Metabolism and Thermodynamics in Biological Systems
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is metabolism in a biological context?
The totality of an organism's chemical reactions, an emergent property of life arising from orderly interactions between molecules.
How does metabolism transform matter and energy?
It transforms matter and energy and is subject to the laws of thermodynamics.
What is an example of bioluminescence in metabolism?
The oxidation of a light-emitting molecule catalyzed by an enzyme.
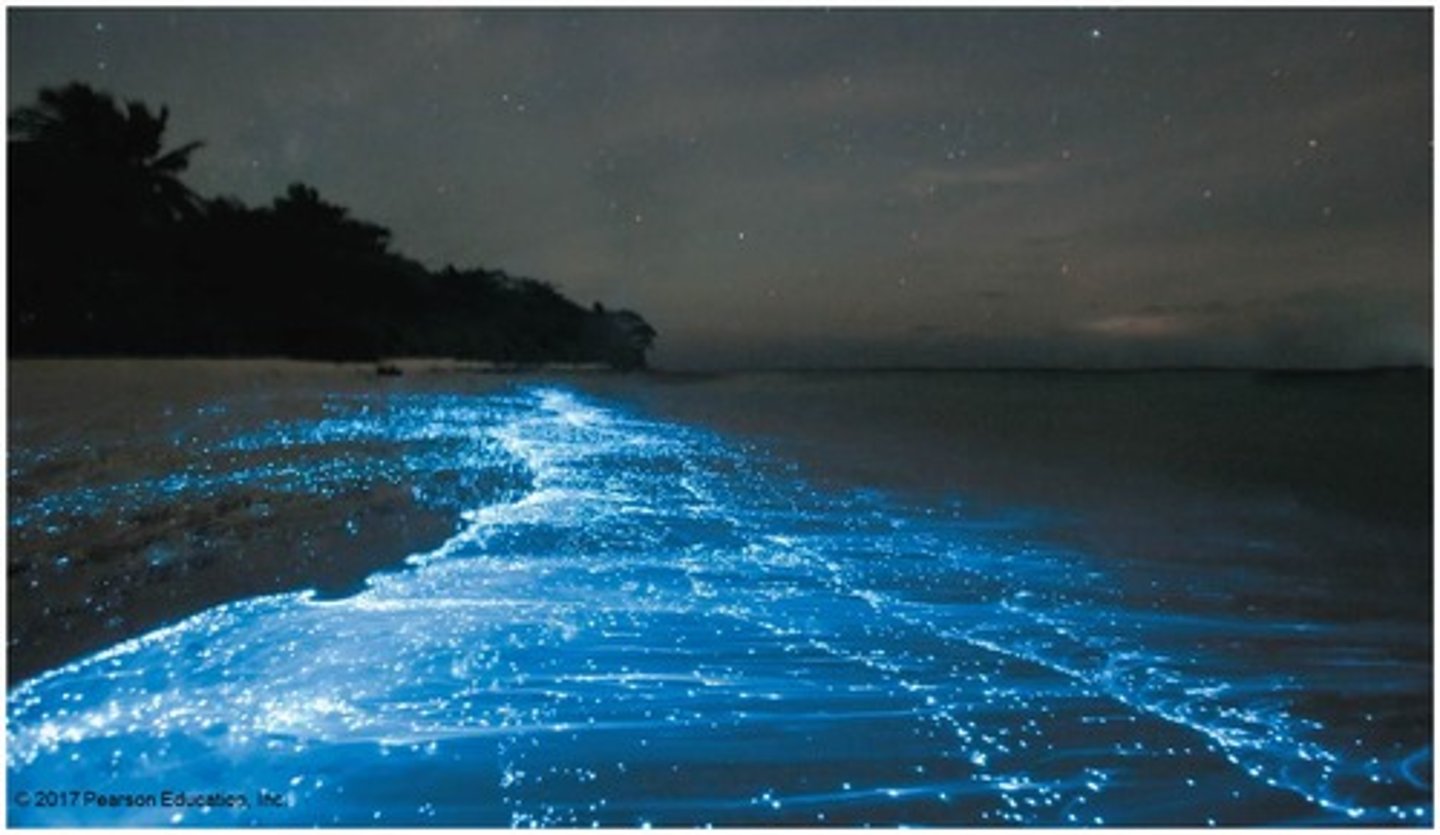

What are metabolic pathways?
Processes that begin with a specific molecule and end with a product, with each step catalyzed by a specific enzyme.
What are the two types of metabolic pathways?
Catabolic pathways and anabolic pathways.
What do catabolic pathways do?
They release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds, such as in cellular respiration.
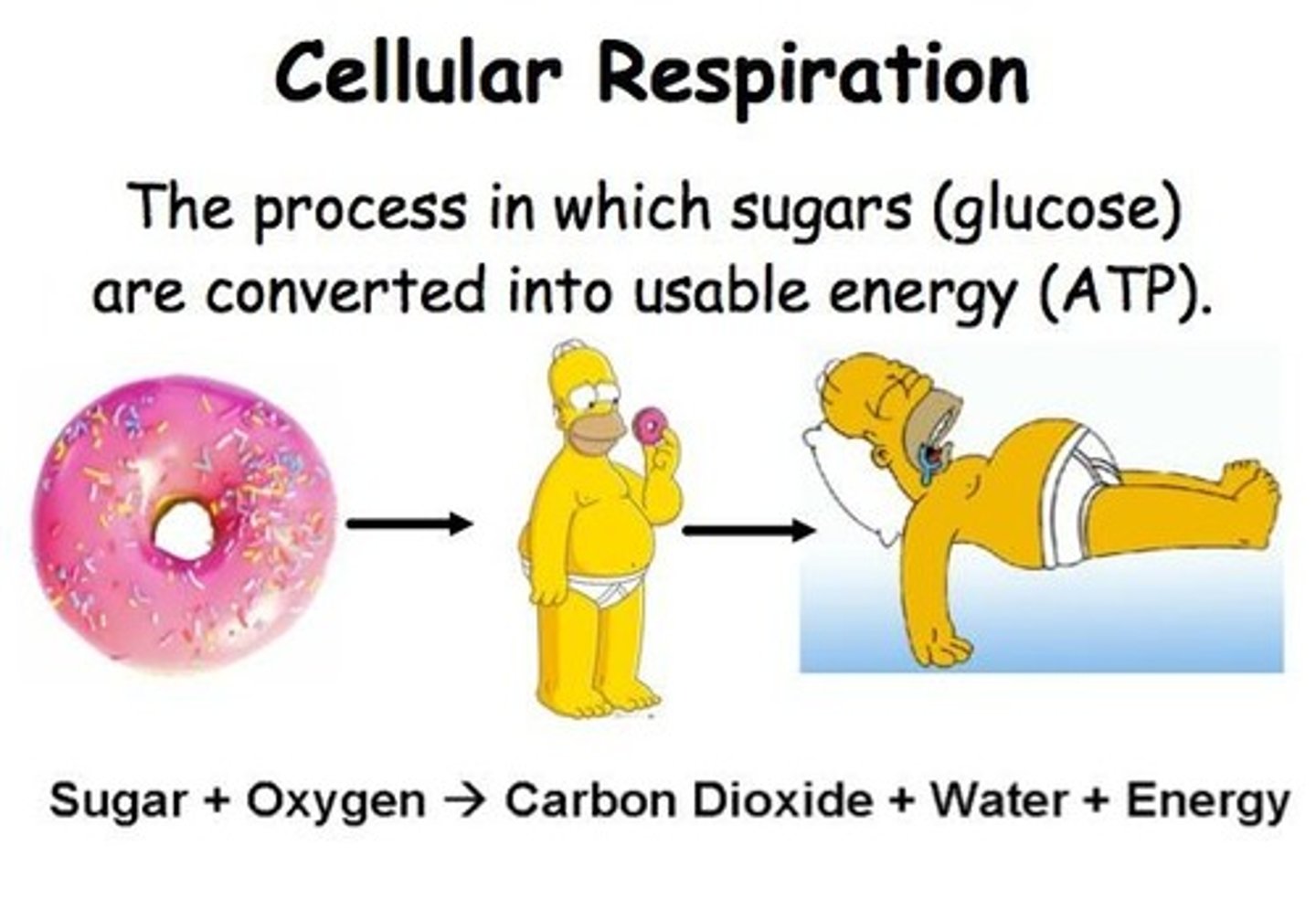
What do anabolic pathways do?
They consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones, like building proteins from amino acids.
What is energy in a biological context?
The capacity to cause change.
What are the forms of energy?
Kinetic energy, thermal energy, heat, potential energy, and chemical energy.
What is thermodynamics?
The study of energy transformations.
What are the types of systems in thermodynamics?
Isolated systems (unable to exchange energy or matter) and open systems (can transfer energy and matter with surroundings).
What is the 1st Law of Thermodynamics?
The principle of conservation of energy; energy of the universe is constant and cannot be created or destroyed.
What is the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics?
During energy transfer or transformation, some energy is unusable and often lost as heat, increasing the universe's entropy.
What is entropy?
A measure of molecular disorder or randomness.
What defines spontaneous processes?
They occur without energy input and must increase the entropy of the universe.
What is free-energy change (ΔG)?
It indicates whether a reaction occurs spontaneously; negative ΔG means the process is spontaneous.
What is the relationship between ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS?
ΔG = ΔH − TΔS, where ΔH is the change in total energy, ΔS is the change in entropy, and T is temperature in Kelvin.
What characterizes exergonic reactions?
They proceed with a net release of free energy and are spontaneous.
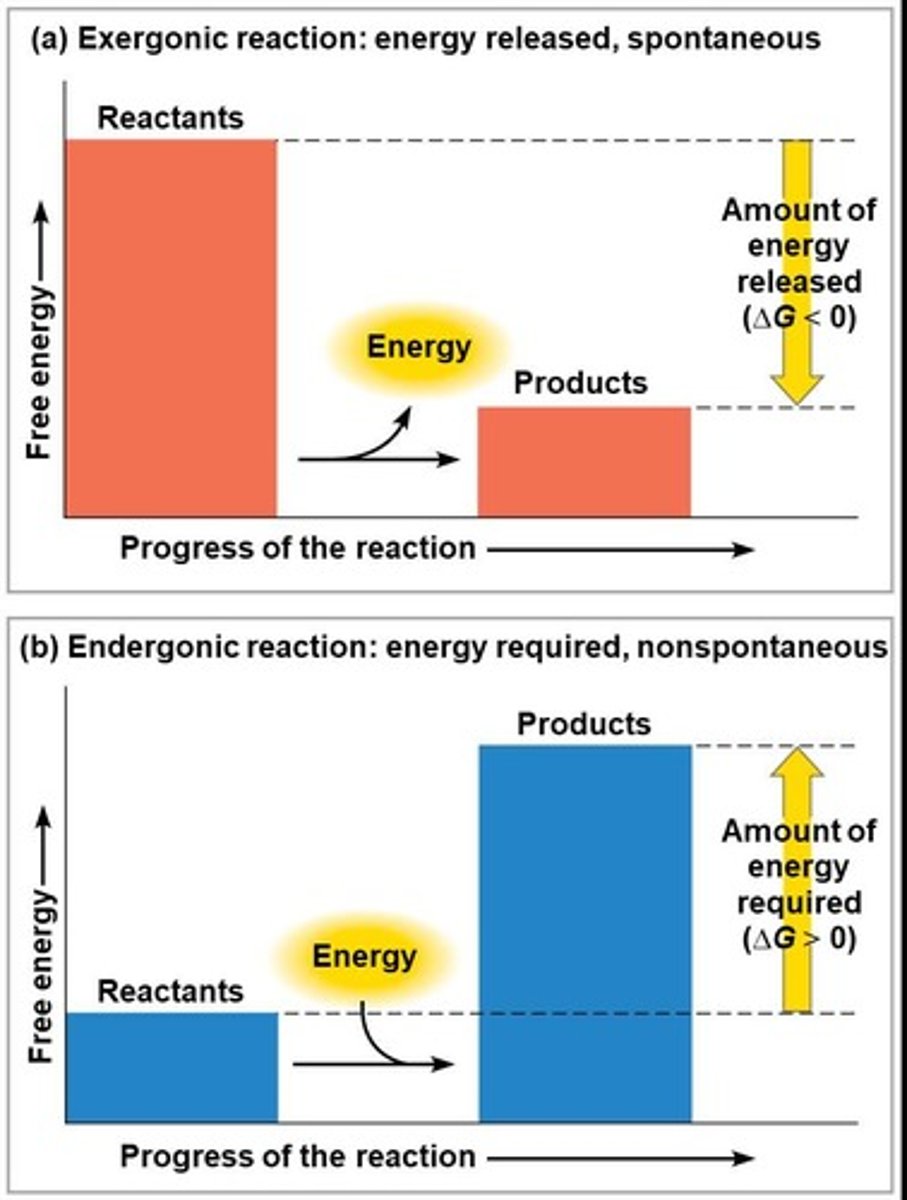
What characterizes endergonic reactions?
They absorb free energy from their surroundings and are nonspontaneous.
How does ATP power cellular work?
By coupling exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions.
What are the types of cellular work powered by ATP?
Chemical work, transport work, and mechanical work.
What is a defining feature of life regarding metabolism?
Metabolism is never at equilibrium; cells are open systems experiencing a constant flow of materials.
What is the significance of free energy in living systems?
It is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell.