Veterinary Parasitology CH8 - Trematodes of Domesticated Animals
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study material for Chapter 8 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
“Forked bowl” or “Lancet fluke”
Affects: Sheep, goats, cattle
Adults live in bile duct
1st intermediate host: Cionella lubrica land snail — Unique in that intermediate hosts are not aquatic
2nd intermediate host: Formica fusca, ant– behavior of both snail and ant can be altered by infection—ant brain infection leads to tetanus of jaw muscles so they stick to the grass
Found: Worldwide
Zoonotic
Operculated egg, adult is only 1-2.5 mm across and 6 to 10 mm long
Oral sucker, ventral sucker, two testes and lateral vitellaria that secrete yolk and help provide nutrition and shell for the egg
Can cause hyperplasia of bile duct leading to obstruction
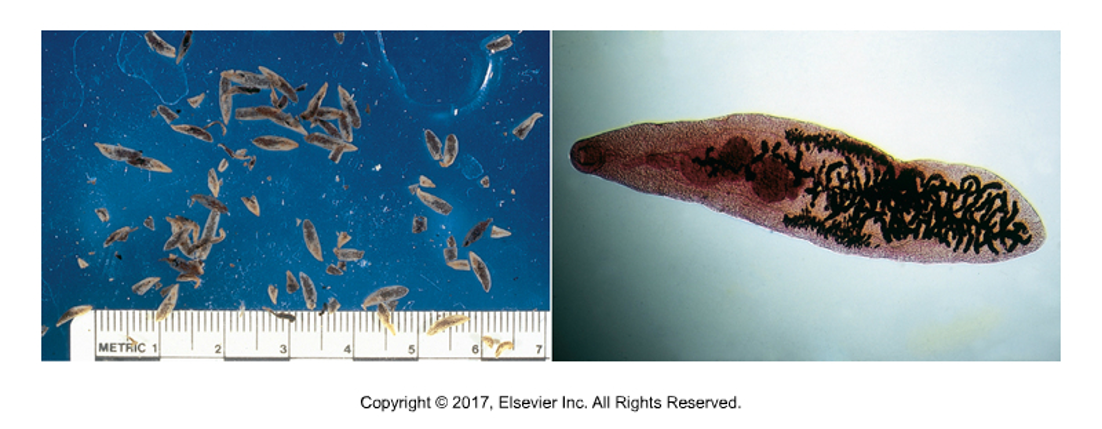
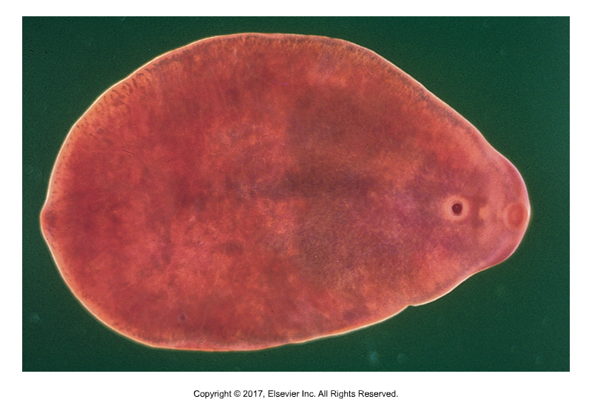
Paramphistomum sp. and Cotylophoron sp.
“Rumen fluke”
1st intermediate host: Aquatic snail
No 2nd intermediate host; metacercariae bind to vegetation
Cause of infection: Ruminants eat vegetation
“Amphistome” means 2 mouths. Obvious oral sucker on one end and ventral sucker is at opposite end.
Adults are not pathogenic, but migration of young flukes can cause problems as they eat the intestinal lining
Not zoonotic
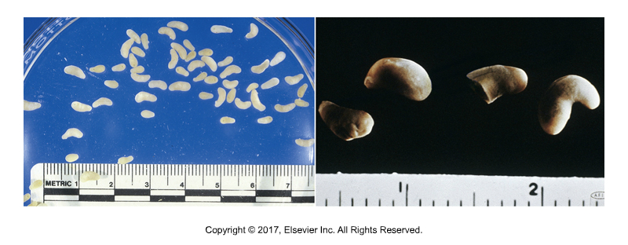
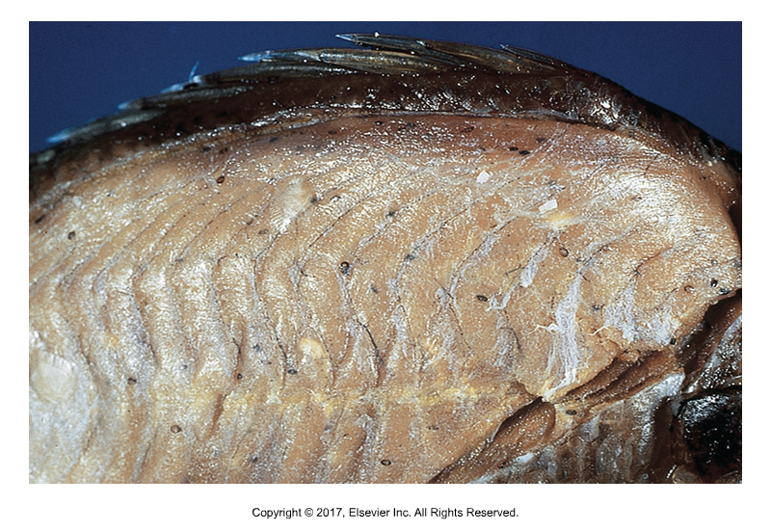
Fasciola hepatica
“Liver fluke”
Affects: Sheep, cattle, goats
Causes “liver rot”
1st intermediate host: Aquatic snail
No 2nd intermediate host
Cause of infection: Ingestion of vegetation with metacercariae
Most economically important, most studied fluke
Adults obstruct bile duct 30 x 13 mm, broad anterior end with cone shape projection, more narrow posterior end
Tan to reddish brown
Eggs found in fecal sedimentation
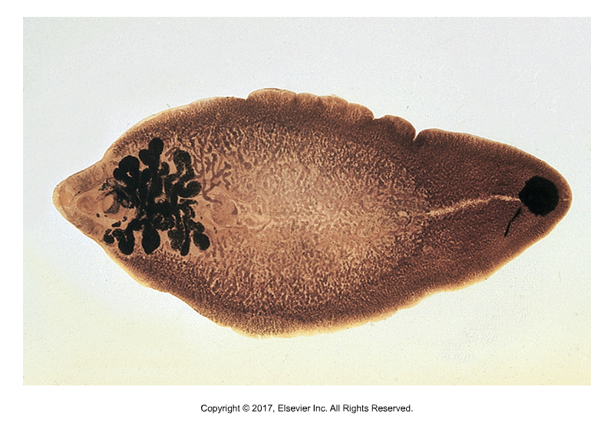
Fasciola magna
Affects: White tailed deer, can use ruminants and sheep as incidental host
1st intermediate host: aquatic snail
No 2nd intermediate host
Cause of infection: Ingestion of vegetation with metacercariae
Adults in liver parenchyma
Not zoonotic
Larger than F. hepatica at 10 cm long, and thicker at 4.5mm
Eggs can be found in fecal sedimentation, but only in deer host
Why do they call the cow or sheep the “dead end host” for Fasciola magna?
Incidental hosts will not release cysts in feces, only found at necropsy — “Dead end host” cannot transmit
Platynosomum fastosum
“Lizard poisoning fluke”
Affects: Cats
Adult in bile ducts
Found in: S. America, Southern U.S. Carribbean, Pacific Islands
1st intermediate host: land snail
2nd intermediate host: lizard
Cause of infection: Ingestion of infected lizards
Not zoonotic
Symptoms: Diarrhea, vomiting, jaundice
Tiny, only 4-8 mm long
Eggs can be found in fecal flotation

NanoIyphyetus salmincola
“Salmon poisoning fluke”
Affects: Dogs
1st intermediate host: Freshwater snail
2nd intermediate host: Salmon
Found in: Pacific Northwest of N. America
Zoonotic
Adult in small intestine, vector for Rickettsia bacteria causing Elokomin fluke fever
Smallest fluke at only 1.1mm in length, white or cream in color
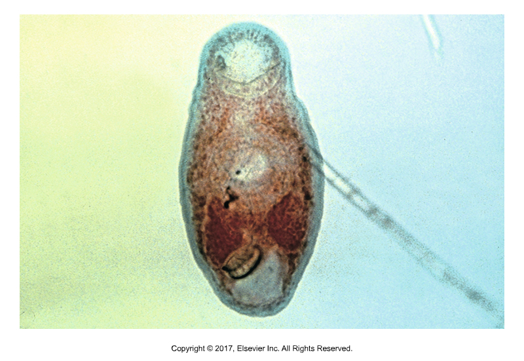
Alaria sp.
Affects: Dogs and cats
Found in: Northern U.S. and Canada
1st intermediate host: Freshwater snail
2nd intermediate host: Frog, snake, mouse
Adult in Small intestine
Not zoonotic
Unique in that front is flat, but posterior half is thick and spherical
Adults are not pathogenic but migrating larvae can be
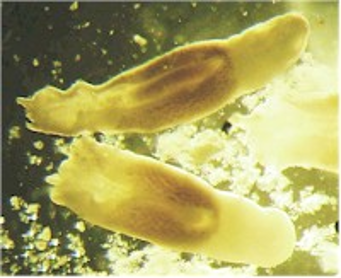
Paragonimus kellicotti
“Lung fluke”
Affects: Dogs and cats
Adult found in lung
1st intermediate host: Operculated snail
2nd intermediate host: Crayfish
Cause of infection: Ingestion of crayfish
Zoonotic
Eggs found in sputum or fecal sedimentation
Adults are thick, brownish red, 16 mm x 8mm, can be seen on X-Ray
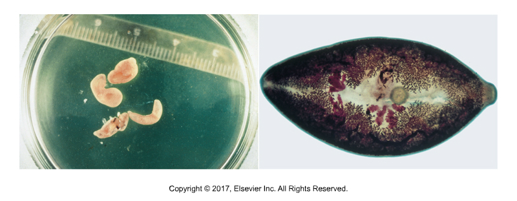
Heterobilharzia americana
“Canine blood fluke”
Found in: N. America, particularly Gulf States (LA, MS)
Zoonotic, but rare
Cause of infection: Metacercariae enter through skin of dog
Adult found in mesenteric veins of intestine and portal veins of liver
Schistosomes “split body” NOT hermaphroditic, male and female of species
Long, thin flukes that can obstruct small veins
Symptoms: Bloody diarrhea, emaciation, anorexia
Egg containing miracidium can be found in fecal sedimentation

Human Blood Flukes
Blood flukes of Schistosoma (Bilharzia) genus can infect human
Found in: Africa, Middle East and Caribbean
Typically species specific so even if cattle or other domestic animals are infected, it is not common to see same species in humans
Cause of infection: Through the skin of humans who come into contact with water containing cercariae
What is Swimmer’s Itch? How is it caused?
Avian blood flukes are also common and can infect snails and then release cercariae that infect humans who swim in water where aquatic birds are migrating, causing Swimmer’s Itch.
What is Black Spot? How can birds get infected with it?
Avian blood flukes that release eggs into the water can infect snails and then release cercariae that infect fish. Metacercariae encyst in muscle and skin and fish increases melanin around them causing Black Spot. Cooked fish with Black Spot should not be able to infect humans, but birds can get infected by eating fish.
