Subcortical Structures
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
subcortical structures
grey matter areas
not part of cortex, islands within white matter
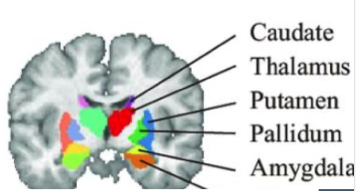
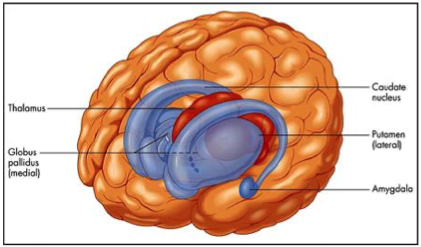
basal ganglia
group of subcortical nuclei
striatum
amygdala
nucleus accumbent
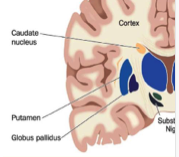
striatum
involved in initiation and regulation of movements: muscle tone, posture, involuntary movements, motor learning
affected by Parkinson’s
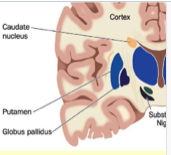
striatum structure
putamen and caudate nucleus
globus pallidus
amygdala
memory, emotions, fear
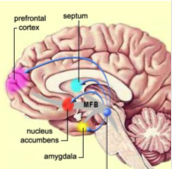
nucleus accumbent
pleasure, reward system, motor functions
thalamus
information form environment first goes to cortex
can be divided into several nuclei with distinct outputs and inputs
thalamus exception
olfaction goes directly to primary olfactory area: Piriform cortex
first order nuclei
lateral geniculate nuclei
medial geniculate nuclei
ventro posterior nuclei
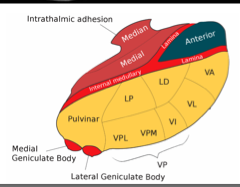
higher order nuclei
role in higher order cognitive functions and network regulation involving prefrontal cortex
involved in learning and memory processes
lateral geniculate nuclei
visual relay
medial geniculate nuclei
auditory relay
ventro posterior nuclei
relays sensory information from body
cerebellum
involved in production of movement
balance, posture, coordination
motor learning
brain stem structure
midbrain
pons
medulla
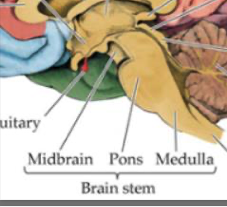
brain stem functions
controls centers for autonomic vital functions
vital functions such as breathing, heart beat, sleeping, blood pressure
connects briain to spinal cord
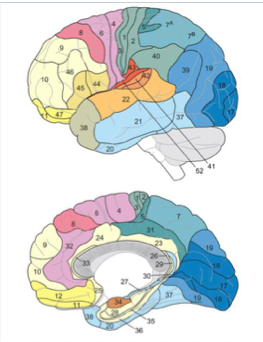
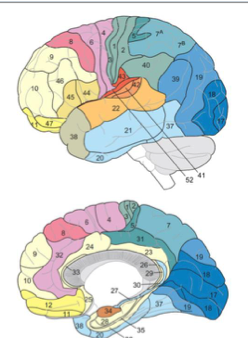
parietal brodmann areas
BA 40, 39
BA 1, 2, 3
BA 40, 39
SMG, ANG
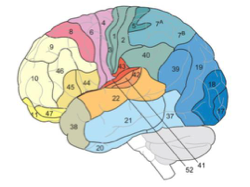
BA 1, 2,3
somatosensory
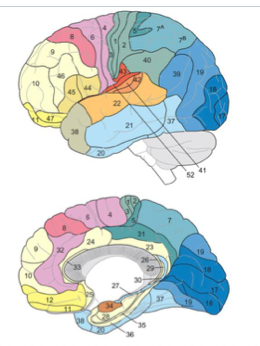
Frontal lobe brodmann area
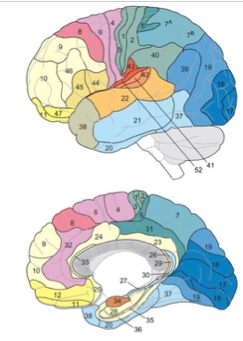
BA 4, 6
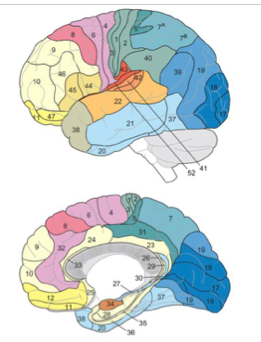
BA 44,45
BA 4, 6
motor
BA 44, 45
Pars Oper, Pars tri
BA 17-18-19
visual
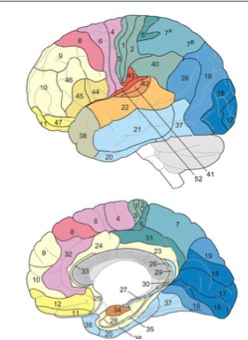
BA 41-42, 22
auditory
occipital lobe brodmann area
BA 17-18-19
temporal lobe brodmann area
BA 41-42, 22
MNI Brain.
compare brains because of difference in size/neuroanatomy: actives in all brain