AP Biology Quiz Cellular Organelles' Structure and Functions
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Don't Fail :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
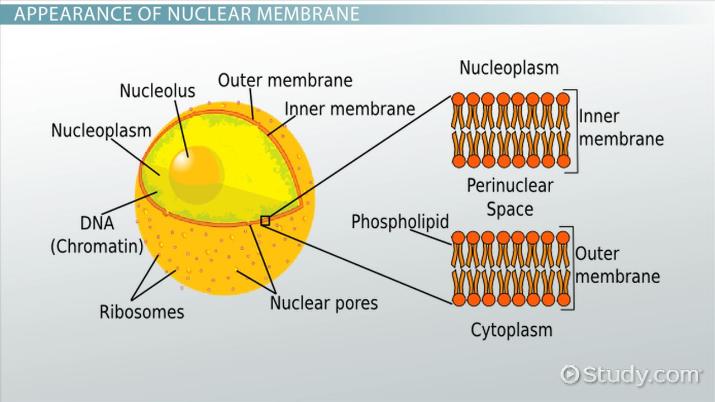
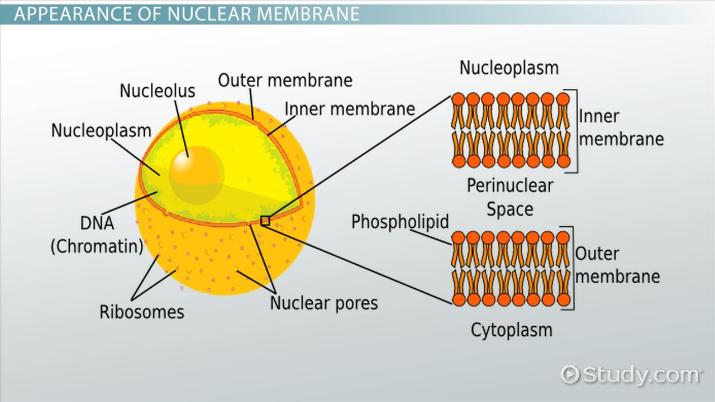
Nucleus
Structure:
Contains the Nuclear Envelope which is made by a double phospholipid bilayer that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Contains Nuclear pores that help regulate what goes in and out of the nucleus
Contains Chromatin which is DNA wrapped in histones
Contains the Nucleolus a dense part of DNA where rRNA are synthesized to form ribosomes
The matrix and lamina provide structural support and help organize genetic material.
Functions:
The nucleus houses the cell's genetic material (DNA), which controls heredity and the blueprint for cellular functions.
Regulates gene expression to control protein synthesis.
The nuclear pores control transport of RNA and proteins essential for gene expression.
Coordinates cell growth, metabolism, and division by regulating DNA replication and transcription of mRNA.
The nucleolus synthesizes rRNA and assembles ribosomal subunits necessary for protein production.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.)
Structure of Rough E.R.
Structure of Smooth E.R.
Golgi Apparatus
Structure:
Composed of a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae
Usually located near the endoplasmic reticulum in the cytoplasm
Has a "cis" face (receiving side) and a "trans" face (shipping side) for processing and dispatching molecules
Function:
Modifies and packages proteins to the right shape
Adds molecular tags (like carbohydrates) to proteins in a process called glycosylation
Also involved in production of lysosomes and secretion of molecules via exocytosis
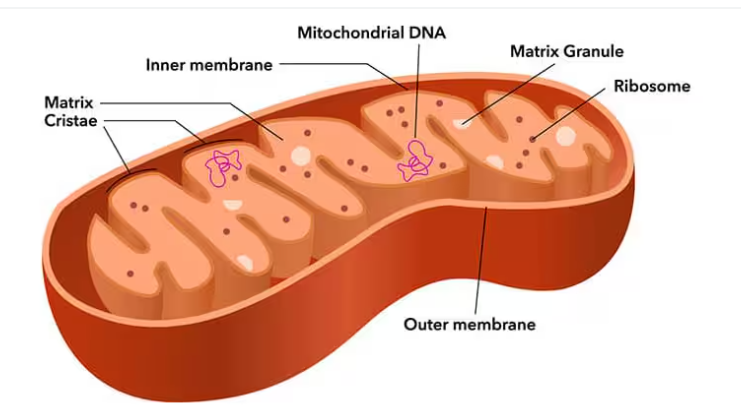
Mitochondria
Structure:
Consists of a double membrane
Smooth outer membrane
Inner membrane is folded into cristae that increases surface are for enzymes that synthesize ATP
Inner membrane creates 2 compartments (Mitochondrial matrix & intermembrane space
Contains ribosomes
Functions:
Helps with Cellular Respiration (Process of using oxygen to generate ATP)
Involved in cell metabolism, growth, and division