
polysaccharide in cell walls of brown algae;
thickener
alveolates shared derived character
alveoli (sacs under PM)
3 groups of alveolates
ciliates
dinoflagellates
apicomplexans
ciliates
cilia; move & feed
features of dinoflagellates
2 flagella; spin
plankton
dinoflagellates bloom
population explosion;
carotenoids;
ex: red tide
apicomplexans
apical complex that penetrates host cells
ex: plasmodium → malaria
rhizaria shared derived character
genetic similarities & shells
2 groups of rhizaria
radiolarians
foraminiferans (forams)
radiolarians
internal skeleton of silica
foraminiferans (forams)
descends from rhizaria;
tests = porous shells of CaCO3;
thick marine sediment : billions of shells
amobozoa branches
slime molds
entamoebas
amobozoa shared derived character
genetic similarities
blob shape
pseudopodia
entamoeba histalytica
amoebic dysentery
opisthokonta branches
nucleariids
fungi
choanoflagellates
animals
opisthokonta shared derived character
genetic similarities
single, posterior flagellum
nucleariids
protists
sister taxon of fungi
choanoflagellates
protists
sister taxon of animals
discoba branches
trypanosome
euglenids
discoba shared derived character
crystalline rod in flagellum
trypanosome
African sleeping sickness
euglenids shared derived character
secondary plastids from green algae
draw the tree of eukarya with the 5 supergroups